Cell membrane

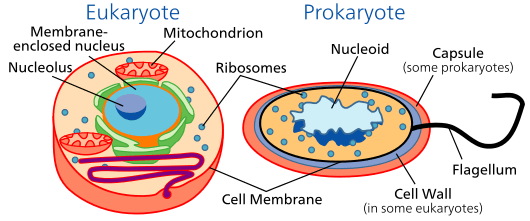
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment.[1][2] The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells.[3] The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings.
It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.[4][5][6]
History
The structure has been variously referred to by different writers as the ectoplast (de Vries, 1885),[7] Plasmahaut (plasma skin, Pfeffer, 1877, 1891),[8] Hautschicht (skin layer, Pfeffer, 1886; used with a different meaning by Hofmeister, 1867), plasmatic membrane (Pfeffer, 1900),[9] plasma membrane, cytoplasmic membrane, cell envelope and cell membrane.[10][11]
Some authors that did not believe that there was a functional permeable boundary at the surface of the cell preferred to use the term plasmalemma (coined by Mast, 1924) to the extern region of the cell.[12][13][14]
Function

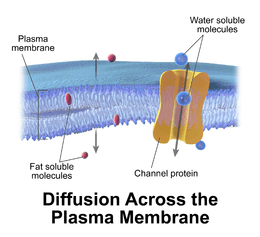
The cell membrane (or plasma membrane or plasmalemma) surrounds the cytoplasm of living cells, physically separating the intracellular components from the extracellular environment. Fungi, bacteria and plants have a cell wall in addition, which provides a mechanical support to the cell and precludes the passage of larger molecules. The cell membrane also plays a role in anchoring the cytoskeleton to provide shape to the cell, and in attaching to the extracellular matrix and other cells to hold them together to form tissues.
The cell membrane is selectively permeable and able to regulate what enters and exits the cell, thus facilitating the transport of materials needed for survival. The movement of substances across the membrane can be either "passive", occurring without the input of cellular energy, or "active", requiring the cell to expend energy in transporting it. The membrane also maintains the cell potential. The cell membrane thus works as a selective filter that allows only certain things to come inside or go outside the cell. The cell employs a number of transport mechanisms that involve biological membranes:
1. Passive osmosis and diffusion: Some substances (small molecules, ions) such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2), can move across the plasma membrane by diffusion, which is a passive transport process. Because the membrane acts as a barrier for certain molecules and ions, they can occur in different concentrations on the two sides of the membrane. Such a concentration gradient across a semipermeable membrane sets up an osmotic flow for the water.
2. Transmembrane protein channels and transporters: Nutrients, such as sugars or amino acids, must enter the cell, and certain products of metabolism must leave the cell. Such molecules diffuse passively through protein channels such as aquaporins (in the case of water (H2O)) in facilitated diffusion or are pumped across the membrane by transmembrane transporters. Protein channel proteins, also called permeases, are usually quite specific, recognizing and transporting only a limited food group of chemical substances, often even only a single substance.
3. Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process in which cells absorb molecules by engulfing them. The plasma membrane creates a small deformation inward, called an invagination, in which the substance to be transported is captured. The deformation then pinches off from the membrane on the inside of the cell, creating a vesicle containing the captured substance. Endocytosis is a pathway for internalizing solid particles ("cell eating" or phagocytosis), small molecules and ions ("cell drinking" or pinocytosis), and macromolecules. Endocytosis requires energy and is thus a form of active transport.
4. Exocytosis: Just as material can be brought into the cell by invagination and formation of a vesicle, the membrane of a vesicle can be fused with the plasma membrane, extruding its contents to the surrounding medium. This is the process of exocytosis. Exocytosis occurs in various cells to remove undigested residues of substances brought in by endocytosis, to secrete substances such as hormones and enzymes, and to transport a substance completely across a cellular barrier. In the process of exocytosis, the undigested waste-containing food vacuole or the secretory vesicle budded from Golgi apparatus, is first moved by cytoskeleton from the interior of the cell to the surface. The vesicle membrane comes in contact with the plasma membrane. The lipid molecules of the two bilayers rearrange themselves and the two membranes are, thus, fused. A passage is formed in the fused membrane and the vesicles discharges its contents outside the cell.
