Heckler & Koch MP5
| Heckler & Koch MP5 | |
|---|---|
|
MP5A3 with a retractable stock and early handguard | |
| Type | Submachine gun |
| Place of origin | West Germany |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1966–present |
| Used by | See Users |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Tilo Möller, Manfred Guhring, Georg Seidl, Helmut Baureuter |
| Designed | 1964–1966 |
| Manufacturer | Heckler & Koch |
| Produced | 1966–present |
| Variants | See Variants |
| Specifications | |
| Weight |
|
| Length |
Fixed stock:
|
| Barrel length |
|
| Width |
|
| Height |
|
|
| |
| Cartridge |
|
| Action | Roller-delayed blowback, closed bolt |
| Rate of fire |
|
| Muzzle velocity |
|
| Effective firing range |
|
| Feed system | 15, 30 or 40 round detachable box magazine and 100-round Beta C-Mag drum magazine |
| Sights | Iron sights. Rear: rotary drum; front: hooded post |
The Heckler & Koch MP5 (from German: Maschinenpistole 5, meaning Submachine gun 5) is a 9mm submachine gun of German design, developed in the 1960s by a team of engineers from the German small arms manufacturer Heckler & Koch GmbH (H&K) of Oberndorf am Neckar. There are over 100 variants of the MP5,[3] including a semi-automatic version.
The MP5 is one of the most widely used submachine guns in the world,[4] having been adopted by 40 nations and numerous military, law enforcement, intelligence, and security organizations.[2] It is widely used by SWAT teams in North America.
In 1999, Heckler & Koch developed the Heckler & Koch UMP, the MP5's successor; both are available as of 2016.[5]
History
Heckler & Koch, encouraged by the success of the G3 automatic rifle, developed a family of small arms consisting of four types of firearms all based on a common G3 design layout and operating principle. The first type was chambered for 7.62×51mm NATO, the second for the 7.62×39mm M43 round, the third for the intermediate 5.56×45mm NATO caliber, and the fourth type for the 9×19mm Parabellum pistol cartridge. The MP5 was created within the fourth group of firearms and was initially known as the HK54.[6]
Work on the MP5 began in 1964 and two years later it was adopted by the German Federal Police, border guard and army special forces.[6]
In 1980, the MP5 achieved iconic status as a result of its use on live television by SAS commandos in Operation Nimrod, where they stormed the Iranian Embassy in London, rescuing hostages and killing five terrorists.[7] The MP5 became a mainstay of SWAT units of law enforcement agencies in the United States since then. However, in the late 1990s, as a result of the North Hollywood shootout, police special response teams have supplanted some MP5s with AR-15-based assault rifles.[8]
The MP5 is manufactured under license in several nations including Greece (formerly at EBO – Hellenic Arms Industry, currently at EAS – Hellenic Defense Systems), Iran (Defense Industries Organization), Mexico (SEDENA), Pakistan (Pakistan Ordnance Factories), Saudi Arabia, Sudan (Military Industry Corporation), Turkey (MKEK), and the United Kingdom (initially at Royal Ordnance, later diverted to Heckler & Koch Great Britain).[9]
Design details
The primary version of the MP5 family is the MP5A2, which is a lightweight, air-cooled, selective fire delayed blowback operated 9×19mm Parabellum weapon with a roller-delayed bolt. It fires from a closed bolt (bolt forward) position.[10]
The fixed, free floating, cold hammer-forged barrel has 6 right-hand grooves with a 1 in 250 mm (1:10 in) rifling twist rate and is pressed and pinned into the receiver.[11]
Features

The first MP5 models used a double-column straight box magazine, but since 1977, slightly curved, steel magazines are used with a 15-round capacity (weighing 0.12 kg) or a 30-round capacity (0.17 kg empty).[11]
The adjustable iron sights (closed type) consist of a rotating rear diopter drum and a front post installed in a hooded ring. The rear sight is adjustable for both windage and elevation with the use of a special tool, being adjusted at the factory for firing at 25m with standard 124 grains FMJ 9×19mm NATO ammunition; the drum provides four different apertures of varying width used to adjust the light entrance in the diopter system, according to the user's eye relief and tactical situation.[12]
The MP5 has a hammer firing mechanism. The trigger group is housed inside an interchangeable polymer trigger module (with an integrated pistol grip) and equipped with a three-position fire mode selector that serves as the manual safety toggle. The "S" or Sicher position in white denotes weapon safe, "E" or Einzelfeuer in red represents single fire, and "F" or Feuerstoß (also marked in red) designates continuous fire. The SEF symbols appear on both sides of the plastic trigger group. The selector lever is actuated with the thumb of the shooting hand and is located only on the left side of the original SEF trigger group or on both sides of the ambidextrous trigger groups. The safety/selector is rotated into the various firing settings or safety position by depressing the tail end of the lever. Tactile clicks (stops) are present at each position to provide a positive stop and prevent inadvertent rotation. The "safe" setting disables the trigger by blocking the hammer release with a solid section of the safety axle located inside the trigger housing.[11]
The non-reciprocating cocking handle is located above the handguard and protrudes from the cocking handle tube at approximately a 45° angle. This rigid control is attached to a tubular piece within the cocking lever housing called the cocking lever support, which in turn, makes contact with the forward extension of the bolt group. It is not however connected to the bolt carrier and therefore cannot be used as a forward assist to fully seat the bolt group. The cocking handle is held in a forward position by a spring detent located in the front end of the cocking lever support which engages in the cocking lever housing. The lever is locked back by pulling it fully to the rear and rotating it slightly clockwise where it can be hooked into an indent in the cocking lever tube.[11]
Operating mechanism
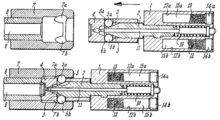
