1760s
| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
| Centuries: | 17th century – 18th century – 19th century |
| Decades: | 1730s 1740s 1750s – 1760s – 1770s 1780s 1790s |
| Years: | 1760 1761 1762 1763 1764 1765 1766 1767 1768 1769 |
| 1760s-related categories: |
Births – Deaths – By country Establishments – Disestablishments |
Events
Contents: 1760 1761 1762 1763 1764 1765 1766 1767 1768 1769
1760
January–June

- January 22 – Seven Years' War – At the Battle of Wandiwash in India, British general Sir Eyre Coote is victorious over the French under the Marquis de Bussy-Castelnau.[1]
- January 28 – Benning Wentworth creates the New Hampshire Grant of Pownal, Vermont.
- February 15 – The British Royal Navy ship HMS Royal Katherine runs aground off Bolt Head in England with the loss of 699 lives.
- February 21–26 – Seven Years' War – At the Battle of Carrickfergus in the north of Ireland, a force of French troops under the command of privateer François Thurot captures and holds the town and castle of Carrickfergus before retiring; the force is defeated (and Thurot killed) in a naval action in the Irish Sea on February 28.[2]
- February 27 – Seven Years' War – French and Indian War & Anglo-Cherokee War: Cherokee natives attack a North Carolina militia stationed at Fort Dobbs in the western part of the province. The attack is repelled by the militia under the command of General Hugh Waddell.
- March 20 – The Great Fire of Boston, Massachusetts, destroys 349 buildings.
- May–July – 'Tacky's War', a slave rebellion, occurs in Jamaica.
- June 4 – Expulsion of the Acadians: New England planters arrive to claim land in Nova Scotia taken from the Acadians.
July–December

Wedding Supper at the wedding of Princess Isabella of Parma and Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, by Martin van Meytens
- July 3 – A lightning strike causes a major fire at Portsmouth Royal Dockyard in England.[3][4]
- July 8 – Seven Years' War – French and Indian War: Battle of Restigouche: British defeat French forces in the last naval battle in New France.
- July 19 – A formal request is made to the Spanish government as to allow the founding of the later city of Mayagüez, Puerto Rico.
- July 31 – Seven Years' War – Battle of Warburg: The Anglo-Hanoverian army of Ferdinand of Brunswick storms Warburg, with a heroic role being played by the English commander Lord Granby.
- August 21 – The church (later cathedral) of Our Lady of Candlemas of Mayagüez (Puerto Rico) is founded, establishing the basis for the founding of the city.
- August 30 – Seven Years' War – Battle of Legnica: By a series of brilliant maneuvers, Frederick the Great manages to defeat the Austrian army of Marshal Laudon before it can unite with that of Marshal Daun.
- September 8 – Seven Years' War: Jeffery Amherst captures Montreal.[5]
- September 18 – The town (later city) of Mayagüez, Puerto Rico, is founded.
- October 5 The wedding of Princess Isabella of Parma and Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, at Hofburg Palace's Redoute Hall - (Redoutensaele) at the former imperial palace in Vienna.[6]
- October 9 – Seven Years' War: Russian troops enter Berlin.
- October 16 – Seven Years' War – Battle of Kloster-Kamp: Ferdinand of Brunswick is beaten back from the Rhine by a French army.
- October 25 – George II of Great Britain dies; his grandson George III ascends to the throne. He reigns until January 1820.
- November 3 – Seven Years' War – Battle of Torgau: In another extremely hard battle, Frederick defeats Daun's Austrians, who withdraw across the Elbe.
