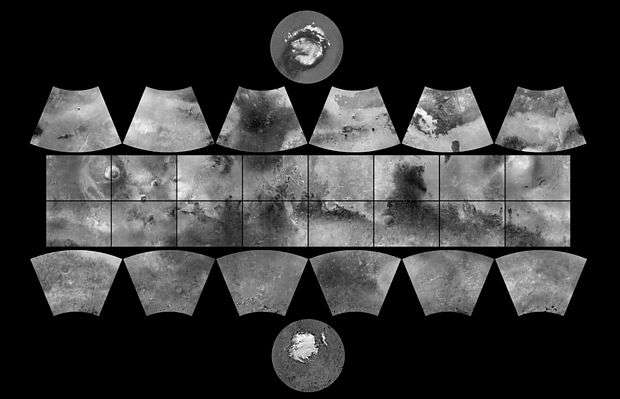
Eridania quadrangle
|
Map of Eridania quadrangle from Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data. The highest elevations are red and the lowest are blue. | |
| Coordinates | 47°30′S 210°00′W / 47.5°S 210°WCoordinates: 47°30′S 210°00′W / 47.5°S 210°W |
|---|---|

The Eridania quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Eridania quadrangle is also referred to as MC-29 (Mars Chart-29).[1]
The Eridania quadrangle lies between 30° and 65° south latitude and 180° and 240° west longitude on the planet Mars. Most of the classic region named Terra Cimmeria is found within this quadrangle. Part of the Electris deposits, a 100–200 meters thick, light-toned deposit covers the Eridania quadrangle.[2] Many slopes in Eridania contain gullies, which are believed to be caused by flowing water.
Martian Gullies
The Eridania quadrangle is the location of gullies that may be due to recent flowing water. Gullies occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Gullies are believed to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. Moreover, they lie on top of sand dunes which themselves are considered to be quite young. Usually, each gully has an alcove, channel, and apron. Some studies have found that gullies occur on slopes that face all directions,[3] others have found that the greater number of gullies are found on poleward facing slopes, especially from 30-44 S.[4][5]
Although many ideas have been put forward to explain them,[6] the most popular involve liquid water coming from an aquifer, from melting at the base of old glaciers, or from the melting of ice in the ground when the climate was warmer.[7][8] Because of the good possibility that liquid water was involved with their formation and that they could be very young, scientists are excited. Maybe the gullies are where we should go to find life.
There is evidence for all three theories. Most of the gully alcove heads occur at the same level, just as one would expect of an aquifer. Various measurements and calculations show that liquid water could exist in aquifers at the usual depths where gullies begin.[9] One variation of this model is that rising hot magma could have melted ice in the ground and caused water to flow in aquifers. Aquifers are layer that allow water to flow. They may consist of porous sandstone. The aquifer layer would be perched on top of another layer that prevents water from going down (in geological terms it would be called impermeable). Because water in an aquifer is prevented from going down, the only direction the trapped water can flow is horizontally. Eventually, water could flow out onto the surface when the aquifer reaches a break—like a crater wall. The resulting flow of water could erode the wall to create gullies.[10] Aquifers are quite common on Earth. A good example is "Weeping Rock" in Zion National Park Utah.[11]
As for the next theory, much of the surface of Mars is covered by a thick smooth mantle that is thought to be a mixture of ice and dust.[12][13][14] This ice-rich mantle, a few yards thick, smooths the land, but in places it has a bumpy texture, resembling the surface of a basketball. The mantle may be like a glacier and under certain conditions the ice that is mixed in the mantle could melt and flow down the slopes and make gullies.[15][16][17] Because there are few craters on this mantle, the mantle is relatively young. An excellent view of this mantle is shown below in the picture of the Ptolemaeus Crater Rim, as seen by HiRISE.[18] The ice-rich mantle may be the result of climate changes.[19] Changes in Mars's orbit and tilt cause significant changes in the distribution of water ice from polar regions down to latitudes equivalent to Texas. During certain climate periods, water vapor leaves polar ice and enters the atmosphere. The water comes back to ground at lower latitudes as deposits of frost or snow mixed generously with dust. The atmosphere of Mars contains a great deal of fine dust particles. Water vapor will condense on the particles, then fall down to the ground due to the additional weight of the water coating. When Mars is at its greatest tilt or obliquity, up to 2 cm of ice could be removed from the summer ice cap and deposited at midlatitudes. This movement of water could last for several thousand years and create a snow layer of up to around 10 meters thick.[20][21] When ice at the top of the mantling layer goes back into the atmosphere, it leaves behind dust, which insulating the remaining ice.[22] Measurements of altitudes and slopes of gullies support the idea that snowpacks or glaciers are associated with gullies. Steeper slopes have more shade which would preserve snow.[4][23] Higher elevations have far fewer gullies because ice would tend to sublimate more in the thin air of the higher altitude.[24]
The third theory might be possible since climate changes may be enough to simply allow ice in the ground to melt and thus form the gullies. During a warmer climate, the first few meters of ground could thaw and produce a "debris flow" similar to those on the dry and cold Greenland east coast.[25] Since the gullies occur on steep slopes only a small decrease of the shear strength of the soil particles is needed to begin the flow. Small amounts of liquid water from melted ground ice could be enough.[26][27] Calculations show that a third of a mm of runoff can be produced each day for 50 days of each Martian year, even under current conditions.[28]
 Gullies in a crater in Eridania, north of the large crater Kepler. Also, features that may be remains of old glaciers are present. One, to the right, has the shape of a tongue. Image taken with Mars Global Surveyor, under the MOC Public Targeting Program.