Prokaryotes
Gram-negative bacteria have both a plasma membrane and an outer membrane separated by periplasm. Other prokaryotes have only a plasma membrane. Prokaryotic cells are also surrounded by a cell wall composed of peptidoglycan (amino acids and sugars). Some eukaryotic cells also have cell walls, but none that are made of peptidoglycan. The outer membrane of gram negative microbes is rich in lipopolysaccharide and thus is different from cell membrane of the microbes. The outer membrane can bleb out into periplasmic protrusions under stess conditions or upon virulence requirements while encountering a host target cell, and thus such blebs may work as virulence organelles.[15]
Structures
Fluid mosaic model
According to the fluid mosaic model of S. J. Singer and G. L. Nicolson (1972), which replaced the earlier model of Davson and Danielli, biological membranes can be considered as a two-dimensional liquid in which lipid and protein molecules diffuse more or less easily.[16] Although the lipid bilayers that form the basis of the membranes do indeed form two-dimensional liquids by themselves, the plasma membrane also contains a large quantity of proteins, which provide more structure. Examples of such structures are protein-protein complexes, pickets and fences formed by the actin-based cytoskeleton, and potentially lipid rafts.
Lipid bilayer
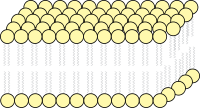
Lipid bilayers form through the process of self-assembly. The cell membrane consists primarily of a thin layer of amphipathic phospholipids that spontaneously arrange so that the hydrophobic "tail" regions are isolated from the surrounding water while the hydrophilic "head" regions interact with the intracellular (cytosolic) and extracellular faces of the resulting bilayer. This forms a continuous, spherical lipid bilayer. Hydrophobic interactions (also known as the hydrophobic effect) are the major driving forces in the formation of lipid bilayers. An increase in interactions between hydrophobic molecules (causing clustering of hydrophobic regions) allows water molecules to bond more freely with each other, increasing the entropy of the system. This complex interaction can include noncovalent interactions such as van der Waals, electrostatic and hydrogen bonds.
Lipid bilayers are generally impermeable to ions and polar molecules. The arrangement of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails of the lipid bilayer prevent polar solutes (ex. amino acids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins, and ions) from diffusing across the membrane, but generally allows for the passive diffusion of hydrophobic molecules. This affords the cell the ability to control the movement of these substances via transmembrane protein complexes such as pores, channels and gates.
Flippases and scramblases concentrate phosphatidyl serine, which carries a negative charge, on the inner membrane. Along with NANA, this creates an extra barrier to charged moieties moving through the membrane.
Membranes serve diverse functions in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. One important role is to regulate the movement of materials into and out of cells. The phospholipid bilayer structure (fluid mosaic model) with specific membrane proteins accounts for the selective permeability of the membrane and passive and active transport mechanisms. In addition, membranes in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotes facilitate the synthesis of ATP through chemiosmosis.
Membrane polarity
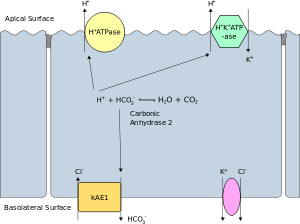
The apical membrane of a polarized cell is the surface of the plasma membrane that faces inward to the lumen. This is particularly evident in epithelial and endothelial cells, but also describes other polarized cells, such as neurons. The basolateral membrane of a polarized cell is the surface of the plasma membrane that forms its basal and lateral surfaces. It faces outwards, towards the interstitium, and away from the lumen. Basolateral membrane is a compound phrase referring to the terms "basal (base) membrane" and "lateral (side) membrane", which, especially in epithelial cells, are identical in composition and activity. Proteins (such as ion channels and pumps) are free to move from the basal to the lateral surface of the cell or vice versa in accordance with the fluid mosaic model. Tight junctions join epithelial cells near their apical surface to prevent the migration of proteins from the basolateral membrane to the apical membrane. The basal and lateral surfaces thus remain roughly equivalent to one another, yet distinct from the apical surface.