The bolt rigidly engages the barrel extension—a cylindrical component welded to the receiver into which the barrel is pinned. The delay mechanism is of the same design as that used in the G3 rifle. The two-part bolt consists of a bolt head with rollers and a bolt carrier. The heavier bolt carrier lies up against the bolt head when the weapon is ready to fire and inclined planes on the front locking piece lie between the rollers and force them out into recesses in the barrel extension.[13]
When fired, expanding propellant gases produced from the burning powder in the cartridge exert rearward pressure on the bolt head transferred through the base of the cartridge case as it is propelled out of the chamber. A portion of this force is transmitted through the rollers projecting from the bolt head, which are cammed inward against the inclined flanks of the locking recesses in the barrel extension and to the angled shoulders of the locking piece. The selected angles of the recesses and the incline on the locking piece produce a velocity ratio of about 4:1 between the bolt carrier and the bolt head. This results in a calculated delay, allowing the projectile to exit the barrel and gas pressure to drop to a safe level before the case is extracted from the chamber.[13]
The delay results from the amount of time it takes for enough recoil energy to be transferred through to the bolt carrier in a sufficient quantity for it to be driven to the rear against the force of inertia of the bolt carrier and the forward pressure exerted against the bolt by the recoil spring. As the rollers are forced inward they displace the locking piece and propel the bolt carrier to the rear. The bolt carrier's rearward velocity is four times that of the bolt head since the cartridge remains in the chamber for a short period of time during the initial recoil impulse. After the bolt carrier has traveled rearward 4 mm, the locking piece is withdrawn fully from the bolt head and the rollers are compressed into the bolt head. Only once the locking rollers are fully cammed into the bolt head can the entire bolt group continue its rearward movement in the receiver, breaking the seal in the chamber and continuing the feeding cycle.[13]
Since the 9×19mm Parabellum cartridge is relatively low powered, the bolt does not have an anti-bounce device like the G3, but instead the bolt carrier contains tungsten granules that prevent the bolt group from bouncing back after impacting the barrel extension. The weapon has a fluted chamber that enhances extraction reliability by bleeding gases backwards into the shallow flutes running along the length of the chamber to prevent the cartridge case from expanding and sticking to the chamber walls (since the bolt is opened under relatively high barrel pressure). A spring extractor is installed inside the bolt head and holds the case securely until it strikes the ejector arm and is thrown out of the ejection port to the right of the receiver. The lever-type ejector is located inside the trigger housing (activated by the movement of the recoiling bolt).[13]
Accessories
In the early 1970s HK introduced a conversion kit for the MP5 that enables it to use rimfire ammunition (.22 LR). This unit consists of a barrel insert, a bolt group and two 20-round magazines. This modification reduces the cyclic rate to 650 rounds/min. It was sold mostly to law enforcement agencies as a way to train recruits on handling the MP5. It used ammunition that was cheaper and had a lower recoil than 9×19mm Parabellum. This reduced training costs and built up skill and confidence in the operators before transitioning them to the full-bore model.
Barrel accessories
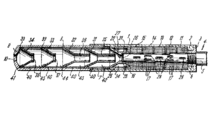
Threading is provided at the muzzle to work with certain muzzle devices made by Heckler & Koch, including: a slotted flash suppressor, blank firing attachment (marked with a red-painted band denoting use with blank ammunition only), an adapter for launching rifle grenades (for use with rifle-style grenades with an inside diameter of 22 mm using a special grenade launching cartridge) and a cup-type attachment used to launch tear gas grenades. An optional three-lugged barrel is also available for mounting a quick-detachable suppressor.
Receiver
The receiver housing has a proprietary claw-rail mounting system that permits the attachment of a standard Heckler & Koch quick-detachable scope mount (also used with the G3, HK33 and G3SG/1). It can be used to mount daytime optical sights (telescopic 4×24), night sights, reflex sights and laser pointers. The mount features two spring-actuated bolts, positioned along the base of the mount, which exert pressure on the receiver to hold the mount in the same position at all times assuring zero retention. All versions of the quick-detachable scope mount provide a sighting tunnel through the mount so that the shooter can continue to use the fixed iron sights with the scope mount attached to the top of the receiver.
A Picatinny rail adapter can be placed on top that locks into the claw rails. This allows the mounting of STANAG scopes and has a lower profile than the claw-rail system.
Handguard
Aftermarket replacement handguards with Picatinny rails are available. Single-rail models have a Picatinny rail along the bottom and triple-rail models have rails along the bottom and sides. They allow the mounting of accessories like flashlights, laser pointers, target designators, vertical foregrips, and bipods.[14]
Variants
The MP5A2 has a fixed buttstock (made of a synthetic polymer), whereas the compact MP5A3 has a retractable metal stock. The stockless MP5A1 has a buttcap with a sling mount for concealed carry; the MP5K series was a further development of this idea.[15]
The MP5A4 (fixed stock) and MP5A5 (sliding stock) models, which were introduced in 1974, are available with four-position trigger groups. The pistol grips are straight, lacking the contoured grip and thumb groove of the MP5A1, MP5A2, and MP5A3. The selector lever stops are marked with bullet pictograms rather than letters or numbers (each symbol represents the number of bullets that will be fired when the trigger is pulled and held rearward with a full magazine inserted in the weapon) and are fully ambidextrous (the selector lever is present on each side of the trigger housing). The additional setting of the fire selector, one place before the fully automatic setting, enables a two or three-shot burst firing mode.