Gullies in a crater in Eridania, north of the large crater Kepler. Also, features that may be remains of old glaciers are present. One, to the right, has the shape of a tongue. Image taken with Mars Global Surveyor, under the MOC Public Targeting Program. HiRISE image showing gullies. The scale bar is 500 meters. Picture taken under the HiWish program.
HiRISE image showing gullies. The scale bar is 500 meters. Picture taken under the HiWish program. Gullies and layers in mantle on a wall, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
Gullies and layers in mantle on a wall, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
Gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Close-up of some gullies from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
Close-up of some gullies from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Close-up of apron on one of the gullies from previous image. Image was taken by HiRISE, under the HiWish program
Close-up of apron on one of the gullies from previous image. Image was taken by HiRISE, under the HiWish program Gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Gullies on two different levels in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Gullies on two different levels in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Wide view of gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Wide view of gullies, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Close view of gully from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Close view of gully from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Wide view of gullies in a crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Wide view of gullies in a crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Close view of gully from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Close view of gully from previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Close view of gully from a previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Curved ridges may have formed by glaciers before the gullies were created.
Close view of gully from a previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Curved ridges may have formed by glaciers before the gullies were created.
Surface
Some surfaces in Eridania are covered with a mantling unit that is believed to be water ice-rich. In some places the surface displays a pitted or dissected texture; these textures are suggestive of material that once held ice that has since disappeared allowing the remaining soil to collapse into the subsurface.[29]
Dust devil tracks
Many areas on Mars, including Eridania, experience the passage of giant dust devils. A thin coating of fine bright dust covers most of the Martian surface. When a dust devil goes by it blows away the coating and exposes the underlying dark surface.
Dust devils occur when the sun warms up the air near a flat, dry surface. The warm air then rises quickly through the cooler air and begins spinning while moving ahead. This spinning, moving cell may pick up dust and sand then leave behind a clean surface.[30]
Dust devils have been seen from the ground and high overhead from orbit. They have even blown the dust off of the solar panels of the two Rovers on Mars, thereby greatly extending their lives.[31] The twin Rovers were designed to last for 3 months, instead they lasted more than six years, and one is still going after 8 years. The pattern of the tracks have been shown to change every few months.[32]
A study that combined data from the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and the Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) found that some large dust devils on Mars have a diameter of 700 meters and last at least 26 minutes.[33]
- Kepler (Martian crater) showing dust devil tracks, as seen by Mars Global Surveyor.
- Pattern of large and small tracks made by giant dust devils as seen by Mars Global Surveyor, under the MOC Public Targeting Program. Location is 55.11 S and 196.63 W.
Palemagnetism
The Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) discovered magnetic stripes in the crust of Mars, especially in the Phaethontis and Eridania quadrangles (Terra Cimmeria and Terra Sirenum).[34][35] The magnetometer on MGS discovered 100 km wide stripes of magnetized crust running roughly parallel for up to 2000 km. These stripes alternate in polarity with the north magnetic pole of one pointing up from the surface and the north magnetic pole of the next pointing down.[36] When similar stripes were discovered on Earth in the 1960s, they were taken as evidence of plate tectonics. Researchers believe these magnetic stripes on Mars are evidence for a short, early period of plate tectonic activity.[37] When the rocks became solid they retained the magnetism that existed at the time. A magnetic field of a planet is believed to be caused by fluid motions under the surface.[38][39][40] However, there are some differences, between the magnetic stripes on Earth and those on Mars. The Martian stripes are wider, much more strongly magnetized, and do not appear to spread out from a middle crustal spreading zone. Because the area containing the magnetic stripes is about 4 billion years old, it is believed that the global magnetic field probably lasted for only the first few hundred million years of Mars' life, when the temperature of the molten iron in the planet's core might have been high enough to mix it into a magnetic dynamo. There are no magnetic fields near large impact basins like Hellas. The shock of the impact may have erased the remnant magnetization in the rock. So, magnetism produced by early fluid motion in the core would not have existed after the impacts.[41]
When molten rock containing magnetic material, such as hematite (Fe2O3), cools and solidifies in the presence of a magnetic field, it becomes magnetized and takes on the polarity of the background field. This magnetism is lost only if the rock is subsequently heated above a particular temperature (the Curie point which is 770 °C for iron). The magnetism left in rocks is a record of the magnetic field when the rock solidified.[42]
Dunes
