Glycogen storage disease type VI
| Glycogen storage disease type VI | |
|---|---|
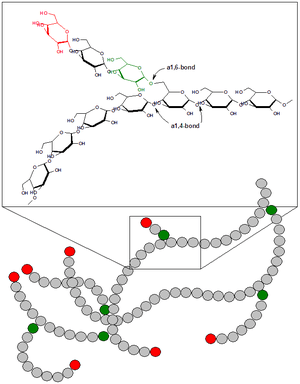 | |
| Glycogen | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | endocrinology |
| ICD-10 | E74.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 271.0 |
| OMIM | 232700 |
| DiseasesDB | 5311 |
| eMedicine | med/912 ped/2564 |
| MeSH | D006013 |
| GeneReviews | |
Glycogen storage disease type VI (GSD VI) is a type of glycogen storage disease caused by a deficiency in liver glycogen phosphorylase or other components of the associated phosphorylase cascade system.[1] It is also known as "Hers' disease", after Henri G. Hers, who characterized it in 1959.[2] The scope of GSD VI now also includes glycogen storage disease type VIII,[1] IX[1] (caused by phosphorylase b kinase deficiency) and X[1] (deficiency protein kinase A).
The incidence of GSD VI is approximately 1 case per 65,000–85,000 births,[1] representing approximately 30% all cases of glycogen storage disease.[1] Approximately 75% of these GSD VI cases result from the X-linked recessive forms of phosphorylase kinase deficiency, all other forms are autosomal recessive.[1]
Signs/symptoms
Patients generally have a benign course, and typically present with hepatomegaly and growth retardation early in childhood. Mild hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and hyperketosis may occur. Lactic acid and uric acid levels may be normal. However, lactic acidosis may occur during fasting.[3]
Genetics