Date unknown
| 1760s by topic: | |
| Arts and Sciences | |
| Archaeology – Architecture – Art – Literature (Poetry) – Music – Science | |
| Countries | |
| Lists of leaders | |
| Colonial governors – State leaders | |
| Birth and death categories | |
| Births – Deaths | |
| Establishments and disestablishments categories | |
| Establishments – Disestablishments | |
| Works category | |
| Works | |
| Gregorian calendar | 2016 MMXVI |
| Ab urbe condita | 2769 |
| Armenian calendar | 1465 ԹՎ ՌՆԿԵ |
| Assyrian calendar | 6766 |
| Bahá'í calendar | 172–173 |
| Bengali calendar | 1423 |
| Berber calendar | 2966 |
| British Regnal year | 64 Eliz. 2 – 65 Eliz. 2 |
| Buddhist calendar | 2560 |
| Burmese calendar | 1378 |
| Byzantine calendar | 7524–7525 |
| Chinese calendar | 乙未年 (Wood Goat) 4712 or 4652 — to — 丙申年 (Fire Monkey) 4713 or 4653 |
| Coptic calendar | 1732–1733 |
| Discordian calendar | 3182 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 2008–2009 |
| Hebrew calendar | 5776–5777 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 2072–2073 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 1937–1938 |
| - Kali Yuga | 5116–5117 |
| Holocene calendar | 12016 |
| Igbo calendar | 1016–1017 |
| Iranian calendar | 1394–1395 |
| Islamic calendar | 1437–1438 |
| Japanese calendar | Heisei 28 (平成28年) |
| Javanese calendar | 1949–1950 |
| Juche calendar | 105 |
| Julian calendar | Gregorian minus 13 days |
| Korean calendar | 4349 |
| Minguo calendar | ROC 105 民國105年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | 548 |
| Thai solar calendar | 2559 |
| Unix time | 1451606400–1483228799 |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1760s. |
- Dr. James Fordyce's two-volume compendium, Sermons for Young Women, is published.
- Western countries pay 3,000,000 ounces of silver for Chinese goods.
- approximate date – Abu Dhabi is founded.
1761
January–June
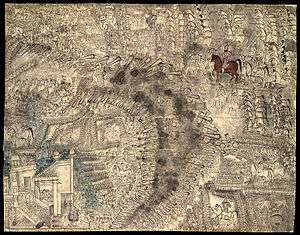
Ahmad Shah Durrani and his coalition decisively defeat the Maratha Confederacy and restore the Mughal Empire to Shah Alam II.
- January 14 – Third Battle of Panipat: Ahmad Shah Durrani and his coalition decisively defeat the Maratha Confederacy and restore the Mughal Empire to Shah Alam II.
- January 16 – The British capture Pondichéry, India from the French.[7]
- February 8 – An earthquake in London breaks chimneys in Limehouse and Poplar.
- March 8 – A second earthquake occurs in North London, Hampstead and Highgate.
- March 31 – Earthquake in Lisbon, Portugal.[8]
- June 6 – A transit of Venus occurs, and is observed from 120 locations around the Earth. Mikhail Lomonosov discovers atmosphere of Venus.
July–December
- July 17 - The first section of the Bridgewater Canal is opened, for the transportation of coal from local mines to Manchester.[9]
- September 8 – King George III of Great Britain marries Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Queen Charlotte).
- September 19 – The slave trade to and within Portugal is forbidden.
- September 22 – King George III and Queen Charlotte are crowned.
- December 16 – Seven Years' War: After four months of siege, the Russians under Pyotr Rumyantsev take the Prussian fortress of Kolberg.
Date unknown
- In Dutch Guyana, a "state" formed by escaped slaves signs a treaty with the local governor.
- Matthew Boulton's Soho Manufactory opens.
- The tune to Twinkle Twinkle Little Star is published in France.
- Faber-Castell Company was founded by Kasper Faber in Nuremberg, Germany.
- Johann Heinrich Lambert found a proof that π is irrational.
- l'Ordre des Chevaliers Maçons Élus Coëns de l'Univers is founded.
1762
January–June
- January 4 – Britain enters the Seven Years' War against Spain and Naples.
- January 5 – Empress Elisabeth of Russia dies and is succeeded by her nephew Peter III. Peter, an admirer of Frederick the Great, immediately opens peace negotiations with the Prussians.
