Shafi'i
| |
|---|
 |
|
Lists |
|
|
The Shafi'i (Arabic: شافعي Shāfiʿī ) madhhab is one of the four schools of Islamic law in Sunni Islam.[1][2] It was founded by the Arab scholar Al-Shafi‘i, a pupil of Malik, in the early 9th century.[3][4] The other three schools of Sunni jurisprudence are Hanafi, Maliki and Hanbali.[1][2]
The Shafi school predominantly relies on the Quran and the Hadiths for Sharia.[3][5] Where passages of Quran and Hadiths are ambiguous, the school first seeks religious law guidance from Ijma – the consensus of Sahabah (Muhammad's companions).[6] If there was no consensus, the Shafi'i school relies on individual opinion (Ijtihad) of the companions of Muhammad, followed by analogy.[3]
The Shafi'i school was, in the early history of Islam, the most followed ideology for Sharia. However, with the Ottoman Empire's expansion and patronage, it was replaced with the Hanafi school in many parts of the Muslim world.[5] One of the many differences between the Shafi'i and Hanafi schools is that the Shafi'i school does not consider Istihsan (the personal preference of Islamic legal scholars) as an acceptable source of religious law because it amounts to "human legislation" of Islamic law.[7]
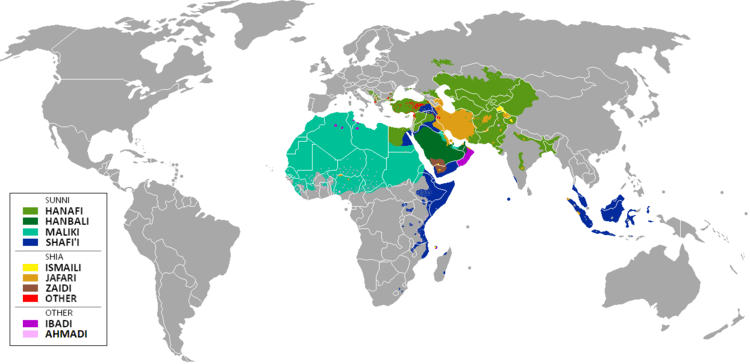
The Shafi'i school is now predominantly found in Somalia, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti, eastern Egypt, the Swahili coast, Yemen, Kurdish regions of the Middle East, Dagestan, Chechen and Ingush regions of the Caucasus, Palestine, Lebanon, Indonesia, Malaysia, Maldives, some coastal parts of Sri Lanka, India, Singapore, Myanmar, Thailand, Brunei, and the Philippines.[8]
Principles
The Shafi'i school of thought stipulates authority to five sources of jurisprudence. In hierarchical order, the school relies upon the following sources for Islamic law: the Quran, the hadiths - that is, sayings, customs and practices of Muhammad, the ijmā' (consensus of Sahabah, the community of Muhammad's companions),[9] the individual opinions of Sahaba with preference to one closest to the issue as Ijtihad, and finally qiyas (analogy).[3] Although al-Shafi'i's legal methodology rejected custom or local practice as a constitutive source of law, this did not mean that he or his followers denied any elasticity in the Shariah.[10] The Shafi'i school also rejects two sources of Sharia that are accepted in other major schools of Islam - Istihsan (juristic preference, promoting the interest of Islam) and Istislah (public interest).[11][12] The jurisprudence principle of Istihsan and Istislah admitted religious laws that had no textual basis in either the Quran or Hadiths, but were based on the opinions of Islamic scholars as promoting the interest of Islam and its universalization goals.[13] The Shafi'i school rejected these two principles stating that these methods rely on subjective human opinions, its potential for corruption and adjustment to political context and time.[11][12]
The foundational text for the Shafi'i school is Al-Risala (or, The Message) by the founder of the school, Al-Shafi'i. It outlines the principles of Shafi'i fiqh as well as the derived jurisprudence.[14] Al-Risala became an influential book to other Sunni Islam fiqhs as well, as the oldest surviving Arabic work on Islamic legal theory.[15]
Shafi'i school
History
The Shafi'i madhhab was spread by Al-Shafi'i students in Cairo, Mecca and Baghdad. It became widely accepted in early history of Islam. The chief representative of the Iraqi school was Abu Ishaq al-Shirazi, whilst in Khorasan, the Shafi'i school was spread by al-Juwayni and al-Iraqi. These two branches merged around Ibn al-Salah and his father, before being reviewed and refined by al-Rafi'i and al-Nawawi.
