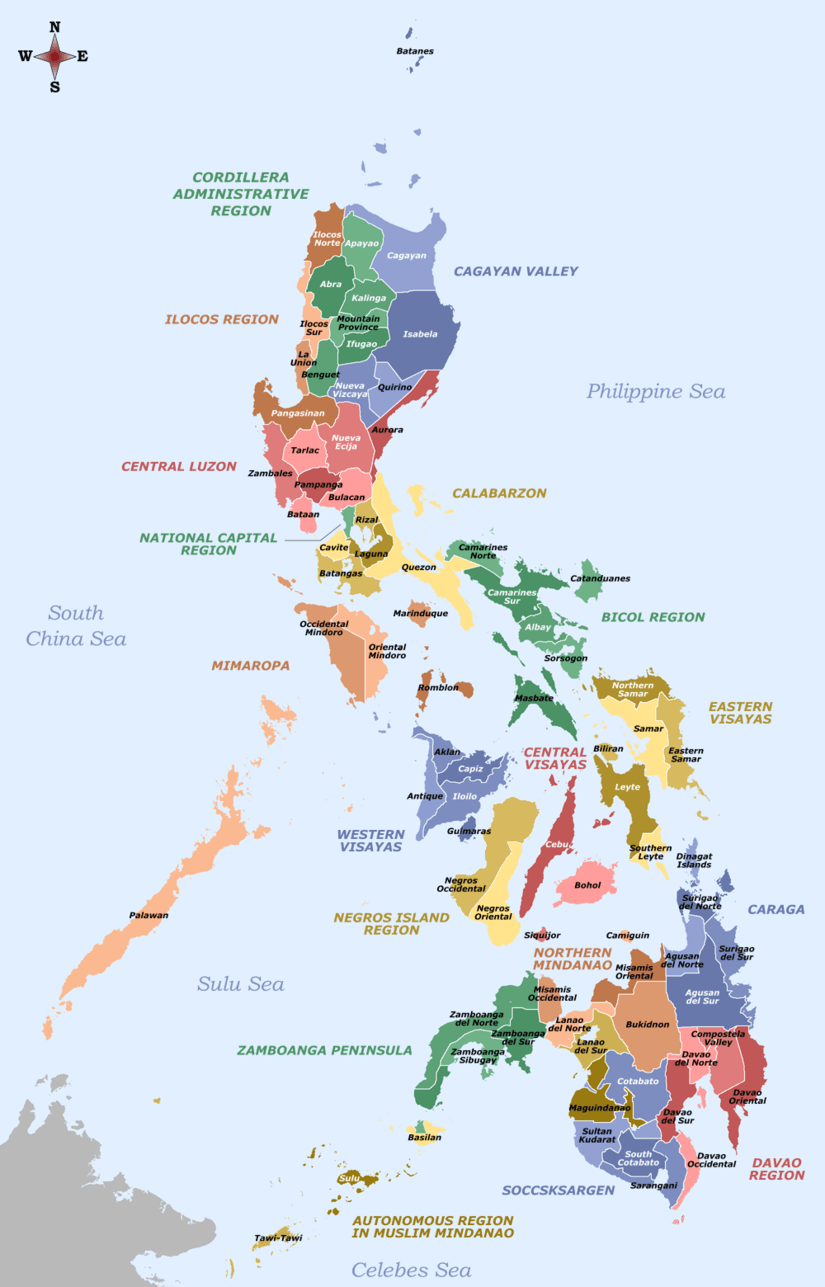
Sarangani
| Sarangani | ||
|---|---|---|
| Province | ||
| Province of Sarangani | ||
| ||
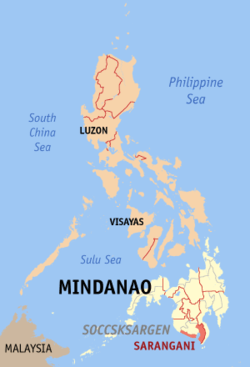 Location in the Philippines | ||
| Coordinates: 5°52′N 125°17′E / 5.87°N 125.28°ECoordinates: 5°52′N 125°17′E / 5.87°N 125.28°E | ||
| Country | Philippines | |
| Region | Soccsksargen (Region XII) | |
| Founded | March 16, 1992 | |
| Capital | Alabel | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlalawigan | |
| • Governor | Steve C. Solon (UNA/PCM) | |
| • Vice Governor | Elmer de Peralta | |
| • Congressman | Ruel Pacquiao | |
| • Sangguniang Panlalawigan |
Members
| |
| Area[1] | ||
| • Total | 3,601.25 km2 (1,390.45 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 37th out of 81 | |
| Population (2015 census)[2] | ||
| • Total | 544,261 | |
| • Rank | 55th out of 81 | |
| • Density | 150/km2 (390/sq mi) | |
| • Density rank | 58th out of 81 | |
| Divisions | ||
| • Independent cities | 0 | |
| • Component cities | 0 | |
| • Municipalities |
7
| |
| • Barangays | 141 | |
| • Districts | Lone district of Sarangani | |
| Time zone | PST (UTC+8) | |
| ZIP code | 9501–9503, 9514–9517 | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)83 | |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-SAR | |
| Spoken languages | ||
| Website |
www | |
Sarangani, or Saraŋgani, is a province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region. Its capital is Alabel. With a 230-kilometre (140 mi) coastline along the Sarangani Bay and Celebes Sea, the province is at the southernmost tip of Mindanao island, and borders South Cotabato and Davao del Sur to the north, Davao Occidental to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south.
