Darwin (operating system)
 | |
| Developer | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Written in | C, C++, Objective-C |
| OS family | Unix (BSD) |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Open source |
| Initial release | November 15, 2000 |
| Latest release | 16.0.0 (September 13, 2016) [±] |
| Platforms | PowerPC, x86, ARM |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (mostly monolithic) |
| Default user interface | Command-line interface |
| License | Mostly Apple Public Source License, with proprietary drivers[1] |
| Official website |
opensource |
Darwin is an open-source Unix operating system released by Apple Inc. in 2000. It is composed of code developed by Apple, as well as code derived from NeXTSTEP, BSD, Mach, and other free software projects.
Darwin forms the core set of components upon which macOS (previously OS X and Mac OS X), iOS, watchOS, and tvOS are based. It is mostly POSIX-compatible, but has never, by itself, been certified as compatible with any version of POSIX. Starting with Leopard, macOS has been certified as compatible with the Single UNIX Specification version 3 (SUSv3).[2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10]
History
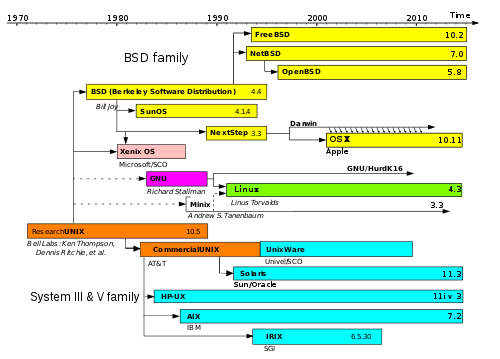
The heritage of Darwin began with NeXT's NeXTSTEP operating system (later, since version 4.0, known as OPENSTEP), first released in 1989. After Apple bought NeXT in 1997, it announced it would base its next operating system on OPENSTEP. This was developed into Rhapsody in 1997, Mac OS X Server 1.0 in 1999, Mac OS X Public Beta in 2000, and Mac OS X 10.0 in 2001. In 2000, the core operating system components of Mac OS X were released as open-source software under the Apple Public Source License (APSL) as Darwin; the higher-level components, such as the Cocoa and Carbon frameworks, remained closed-source.
Up to Darwin 8.0.1, Apple released a binary installer (as an ISO image) after each major Mac OS X release that allowed one to install Darwin on PowerPC and Intel x86 systems as a standalone operating system. Minor updates were released as packages that were installed separately. Darwin is now only available as source code,[11] except for the ARM variant, which has not been released in any form separately from iOS. However, the older versions of Darwin are still available in binary form,[12] and a hobbyist developer winocm took the official Darwin source code and ported it to ARM.[13]
Design
Kernel
The kernel of Darwin is XNU, a hybrid kernel that combines the Mach 3 microkernel, various elements of BSD (including the process model, network stack, and virtual file system),[14] and an object-oriented device driver API called I/O Kit.[15] The hybrid kernel design leverages the flexibility of a microkernel and the performance of a monolithic kernel.
Hardware and software support
Darwin currently includes support for the 64-bit x86-64 variant of the Intel x86 processors used in Macs and the 64-bit ARM processors used in the iPhone 5S and later, the 6th generation iPod Touch and later, the iPad Air and iPad Pro, and the fourth generation Apple TV, as well as the 32-bit ARM processors used in the iPhone 5C and older, earlier generations of the iPod Touch, the iPad up to the fourth generation, and the second and third generation Apple TV. An open-source port of the XNU kernel exists that supports Darwin on Intel and AMD x86 platforms not officially supported by Apple, although it does not appear to have been updated since 2009.[16] An open-source port of the XNU kernel also exists for ARM platforms.[17] Older versions supported some or all of 32-bit PowerPC, 64-bit PowerPC, and 32-bit x86.
It supports the POSIX API by way of its BSD lineage and a large number of programs written for various other UNIX-like systems can be compiled on Darwin with no changes to the source code.
Darwin does not include many of the defining elements of macOS, such as the Carbon and Cocoa APIs or the Quartz Compositor and Aqua user interface, and thus cannot run Mac applications. It does, however, support a number of lesser known features of macOS, such as mDNSResponder, which is the multicast DNS responder and a core component of the Bonjour networking technology, and launchd, an advanced service management framework.