- February 5 – The Great Holocaust of the Sikhs is carried out by the forces of Ahmed Shah Abdali in Punjab. In all, around 30,000 men, women and children perish in this campaign of slaughter.
- May 15 – The Treaty of Saint Petersburg ends the war between Russia and Prussia.
- May 22 – The Treaty of Hamburg takes Sweden out of the war against Prussia.
- June 24 – Battle of Wilhelmsthal: The Anglo-Hanoverian army of Ferdinand of Brunswick defeats the French forces in Westphalia. The British commander Lord Granby distinguishes himself.
July–December
- July 9 – Catherine II becomes empress of Russia upon the deposition of her husband Peter III. The incipient Russo-Prussian alliance falls apart, but Russia does not rejoin the war.
- July 21 – Battle of Burkersdorf: In his last major battle, Frederick defeats Marshal Daun in Silesia.

- August 13 – Seven Years' War: The Battle of Havana concludes after more than two months with the surrender of Havana by Spain to Great Britain.
- September – Empress Go-Sakuramachi succeeds her brother Emperor Momozono on the throne of Japan.
- September 15 – Battle of Signal Hill: British troops defeat the French.
- September 24–October 5 – Battle of Manila: Troops of the British East India Company take Manila from the Spanish, leading to the British occupation of Manila and its being made an open port.
- October 29 – Battle of Freiberg: Prince Henry of Prussia, Frederick's brother, defeats the Austrian army of Marshal Serbelloni.
- November 13 – Treaty of Fontainebleau, a secret agreement in which Louis XV of France cedes Louisiana (New France) to Charles III of Spain.
Date unknown
- Louis XV orders the construction of the Petit Trianon, in the park of the Palace of Versailles, for his mistress Madame de Pompadour.
- Neolin, a Delaware tribe prophet, begins to preach in America.
- The North Carolina General Assembly incorporates Kingston, named for King George III of the United Kingdom, as the county seat of Dobbs County, North Carolina. The name is later shortened to Kinston in 1784.
- The town of Charlottesville, Virginia, is founded.
- Building of the Plymouth Synagogue in Plymouth, England, the oldest built by Ashkenazi Jews in the English-speaking world.
- French philosopher Jean-Jacques Rousseau publishes his famous books, The Social Contract and Émile, or On Education
- James Stuart and Nicholas Revett's architectural treatise Antiquities of Athens.
1763
January–June
- February 1 – The Royal Colony of North Carolina officially creates Mecklenburg County from the western portion of Anson County. The county is named for Queen Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, who married George III of the United Kingdom in 1761.
- February 10 – French and Indian War/Seven Years' War: The Treaty of Paris ends the war and France cedes Canada (New France) to Great Britain.[10]
- February 15 – The Treaty of Hubertusburg puts an end to the Seven Years' War between Prussia and Austria and their allies.
- February 23 – The Berbice Slave Uprising starts in the former Dutch colony of Berbice.
- March 1 – Charles Townshend becomes President of the Board of Trade in the British government.
- May 7 – Chief Pontiac begins the "Conspiracy of Pontiac" by attacking British forces at Fort Detroit.
- June 2 – Pontiac's Rebellion: At what is now Mackinaw City, Michigan, Chippewas capture Fort Michilimackinac by diverting the garrison's attention with a game of lacrosse, then chasing a ball into the fort.
- June 28 – A magnitude 6.2 earthquake shakes Hungary and Slovakia with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). Damage is limited, but 83 are killed.[11]
July–December
- July 7 – The British East India Company declare Mir Qasim, the Nawab of Bengal, to be deposed.[12][13]
- August 2 – Mir Qasim routed at Odwa Nala.[12] He flees to Patna, where he massacres the English garrison,[13] but is subsequently defeated at Katwa, Murshidabad, Giria, Sooty, Udayanala and Munger.
- August 5 – Pontiac's War – Battle of Bushy Run: British forces led by Henry Bouquet defeat Chief Pontiac's Indians at Bushy Run in the Pennsylvania backcountry.