A variant with the last trigger group designated the MP5-N (N—Navy) was developed in 1986 for the United States Navy. This model has a collapsible stock, a tritium-illuminated front sight post and a 225 mm (8.9 in) threaded barrel for use with a stainless steel sound suppressor made by Knight's Armament Company together with quieter subsonic ammunition. It had ambidextrous controls, a straight pistol grip, pictogram markings, and originally had a four-position selector (Safe, Semi-Auto, 3-Round Burst, Full Auto). This was replaced with a similar three-position ambidextrous selector after an improperly-reassembled trigger group spontaneously fired during an exercise. The "Navy"-style ambidextrous trigger group later became standard, replacing the classic "SEF".
| Type | Positions | Settings | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEF | 3-position | Safe (Sicher), semi-auto (Einzelfeuer), fully auto (Feuerstoß) | Left-side |
| SF | 2-position | Safe & semi-auto (Fire) | Ambidextrous |
| Navy | 4-position | Safe, semi-auto, 2- or 3-round burst, fully auto | Ambidextrous |
| Navy | 3-position | Safe, semi-auto, fully auto | Ambidextrous |
| Setting | Marking system | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Letter | Pictogram | |
| Safe | Marked by a white numeral "0" | Marked by a white letter "S" | Marked by a white pictogram of a bullet symbol inside a closed rectangle with an "X" through it. |
| Semi-automatic fire | Marked by a red numeral "1" | Marked by a red letter "E" | Marked by a red pictogram of a bullet symbol inside a closed rectangle. |
| Burst fire | Marked by a red numeral "2" or "3" | Marked by a red numeral "2" or "3" | Marked by a red pictogram of 2 or 3 bullets in a line inside a closed rectangle. |
| Fully automatic fire | Marked by a red numeral "30" | Marked by a red letter "F" | Marked by a red pictogram of 7 bullets in a line inside a rectangle with an open end facing the muzzle. |
Plastic training variants
H&K offers dedicated training variants of these weapons, designated MP5A4PT and MP5A5PT (PT—Plastic Training), modified to fire a plastic 9×19mm PT training cartridge produced by Dynamit Nobel of Germany. These weapons operate like the standard MP5 but have a floating chamber and both rollers have been omitted from the bolt to function properly when firing the lighter plastic projectiles. To help identify these weapons blue dots were painted on their cocking handles and additional lettering provided. The PT variant can be configured with various buttstocks and trigger groups and was developed for the West German Police and Border Guard.[16]
Semi-auto only variants
The MP5SFA2 (SF – single-fire) was developed in 1986 in response to the American FBI solicitation for a "9 mm Single-fire Carbine". It is the same as the MP5A2 but is fitted with an ambidextrous semi-automatic only trigger group. The MP5SFA3 is similar except it has a retractable metal stock like the MP5A3. Versions delivered after December 1991 are assembled with select-fire bolt carriers allowing fully automatic operation when used with the appropriate trigger module.[17]
The two-position trigger unit was used in the single-fire HK94 carbine that was produced specifically for the civilian market with a 420 mm (16.5 in) barrel.[16]
Suppressed variants
In 1974 H&K initiated design work on a sound-suppressed variant of the MP5, designated the MP5SD (SD—Schalldämpfer German for "sound suppressor"), which features an integral but detachable aluminium sound suppressor and a lightweight bolt. The weapon's 146 mm (5.7 in) barrel has 30 2.5 mm (0.1 in) ports drilled forward of the chamber through which escaping gases are diverted to the surrounding sealed tubular casing that is screwed onto threading on the barrel’s external surface just prior to the ported segment. The suppressor itself is divided into two stages; the initial segment surrounding the ported barrel serves as an expansion chamber for the propellant gases, reducing gas pressure to slow down the acceleration of the projectile. The second, decompression stage occupies the remaining length of the suppressor tube and contains a stamped metal helix separator with several compartments which increase the gas volume and decrease its temperature, deflecting the gases as they exit the muzzle, so muffling the exit report. The bullet leaves the muzzle at subsonic velocity, so it does not generate a sonic shock wave in flight. As a result of reducing the barrel’s length and venting propellant gases into the suppressor, the bullet’s muzzle velocity was lowered anywhere from 16% to 26% (depending on the ammunition used) while maintaining the weapon’s automation and reliability. The weapon was designed to be used with standard supersonic ammunition with the suppressor on at all times.[11]
The MP5SD is produced exclusively by H&K in several versions: the MP5SD1 and MP5SD4 (both have a receiver end cap instead of a buttstock), MP5SD2 and MP5SD5 (equipped with a fixed synthetic buttstock) and the MP5SD3 and MP5SD6 (fitted with a collapsible metal stock). The MP5SD1, MP5SD2 and MP5SD3 use a standard 'SEF' trigger group (from the MP5A2 and MP5A3), while the MP5SD4, MP5SD5, and MP5SD6 use the 'Navy' trigger group—a trigger module with a mechanically limited 3-round burst mode and ambidextrous selector controls (from the MP5A4 and MP5A5). A suppressed version was produced for the U.S. Navy – designated the MP5SD-N, which is a version of the MP5SD3 with a retractable metal stock, front sight post with tritium-illuminated dot and a stainless steel suppressor. This model has a modified cocking handle support to account for the slightly larger outside diameter of the suppressor. The design of the suppressor allows the weapon to be fired with water inside, should water enter the device during operation in or near water.[18]
