Economy of the Republic of Macedonia
 | |
| Currency | 1 Macedonian Denar (MKD) = 100 Deni |
|---|---|
| calendar уеаr | |
Trade organisations | WTO, CEFTA |
| Statistics | |
| GDP |
|
| GDP rank | 131th (PPP, 2015 est.) |
GDP growth |
|
GDP per capita |
|
GDP by sector | agriculture: 10.2%; industry: 24.9%; services: 64.9% (2015 est.) |
|
| |
Population below poverty line |
|
|
| |
Labour force |
|
Labour force by occupation | agriculture: 18.3%; industry: 29.1%; services: 52.6% (2014 est.) |
| Unemployment |
|
Average gross salary | 32,794 MKD / 606 $, monthly (Apr. 2016)[4] |
| 22,356 MKD / 413 $, monthly (Apr. 2016)[5] | |
Main industries | food processing, beverages, textiles, chemicals, iron, steel, cement, energy, pharmaceuticals |
| 10th[6] | |
| External | |
| Exports |
|
Export goods | food, beverages, tobacco; textiles, miscellaneous manufactures, iron, steel, automotive parts, buses |
Main export partners |
|
| Imports |
|
Import goods | machinery and equipment, automobiles, chemicals, fuels, food products |
Main import partners |
|
FDI stock |
|
Gross external debt |
|
| Public finances | |
| 40.3% of GDP (2015 est.) | |
| -3.7% of GDP (2015 est.) | |
| Revenues |
|
|
Standard & Poor's:[9] BB-(Domestic) BB-(Foreign) BB(T&C Assessment) Outlook: Stable[10] Fitch:[10] BB+ Outlook: Stable | |
Foreign reserves |
|
The breakup of Yugoslavia in 1991 deprived the Economy of the Republic of Macedonia, then its poorest republic (only 5% of the total federal output of goods and services), of its key protected markets and large transfer payments from the center. An absence of infrastructure, United Nations sanctions on its largest market Federal Republic of Yugoslavia,[11] and a Greek economic embargo hindered economic growth until 1996.
Worker remittances and foreign aid have softened the subsequent volatile recovery period. GDP has increased each year except in 2001, rising by 5% in 2000. However, growth in 1999 was held down by the severe regional economic dislocations caused by the Kosovo war.
Successful privatization in 2000 boosted the country's reserves to over $700 million. Also, the leadership demonstrated a continuing commitment to economic reform, free trade, and regional integration. The economy can meet its basic food needs but depends on outside sources for all of its oil and gas and most of its modern machinery and parts. Inflation jumped to 11% in 2000, largely due to higher oil prices.
The Republic of Macedonia experiences one of Europe's biggest growth rates at an average of 4% (even during the political crisis) making it comparable to nations such as Romania and Poland.
History
Macedonia's economy has almost always been completely agricultural in nature from the beginning of the Ottoman Empire when it was part of the District of Skopje and Province of Salonika. It concentrated on pasture farming and vineyard growing. Opium poppy, introduced into the region in 1835, became an important crop as well by the late 19th century, and remained so until the 1930s.[12]
The role of industry in the region's economy increased during the industrial age. Macedonia was responsible for large outputs of textiles and several other goods in the Ottoman Empire. However outdated techniques to produce the goods persisted. The stagnation of Macedonian economy began under the rulership of the Kingdom of Serbia.
When World War II ended, the local economy began to experience revitalization by way of subsidies from Federal Belgrade. The subsidies assisted Macedonia to redevelop its lost industry and shift its agricultural-centered economy to an industry-centered economy with new hearts of industry emerging all over the country in Veles, Bitola, Stip and Kumanovo. Previously, Skopje was the only industrial center in Macedonia, this expanded to several other cities during Socialist Yugoslavia.