- August – Fire in Smyrna, Ottoman Empire, destroys 2,600 houses.
- September 1 – Catherine II of Russia endorses Ivan Betskoy's plans for a Foundling Home in Moscow.
- October 7 – The Royal Proclamation of 1763 is issued by George III of the United Kingdom, restricting westward expansion of British North America and stabilizing relations with indigenous peoples of the Americas.
- November 24 – Bayes' theorem is first announced.[14]
- December 2 – Touro Synagogue, Newport, Rhode Island, dedicated; by the end of the 20th century this will be the oldest surviving synagogue in North America.
- December 14 – The Paxton Boys massacre six Conestoga Indians in their homes in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania When the 16 survivors are sheltered in the Lancaster workhouse (jail), the Paxton Boys ride into town and kill them as well, on December 27.
Date unknown
- Little Hagia Sophia in Istanbul, Ottoman Empire, damaged in an earthquake.
- The seat of colonial administration in the Viceroyalty of Brazil is moved from Salvador to Rio de Janeiro.
- Joseph Haydn writes his Symphony No. 13.
- The Russo-Circassian War begins when the Russian Empire attempts to annex Circassia.
1764
January–June
- January 7 – Siculicidium: Hundreds of innocent Székely people are murdered by the Austrians in a massacre at Madéfalva (Transylvania, Kingdom of Hungary).
- January 19 – John Wilkes is expelled from the House of Commons of Great Britain for seditious libel.
- February 15 – The American city of St. Louis is established.
- April 5 – The Sugar Act is passed in Great Britain.
- June 21 – The English-language Quebec Gazette is established in Quebec City, Canada. As of 2014, it is the oldest surviving newspaper in North America.
- June 29 – A Level 5 tornado hits Woldegk, Germany.
July–December
- September 7 – Stanisław August Poniatowski is elected as the King of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
- October 15 – English scholar Edward Gibbon conceives the idea of writing The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire "as I sat musing amid the ruins of the Capitol".
- October 22 – Battle of Buxar: The British East India Company defeats the combined armies of Mir Qasim, the Nawab of Bengal, the Nawab of Awadh, and Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II.
- November 9 – Mary Campbell, a captive of the Lenape during the French and Indian War, is turned over to forces commanded by Colonel Henry Bouquet.
- November 16 – Chief Pontiac surrenders to the British.
Date unknown
- The Royal Colony of North Carolina establishes a new county from the eastern portion of Granville County and names it Bute County for John Stuart, 3rd Earl of Bute, who had recently resigned his post as Prime Minister of Great Britain. In 1779 the State of North Carolina abolishes the county when it forms Warren County from the northern portion and Franklin County from the southern portion.
- The French government withdraws the wartime taxes.
1765
January–June
- January 23 – Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor marries Princess Maria Josepha of Bavaria in Vienna.
- March 9 – After a public campaign by the writer Voltaire, judges in Paris posthumously exonerate Jean Calas of murdering his son. Calas had been tortured and executed in 1762 on the charge, though his son may have committed suicide.
- March 22 – The Parliament of Great Britain passes the Stamp Act, imposing the first direct tax levied from Great Britain on the thirteen American colonies. This is to help pay for British military operations in North America.
- March 24 – Great Britain passes the Quartering Act, requiring the thirteen American colonies to house British troops.
- May – James Watt makes a breakthrough in the development of the steam engine by constructing a model with a separate condenser.
- May 18 – Fire destroys one quarter of the town of Montreal, Quebec.
- June 21 – The Isle of Man is brought under British control, the Isle of Man Purchase Act (coming into force 10 May) confirming HM Treasury's purchase of the feudal rights of the Dukes of Atholl as Lord of Mann over the island and revesting them into the British Crown.[15]
July–December
- August 9 – Russian Empress Catherine II issues a decree authorizing the new way to produce vodka (by freezing).