MP5K
In 1976 a shortened version of the MP5A2 was introduced; the MP5K (K from the German word Kurz = "short") was designed for close quarters battle use by clandestine operations and special services. The MP5K does not have a shoulder stock (the receiver end was covered with a flat end cap, featuring a buffer on the inside and a sling loop on the outside), and the bolt and receiver were shortened at the rear. The resultant lighter bolt led to a higher rate of fire than the standard MP5. The barrel, cocking handle and its cover were shortened and a vertical foregrip was used to replace the standard handguard. The barrel ends at the base of the front sight, which prevents the use of any sort of muzzle device.[12]
The MP5K is produced (by Heckler & Koch and under license in Iran and Turkey) in four different versions: the MP5K, MP5KA4, MP5KA1, MP5KA5, where the first two variants have adjustable, open-type iron sights (with a notched rotary drum), and the two remaining variants – fixed open sights; however, the front sight post was changed and a notch was cut into the receiver top cover. The MP5K retained the capability to use optical sights through the use of an adapter.[12]
A civilian semiautomatic derivative of the MP5K known as the SP89 was produced that had a foregrip with a muzzle guard in place of the vertical grip.[19]
In 1991 a further variant of the MP5K was developed, designated the MP5K-PDW (PDW—Personal Defense Weapon) that retained the compact dimensions of the MP5K but restored the fire handling characteristics of the full-size MP5A2. The MP5K-PDW uses a side-folding synthetic shoulder stock (made by the U.S. company Choate Machine and Tool), a "Navy" trigger group, a front sight post with a built-in tritium insert and a slightly lengthened threaded, three-lug barrel (analogous to the MP5-N). The stock can be removed and replaced with a receiver endplate; a rotary drum with apertures from the MP5A2 can also be used.[20]
Larger caliber versions
In 1991, Heckler & Koch introduced the MP5/10 (chambered in 10mm Auto) and MP5/40 (chambered for the .40 S&W cartridge), which are based on the MP5A4 and MP5A5. These weapons were assembled in fixed and retractable stock configurations (without a separate designation) and are fed from translucent 30-round polymer box magazines. These weapons include a bolt hold-open device, which captures the bolt group in its rear position after expending the last cartridge from the magazine. The bolt is then released by pressing a lever positioned on the left side of the receiver. Both weapons use a barrel with 6 right-hand grooves and a 380 mm (1:15 in) twist rate, and like the MP5-N, both have a 3-lugged muzzle device and a tritium-illuminated front sight aiming dot.[21]
Problems with the MP5/10 and MP5/40 led to their discontinuation, although Heckler & Koch continues to provide support and spare parts.[21]
Variants list


- HK54: The original model that was produced in 1964. It had a charcoal-gray phosphated finish rather than the matte-black finish used on later models and had narrow slotted metal handguards. Its major differences were that it had a longer and heavier bolt carrier than the MP5 and a flip up "ladder"-style rear sight (like the early G3 rifle) rather than the MP5's aperture sight. Its original 15- or 30-round steel magazines were straight rather than curved, had a plastic follower, and were reinforced with ribs (thus their nickname of "waffle"-type magazines).[22]
- MP5: A slightly modified version of the HK54 first created in 1966. It has a matte-black phosphated finish instead of the grayish finish. It originally had the narrow checkered metal "Slimline" handguards in the place of the HK54's narrow slotted metal ones. These were later replaced by the thicker "Tropical" handguards. The proprietary Heckler & Koch "claw mount" rails for mounting optical and electronic scopes were added around 1973. The improved 15- and 30-round magazines were adopted in 1977; they were curved, had unribbed sides, and had chromed-steel followers.[22]
- MP5A1: No buttstock (endplate/receiver cap in place of buttstock), "SEF" trigger group.[22]
- MP5A2: Fixed buttstock, "SEF" trigger group.[22]
- MP5SFA2: Fixed buttstock, single-fire (SE) trigger group.[22]
- MP5A3: Retractable buttstock,"SEF" trigger group.[22]
- MP5SFA3: Semi-automatic carbine version of MP5A3. Retractable buttstock and single-fire (SF) trigger group.[22]
- MP5A4: Fixed buttstock, 3-round burst trigger group.[22]
- MP5A5: Retractable buttstock, 3-round burst trigger group.[22]
- MP5-N: Model developed specifically for the U.S. Navy. Ambidextrous "Navy" trigger group, 3-lug/threaded barrel for attaching a sound suppressor; rubber-padded retractable stock.[12]
- MP5F: Model developed specifically for the French military. Rubber-padded retractable stock, ambidextrous sling loops/bolts and internal modifications to handle high-pressure ammunition.[12]
- MP5K: Short (Kurz) version created in 1976. It has a shortened 4.5 in (114 mm) barrel, shorter trigger group frame, and a vertical foregrip rather than a handguard. There are no MP5KA2 or MP5KA3 models because it does not come with a fixed or retractable stock.[12]
- MP5K Prototype: A stockless, cut-down MP5A2 with regular iron sights and an open vertical foregrip. It was created in 1976.
- MP5KA1: MP5K with smooth upper surface and small low-profile iron sights; "SEF" trigger group.[12]
- MP5KA4: MP5K with regular iron sights; four-position 3-round burst trigger group.[12]
- MP5KA5: MP5K with smooth upper surface and small low-profile iron sights; four-position 3-round burst trigger group.