After the fall of Socialist Yugoslavia, the economy experienced several shocks that damaged the local economy. Starting with the Western embargo on the Yugoslavian common market, and ending with the Greek embargo on Macedonia over the country's name. The economy began to recover in 1995 and experienced a full recovery after the 2001 insurgency by ethnic Albanians. Macedonia's GDP grew by an average of 6% on a yearly basis until the 2008 economic crisis when its economy contracted with the rest of the world. The global crisis had little impact on the country due to Macedonian banks' stringent rules. Macedonia today maintains a low debt-to-GDP ratio and is experiencing a revitalized investment interest by companies from Turkey,Algeria, Albania, and others.
Economic Activity

Macedonia is vulnerable to economic developments in Europe - due to strong banking and trade ties - and dependent on regional integration and progress toward EU membership for continued economic growth. At independence in September 1991, Macedonia was the least developed of the Yugoslav republics, producing a mere 5% of the total federal output of goods and services. The collapse of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia ended transfer payments from the central government and eliminated advantages from inclusion in a de facto free trade area. An absence of infrastructure, UN sanctions on the downsized Yugoslavia, and a Greek economic embargo over a dispute about the country's constitutional name and flag hindered economic growth until 1996. Since then, Macedonia has maintained macroeconomic stability with low inflation, but it has so far lagged the region in attracting foreign investment and creating jobs, despite making extensive fiscal and business sector reforms. Official unemployment remains high at 24.6% (2015, Q4), but may be overstated based on the existence of an extensive gray market that is not captured by official statistics. In the wake of the global economic downturn, Macedonia has experienced decreased foreign direct investment, lowered credit availability, and a large trade deficit. However, as a result of conservative fiscal policies and a sound financial system, in 2010 the country credit rating improved slightly to BB+ and was kept at that level in 2011. Macroeconomic stability has been maintained by a prudent monetary policy, which keeps the domestic currency pegged against the euro. As a result, GDP growth was modest, but positive, in 2010 and 2011, and inflation was under control. Latest data from Macedonia's State Statistical Office show that overall, output for 2012 dropped by 6.6 percent compared to 2011.[13]
Macroeconomics

Real GDP in the first half of 2011 increased by 5.2%. This robust growth was mainly driven by 23.6% growth in the construction sector; 13.2% in mining, quarrying, and manufacturing; 12.4% in wholesale and retail trade; and 4.2% in transport and communication services. Industrial output in the first 8 months of 2011 was 7.5% higher than in the same period of 2010. Low public and external debt and a comfortable level of foreign exchange reserves allowed for further relaxation of monetary policy, with the reference interest rate of the Central Bank decreasing to 4%. Due to rising prices for energy, fuel, and food on international markets, inflation increased in the first half of 2011, but later decreased to an annualized rate of 3.4% at the end of September. The official unemployment rate dropped to 24.6% in the fourth quarter of 2015, but remained one of the highest in Europe. Many people work in the gray economy, and many experts estimate Macedonia's actual unemployment is lower.

The government budget has generally kept within projections. The budget deficit at the end of August 2011 reached about 2% of GDP, and fiscal authorities seemed committed to keeping it under the projected target of 2.5% of GDP by the end of the year. In addition to 220 million euros (approx. $298 million) drawn from an IMF Precautionary Credit Line (PCL) in March, financing mostly came from domestic borrowing. However, by the end of the year a financing gap remained of about 50 million to 60 million euros (approx. $67 million to $81 million), which the government plans to cover by borrowing from international capital markets, supported by a policy-based guarantee by the World Bank. The central government's public debt remained low at 26% of GDP, but represents a gradual increase from previous years. Despite lowering the Central Bank bills rate, the Central Bank has not changed liquidity indicators for banks or the reserve requirement since 2009, curbing credit growth to 7.5% in the first three-quarters of 2011. Nikola Gruevski says the government will pay off its entire debt to the private sector by February 2013 in order to improve the economy's overall liquidity.[14] Macedonia's external trade struggled in 2010 due to the slow recovery from the economic crisis of its main trading partners, particularly EU members. Starting from a very low base, export growth in the first 8 months of 2011 reached 41.7%, topping import growth of 36.8%. The trade deficit has widened to 18.3% of GDP, approaching the end-year target of 21.9% of GDP. At the same time, the current account balance deficit significantly improved and the end-year projection was revised upward to 5.5% of GDP. This was due primarily to a 4.4% higher inflow of current transfers, mostly during the summer, and came despite a poor level of foreign direct investment (FDI) of only $237.2 million by end-July 2011. Foreign currency reserves remained at about $2.6 billion, a level that comfortably covers 4 months of imports and about 110% of the country's short-term debt.