The Shafi'i jurisprudence was adopted as the official law during the Great Seljuq Empire, Zengid dynasty, Ayyubid dynasty and later the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo), where it saw its widest application. It was also adopted by the Kathiri state in Hadhramawt and most of rule of the Sharif of Mecca.
With the establishment and expansion of Ottoman Empire in West Asia and Turkic Sultanates in Central and South Asia, Shafi'i school was replaced with Hanafi school, in part because Hanafites allowed Istihsan (juristic preference) that allowed the rulers flexibility in interpreting the religious law to their administrative preferences.[7] The Sultanates along the littoral regions of the Horn of Africa and the Arabian peninsula adhered to the Shafi'i school and were the primary drivers of its maritime military expansion into many Asian and East African coastal regions of the Indian Ocean, particularly from the 12th through the 18th century.[16][17]
Demographics
The Shafi'i school is presently predominant in the following parts of the Muslim world:[8]
- Africa: Djibouti, Somalia, Ethiopia, Eritrea, eastern Egypt, and the Swahili Coast.[18]
- Middle East: Yemen, Kurdish regions of the Middle East, Caucasus region, Israel, Lebanon, minor parts of Jordan, Palestine and Saudi Arabia
- Caucasus: Chechnya, Ingushetia and parts of Azerbaijan[19]
- Asia: Indonesia, Malaysia, Maldives, Sri Lanka, western coast of Indian peninsula, Singapore, Myanmar, Thailand, Brunei, and the southern Philippines.
Shafi'i school is the second largest school of Sunni madhhabs by number of adherents, states Saeed in his 2008 book.[2] However, a UNC publication considers the Maliki school as second largest, and the Hanafi madhhab the largest, with Shafi'i as third largest.[8] The demographic data by each fiqh, for each nation, are unavailable and the relative demographic size are estimates.
Notable Shafi'i's
Contemporary Shafi'i scholars
- Wahba Zuhayli
- Ali Gomaa
- Habib Umar bin Hafiz
- Habib Ali al-Jifri
- Abdullah al-Harari
- Afifi al-Akiti
- Hasyim Muzadi
- Aboobacker Ahmad
- Nuh Ha Mim Keller
- Mohammad Salim Al-Awa
- Ahmed Kuftaro
- Ahmad Syafi'i Maarif
- Syed Muhammad Naquib al-Attas
- Taha Jabir Alalwani
- Zaid Shakir
- Cherussery Zainuddeen Musliyar
See also
- Islamic schools and branches
- Sharia
- Salat
- Wudu
- Adhan
- Islamic views on sin
- Blasphemy in Islam
- Apostasy in Islam
Notes
- 1 2 Hallaq 2009, p. 31.
- 1 2 3 Abdullah Saeed (2008), The Qur'an: An Introduction, Routledge, ISBN 978-0415421256, p. 17
- 1 2 3 4 Hisham M. Ramadan (2006), Understanding Islamic Law: From Classical to Contemporary, Rowman Altamira, ISBN 978-0759109919, pp. 27-28
- ↑ Hashim Kamali 2008, p. 77.
- 1 2 Shafi'iyyah Bulend Shanay, Lancaster University
- ↑ Syafiq Hasyim (2005), Understanding Women in Islam: An Indonesian Perspective, Equinox, ISBN 978-9793780191, pp. 75-77
- 1 2 Wael B. Hallaq (2009), Sharī'a: Theory, Practice, Transformations, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521861472, pp. 58-71
- 1 2 3 Jurisprudence and Law - Islam Reorienting the Veil, University of North Carolina (2009)
- ↑ Badr al-Din al-Zarkashi (1393), Al-Bahr Al-Muhit, Vol 6, pp 209
- ↑ A.C. Brown, Jonathan (2014). Misquoting Muhammad: The Challenge and Choices of Interpreting the Prophet's Legacy. Oneworld Publications. p. 39. ISBN 978-1780744209.