- MP5K-N: MP5K with "Navy" trigger group and 3-lug/threaded barrel for mounting suppressors or other muzzle attachments.[12]
- MP5K-PDW: Personal Defense Weapon; MP5K-N variant introduced in 1991 for issue to special operations aircraft or vehicle crews. It adds a Choate side-folding stock, 5-inch 3-lug barrel for mounting a quick-detachable Qual-A-Tec suppressor, and an ambidextrous 4-position trigger group with a 3-round burst mode. A shoulder cross-draw or thigh quick-draw holster is available.[20]
- MP5SD: An MP5 model with an integrated suppressor (Schalldämpfer) created in 1974.[23]
- MP5SD1: No buttstock (endplate/receiver cap in place of buttstock), "SEF" trigger group, integrated suppressor[23]
- MP5SD2: Fixed buttstock, "SEF" trigger group, integrated suppressor.[23]
- MP5SD3: Retractable buttstock, "SEF" trigger group, integrated suppressor.[23]
- MP5SD4: No buttstock (endplate/receiver cap in place of buttstock), 3-round burst trigger group, integrated suppressor.[23]
- MP5SD5: Fixed buttstock, 3-round burst trigger group, integrated suppressor.[20]
- MP5SD6: Retractable buttstock, 3-round burst trigger group, integrated suppressor.[20]
- MP5SD-N1: Fixed buttstock, "Navy" trigger group, KAC stainless steel suppressor.[20]
- MP5SD-N2: Retractable buttstock, "Navy" trigger group, KAC stainless steel suppressor.[20]
- MP5/10: Chambered in 10mm Auto, available in various stock/trigger group configurations. It was produced from 1992 to 2000.[20]
- MP5/40: Chambered in .40 S&W, available in various stock/trigger group configurations. It was produced from 1992 to 2000.[24]
Civilian market versions
- HK94: American import model of the MP5 with an exposed 16.54-inch [420mm] barrel and special SF (safe/semi-automatic) trigger group, designed for civilian use.
A barrel-mounted vertical foregrip and a ventilated barrel shroud were available for the stock HK94. The HK94 was made from 1983 to 1989, in three different configurations:- The HK94A2 had a fixed stock, an overall length of 34.59 inches [829 mm], and weighed 6.43 lbs. [2.92 kg.]. In 1991, the state of California imported 420 HK-94A2s, mostly for their state Department of Corrections; it was the last batch of HK-94s imported into the United States.[19]
- The HK94A3 had a retractable stock, an overall length of 27.58 inches [700 mm] collapsed and 34.05 inches [865 mm] extended and weighed 7.18 lbs. [3.26 kg].[19]
- The HK94/SG-1 (ScharfschutzenGewehr, "sharp-shooting rifle") was designed for short-range sniping in built-up areas like cities or prisons. It proved to be unsuitable for its designed purpose, due to its poor penetration and stopping power , and most went to target shooters and collectors. It had a fixed match stock with a rubber buttpad and an adjustable cheekpiece, folding bipod, flash hider, and a 6 × 42mm Leupold VIII Adjustable Objective scope. It had an overall length of 40.39 inches [1026mm] and a weight of 9.25 lbs. [4.2 kg]. Its mean standard retail price (MSRP) in 1986 was US$1,525; this was more than twice what a stock HK94A2 (US$650) or HK94A3 (US$720) cost. Only 50 were imported into the United States; authentic models have serial numbers running in the 43XX range.
As an aftermarket modification, a PSG-1 trigger pack with target pistol grip and match trigger could be added by a gunsmith by changing the ejector and hammer spring. The 6× Leupold scope was calibrated for .223 Remington rounds, so other scopes were often substituted.
- SP89: Sport Pistole M1989. Semi-automatic only version of the MP5K designed for civilian use. It lacked a vertical foregrip to make it compliant with the National Firearms Act. It was made from 1989 to 1994.[22]
Foreign variant copies
- T-94 ZSG (Ziviles Sportgewehr, "Civilian Sport Rifle"): Turkish MP5 semi-automatic-only clone manufactured by MKE for the civilian European sport shooting market.[25] The models available are the T-94P (HK94A2), T-94A (MP5A2), T-94K (MP5K), and T-94SD (MP5SD2). The T-94SD comes with a functioning integral silencer. The solid stocks are welded to the lower receiver to prevent the mounting of a retractable stock or receiver cap.
The AT-94 series, designed for the American market, is modified so that full-auto and 90-series trigger packs cannot be fitted.[26] - MP-10: A Philippine submachine gun manufactured by Special Weapons Inc. based on the MP5. The SP-10 is a civilian semi-auto copy.
- POF SMG-PK and SMG-PK-1: Pakistan Ordnance Factory copies of the MP5K. The select fire SMG-PK is identical to the MP5KA4. The SMG-PK-1 is similar except it has a short retractable stock.
- POF-4 PISTOL: Pakistan Ordnance Factory semi-auto copy of the MP5K.
- POF-5 PISTOL: Pakistan Ordnance Factory semi-auto copy of the MP5.POF-5
- OFB Animika 9mm: Indian Ordnance Factory copy of MP5.[27]
- LDT HSG-94: made by Luxembourg Defence Technology, semi-auto copy of the MP5 LDT HSG-94
- LDT HSG-94K: made by Luxembourg Defence Technology, semi-auto copy of the MP5K, sold with a collapsible stock. LDT HSG-94K
Contrary to popular belief, the S-U-O marked lowers (in lieu of S-E-F) commonly found on many MP5 clones and conversion were not manufactured in Malaysia, but were in fact German made as part of a large contract of HK33s, MP5s and several other H&K weapons.
Manufacturers
-
 China: Manufactured by Norinco as the NR-08 (a clone of the MP5A4) and NR-08A (a clone of the MP5A5) and CS/LS3.
China: Manufactured by Norinco as the NR-08 (a clone of the MP5A4) and NR-08A (a clone of the MP5A5) and CS/LS3. -
 France: Manufactured under license by MAS as the MP5F.
