International Orienteering Federation
 | |
|
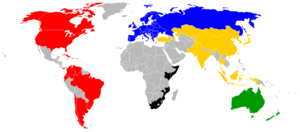
Map of the members of the IOF according to their region. | |
| Abbreviation | IOF |
|---|---|
| Formation | May 21, 1961 |
| Type | Federation of national sports associations |
| Headquarters |
Drottninggatan 47 3-1/2 tr Karlstad Sweden |
Region served | Worldwide |
Membership | 73 national federations |
President | Brian Porteous |
Secretary General | Tom Hollowell |
| Affiliations | International Olympic Committee |
| Website |
www |
The International Orienteering Federation (IOF) is the international governing body of the sport of orienteering. The IOF head office is located in Karlstad, Sweden.[1]
The IOF governs four orienteering disciplines: foot orienteering, mountain bike orienteering, ski orienteering, and trail orienteering.[2]
History
The IOF was founded on 21 May 1961 at a Congress held in Copenhagen, Denmark by the orienteering national federations of Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, the Federal Republic of Germany, the German Democratic Republic, Finland, Hungary, Norway, Sweden and Switzerland.[3] By 1969, the IOF represented 16 countries, including its first two non-European member federations representing Japan and Canada,[4] and in 1977 the IOF was recognised by the International Olympic Committee.[3]
Membership
As of January 2016, the membership of the IOF comprises 80 national orienteering federations, of which 56 are members, 24 are provisional members,[5] divided into six geographical regions.[6]
Africa
6 Members, 1 Provisional Member
|
Asia
14 Members, 2 Provisional Members
|
|
Europe
40 Members
|
|
|
North America
5 Members
|
|
Oceania
2 Members
South America
9 Members
|
Governance structure
The IOF is governed by an elected Council consisting of a President, a Senior Vice President, two Vice Presidents, and seven other Council members.[8] Day-to-day operations of the IOF are the responsibility of the IOF Secretary General.[1] Several standing commissions of the IOF are responsible for the development of the sport worldwide. These commissions include: Foot Orienteering, MTB Orienteering, Ski Orienteering, Trail Orienteering, Environment, IT, Map, Medical, and Rules.
Presidents[9]
- Erik Tobé (1961—1975)
- Lasse Heideman (1975—1982)
- Bengt Saltin (1982—1988)
- Heinz Tschudin (1988—1994)
- Sue Harvey (1994—2004)
- Åke Jacobson (2004—2012)
- Brian Porteous (2012—)
Affiliations
Since 1977, the IOF has been recognised by the International Olympic Committee.[3]
The IOF is also a member of the following organisations:[3]
- Association of IOC Recognised International Sports Federations (ARISF)
- International World Games Association (IWGA)
- International Masters Games Association (IMGA)
- SportAccord
Publications
The IOF publishes a wide variety of journals and reference works related to the sport. These include Orienteering World, an annual magazine, The Scientific Journal of Orienteering, the OZine,[10] and official editions of the rules of IOF sanctioned orienteering[11] and specifications for orienteering maps.[12]
References
- 1 2 "Secretariat". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ↑ "About the IOF". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- 1 2 3 4 "History". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ↑ Dandenong Ranges Orienteering Club. "Orienteering History". Momentech Software Services. Archived from the original on 2006-01-08. Retrieved 2006-02-19.
- ↑ "National Federations". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ↑ "Regions". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ↑ lof.lv
- ↑ "Council". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ↑ "Past and present Councils". IOF. Retrieved 2013-12-23.
- ↑ "Publications". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ↑ "Rules". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ↑ "Mapping". International Orienteering Federation. Retrieved 2011-08-02.