In October 2010, the World Bank Board of Directors approved a new Country Partnership Strategy (CPS) with Macedonia for the period 2011-2014. This CPS will provide the country assistance of about $100 million in funding for the first 2 years to improve competitiveness, strengthen employability and social protection, and increase the use of sustainable energy. This assistance also includes a commitment of $30 million in direct budget support in the form of a policy-based guarantee by the World Bank to the government to facilitate its access to financing from international capital markets, a process that had been started as of November 2011.
Macedonia became the first country eligible for the IMF’s Precautionary Credit Line in January 2011. This program gives Macedonia a line of credit worth 475 million euros (about $675 million) over 2 years, intended to be accessed only in case of need brought about by external shocks. The credit line was approved after extensive consultations with the IMF in October and December 2010. The IMF expects that there will be no additional withdrawals from the PCL. Macedonia has the best economic freedom in the region, according to the 2012 Index of Economic Freedom, released in January, 2012 by the conservative U.S. think tank Heritage Foundation and the Wall Street Journal.[15]
Macroeconomic trends
GDP Year 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 GDP (USD Billions) 15.5 2.3 2.5 3.3 4.4 4.4 3.7 3.5 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.7 5.0 5.9 5.7 6.9 8.6 9.1 9.7 9.1 10.1 10.7 11.4 12.2 13.0 13.8 GDP (PPP) (USD Billions) 10.7 10.3 9.7 9.7 9.8 10.1 10.5 10.9 11.6 12.4 12.1 12.4 13.0 14.3 15.4 16.7 18.3 19.6 19.6 19.9 20.8 21.8 23.0 24.3 25.7 27.2 GDP growth rate n/a -6.6% -7.5% -1.8% -1.1% 1.2% 1.3% 3.3% 4.3% 4.5% -4.5% 0.8% 2.8% 4.6% 4.3% 4.9% 6.1% 5.0% 0.9% 0.7% 2.9% 3.6% 4.1% 4.0% 3.9% 3.9% GDP Per Capita (USD) 8115 1201 1315 1734 2269 2232 1883 1795 1837 1785 1704 1861 2489 2930 2801 3387 4252 4468 4749 4431 4911 5228 5525 5908 6290 6654 GDP (PPP) per capita 5617 5341 5025 5013 5031 5153 5298 5512 5811 6182 6016 6149 6443 7049 7599 8225 8962 9600 9584 9727 10112 10608 11176 11176 12430 13135 Source: IMF[16]
Trade
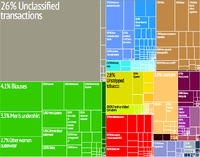
Macedonia remains committed to pursuing membership in the European Union and NATO. It became a full World Trade Organization (WTO) member in April 2003. Following a 1997 cooperation agreement with the European Union (EU), Macedonia signed a Stabilization and Association Agreement with the EU in April 2001, giving Macedonia duty-free access to European markets. In December 2005, it moved a step forward, obtaining candidate country status for EU accession. Macedonia has had a foreign trade deficit since 1994, which reached a record high of $2.873 billion in 2008, or 30.2% of GDP. Total trade in 2010 (imports plus exports of goods and services) was $8.752 billion, and the trade deficit amounted to $2.149 billion, or 23.4% of GDP. In the first 8 months of 2011, total trade was $7.470 billion and the trade deficit was $1.778 billion. A significant 56.5% of Macedonia's total trade was with EU countries. Macedonia's major trading partners are Germany, Greece, Serbia, Bulgaria, Russia, and Italy. In 2010, total trade between Macedonia and the United States was $116.6 million, and in the first 8 months of 2011 it was $65 million. U.S. meat, mainly poultry, and electrical machinery and equipment have been particularly attractive to Macedonia importers. Principal Macedonian exports to the United States are tobacco, apparel, iron, and steel.