France: Manufactured under license by MAS as the MP5F. -
 Greece: Manufactured under license by EAS (Ellinika Amyntika Systimata: "Hellenic Defence Systems").[28]
Greece: Manufactured under license by EAS (Ellinika Amyntika Systimata: "Hellenic Defence Systems").[28] -
 Iran: Manufactured under license by DIO as the Tondar (MP5A3) and Tondar Light (MP5K).[9]
Iran: Manufactured under license by DIO as the Tondar (MP5A3) and Tondar Light (MP5K).[9] -
 Luxembourg: manufactured by Luxembourg Defence Technology using POF-made parts
Luxembourg: manufactured by Luxembourg Defence Technology using POF-made parts -
 Mexico: Manufactured under license by SEDENA.[29]
Mexico: Manufactured under license by SEDENA.[29] -
 Pakistan: Manufactured under license by Pakistan Ordnance Factories[30] as the MP5P and also POF-5.[31][32]
Pakistan: Manufactured under license by Pakistan Ordnance Factories[30] as the MP5P and also POF-5.[31][32] -
 Saudi Arabia: Manufactured under license by Al Kharj Arsenal, Military Industries Corporation.[33]
Saudi Arabia: Manufactured under license by Al Kharj Arsenal, Military Industries Corporation.[33] -
 Sudan: Manufactured by Military Industry Corporation as the Tihraga (MP5A3), a clone of the Iranian Tondar.[34]
Sudan: Manufactured by Military Industry Corporation as the Tihraga (MP5A3), a clone of the Iranian Tondar.[34] -
 Switzerland: Manufactured under license by Brügger & Thomet.
Switzerland: Manufactured under license by Brügger & Thomet. -
 Turkey: Manufactured by MKEK.[35] Their trigger groups are marked: E (Safe), T (Semi-Auto) and S (Full Auto) instead of SEF.
Turkey: Manufactured by MKEK.[35] Their trigger groups are marked: E (Safe), T (Semi-Auto) and S (Full Auto) instead of SEF. -
 United Kingdom: Manufactured under license by Royal Small Arms Factory – Enfield.[9]
United Kingdom: Manufactured under license by Royal Small Arms Factory – Enfield.[9]
Users
Gallery
- An USAF Air Traffic Control Detachment officer fires an MP5K at the Baghdad International Airport firing range.
 U.S. Navy SEALs armed with MP5-Ns on a training exercise.
U.S. Navy SEALs armed with MP5-Ns on a training exercise.- A member of SEAL Team 8 with an MP5-N variant in February 1991.

 West German pro-marxist terrorist group Red Army Faction depicted the MP5 in their insignia, shown here.[123]
West German pro-marxist terrorist group Red Army Faction depicted the MP5 in their insignia, shown here.[123]
See also
References
- Cutshaw, Charles Q. (28 February 2011). Tactical Small Arms of the 21st Century: A Complete Guide to Small Arms From Around the World. Iola, Wisconsin: Gun Digest Books. ISBN 1-4402-2709-8.
- Dockery, Kevin (2007). Future Weapons. New York: Penguin Group (USA) Incorporated. ISBN 978-0-425-21750-4.
- Ezell, Edward Clinton; Smith, Walter Harold Black; Smith, Joseph Edward (1973). Small Arms of the World: A Basic Manual of Small Arms, the Classic (121 ed.). Woodbridge, Virginia: Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-85368-189-2.
- James, Frank W. (1 January 2003). Heckler and Koch's Mp5 Submachine Gun. Iola, Wisconsin: Krause Publications. ISBN 978-0-937752-15-9.
- Rottman, Gordon L. (1993). Armies of the Gulf War. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-85532-277-6.
- Thompson, Leroy (20 July 2014). The MP5 Submachine Gun. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78200-917-7.
- Tilstra, Russell C. (2012). Small Arms for Urban Combat. US: McFarland. ISBN 978-0-7864-6523-1.
Footnotes
- ↑ "Heckler & Koch – USA". Hk-usa.com. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- 1 2 Tilstra 2012, p. 42.
- ↑ "H&K Web site, MP5 overview". Heckler-koch.com. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ Hogg, Ian (2002). Jane's Guns Recognition Guide. Jane's Information Group. ISBN 0-00-712760-X.
- ↑ Dockery 3007, p. 220.
- 1 2 Thompson 2014, p. 8.
- ↑ Grine, Joe (February 9, 2013). "Gun Review: HK SL8-6". The Truth About Guns. Retrieved January 7, 2015.
- ↑ "Gun Review HK SL8-6". 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 "Report: Profiling the Small Arms Industry – World Policy Institute – Research Project". World Policy Institute. November 2000. Retrieved 2010-07-15.
- ↑ Thompson 2014, p. 12.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Thompson 2014, p. 18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thompson 2014, p. 19.
- 1 2 3 4 Thompson 2014, p. 68.
- ↑ Thompson 2014, p. 24.
- ↑ Cutshaw 2011, p. 154.
- 1 2 Thompson 2014, p. 29.
- ↑ Thompson 2014, p. 47.
- ↑ Thompson 2014, p. 5.
- 1 2 3 Thompson 2014, p. 30.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Thompson 2014, p. 20.
- 1 2 Thompson 2014, p. 23.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Thompson 2014, p. 13.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Thompson 2014, p. 15.
- ↑ Thompson 2014, p. 21.
- ↑ "MKEK - Mechanical and Chemical Industry Company". mkek.gov.tr. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- ↑ "MKE (AT94K/AT94P) Turkish HK Contracts...". Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ↑ "Unnamed: India's Ordnance Factory Board 'ANAMIKA' MP5 - The Firearm Blog". thefirearmblog.com. 16 June 2016. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- ↑ "Hellenic Defense Systems". Eas.gr. Retrieved 2009-06-26.
