Ketose
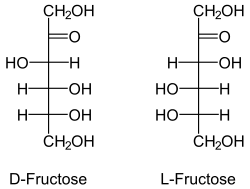
Fructose, an example of a ketose. The ketone group is the double-
bonded oxygen.
bonded oxygen.
A ketose is a monosaccharide containing one ketone group per molecule.[1][2]
With three carbon atoms, dihydroxyacetone is the simplest of all ketoses and is the only one having no optical activity. Ketoses can isomerize into an aldose when the carbonyl group is located at the end of the molecule. Such ketoses are reducing sugars.
List of ketoses

Family tree of D-ketoses up to hexoses: dihydroxyacetone (1); D-erythrulose (2); D-ribulose (3a); D-xylulose (3b); D-psicose (4a); D-fructose (4b); D-sorbose (4c); D-tagatose (4d)
All ketoses listed here are 2-ketones:
- Trioses: dihydroxyacetone
- Tetroses: erythrulose
- Pentoses: ribulose, xylulose
- Hexoses: fructose, psicose, sorbose, tagatose
- Heptoses: sedoheptulose
- Octoses: D-manno-octulose (the basis for KDO)
- Nonoses: D-glycero-D-galacto-nonulose (the basis for neuraminic acid)
Qualitative reaction
General qualitative reaction for ketoses is Seliwanoff's test.
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/16/2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.