Membrane structures
Cell membrane can form different types of "supramembrane" structures such as caveola, postsynaptic density, podosome, invadopodium, focal adhesion, and different types of cell junctions. These structures are usually responsible for cell adhesion, communication, endocytosis and exocytosis. They can be visualized by electron microscopy or fluorescence microscopy. They are composed of specific proteins, such as integrins and cadherins.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is found underlying the cell membrane in the cytoplasm and provides a scaffolding for membrane proteins to anchor to, as well as forming organelles that extend from the cell. Indeed, cytoskeletal elements interact extensively and intimately with the cell membrane.[17] Anchoring proteins restricts them to a particular cell surface — for example, the apical surface of epithelial cells that line the vertebrate gut — and limits how far they may diffuse within the bilayer. The cytoskeleton is able to form appendage-like organelles, such as cilia, which are microtubule-based extensions covered by the cell membrane, and filopodia, which are actin-based extensions. These extensions are ensheathed in membrane and project from the surface of the cell in order to sense the external environment and/or make contact with the substrate or other cells. The apical surfaces of epithelial cells are dense with actin-based finger-like projections known as microvilli, which increase cell surface area and thereby increase the absorption rate of nutrients. Localized decoupling of the cytoskeleton and cell membrane results in formation of a bleb.
Composition
Cell membranes contain a variety of biological molecules, notably lipids and proteins. Material is incorporated into the membrane, or deleted from it, by a variety of mechanisms:
- Fusion of intracellular vesicles with the membrane (exocytosis) not only excretes the contents of the vesicle but also incorporates the vesicle membrane's components into the cell membrane. The membrane may form blebs around extracellular material that pinch off to become vesicles (endocytosis).
- If a membrane is continuous with a tubular structure made of membrane material, then material from the tube can be drawn into the membrane continuously.
- Although the concentration of membrane components in the aqueous phase is low (stable membrane components have low solubility in water), there is an exchange of molecules between the lipid and aqueous phases.
Lipids

The cell membrane consists of three classes of amphipathic lipids: phospholipids, glycolipids, and sterols. The amount of each depends upon the type of cell, but in the majority of cases phospholipids are the most abundant.[18] In RBC studies, 30% of the plasma membrane is lipid.
The fatty chains in phospholipids and glycolipids usually contain an even number of carbon atoms, typically between 16 and 20. The 16- and 18-carbon fatty acids are the most common. Fatty acids may be saturated or unsaturated, with the configuration of the double bonds nearly always "cis". The length and the degree of unsaturation of fatty acid chains have a profound effect on membrane fluidity[19] as unsaturated lipids create a kink, preventing the fatty acids from packing together as tightly, thus decreasing the melting temperature (increasing the fluidity) of the membrane. The ability of some organisms to regulate the fluidity of their cell membranes by altering lipid composition is called homeoviscous adaptation.
The entire membrane is held together via non-covalent interaction of hydrophobic tails, however the structure is quite fluid and not fixed rigidly in place. Under physiological conditions phospholipid molecules in the cell membrane are in the liquid crystalline state. It means the lipid molecules are free to diffuse and exhibit rapid lateral diffusion along the layer in which they are present. However, the exchange of phospholipid molecules between intracellular and extracellular leaflets of the bilayer is a very slow process. Lipid rafts and caveolae are examples of cholesterol-enriched microdomains in the cell membrane. Also, a fraction of the lipid in direct contact with integral membrane proteins, which is tightly bound to the protein surface is called annular lipid shell; it behaves as a part of protein complex.