- 1 2 Thompson 2014, p. 69.
- ↑ "Infantry Weapons – SMG PK". Pakistan Ordnance Factories.
- ↑ Firearms, Atlantic. "POF-5 9mm Semi Auto Pistol , Pakistan Ordnance Factories ( POF )". Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ↑ Firearms, Atlantic. "POF 5PK 9mm Pistol". Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ↑ "MP5 Submachine Gun Cal 9X19 mm". En.mic.org.sa. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "Military Industry Corporation (MIC) Official Website". Mic.sd. Retrieved 2009-06-26.
- ↑ "Turkey MKEK MP5". MKEK. Retrieved 2009-06-26.
- ↑ "Viktimat u vranë me plumba 9mm". Top-channel.tv. 2011-01-23. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ Gander, Terry J.; Hogg, Ian V. Jane's Infantry Weapons 1995/1996. Jane's Information Group; 21 edition (May 1995). ISBN 978-0-7106-1241-0.
- ↑ Force, Air. "Page cannot be found - Royal Australian Air Force". Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ↑ "TAG East operations (image)". Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ↑ Gillett, Ross (1987). Australia's Armed Forces of the Eighties. Sydney, Australia: Cupress Ltd. pp. 105–106. ISBN 978-0-86777-081-0.
- ↑ "TRG raid McLeod rental property". Perthnow.com.au. 2010-01-13. Retrieved 2012-12-30.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Thompson 2014, p. 67.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Jones 2009, p. 514.
- ↑ "MP5 Submachine Gun". BDMilitary.com – The voice of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "АЛМАЗ – антитерор". YouTube. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "KGB vs FSB shooting". YouTube. Retrieved 2015-01-03.
- ↑ Ezell 1973, p. 286.
- ↑ "Etpu" (PDF). Defense Treaty Ready Inspection Readiness Program. Retrieved 2011-01-29.
- ↑ Dan Beaumont ARCHIVES (3 December 2011). "Denis Lortie « fusillade au Parlement de Québec », SRC, 8 mai 1984". Retrieved 11 July 2016 – via YouTube.
- ↑ "CASR — Canadian American Strategic Review — DND 101 — Canadian Forces Small Arms — Specialist Weapons — A Visual Guide". Retrieved 2014-03-03.
- ↑ "Chongqing police SWAT team". YouTube. 2011-03-24. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "uea21". YouTube. 2009-02-15. Retrieved 2012-12-30.
- ↑ "U ATJ Lučko završen tečaj FBI-a". Ezadar.hr. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "zbrane.indd" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "Policía y CTE realizan intercambio de armas" (in Spanish). Telerama. 2011-06-07. Retrieved 2012-06-19.
- ↑ Bennett, R M (31 August 2011). "Egypt". Elite Forces. Ebury Publishing. pp. 199–200. ISBN 978-0-7535-4764-9. Retrieved 19 August 2013.
- ↑ "Terre – HK MP5 A5" (in French). Defense.gouv.fr. Archived from the original on March 14, 2008. Retrieved 2009-06-26.
- ↑ "Terre – HK MP5 SD3" (in French). Defense.gouv.fr. Archived from the original on March 16, 2008. Retrieved 2009-06-26.
- ↑ "David Birman - LinkedIn". Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ↑ "Modern Firearms – Heckler Koch HK MP-5 submacine gun". World.guns.ru. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "Maschinenpistole MP5K". streitkraeftebasis.de. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- 1 2 3 , Miller, David (2001). The Illustrated Directory of 20th Century Guns. Salamander Books Ltd. ISBN 978-1-84065-245-1.
- ↑ "Greece Ministry of Public Order Press Office: Special Anti-Terrorist Unit" (PDF). Official Website of the Hellenic Police. July 2004. Retrieved 2009-10-13.
- ↑ "Hong Kong Police – Airport Security Unit". hkdigit.blogspot.com. 1007-06-12. Retrieved 2010-10-31. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Hungarian Ground Forces
- ↑ "Gæslan keypti hríðskotabyssur". Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ↑ "Sérsveitin í brennidepli", Fréttablaðið, March 6. 2004, p. 18, Dagur – Tíminn, Akureyri, March 8. 1997, p. 20.
- ↑ "Force One to get MP5 guns". dnaindia.com. 2009-01-16. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ Unnithan, Sandeep (August 22, 2008). "If Looks Could Kill". India Today (Online). Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- ↑ "ARW Equipment". Fianoglach.ie. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "Arma dei Carabinieri – Home – L'Arma – Oggi – Armamento – Armamento speciale – Pistola Mitragliatrice Heckler & Koch MP5". Carabinieri.it. 2005-11-16. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "SBU(海上自衛隊特別警備隊)の動画". Special-operations.info. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ 日本の特殊部隊 (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2012-11-16.
- ↑ "Unofficial SST Page" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2010-05-27.
- ↑ 陸上自衛隊唯一の特殊部隊 特殊作戦群の解説 (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2012-11-28. Retrieved 2012-11-28.
- ↑ "自衛隊の採用する銃器". Jieitaisaiyou.web.fc2.com. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ Rottman 1993, p. 53.
- ↑ "Sh25m Kenya heist puzzle". Capital FM Kenya. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "Germany's Unseen Hand in Kenya Crisis". The African Executive. 2008-02-06. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "Annual Report 2011 > Landespolizei" (PDF). Landespolizei. Retrieved 2012-06-18.
- ↑ "About the Security Corps > Landespolizei" (PDF). Landespolizei. Retrieved 2012-06-18.
