Encephalitis
| Encephalitis | |
|---|---|
|
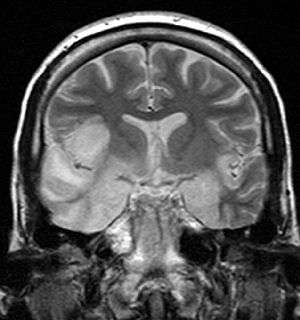
Coronal T2-weighted MR image shows high signal in the temporal lobes including hippocampal formations and parahippocampal gyrae, insulae, and right inferior frontal gyrus. A brain biopsy was performed and the histology was consistent with encephalitis. PCR was repeated on the biopsy specimen and was positive for HSV | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Neurology, infectious disease |
| ICD-10 | A83-A86, B94.1, G05 |
| ICD-9-CM | 323 |
| DiseasesDB | 22543 |
| MedlinePlus | 001415 |
| eMedicine | emerg/163 |
| MeSH | D004660 |
Encephalitis is a sudden onset inflammation of the brain.[1] Encephalitis with meningitis is known as meningoencephalitis. Symptoms include headache, fever, confusion, drowsiness, and fatigue. Further symptoms include seizures or convulsions, tremors, hallucinations, stroke, and memory problems.[2] In 2013, encephalitis was estimated to have resulted in 77,000 deaths worldwide, down from 92,000 in 1990.[3] The word is from Ancient Greek ἐγκέφαλος, enképhalos "brain",[4] composed of ἐν, en, "in" and κεφαλή, kephalé, "head", and the medical suffix -itis "inflammation".
Signs and symptoms
Adult patients with encephalitis present with acute onset of fever, headache, confusion, and sometimes seizures. Younger children or infants may present irritability, poor appetite and fever.[5] Neurological examinations usually reveal a drowsy or confused patient. Stiff neck, due to the irritation of the meninges covering the brain, indicates that the patient has either meningitis or meningoencephalitis.[6]
Cause
Viral
Viral encephalitis can occur either as a direct effect of an acute infection, or as one of the sequelae of a latent infection. The most common causes of acute viral encephalitis are rabies virus, HSV infection, poliovirus, and measles virus.[7]
Other possible viral causes are arbovirus (St. Louis encephalitis, West Nile encephalitis virus), bunyavirus (La Crosse strain), arenavirus (lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus) and reovirus (Colorado tick virus)[8]
Bacterial and other
It can be caused by a bacterial infection, such as bacterial meningitis,[9] or may be a complication of a current infectious disease syphilis (secondary encephalitis).[10]
Certain parasitic or protozoal infestations, such as toxoplasmosis, malaria, or primary amoebic meningoencephalitis, can also cause encephalitis in people with compromised immune systems. Lyme disease and/or Bartonella henselae may also cause encephalitis.
Other bacterial pathogens, like Mycoplasma and those causing rickettsial disease, cause inflammation of the meninges and consequently encephalitis. A non-infectious cause includes acute disseminated encephalitis which is demyelinated.[11]
Limbic encephalitis
Limbic encephalitis refers to inflammatory disease confined to the limbic system of the brain. The clinical presentation often includes disorientation, disinhibition, memory loss, seizures, and behavioral anomalies. MRI imaging reveals T2 hyperintensity in the structures of the medial temporal lobes, and in some cases, other limbic structures. Some cases of limbic encephalitis are of autoimmune origin.[12]
Autoimmune encephalitis
Autoimmune encephalitis signs can include catatonia, psychosis, abnormal movements, and autonomic dysregulation. Antibody-mediated anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate-receptor encephalitis and Rasmussen encephalitis are examples of autoimmune encephalitis.[13]
Encephalitis lethargica
Encephalitis lethargica is identified by high fever, headache, delayed physical response, and lethargy. Individuals can exhibit upper body weakness, muscular pains, and tremors, though the cause of encephalitis lethargica is not currently known. From 1917 to 1928, an epidemic of encephalitis lethargica occurred worldwide.[14]
Diagnosis
Diagnosing encephalitis is done via a variety of tests:[15]
- Brain scan, done by MRI, can determine inflammation and differentiate from other possible causes.
- EEG, in monitoring brain activity, encephalitis will produce abnormal signal.
- Lumbar puncture (spinal tap), this helps determine via a test using the cerebral-spinal fluid, obtained from the lumbar region.
