Dohan river
The Dohan river (Hindi: दोहान नदी), is a rain-fed river originates from Rajasthan and flows to Rewari district of Haryana.[1][2]
Basin
The Dohan river originates from Aravalli Range Mandoli village from the western slopes of the Dohan Protected Forest hills and flows towards north-east. The Krishnawati River, another independent River, flows north-east for about 42 km in Rajasthan and subsequently disappears
in Haryana. The drainage pattern for both is dendritic.
Indus Valley Civilisation archaeological findings

Harrapan period earthenware (Pottery) found on the Sahibi riverbed by INTACH-Rewari, at Hansaka village, Rewari District, 2012
Archaeological findings on the Sahibi River have confirmed habitations on its banks before the Harappan and pre-Mahabharata periods. Both handmade and wheel-made earthernware dated from 3309–2709 BCE and 2879–2384 BCE has been found on the banks of the Sahibi River at Jodhpura. INTACH-Rewari found pottery on the Sahibi riverbed at Hansaka in the Rewari district. A red stone statue of Vamana Dev was found in the Sahibi riverbed near Bawal in 2002; the statue is now displayed at the Shri Krishna Museum, Kurukshetra. Other artifacts discovered in the Sahibi River include arrowheads, fishhooks, appearheads, awls, and chisels.[3]
Identification with Vedic rivers
Several modern scholars identify the old Ghaggar-Hakra River (of which Tangri river is a tributary) as the Sarasvati river and the Sahibi River with the Drishadvati river of Vedic period, on the banks of which Indus-Sarasvati civilisation developed. such scholars include Bhargava[4] The Drishadwati River formed one border of the Vedic state of Brahmavarta and was mentioned in the Rigveda, the Manusmriti, and the Brahmin Granths texts.
Gallery
See also
References
- ↑ Sahibi river
- ↑ Books: Page 41, 42, 43, 44, 47 (b) Sahibi Nadi (River), River Pollution, By A.k.jain
- ↑ A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India from the stone age to the 12th century, Pearson 2009, page 116
- ↑ "Location of Brahmavarta and Drishadwati River is important to find earliest alignment of Saraswati River", Sudhir Bhargava, International Conference, 20–22 Nov. 2009, "Saraswati-a perspective" pages 114–117, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra, Organised by: Saraswati Nadi Shodh Sansthan, Haryana.
External links
 |
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yamuna. |
Coordinates: 28°29′N 76°44′E / 28.483°N 76.733°E / 28.483; 76.733
|
|---|
|
| Rivers | |
|---|
|
| Lakes | |
|---|
|
| Dams | |
|---|
|
| Canals | |
|---|
|
| Hydrography of surrounding areas |
- Gujarat
- Madhya Pradesh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Haryana
- Punjab, India
- Pakistan
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
| North Haryana Rivers | |
|---|
|
| South Haryana Rivers | |
|---|
|
| Canals | |
|---|
|
| Seasonal Waterfalls | |
|---|
|
| Hot Water Springs | |
|---|
|
| Lakes | |
|---|
|
| Dams, Barrages | |
|---|
|
| Bridges | |
|---|
|
| Hydrography of surrounding areas |
- Himachal Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- Uttar Pradesh
- Rajasthan
- Punjab
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
| Inland rivers | |
|---|
|
| Inland lakes, deltas, etc. | |
|---|
|
| Coastal | |
|---|
|
| Categories |
- Lakes of Bangladesh / India / Nepal / Pakistan
- Reservoirs and dams in India
- Rivers of Bangladesh / Bhutan / India / Nepal / Pakistan
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
|
|
| Topics | |
|---|
|
| Divisions | |
|---|
|
| Districts | |
|---|
|
| Major cities | |
|---|
|
| Culture | |
|---|
|
| Economy |
- Power stations and power organisations
|
|---|
|
| Places of interest |
|---|
| | Indus Valley Civilization | |
|---|
| | Archaeological | |
|---|
| | Forts | |
|---|
| | Hills | |
|---|
| | Caves | |
|---|
| | Historical | |
|---|
| | Wildlife Sanctuary | |
|---|
| | Endangered Wildlife Breeding | |
|---|
| | Zoos in Haryana | |
|---|
| | Herbal Parks | |
|---|
| | Lakes | |
|---|
| | Dams | |
|---|
| | Rivers | |
|---|
| | Religious | |
|---|
| | Offices | |
|---|
| | Public places | |
|---|
| | Extreme Corners of Haryana | |
|---|
| | Highest-lowest of Haryana | |
|---|
| | Oldest of Haryana | |
|---|
|
|
| |
|---|
| | Elections | |
|---|
| | Chief Ministers | |
|---|
| | Governors | |
|---|
| | State agencies |
- Dakshin Haryana Bijli Vitran Nigam
- Debt Conciliation Board
- Doordarshan Haryana
- Foreign Investment and NRI Cell
- Forests Department, Haryana
- Department of Economic and Statistical Analysis, Haryana
- Department of Environment, Haryana
- Department of Excise & Taxation, Haryana
- Department of Finance, Haryana
- Department of Industries & Commerce, Haryana
- Department of Industrial Training & Vocational Education, Haryana
- Department of Institutional Finance & Credit Control, Haryana
- Department of Labour & Employment, Haryana
- Department of Land records & Consolidation, Haryana
- Department of Revenue and Disaster Management, Haryana
- Department of Rehabilitation, Haryana
- Department of Higher Education, Haryana
- Department of School Education, Haryana
- Department of Elementary Education, Haryana
- Haryana Board of School Education
- Haryana Civil Medical Services
- Haryana Environment Protection Council
- Haryana Land Record Information System
- Haryana Power Generation Corporation Limited
- Haryana Police
- Haryana Roadways
- Haryana Seeds Development Corporation
- Haryana State Directorate of Archaeology & Museums
- Haryana State Legal Services Authority, Haryana
- Haryana Tourism Corporation Limited
- Haryana Urban Development Authority
- Haryana Waqf Board
- State Counselling Board, Haryana
- Uttar Haryana Bijli Vitran Nigam
|
|---|
|
|
| Sports |
|---|
| | Venues | |
|---|
| | Associations | |
|---|
| | Teams | |
|---|
|
|
-
 Portal: Haryana Portal: Haryana
-
 Category: Haryana Category: Haryana
-
 Wikiproject: Haryana Wikiproject: Haryana
|
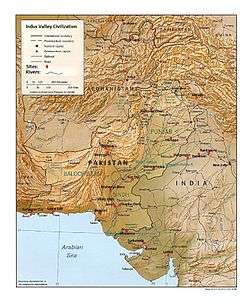 Indus-Sarasvati civilisation major sites
Indus-Sarasvati civilisation major sites