License
In July 2003, Apple released Darwin under version 2.0 of the Apple Public Source License (APSL), which the Free Software Foundation (FSF) classifies as a free software license incompatible with the GNU General Public License.[18] Previous versions were released under an earlier version of the APSL license, which did not meet the FSF definition of free software, although it did meet the requirements of the Open Source Definition.[19]
Mascot

The Darwin developers decided to adopt a mascot in 2000, and chose Hexley the Platypus, over other contenders, such as an Aqua Darwin fish, Clarus the Dogcow, and an orca. Hexley is a cartoon platypus who – mimicking the BSD Daemon – usually wears a cap resembling a demon's horns and carries a trident which symbolizes the forking of processes. Hexley was designed by Jon Hooper. Apple does not sanction Hexley as a logo for Darwin.[20]
The name Hexley is an accidental misspelling of the last name of Thomas Henry Huxley, a 19th-century English biologist who was a well-known champion of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution (nicknamed "Darwin's bulldog"). The name was chosen under the misunderstanding that he was an assistant of Darwin, rather than a prominent biologist in his own right. By the time the spelling mistake had been discovered, it was deemed too late to change, and the erroneous name was kept.[21]
Release history
The following is a table of major Darwin releases with their dates of release and their corresponding macOS releases.[22] Note that the corresponding macOS release may have been released on a different date; refer to the macOS pages for those dates.
| Version | Date | Corresponding releases | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | March 16, 1999 | Mac OS X developer previews |
|
| 0.2 | November 10, 1999 | Developer preview 2 | |
| 1.0 | February 2000 | Developer preview 3 | |
| 1.1 | April 5, 2000 | Developer preview 4 | |
| 1.2.1 | November 15, 2000 | Mac OS X Public Beta | Code-named "Kodiak" |
| 1.3.1 | April 13, 2001 | Mac OS X v10.0 |
|
| 1.4.1 | October 2, 2001 | Mac OS X v10.1 | |
| 5.1 | November 12, 2001 |
| |
| 5.5 | June 5, 2002 | Mac OS X v10.1.5 | |
| 6.0.1 | September 23, 2002 | Mac OS X v10.2 |
|
| 6.8 | October 3, 2003 | Mac OS X v10.2.8 | |
| 7.0 | October 24, 2003 | Mac OS X Panther |
|
| 7.9 | April 15, 2005 | Mac OS X v10.3.9 | |
| 8.0 | April 29, 2005 | Mac OS X Tiger Mac OS X for Apple TV |
|
| 8.11 | November 14, 2007 | Mac OS X v10.4.11 | |
| 9.0 | October 26, 2007 | Mac OS X Leopard iPhone OS 1 |
|
| 9.8 | August 5, 2009 | Mac OS X v.10.5.8 | |
| 10.0 | August 28, 2009 | Mac OS X Snow Leopard iOS 4 |
|
| 10.8 | June 23, 2011 | Mac OS X v10.6.8 | |
| 11.0.0 | July 20, 2011 | Mac OS X Lion iOS 5[29] |
|
| 11.4.2 | October 4, 2012 | Mac OS X v10.7.5 (supplemental) | |
| 12.0.0 | February 16, 2012 | OS X Mountain Lion |
|
| 12.6.0 | January 27, 2015 | OS X v10.8.5 (with Security Update 2015-001) | |
| 13.0.0 | June 11, 2013 | OS X Mavericks iOS 6 |
OS X v10.9.0 |
| 13.4.0 | September 17, 2014 | OS X v10.9.5 | |
| 14.0.0 | September 18, 2014 | OS X Yosemite iOS 7, iOS 8 |
OS X v10.10.0 |
| 14.5.0 | August 13, 2015 | OS X v10.10.5 | |
| 15.0.0 | September 16, 2015 | OS X El Capitan iOS 9 |
OS X v10.11.0 and iOS 9.0 |
| 15.6.0 | July 18, 2016 | OS X v10.11.6 and iOS 9.3.3 | |
| 16.0.0 | September 13, 2016 | macOS Sierra iOS 10 |
|
| 16.1.0 | October 24, 2016 |
|
The jump in version numbers from Darwin 1.4.1 to 5.1 with the release of Mac OS X v10.1.1 was designed to tie Darwin to the Mac OS X version and build numbering system, which in turn is inherited from NeXTSTEP. In the build numbering system of macOS, every version has a unique beginning build number, which identifies what whole version of macOS it is part of. Mac OS X v10.0 had build numbers starting with 4, 10.1 had build numbers starting with 5, and so forth (earlier build numbers represented developer releases). The point release number in the Darwin version is always the same as the second point number in the macOS version. In the case of Mac OS X v10.1.1 (the version where the jump in version numbers was made), this was build 5M28 and the 10.1.1 release, from which a version number of 5.1 was derived.[30]
The command uname -r in Terminal will show the Darwin version number, and the command uname -v will show the XNU build version string, which includes the Darwin version number.