In animal cells cholesterol is normally found dispersed in varying degrees throughout cell membranes, in the irregular spaces between the hydrophobic tails of the membrane lipids, where it confers a stiffening and strengthening effect on the membrane.[3]
Phospholipids forming lipid vesicles
Lipid vesicles or liposomes are circular pockets that are enclosed by a lipid bilayer. These structures are used in laboratories to study the effects of chemicals in cells by delivering these chemicals directly to the cell, as well as getting more insight into cell membrane permeability. Lipid vesicles and liposomes are formed by first suspending a lipid in an aqueous solution then agitating the mixture through sonication, resulting in a vesicle. By measuring the rate of efflux from that of the inside of the vesicle to the ambient solution, allows researcher to better understand membrane permeability. Vesicles can be formed with molecules and ions inside the vesicle by forming the vesicle with the desired molecule or ion present in the solution. Proteins can also be embedded into the membrane through solubilizing the desired proteins in the presence of detergents and attaching them to the phospholipids in which the liposome is formed. These provide researchers with a tool to examine various membrane protein functions.
Carbohydrates
Plasma membranes also contain carbohydrates, predominantly glycoproteins, but with some glycolipids (cerebrosides and gangliosides). For the most part, no glycosylation occurs on membranes within the cell; rather generally glycosylation occurs on the extracellular surface of the plasma membrane. The glycocalyx is an important feature in all cells, especially epithelia with microvilli. Recent data suggest the glycocalyx participates in cell adhesion, lymphocyte homing, and many others. The penultimate sugar is galactose and the terminal sugar is sialic acid, as the sugar backbone is modified in the Golgi apparatus. Sialic acid carries a negative charge, providing an external barrier to charged particles.
Proteins
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Integral proteins or transmembrane proteins | Span the membrane and have a hydrophilic cytosolic domain, which interacts with internal molecules, a hydrophobic membrane-spanning domain that anchors it within the cell membrane, and a hydrophilic extracellular domain that interacts with external molecules. The hydrophobic domain consists of one, multiple, or a combination of α-helices and β sheet protein motifs. | Ion channels, proton pumps, G protein-coupled receptor |
| Lipid anchored proteins | Covalently bound to single or multiple lipid molecules; hydrophobically insert into the cell membrane and anchor the protein. The protein itself is not in contact with the membrane. | G proteins |
| Peripheral proteins | Attached to integral membrane proteins, or associated with peripheral regions of the lipid bilayer. These proteins tend to have only temporary interactions with biological membranes, and once reacted, the molecule dissociates to carry on its work in the cytoplasm. | Some enzymes, some hormones |
The cell membrane has large content of proteins, typically around 50% of membrane volume[19] These proteins are important for cell because they are responsible for various biological activities. Approximately a third of the genes in yeast code specifically for them, and this number is even higher in multicellular organisms.[18]
The cell membrane, being exposed to the outside environment, is an important site of cell–cell communication. As such, a large variety of protein receptors and identification proteins, such as antigens, are present on the surface of the membrane. Functions of membrane proteins can also include cell–cell contact, surface recognition, cytoskeleton contact, signaling, enzymatic activity, or transporting substances across the membrane.
Most membrane proteins must be inserted in some way into the membrane. For this to occur, an N-terminus "signal sequence" of amino acids directs proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum, which inserts the proteins into a lipid bilayer. Once inserted, the proteins are then transported to their final destination in vesicles, where the vesicle fuses with the target membrane.
Variation
The cell membrane has different lipid and protein compositions in distinct types of cells and may have therefore specific names for certain cell types:
- Sarcolemma in myocytes
- Oolemma in oocytes
- Axolemma in neuronal processes - axons
- Historically, the plasma membrane was also referred to as the plasmalemma
Permeability
The permeability of a membrane is the rate of passive diffusion of molecules through the membrane. These molecules are known as permeant molecules. Permeability depends mainly on the electric charge and polarity of the molecule and to a lesser extent the molar mass of the molecule. Due to the cell membrane's hydrophobic nature, small electrically neutral molecules pass through the membrane more easily than charged, large ones. The inability of charged molecules to pass through the cell membrane results in pH partition of substances throughout the fluid compartments of the body.