Sarangani is part of the South Cotabato-Cotabato-Sultan Kudarat-Sarangani-General Santos City (SOCCSKSARGEN) development cluster, and is linked by paved roads to the international airport and harbor of General Santos City.
The province is divided into two sections, separated by the Sarangani Bay and General Santos City, and it used to be part of South Cotabato until it was made an independent province in 1992.[3]
History
The island of Sarangani (now part of Davao Occidental) was named by Spanish explorer Ruy López de Villalobos in 1543 as Antonia, in honor of Antonio de Mendoza y Pacheco who commissioned the Villalobos expedition to the Philippines. The early inhabitants who first inhabited Sarangani were the indigenous natives, called MunaTo, a native term for "first people."[4]
In 1942, the Japanese troops occupied Southern Cotabato. In 1945, Filipino troops of the 6th, 10th, 101st and 102nd Infantry Division of the Philippine Commonwealth Army and 10th Infantry Regiment of the Philippine Constabulary entered in and liberated Southern Cotabato and fought against the Japanese Imperial Army forces during the Battle of Cotabato at the end of World War II under the Japanese Occupation.
Before its inception in 1992, Sarangani was part of South Cotabato as the Third District of South Cotabato. The province was created by Republic Act No. 7228 on March 16, 1992,[3] penned by Congressman James L. Chiongbian. His wife, Priscilla L. Chiongbian, was the first Governor of Sarangani.
Geography
Sarangani covers a total area of 3,601.25 square kilometres (1,390.45 sq mi)[5] occupying the southern tip of the SOCCSKSARGEN in central Mindanao. The province is bordered on the central-north by South Cotabato, northeast by Davao del Sur, east by Davao Occidental, south by the Sarangani Bay and Celebes Sea, and northwest by Sultan Kudarat.

Sarangani is divided into two (eastern and western) sections, separated by the Sarangani Bay and General Santos City in the middle. The western portion comprises the towns of Maitum, Kiamba, and Maasim, and is bounded on the north by South Cotabato and on the northwest by Sultan Kudarat. The eastern section consists of Alabel, Glan, Malapatan, and Malungon.