Derived projects
Due to the free software nature of Darwin, there are many projects that aim to modify or enhance the operating system.
OpenDarwin
OpenDarwin was a community-led operating system based on the Darwin system. It was founded in April 2002 by Apple Inc. and Internet Systems Consortium. Its goal was to increase collaboration between Apple developers and the free software community. Apple benefited from the project because improvements to OpenDarwin would be incorporated into Darwin releases; and the free/open source community benefited from being given complete control over its own operating system, which could then be used in free software distributions such as GNU-Darwin.[31]
On July 25, 2006, the OpenDarwin team announced that the project was shutting down, as they felt OpenDarwin had "become a mere hosting facility for Mac OS X related projects," and that the efforts to create a standalone Darwin operating system had failed. They also state: "Availability of sources, interaction with Apple representatives, difficulty building and tracking sources, and a lack of interest from the community have all contributed to this."[32] The last stable release was version 7.2.1, released on July 16, 2004.
PureDarwin
In 2007, the PureDarwin project was launched to continue where OpenDarwin left off. PureDarwin is currently working to produce a release based on Darwin 14.5. available based on Darwin 10.10.5. This release will have X11, DTrace, [33] PureDarwin nano is another release of PureDarwin that is intended to be minimalistic cli only build with networking.
Other
- MacPorts (formerly DarwinPorts), Fink, and Homebrew are well known projects to port UNIX programs to the Darwin operating system and provide package management. In addition, several standard UNIX package managers—such as RPM, pkgsrc, and Portage—have Darwin ports. Some of these operate in their own namespace so as not to interfere with the base system.
- GNU-Darwin is a project that ports packages of free software to Darwin.
- The Darwine project is a port of Wine that allows one to run Microsoft Windows software on Darwin.
- SEDarwin is a port of TrustedBSD mandatory access control framework and portions of the SELinux framework to Darwin.[34] It was incorporated into Mac OS X 10.5.[35]
- The Darbat project is an experimental port of Darwin to the L4 microkernel family. It aims to be binary compatible with existing Darwin binaries.[36]
- There are various projects that focus on driver support: e.g., wireless drivers,[37][38] wired NIC drivers[39][40][41] modem drivers,[42] card readers,[43] and the ext2 and ext3 file systems.[44][45]
See also
References
- ↑ "Binary Drivers required for PureDarwin". Retrieved July 20, 2009.
- ↑ "Mac OS X Leopard - Technology - UNIX". Leopard Technology Overview. Apple Inc. Archived from the original on December 27, 2008.
Leopard is now an Open Brand UNIX 03 Registered Product, conforming to the SUSv3 and POSIX 1003.1 specifications for the C API, Shell Utilities, and Threads.
- ↑ The Open Group (May 18, 2007). "Mac OS X Version 10.5 Leopard on Intel-based Macintosh computers certification". Retrieved February 11, 2013.
- ↑ "Mac OS X Version 10.6 on Intel-based Macintosh computers". The Open Group. Retrieved December 4, 2014.
- ↑ "Apple technology brief on UNIX" (PDF). Apple. Retrieved November 5, 2008.
- ↑ "Mac OS X Version 10.8 on Intel-based Macintosh computers". The Open Group. Retrieved December 4, 2014.
- ↑ "OS X Version 10.9 on Intel-based Macintosh computers". The Open Group. Retrieved December 4, 2014.
- ↑ "OS X version 10.10 Yosemite on Intel-based Mac computers". The Open Group. Retrieved December 4, 2014.
- ↑ "OS X version 10.11 El Capitan on Intel-based Mac computers". The Open Group. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- ↑ "macOS version 10.12 Sierra on Intel-based Mac computers". The Open Group. Retrieved September 29, 2016.