- August 16 – Treaty of Allahabad was signed. The Treaty marks the political and constitutional involvement and the beginning of Company rule in India.[16]
- August 14 – In protest at the Stamp Act, Bostonians attack the home of official Andrew Oliver.
- August 18 – Josef II becomes Holy Roman Emperor.
- August 26 – In protest at the Stamp Act, Bostonians destroy home of lieutenant governor Thomas Hutchinson.
- September 6 – Jean-Jacques Rousseau's house in Switzerland is stoned by a mob.
- September 21 – François Antoine announces he has killed the Beast of Gévaudan.
- October 17 – The Pennsylvania Gazette reports that a Mr. McCullough, the Distributor of Stamps for the Royal Colony of North Carolina, has resigned his post in protest at the Stamp Act. A Dr. Huston is appointed to the position.
- November 1 – The Stamp Act goes into effect in the thirteen American colonies.
- December 12 – The Pennsylvania Gazette reports that Dr. Huston, the recently instated Distributor of Stamps for the Royal Colony of North Carolina, has resigned his post in protest at the Stamp Act.
Date unknown
- The first chocolate factory in the Thirteen Colonies is established by Dr. James Baker at Dorchester, Massachusetts.
- The first true restaurant opens in Paris, where a tavern-keeper named Boulanger sells cooked dishes at an all-night place on the Rue Bailleul.
- In Lisbon, the auto-da-fé parade (often an excuse for violence against Jews or Christian 'heretics') is abolished.
- Desai Atash Behram is established in Navsari, India.
1766
January–June
- January 1 – Charles Edward Stuart ("Bonnie Prince Charlie") becomes the new Stuart claimant to the throne of Great Britain as King Charles III and figurehead for Jacobitism. [17]
- January 14 – Christian VII becomes King of Denmark.
- February 5 – An observer in Wilmington, North Carolina reports to the Edinburgh newspaper Caledonian Mercury that three ships have been seized by British men-of-war on the charge of carrying official documents without stamps. The strict enforcement causes seven other ships to leave Wilmington for other ports.
- February 13 – John Mills is elected a Fellow of the Royal Society with Benjamin Franklin as one of his sponsors.
- February 18 – Meermin slave mutiny: captive Malagasy people seize a Dutch East India Company slave ship in the Indian Ocean.
- February 20 – The Pennsylvania Gazette reports that a British sloop outside of Wilmington, North Carolina has seized a sloop sailing from Philadelphia and another sailing from Saint Christopher on the charge of carrying official documents without stamps. In response, local residents threaten to burn a Royal Man-of-War attempting to deliver stamps to Wilmington, forcing the ship to return to the mouth of the Cape Fear River.
- February 23 – Lorraine becomes French again on the death of Stanisław Leszczyński, King of Poland and last Duke of Lorraine.
- February – Ferocious wolf attacks occur in France, such as the Beast of Gévaudan or Wolves of Périgord.
- March 5 – Antonio de Ulloa, the first Spanish governor of Louisiana, arrives in New Orleans.
- March 18 – American Revolution: The British Parliament repeals the Stamp Act which has been very unpopular in the British colonies. The persuasion of Benjamin Franklin is considered partly responsible. The Declaratory Act asserts the right of Britain to bind the colonies in all other respects.
- May 30 – Opening of Theatre Royal, Bristol, England. Also this year in England, the surviving Georgian Theatre (Stockton-on-Tees) opens as a playhouse.
July–December
- July 1 – François-Jean de la Barre, a young French nobleman, is tortured and beheaded before his body is burnt on a pyre along with a copy of Voltaire's Dictionnaire philosophique nailed to his torso for the crime of not saluting a Roman Catholic religious procession in Abbeville and for other sacrileges including desecrating a crucifix.
- November 10 – The last Colonial governor of New Jersey, William Franklin, signs the charter of Queen's College (later renamed Rutgers University).
- November 27 – An observer in New York City, in the Province of New York, reports to the Pennsylvania Gazette that a British sloop of war is searching all vessels passing near Cape Lookout, North Carolina and that some vessels have been seized.