- Blood test
- Urine analysis
Treatment
Treatment (which is based on supportive care) is as follows:[16]
- Antiviral medications (if virus is cause)
- Antibiotics, (if bacteria is cause)
- Steroids are used to reduce brain swell
- Sedatives for restlessness
- Acetaminophen for fever
- Physical therapy (if brain is affected post-infection)
Prevention
Vaccination is available against tick-borne[17] and Japanese encephalitis[18] and should be considered for at-risk individuals. Post-infectious encephalomyelitis complicating smallpox vaccination is avoidable, for all intents and purposes, as smallpox is nearly eradicated.[19] Contraindication to Pertussis immunization should be observed in patients with encephalitis.[20]
Epidemiology
The number of new cases a year of acute encephalitis in Western countries is 7.4 cases per 100,000 population per year. In tropical countries, the incidence is 6.34 per 100,000 per year.[21] In 2013 encephalitis was estimated to have resulted in 77,000 deaths, down from 92,000 in 1990.[3] Herpes simplex encephalitis has an incidence of 2–4 per million population per year.[22]
See also
- Rasmussen's encephalitis
- Bickerstaff's encephalitis
- La Crosse encephalitis
- Wernicke's encephalopathy
- Meningitis
- Cerebritis
- Encephalomyelitis
- Zika Virus
- Naegleriasis (primary amoebic meningoencephalitis/PAM)
References
- ↑ "encephalitis".
- ↑ "Meningitis and Encephalitis Fact Sheet: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)". www.ninds.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- 1 2 GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (17 December 2014). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604
 . PMID 25530442.
. PMID 25530442. - ↑ "Woodhouse's English-Greek Dictionary" (in German). The University of Chicago Library. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
- ↑ "Symptoms of encephalitis". NHS. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- ↑ Shmaefsky, Brian; Babcock, Hilary (2010-01-01). Meningitis. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 9781438132167.
- ↑ Fisher, D. L.; Defres, S.; Solomon, T. (2015). "Measles-induced encephalitis". QJM. 108 (3): 177–182. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcu113. PMID 24865261.
- ↑ Kennedy, P. G. E. (2004-03-01). "Viral Encephalitis: Causes, Differential Diagnosis, and Management". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 75 (suppl 1): i10–i15. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.034280. ISSN 1468-330X. PMC 1765650
 . PMID 14978145.
. PMID 14978145. - ↑ Ashar, Bimal H.; Miller, Redonda G.; Sisson, Stephen D. (2012-01-01). Johns Hopkins Internal Medicine Board Review: Certification and Recertification. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 1455706922.
- ↑ Hama, Kiwa; Ishiguchi, Hiroshi; Tuji, Tomikimi; Miwa, Hideto; Kondo, Tomoyoshi (2008-01-01). "Neurosyphilis with Mesiotemporal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Abnormalities". Internal Medicine. 47 (20): 1813–1817. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.47.0983.
- ↑ "Encephalitis: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology".
- ↑ Larner, A. J. (2013-05-02). Neuropsychological Neurology: The Neurocognitive Impairments of Neurological Disorders. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107607606.
- ↑ Armangue, Thaís; Petit-Pedrol, Mar; Dalmau, Josep (2012-11-01). "Autoimmune Encephalitis in Children". Journal of child neurology. 27 (11): 1460–1469. doi:10.1177/0883073812448838. ISSN 0883-0738. PMC 3705178
 . PMID 22935553.
. PMID 22935553. - ↑ "Encephalitis Lethargica Information Page: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)". www.ninds.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Encephalitis - Diagnosis - NHS Choices". www.nhs.uk. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Encephalitis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ "Tick-borne Encephalitis". Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- ↑ "Japanese encephalitis". Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- ↑ "CDC Media Statement on Newly Discovered Smallpox Specimens". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2016-05-19.
- ↑ "CDC - Vaccines - Contraindications and Precautions to Commonly Used Vaccines in Adults". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- ↑ Jmor F, Emsley HC, et al. (October 2008). "The incidence of acute encephalitis syndrome in Western industrialised and tropical countries" (PDF). Virology Journal. 5 (134): 134. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-5-134. PMC 2583971
 . PMID 18973679.
. PMID 18973679. - ↑ Rozenberg, F; Deback C; Agut H (June 2011). "Herpes simplex encephalitis: from virus to therapy". Infectious Disorders Drug Targets. 11 (3): 235–250. doi:10.2174/187152611795768088. PMID 21488834.
Further reading
- Steiner, I.; Budka, H.; Chaudhuri, A.; Koskiniemi, M.; Sainio, K.; Salonen, O.; Kennedy, P. G. E. (1 May 2005). "Viral encephalitis: a review of diagnostic methods and guidelines for management". European Journal of Neurology. 12 (5): 331–343. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2005.01126.x. ISSN 1468-1331. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- Basavaraju, Sridhar V.; Kuehnert, Matthew J.; Zaki, Sherif R.; Sejvar, James J. (September 2014). "Encephalitis Caused by Pathogens Transmitted through Organ Transplants, United States, 2002–2013". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 20 (9): 1443–1451. doi:10.3201/eid2009.131332.
- Information, National Center for Biotechnology; Pike, U. S. National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville; MD, Bethesda; Usa, 20894. "Encephalitis - National Library of Medicine". PubMed Health. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
- "AccessMedicine | Content". accessmedicine.mhmedical.com. Retrieved 2015-08-05.
External links
- The Encephalitis Society – A Global resource on Encephalitis
- Autoimmune Encephalitis Alliance
- WHO: Viral Encephalitis