See also
- Ammonium transporter
- Annular lipid shell
- AP2 adaptors
- Artificial cell
- Bacterial cell structure
- Bangstad syndrome
- Cell cortex
- Cell damage, including damage to cell membrane
- Cell theory
- Elasticity of cell membranes
- Gram-positive bacteria
- Membrane models
- History of cell membrane theory
- Lipid raft
- Trogocytosis
Notes and references
- ↑ Kimball's Biology pages, Cell Membranes
- ↑ Singleton P (1999). Bacteria in Biology, Biotechnology and Medicine (5th ed.). New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-98880-4.
- 1 2 Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). New York: Garland Science. ISBN 0-8153-3218-1.
- ↑ Budin, Itay; Devaraj, Neal K. (December 29, 2011). "Membrane Assembly Driven by a Biomimetic Coupling Reaction". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 134 (2): 751–753. doi:10.1021/ja2076873. Retrieved February 18, 2012.
- ↑ Staff (January 25, 2012). "Chemists Synthesize Artificial Cell Membrane". ScienceDaily. Retrieved February 18, 2012.
- ↑ Staff (January 26, 2012). "Chemists create artificial cell membrane". kurzweilai.net. Retrieved February 18, 2012.
- ↑ de Vries, H. 1885. Plasmolytische Studien über die Wand der Vakuolen. Jahrb. wiss. Bot. 16, 465–598
- ↑ Pfeffer, W. 1877. Osmotische Untersuchungen: Studien zur Zell Mechanik. Engelmann, Leipzig.
- ↑ Pfeffer , W. , 1900–1906. The Physiology of Plants, . Translated by A. J. Ewart from the 2nd German ed. of Pflanzenphysiologie, 1897-1904, . Clarendon Press, Oxford.
- ↑ Sharp, L. W. (1921). Introduction To Cytology. New York: McGraw Hill, p. 42.
- ↑ Kleinzeller, A. 1999. Charles Ernest Overton’s concept of a cell membrane. In: Membrane permeability: 100 years since Ernest Overton (ed. Deamer D.W., Kleinzeller A., Fambrough D.M.), pp. 1–18, Academic Press, San Diego, .
- ↑ Mast, S. O. 1924. Structure and locomotion in Amoeba proteus. Anat. Rec. 29: 88, .
- ↑ Plowe, J. Q. (1931). Membranes in the plant cell. I. Morphological membranes at protoplasmic surfaces. Protoplasma 12, 196-220, .
- ↑ Wayne, R. 2009. Plant Cell Biology: From Astronomy to Zoology. Amsterdam: Elsevier/Academic Press, p. 17.
- ↑ YashRoy, R.C. (1999). "A structural model for virulence organellae of gram negative organisms with reference to Salmonella pathogenicity in chicken ileum". Indian Journal of Poultry Science. 34 (2): 213–219.
- ↑ Singer SJ, Nicolson GL (Feb 1972). "The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes". Science. 175 (4023): 720–31. doi:10.1126/science.175.4023.720. PMID 4333397.
- ↑ Doherty GJ, McMahon HT (2008). "Mediation, Modulation and Consequences of Membrane-Cytoskeleton Interactions". Annual Review of Biophysics. 37: 65–95. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.125912. PMID 18573073.
- 1 2 Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky LS, et al. (2004). Molecular Cell Biology (4th ed.). New York: Scientific American Books. ISBN 0-7167-3136-3.
- 1 2 Jesse Gray; Shana Groeschler; Tony Le; Zara Gonzalez (2002). "Membrane Structure" (SWF). Davidson College. Retrieved 2007-01-11.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cell membrane. |
- Lipids, Membranes and Vesicle Trafficking - The Virtual Library of Biochemistry and Cell Biology
- Cell membrane protein extraction protocol
- Membrane homeostasis, tension regulation, mechanosensitive membrane exchange and membrane traffic
- 3D structures of proteins associated with plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells
- Lipid composition and proteins of some eukariotic membranes