- November 29 – Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart returns to Salzburg after the Mozart family grand tour of Europe.
- December 2 – The Law on the Freedom of Printing abolishes censorship in Sweden and guarantees freedom of the press, making Sweden the first country of the world to introduce constitutional protection of press freedom and to pass wide-ranging freedom of information legislation.
- December 5 – James Christie holds the first sale at Christie's auction house in London.
Date unknown
- The Burmese begin to invade the Thai kingdom of Ayutthaya.
- Childsburgh, the Orange County, North Carolina county seat laid out as Corbin Town in 1754 and renamed in 1759, is renamed Hillsborough in honor of Wills Hill, 1st Marquess of Downshire, Earl of Hillsborough.
1767

Tahiti & Pitcairn Island are sighted.
January–June
- January 1 – First annual volume of The Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris, produced by British Astronomer Royal Nevil Maskelyne at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, gives navigators the means to find longitude at sea using tables of lunar distance.[18]
- January 9 – William Tryon, governor of the Royal Colony of North Carolina, signs a contract with architect John Hawks to build Tryon Palace, a lavish Georgian style governor's mansion on the New Bern waterfront.
- April 2 – Suppression of the Society of Jesus in the Spanish Empire and Kingdom of Naples.
- April 7 – Troops of the Burmese Konbaung Dynasty sack the Siamese city of Ayutthaya, ending the Burmese–Siamese War (1765–67) and bringing the four-century-old Ayutthaya Kingdom to an end.
- June 17 – British Royal Navy Captain Samuel Wallis becomes the first European to visit the island of Tahiti in the Pacific Ocean, during HMS Dolphin's second circumnavigation;[19][20] he also sights Mehetia.
July–December
- July 3
- The Pitcairn Island in the Pacific Ocean is sighted from HMS Swallow by 15-year-old Midshipman Robert Pitcairn on a British Royal Navy expeditionary voyage commanded by Philip Carteret, the first definite European sighting.
- Norway's oldest newspaper still in print, Adresseavisen, is first published.
- August 26 – Construction begins on Tryon Palace in New Bern, North Carolina. The construction proves more expensive than initially expected, leading the government to increase local taxes. This stirs resentment among some North Carolinians and helps prolong the War of the Regulation.
- Autumn – North Carolina woodsman Daniel Boone goes through the Cumberland Gap and reaches Kentucky, in defiance of the Royal Proclamation of 1763 issued by George III of Great Britain. He discovers a rich hunting ground, contested by several Native American tribes.
1768
January–June

January 9: Philip Astley circus.
- January 9 – Philip Astley stages the first modern circus, with acrobats on galloping horses, in London.
- February 11 – Samuel Adams's circular letter is issued by the Massachusetts House of Representatives and sent to the other Thirteen Colonies. Refusal to revoke the letter will result in dissolution of the Massachusetts Assembly and (from October) incur the institution of martial law to prevent civil unrest.
- February 29 – A group of the szlachta, Polish nobles, establishes the Bar Confederation to defend the internal and external independence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth against Russian influence and against King Stanisław II Augustus.
- May 10 – John Wilkes is imprisoned for writing an article for The North Briton severely criticizing King George III of Great Britain. This action provokes protesters to riot; in the Southwark district of London, troops fire on the mob, killing seven, the Massacre of St George's Fields.[21]
- May 15 – After the Treaty of Versailles, the island of Corsica is ceded by Genoa to France.
- June 20 – Russo-Turkish War (1768–74), Russia captured the fortress of Bar.
July–December
- August 8 – James Cook departs from Plymouth on his first voyage of discovery.[22]
The Petit Trianon
- August 26 – The ship, The Endeavour set sail
- December 1 – The slave ship Fredensborg sinks off Tromøy in Norway.
- December 10 – Royal Academy founded in London, with Joshua Reynolds as its first President.[10]
- December 15 – The king's refusal to sign state documents results in the December Crisis (1768) in Sweden.