- 1 2 Istislah The Oxford Dictionary of Islam, Oxford University Press
- 1 2 Istihsan The Oxford Dictionary of Islam, Oxford University Press
- ↑ Lloyd Ridgeon (2003), Major World Religions: From Their Origins To The Present, Routledge, ISBN 978-0415297967, pp. 259-262
- ↑ Majid Khadduri (1961), Islamic Jurisprudence: Shafi'i's Risala, Johns Hopkins University Press, pp. 14-22
- ↑ Joseph Lowry (Translator), Al-Shafi'i - The Epistle on Legal Theory, Risalah fi usul al-fiqh, New York University Press, 2013, ISBN 978-0814769980
- ↑ Randall L. Pouwels (2002), Horn and Crescent: Cultural Change and Traditional Islam, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521523097, pp 88-159
- ↑ MN Pearson (2000), The Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, in The History of Islam in Africa (Ed: Nehemia Levtzion, Randall Pouwels), Ohio University Press, ISBN 978-0821412978, Chapter 2
- ↑ UNION OF THE COMOROS 2013 INTERNATIONAL RELIGIOUS FREEDOM REPORT U.S. State Department (2014), Quote: "The law provides sanctions for any religious practice other than the Sunni Shafi’i doctrine of Islam and for prosecution of converts from Islam, and bans proselytizing for any religion except Islam."
- ↑ Islam in Azerbaijan (Historical Background), Altay Goyushov, CAUCASUS ANALYTICAL DIGEST No. 44, 20 November 2012
- ↑ A.C. Brown, Jonathan (2014). Misquoting Muhammad: The Challenge and Choices of Interpreting the Prophet's Legacy. Oneworld Publications. p. 105. ISBN 978-1780744209.
- ↑ A.C. Brown, Jonathan (2014). Misquoting Muhammad: The Challenge and Choices of Interpreting the Prophet's Legacy. Oneworld Publications. p. 303. ISBN 978-1780744209.
References
- Hallaq, Wael B. (2009). An Introduction to Islamic Law. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521678735.
- Hashim Kamali, Mohammad (2008). Shari'ah Law: An Introduction. Oneworld Publications. ISBN 978-1851685653.
- Yahia, Mohyddin (2009). Shafi'i et les deux sources de la loi islamique, Turnhout: Brepols Publishers, ISBN 978-2-503-53181-6
- Rippin, Andrew (2005). Muslims: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices (3rd ed.). London: Routledge. pp. 90–93. ISBN 0-415-34888-9.
- Calder, Norman, Jawid Mojaddedi, and Andrew Rippin (2003). Classical Islam: A Sourcebook of Religious Literature. London: Routledge. Section 7.1.
- Schacht, Joseph (1950). The Origins of Muhammadan Jurisprudence. Oxford: Oxford University. pp. 16.
- Khadduri, Majid (1987). Islamic Jurisprudence: Shafi'i's Risala. Cambridge: Islamic Texts Society. pp. 286.
- Abd Majid, Mahmood (2007). Tajdid Fiqh Al-Imam Al-Syafi'i. Seminar pemikiran Tajdid Imam As Shafie 2007.
- al-Shafi'i,Muhammad b. Idris,"The Book of the Amalgamation of Knowledge" translated by A.Y. Musa in Hadith as Scripture: Discussions on The Authority Of Prophetic Traditions in Islam, New York: Palgrave, 2008
Further reading
- Joseph Lowry (Translator), Al-Shafi'i - The Epistle on Legal Theory (Risalah fi usul al-fiqh), New York University Press, 2013, ISBN 978-0814769980
- Cilardo, Agostino, Shafi'i Fiqh, in Muhammad in History, Thought, and Culture: An Encyclopedia of the Prophet of God (2 vols.), Edited by C. Fitzpatrick and A. Walker, Santa Barbara, ABC-CLIO, 2014. ISBN 1610691776
External links
- Shafi'iyyah Bulend Shanay, Lancaster University
- Al-Shafi'i Risala Majid Khadduri (Translator), 1961
- Music and Its Effects Ahmed Sheriff, Tanzania, Why it was forbidden?, pp. 50–55