Macedonia has bilateral free trade agreements with Ukraine, Turkey, and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA—Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein). Bilateral agreements with Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Serbia, Montenegro, Rep. of Kosovo, and Moldova were replaced by membership in the Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA). Macedonia also has concluded an “Agreement for Promotion and Protection of Foreign Direct Investments” with Albania, Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Belarus, Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Egypt, Iran, Italy, India, Spain, Serbia, Montenegro, People’s Republic of China, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, Poland, Romania, Russia, Slovenia, Turkey, Ukraine, Hungary, Finland, France, the Netherlands, Croatia, Czech Republic, Switzerland, and Sweden.
Unemployment
Unemployment is a continuing problem in the Republic's economy where a large percentage of the Republic's qualified labor force cannot find work. Many Macedonians lost their jobs with the collapse of Yugoslavia. As a result, national unemployment was above 35%(37.30% in 2005), but in recent years that number has dropped to 24% (2016, Q2),[17][18] with population below the poverty line also dropping from 30.4% (2011) to 22.1% (2014), it is reasonable to assume that based on the trend over the past few years further falls are likely for both unemployment and poverty.[19] Full time employment has risen steadily over the last few years,[20] with part time employment trending slightly downward over the same period resulting in a overall increase to employment, wages increased sharply after 2008, with steady increases continuing into 2016[21]
References
- ↑ https://www.gfmag.com/global-data/country-data/macedonia-gdp-country-report
- ↑ http://data.worldbank.org/country/macedonia-fyr. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ "Active population". State Statistical Office of the Republic of Macedonia. Retrieved 2016-03-15.
- ↑ "Average monthly gross wage paid per employee". State Statistical Office of the Republic of Macedonia. Retrieved 2016-03-26.
- ↑ "Average monthly net wage paid per employee". State Statistical Office of the Republic of Macedonia. Retrieved 2016-03-26.
- ↑ "Ease of Doing Business in Macedonia". Doing Business 2016. World Bank Group. Retrieved 2015-10-29.
- ↑ "Export Partners of Republic of Macedonia". CIA World Factbook. 2015. Retrieved 2016-08-04.
- ↑ "Import Partners of Republic of Macedonia". CIA World Factbook. 2015. Retrieved 2016-08-04.
- ↑ "Sovereigns rating list". Standard & Poor's. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- 1 2 Rogers, Simon; Sedghi, Ami (15 April 2011). "How Fitch, Moody's and S&P rate each country's credit rating". The Guardian. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- ↑ "Doing Business in Macedonia, FYR 2013". World Bank. Retrieved 2012-10-21.
- ↑ Македонскиот опиум бил најбаран и се извезувал во цел свет – еве зошто престанало производството (Macedonian opium was top quality and was exported all over the world. Here's why its production ceased.) 2013-07-05. Source of this publication is given as: Vladan Jovanovic (Владан Јовановиќ), „Македонски опиум: за финансиските и политичките размери на феноменот (1918-1941)“ (Macedonian opium: on the financial and political dimensions of the phenomenon), Годишњак за социјална историја (Yearbook of Social History), vol XVI no. 3, Belgrade, 2009, pp 69-79.
- ↑ "Macedonia's Output Drops for Entire Year". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ "Macedonia PM Vows to Repay Private Sector Debt". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ "Serbia, Bosnia Rank Low on Economic Freedom Index". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ↑ IMF
- ↑ "Republic of Macedonia, State Statistical Office".
- ↑ (PDF) http://www.stat.gov.mk/pdf/2016/2.1.16.05.pdf. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ http://ieconomics.com/macedonia-unemployment-rate-forecast. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ http://ieconomics.com/macedonia-full-time-employment. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ http://ieconomics.com/macedonia-wages. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Economy of the Republic of Macedonia. |
- Ministry of Economy of Republic of Macedonia
- Invest Macedonia
- Directorate for Technological Industrial Development Zones