- December 21 – King Prithvi Narayan Shah unifies several small kingdoms to establish the modern-day Nepal. This kingdom will collapse in 2008.
- December 28 – Taksin is crowned as ruler of the Thonburi Kingdom in Thailand (through conquest) and establishes Thonburi as a capital.
Date unknown
- The Petit Trianon, originally designed for Madame de Pompadour, is completed in the park of the Palace of Versailles and inaugurated by Louis XV of France.
- New Smyrna, Florida, the largest attempt at colonization by the British in the New World, is founded by Dr. Andrew Turnbull.
- A Secretary of State for the colonies is appointed in Britain.
- Louis XV of France appoints René de Maupeou as chancellor and orders him to crush the judicial opposition.
- Members of the Royal Society of Arts wrote The Complete Farmer: Or, a General Dictionary of Husbandry published in weekly numbers.
- Louis Antoine de Bougainville discovers the Bougainville Strait and Bougainville Island.
- First of the weekly numbers of the Encyclopædia Britannica, edited by William Smellie, are published in Edinburgh; one hundred are planned.
- The Steller's sea cow, discovered on Bering Island in 1741, is driven to extinction.
1769
January–June
- March 16 – Louis Antoine de Bougainville returns to Saint-Malo following a three-year circumnavigation of the world with the ships La Boudeuse and Étoile, with the loss of only seven out of 330 men; among the members of the expedition was Jeanne Baré, the first woman known to have circumnavigated the globe. She returned to France some time after Bougainville and his ships.
- April 13 – James Cook arrives in Tahiti on the ship HM Bark Endeavour, preparing for the 1769 Transit of Venus observed from Tahiti on June 3. After the voyage, the data is found to be inaccurate in determining the distance between the Sun and Earth.
- April 29 – James Watt is granted a British patent for "A method of lessening the consumption of steam in steam engines" – the separate condenser,[23] a key improvement (first devised by Watt in 1765) which stimulates the Industrial Revolution.[18]
- May 9 – France conquers Corsica.
- May 14 – Charles III of Spain sends Spanish missionaries, who found California missions in San Diego, Santa Barbara, San Francisco and Monterey and begin the settlement of California.
- May 19 – Pope Clement XIV succeeds Pope Clement XIII as the 249th pope.
- June 3 (O.S.) – A transit of Venus is followed five hours later by a total solar eclipse, the shortest such interval in historical times. The transit is viewed by King George III of Great Britain at the Kew Observatory.

- June 7 – Frontiersman Daniel Boone first begins to explore modern-day Kentucky.
July–December
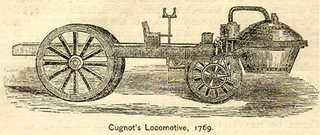
October 23: Cugnot's steam-wagon.
- July 3 – Richard Arkwright patents a spinning frame in England able to weave fabric mechanically.[24]
- July 16 – Father Junípero Serra founds Mission San Diego de Alcalá, the first of the 21 California missions.
- August 3 – The party of Gaspar de Portolà becomes the first white group to set foot in the area now known as Santa Monica, California.
- August 18 – the Brescia Explosion; the city of Brescia, Italy is devastated when the Church of San Nazaro is struck by lightning. The resulting fire ignites 200,000 lb (90,000 kg) of gunpowder being stored there, causing a massive explosion which destroys 1/6 of the city and kills 3,000 people. The disaster prompts the Roman Catholic Church to abandon their religious objection to using lightning rods to protect their property.
- September – Massive droughts in Bengal, which lead to the Bengal famine of 1770 in which ten million people, a third of the population, will die, the worst natural disaster in human history (in terms of lives lost). The Maharajah of Mysore forces the British to agree a treaty of mutual assistance in view of the famine, but the British East India Company increases its demands on the Bengali people to keep profits up.
- September 6–9 – David Garrick holds a Shakespeare Jubilee festival at Stratford-upon-Avon in England.