- ↑ "Lietuvos kariuomenė :: Ginkluotė ir karinė technika » Pistoletai-kulkosvaidžiai » Pistoletas – kulkosvaidis MP-5" (in Lithuanian). Kariuomene.kam.lt. 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "Lithuania: Special Operations and Counterterrorist Forces". Special Operations.Com. Retrieved 2013-10-05.
- ↑ "Equipement :: Unité Spéciale de la Police ::". USP.LU. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "Ops Daulat Ground Operation, Lahad Datu Crisis picture gallery". malaysiamilitarypower.blogspot.com.au. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ↑ Royal Malaysia Police (July 2009). "Airport Security Course 1/2009". Royal Malaysia Police. Retrieved 2015-07-24.
- ↑ Royal Malaysian Customs Academy (2010). "Royal Malaysian Customs Academy: Firing range". Royal Malaysian Customs. Retrieved 2011-08-22.
- ↑ Muhammad, Zuridan (July 2009). "Malaysian Special Forces". TEMPUR. Retrieved 2013-07-20.
- ↑ Thompson, Leroy (December 2008). "MAST – SWAT Team of Marine Police". Special Weapons. Retrieved 2009-11-29.
- ↑ "United Nations Register of Conventional Arms". Un.org. Retrieved 2012-12-30.
- ↑ "Dienst Koninklijke en Diplomatieke Beveiliging (DKDB) KLPD". Arrestatieteam.nl. Retrieved 2011-01-29.
- ↑ Media Works NZ / TV3 Documentary – Inside New Zealand – NZSAS: First Among Equals. TVNZ Documentary – Line of Fire. www.army.mil.nz/our-army/nzsas
- ↑ "''En liten røver med trøkk i (Norwegian article on the Heckler & Koch deal)''". Mil.no. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "Kjent skyldig av juryen – beskyttes av væpnet politi – VG Nett om Gjengkriminalitet". Vg.no. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "Pakistan Army".
- ↑ "Rice Not Guns – German Arms in the Philippines". Bits.de. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ Sebastian Miernik. "//- Strona poświęcona Wojskowej Formacji Specjalnej GROM -//". Grom.mil.pl. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ Mateus, Bruno Contreiras (July 6, 2008). "Superpolícias Preparados para o Pior" (in Portuguese). Correio da Manhã. Retrieved 2009-10-23.
- ↑ "Blue Paper :: 아덴만 여명작전! 부산에서 재현되다!". Blue-paper.tistory.com. 2012-01-20. Retrieved 2012-12-30.
- ↑ de Mihai DIAC (5 March 2008). "Armament ultrasofisticat pentru Forţele Speciale ale Armatei Române – Gandul". Gandul.info. Retrieved 2013-08-08.
- ↑ Sorin A. Crasmarelu (2006). "Romanian Intelligence Service's Anti-Terrorism Brigade". geocities.ws. Retrieved 2015-12-07.
- ↑ "Спецподразделения МВД вооружатся австрийскими пистолетами". Lenta.ru. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ http://i.imgur.com/qKoBQl3.jpg
- ↑ http://i.imgur.com/mByo8fo.jpg
- ↑ "Фото". Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ↑ "Singapurske Specijalne Postrojbe" (in Croatian). Hrvatski Vojnik Magazine. Retrieved 2009-10-25.
- ↑ "Home Team Convention" (PDF). Police Life Monthly. Singapore Police Force. 37 (9): 7. September 2011. ISSN 0217-8699. Retrieved 3 February 2012.
- ↑ "Vigilance, Valour and Victory" (PDF). Police Life Monthly. Singapore Police Force. 37 (1): 22. January 2011. ISSN 0217-8699. Retrieved 3 February 2012.
- ↑ "Official page of Slovak special units" (in Slovak).
- ↑ "Special Police Unit exercise". Policija.si. 2011-08-02. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "Carte Blanche – M-Net". Beta.mnet.co.za. Retrieved 2011-01-29.
- ↑ "Web Del Grupo Especial De Operaciones (GEO)" (in Spanish). Official Website of the Spanish National Police Corps. Retrieved 2014-07-15.
- ↑ Henrik Svensk. "kulsprutepistol 45 b kpist k-pist 45". Soldf.com. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "Спецпідрозділ "ОМЕГА"". YouTube. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ "Press – Police Ombudsman for Northern Ireland". Policeombudsman.org. Retrieved 2011-01-29.
- ↑ Moore, Matthew. "Armed officers placed on routine foot patrol for first time". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ Sussex Police Uncovered – Tactical Firearms Unit
- ↑ "HECKLER AND KOCH MP5 SMG". Olive-drab.com. Retrieved 2012-12-29.
- ↑ Ambinder, Marc (March 2011). "Inside the Secret Service". The Atlantic. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ↑ Diez, Octavio (2000). Armament and Technology. Lema Publications, S.L. ISBN 978-84-8463-013-5.
- ↑ Moore, Malcolm (2008-06-11). "Pope Benedict XVI sets up anti-terrorist squad". The Daily Telegraph. London.
- ↑ "Vietnam People's Army pictures – Page 73". Retrieved 2013-08-08.
- ↑ Patrick Donahue (February 12, 2007). "German Red Army Faction Member Wins Early Release". Bloomberg. Retrieved December 12, 2011.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- Heckler & Koch MP5 at the Internet Movie Firearms Database
- Heckler & Koch—official pages: MP5A series, MP5SD, MP5-N, MP5K, MP5SF
- 2008 Heckler & Koch Military and LE brochure
- HKPRO: MP5, MP5K, MP5SD, MP5/10 & MP5/40
- REMTEK: MP5, MP5K, MP5K PDW, MP5SD, MP5/10