Administrative divisions
Sarangani comprises 7 municipalities. A single legislative district encompasses all towns.[5]
| Municipality [lower-roman 1] | Population | ±% p.a. | Area[5] | Density (2015) | Brgy. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (2015)[2] | (2010)[6] | km2 | sq mi | /km2 | /sq mi | |||||||
| 6°06′10″N 125°17′31″E / 6.1027°N 125.2920°E | Alabel | † | 14.8% | 80,359 | 75,477 | +1.20% | 510.98 | 197.29 | 160 | 410 | 13 | |
| 5°49′21″N 125°12′17″E / 5.8225°N 125.2046°E | Glan | 21.7% | 118,263 | 106,518 | +2.01% | 610.30 | 235.64 | 190 | 490 | 31 | ||
| 5°59′19″N 124°37′27″E / 5.9885°N 124.6241°E | Kiamba | 11.2% | 61,058 | 54,871 | +2.06% | 328.68 | 126.90 | 190 | 490 | 19 | ||
| 5°51′40″N 124°59′48″E / 5.8610°N 124.9967°E | Maasim | 10.9% | 59,468 | 52,933 | +2.24% | 500.43 | 193.22 | 120 | 310 | 16 | ||
| 6°03′41″N 124°29′45″E / 6.0613°N 124.4957°E | Maitum | 8.2% | 44,595 | 41,675 | +1.30% | 290.66 | 112.22 | 150 | 390 | 19 | ||
| 5°58′15″N 125°17′18″E / 5.9707°N 125.2882°E | Malapatan | 14.1% | 76,914 | 72,386 | +1.16% | 609.28 | 235.24 | 130 | 340 | 12 | ||
| 6°22′31″N 125°16′18″E / 6.3752°N 125.2717°E | Malungon | 19.0% | 103,604 | 95,044 | +1.66% | 750.92 | 289.93 | 140 | 360 | 31 | ||
| Total | 544,261 | 498,904 | +1.67% | 3,601.25 | 1,390.45 | 150 | 390 | 141 | ||||
| † Provincial capital | Municipality | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Demographics
| Population census of Sarangani | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[2][6][7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
The population of Sarangani in the 2015 census was 544,261 people,[2] with a density of 150 inhabitants per square kilometre or 390 inhabitants per square mile.
Religion
Christianity in the form of Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion in the province comprising 63% of the population. Other religious affiliations belong to the following denominations: Islam (9%), United Church of Christ in the Philippines (6%), other Protestant Churches (6%), Alliance of Bible Church Community (3%) and Iglesia Ni Cristo (2%) (Saranggani & GSC Census, 1990). The remainder is usually divided among other Christian Churches.
Economy
Coconut, corn, rice, banana, mango, durian, rubber, and sugarcane are major crops now being planted by the inhabitants. The province has plantations (mango, banana, pineapple, asparagus), cattle ranches, and commercial fishponds that have been operating in the area, some of which having existed as far back as 40 years.
Electricity comes from the National Power Corporation, and augmented by a 50 MW power plant in Alabel, the province’s capital. Water is provided for by sustainable spring development projects.
Government
|
|
Tourism
Sarangani celebrates its foundation anniversary every November, named as MunaTo Festival.[8]
Sarangani has ancient burial jars, discovered by archaeologists from the National Museum in Ayub Cave in Maitum, in 1991 and in 2008, and at Sagel Cave in Maitum (now declared by National Historical Institute as a national historical site). Amid Mindanao's armed conflicts, artifacts found thereat prove settlements of pre-historic civilization in Maitum.[8][9]
References
- ↑ "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Retrieved 13 May 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 "Region XII (SOCCSKSARGEN)". Census of Population (2015): Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay (Report). PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- 1 2 "An Act Creating the Province of Sarangani" (PDF). House of Representatives of the Philippines. 16 March 1992. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ↑ balita.ph/2008, Man-made island resort now a Sarangani landmark
- 1 2 3 "Province: Sarangani". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- 1 2 "Region XII (SOCCSKSARGEN)". Census of Population and Housing (2010): Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay (Report). NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ↑ "Region XII (SOCCSKSARGEN)". Census of Population (1995, 2000 and 2007): Total Population by Province, City and Municipality (Report). NSO. Archived from the original on 24 June 2011.
- 1 2 "'MunaTo' festival". Manila Bulletin. 29 November 2013. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
The provincial government started their celebration of its 21st foundation anniversary on Thursday and officially opened its 11th “MunaTo Festival” starting November 27 and will run up to December 6, this year.
- ↑ Pelima, Russtum G. (10 November 2008). "Island resort now Sarangani landmark". Philippine Information Agency. PIO Sarangani/ICC GenSan. Archived from the original on 11 February 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
Despite armed conflicts occurring in Mindanao, artifacts found by archaeologists from the National Museum in Ayub Cave in 1991 and Sagel Cave this year prove settlements of pre-historic civilization in Maitum.
External links
-
 Media related to Sarangani at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Sarangani at Wikimedia Commons -
 Geographic data related to Sarangani at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Sarangani at OpenStreetMap - Official Website of the Provincial Government of Sarangani
- Local Governance Performance Management System
 |
South Cotabato |  | ||
| Sultan Kudarat | |
Sarangani Bay | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Celebes Sea |
 |
Davao del Sur |  | ||
| South Cotabato Sarangani Bay |
|
Davao Occidental | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Celebes Sea |