- September 10 – Russo-Turkish War (1768–74): Russian forces take the Ottoman fortress of Chocim in Bukovina.
- October 7– James Cook lands in New Zealand at Poverty Bay.
- October 23 – Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot demonstrates a steam-powered artillery tractor (see drawing) in France.
"Mechanical Turk" chess machine.
- December 13
- Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire is established as John Wentworth, the Royal Governor, conveys a charter from King George III of England.
- (or December 22) – Sino-Burmese War (1765–69) ended by truce.
Date unknown
- Authorized King James Version of the Bible in the Oxford standard text edited by Benjamin Blayney published in England.
References
- ↑ Williams, Hywel (2005). Cassell's Chronology of World History. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 320. ISBN 0-304-35730-8.
- ↑ Rodger, N. A. M. (2006). The Command of the Ocean: A Naval History of Britain, 1649–1815. London: Penguin Books; National Maritime Museum. p. 283. ISBN 0-14-102690-1.
- ↑ "Portsmouth Dockyard". Battleships-Cruisers.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-09-27.
- ↑ "Chronology Of Events In Portsmouth – 1700-1799". History In Portsmouth. Retrieved 2011-09-27.
- ↑ Palmer, Alan; Palmer, Veronica (1992). The Chronology of British History. London: Century Ltd. p. 222. ISBN 0-7126-5616-2.
- ↑ "wedding-supper". www.google.com. Retrieved 22 August 2016.
- ↑ "Historical Events for Year 1761 | OnThisDay.com". Historyorb.com. Retrieved 2016-06-30.
- ↑ "Landmarks of World History: A Chronology of Remarkable Natural Phenomena: Eighteenth Century 1761-1770". The Gallery of Natural Phenomena. 2010. Retrieved 2016-02-01.
- ↑ BBC History, July 2011, p 12
- 1 2 Penguin Pocket On This Day. Penguin Reference Library. 2006. ISBN 0-14-102715-0.
- ↑ National Geophysical Data Center / World Data Service (NGDC/WDS), Significant Earthquake Database, National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA, doi:10.7289/V5TD9V7K
- 1 2 Williams, Hywel (2005). Cassell's Chronology of World History. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 322. ISBN 0-304-35730-8.
- 1 2 "Murshidabad". Archived from the original on March 3, 2012. Retrieved 2012-02-29.
- ↑ "A Letter from the Late Reverend Mr. Thomas Bayes, F.R.S. to John Canton, M.A. and F.R.S." (PDF). 1763-11-24. Retrieved 2012-03-01.
- ↑ Hartley Booth, V. E.; Sells, Peter (1980). British extradition law and procedure: including extradition between the United Kingdom and foreign states, the Commonwealth and dependent countries and the Republic of Ireland. Alphen aan den Rijn: Sijthoff & Noordhoff. p. 5. ISBN 978-90-286-0079-9. OCLC 6890466.
- ↑ Bhattacherje, S. B. (May 1, 2009). Encyclopaedia of Indian Events & Dates. Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. pp. A–96. Retrieved March 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Historical Events for Year 1766 | OnThisDay.com". Historyorb.com. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- 1 2 Palmer, Alan; Palmer, Veronica (1992). The Chronology of British History. London: Century Ltd. pp. 224–225. ISBN 0-7126-5616-2.
- ↑ Laneyrie-Dagen, Nadeije, ed. (1996). Les Grands Explorateurs. Larousse. p. 181. ISBN 2-03-505305-6.
- ↑ Collingridge, Geo. (1903). "Who Discovered Tahiti?". Journal of the Polynesian Society. 12: 184–186.
- ↑ "St. George's Field Riot". Spartacus. Retrieved 2012-03-03.
- ↑ "Cook's Journal: Daily Entries, 7 August 1768". Archived from the original on September 23, 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-10.
- ↑ Patent 913; specification accepted January 5.
- ↑ Williams, Hywel (2005). Cassell's Chronology of World History. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 325. ISBN 0-304-35730-8.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.