- ↑ Hubbard, Jordan (October 31, 2007). "Re: Darwin 9.0 Source Code Available."". darwinos-users (Mailing list). Retrieved November 27, 2007.
- ↑ opensource
.apple .com /static /iso - ↑ github
.com /darwin-on-arm /xnu - ↑ "Mac Technology Overview: Kernel and Device Drivers Layer". Apple Developer Connection. Retrieved February 11, 2013.
- ↑ Singh, Amit (January 7, 2004). "XNU: The Kernel". Retrieved February 11, 2013.
- ↑ "Voodoo XNU Kernel Source". Requires an Apache SVN client.
- ↑ "XNU on ARMv7".
- ↑ "FSF's Opinion of the Apple Public Source License (APSL) 2.0".
- ↑ "The Problems with older versions of the Apple Public Source License (APSL)".
- ↑ Hooper, Jon. "Homepage of Hexley the DarwinOS mascot". Retrieved November 30, 2008.
- ↑ Hooper, Jon. "Hexley Darwin Mascot History". Retrieved November 30, 2008.
- ↑ "Open Source Releases". Apple Developer Connection. Retrieved February 11, 2013.
- ↑ "Technical Note TN2029: Mac OS X v10.1". Apple Developer Connection. Archived from the original on November 14, 2001.
- ↑ Siracusa, John (September 5, 2002). "Mac OS X 10.2 Jaguar". Ars Technica. Retrieved May 31, 2008.
- ↑ Siracusa, John (November 9, 2003). "Mac OS X 10.3 Panther". Ars Technica. Retrieved May 31, 2008.
- ↑ Siracusa, John (April 28, 2005). "Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger". Ars Technica. Retrieved May 30, 2008.
- ↑ Siracusa, John (October 28, 2007). "Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard: the Ars Technica review". Ars Technica. Retrieved May 30, 2008.
- ↑ Siracusa, John (August 31, 2009). "Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard: the Ars Technica review". Ars Technica. Retrieved November 29, 2009.
- ↑ As found on a jailbroken iPhone 4S
- ↑ Prabhakar, Ernie (November 9, 2001). "Darwin Version - New Scheme in Software Update 1". darwin-development (Mailing list). Retrieved June 2, 2008.
- ↑ "OpenDarwin". OpenDarwin Project. Archived from the original on January 6, 2006.
- ↑ OpenDarwin Core Team and Administrators (July 25, 2006). "OpenDarwin Shutting Down". OpenDarwin Project. Archived from the original on August 4, 2006.
- ↑ "PureDarwin Download Page".
- ↑ "Security Enhanced Darwin". SEDarwin. January 22, 2007. Archived from the original on October 5, 2011.
- ↑ "What's New In Mac OS X: Mac OS X v10.5". Mac OS X Reference Library. Apple Inc. November 13, 2009. Archived from the original on December 8, 2009.
- ↑ "L4/Darwin (aka Darbat)". Ertos.nicta.com.au. May 9, 2007. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013.
- ↑ yuriwho (May 5, 2002). "WirelessDriver Home Page". Wirelessdriver.sourceforge.net. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ "iwi2200 Darwin". SourceForge. March 27, 2009. Retrieved June 13, 2010.
- ↑ "Port BSD tulip driver(s) to Darwin OS | Download Port BSD tulip driver(s) to Darwin OS software for free at". Sourceforge.net. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ "RealTek network driver for Mac OS X/Darwin". SourceForge. March 15, 2006. Retrieved June 3, 2010. Project inactive since March 15, 2006.
- ↑ fansui; et al. (August 1, 2007). "RTL8150LMEthernet". SourceForge. Retrieved June 13, 2010.
- ↑ "ZyXEL Modem Drivers for OS X/Darwin | Download ZyXEL Modem Drivers for OS X/Darwin software for free at". Sourceforge.net. May 14, 2002. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ "Mac OS X PC Card ATA Driver". Pccardata.sourceforge.net. December 20, 2001. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ "Mac OS X Ext2 Filesystem | Download Mac OS X Ext2 Filesystem software for free at". Sourceforge.net. October 14, 2002. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ "ext2 filesystem in user space". SourceForge. July 14, 2008. Retrieved June 13, 2010.
External links
- Hexley, the Darwin mascot
- PureDarwin.org
- Darwin Releases at Apple Developer Connection
- Darwin Build Number List