Dunes, including barchans are present in the Eridania quadrangle and some pictures below. When there are perfect conditions for producing sand dunes, steady wind in one direction and just enough sand, a barchan sand dune forms. Barchans have a gentle slope on the wind side and a much steeper slope on the lee side where horns or a notch often forms.[43] The whole dune may appear to move with the wind. Observing dunes on Mars can tell us how strong the winds are, as well as their direction. If pictures are taken at regular intervals, one may see changes in the dunes or possibly in ripples on the dune’s surface. On Mars dunes are often dark in color because they were formed from the common, volcanic rock basalt. In the dry environment, dark minerals in basalt, like olivine and pyroxene, do not break down as they do on Earth. Although rare, some dark sand is found on Hawaii which also has many volcanoes discharging basalt. Barchan is a Russian term because this type of dune was first seen in the desert regions of Turkistan.[44] Some of the wind on Mars is created when the dry ice at the poles is heated in the spring. At that time, the solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) sublimates or changes directly to a gas and rushes away at high speeds. Each Martian year 30% of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere freezes out and covers the pole that is experiencing winter, so there is a great potential for strong winds.[45]
 Huggins Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Huggins Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).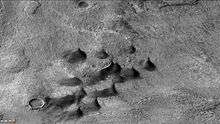 Dunes and dust devil tracks on floor of Huggins Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Dark streaks on dunes are dust devil tracks. Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image of Huggins Crater.
Dunes and dust devil tracks on floor of Huggins Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Dark streaks on dunes are dust devil tracks. Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image of Huggins Crater. Hadley Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Hadley Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).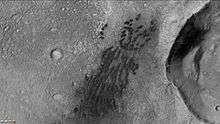 Dunes on floor of Hadley Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image of Hadley Crater.
Dunes on floor of Hadley Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image of Hadley Crater. Dark dunes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Dark dunes are composed of the igneous rock basalt. The dark box in the center of the photo shows the area enlarged in the next image. The scale is 500 meters long.
Dark dunes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Dark dunes are composed of the igneous rock basalt. The dark box in the center of the photo shows the area enlarged in the next image. The scale is 500 meters long. Close up of dark dunes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. The image is a little more than 1 km in its longest dimension. The location of this image is shown in the previous image.
Close up of dark dunes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. The image is a little more than 1 km in its longest dimension. The location of this image is shown in the previous image. Dunes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Eridania quadrangle.
Dunes, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Eridania quadrangle. Dunes on crater floor, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Dunes on crater floor, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Glacial features
 Glacial features in Arrhenius Crater, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program. Arrows point to old glaciers.
Glacial features in Arrhenius Crater, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program. Arrows point to old glaciers. Cruls Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Arrows indicate old glaciers.
Cruls Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Arrows indicate old glaciers. Old glaciers in Cruls Crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
Old glaciers in Cruls Crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Romer Lake's Elephant Foot Glacier in the Earth's Arctic, as seen by Landsat 8. This picture shows several glaciers that have the same shape as many features on Mars that are believed to also be glaciers.
Romer Lake's Elephant Foot Glacier in the Earth's Arctic, as seen by Landsat 8. This picture shows several glaciers that have the same shape as many features on Mars that are believed to also be glaciers.
Lake
The Eridania Basin, located near 180 E and 30 South, is believed to have contained a large lake with a depth of 1 km in places.[46] The basin is composed of a group of eroded and connected topographically impact basins. The lake has been estimated to have an area of 3, 000, 000 square kilometers. Water from this lake entered Ma’adim Vallis which starts at the lake's north boundary.[47] It is surrounded by valley networks that all end at the same elevation, suggesting that they emptied into a lake.[48] Mg-rich clay minerals and opaline silica have been detected in the area.[49] These minerals are consistent with the presence of a large lake.[47]
Craters
 Crater floor with the shape of an odd face, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. The box indicates where the next picture is located.
Crater floor with the shape of an odd face, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. The box indicates where the next picture is located. Close-up of a portion of a crater wall indicated in the previous photo. There seems to be grooves in the wall. Picture was taken with HiRISE under HiWish program.
Close-up of a portion of a crater wall indicated in the previous photo. There seems to be grooves in the wall. Picture was taken with HiRISE under HiWish program. Surface on crater floor, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
Surface on crater floor, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.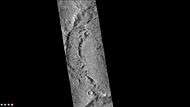 Arrhenius Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Arrhenius Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Wells Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Wells Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).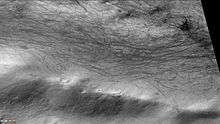 Dust devil tracks along rim of Wells Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of previous image of Wells Crater.
Dust devil tracks along rim of Wells Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of previous image of Wells Crater.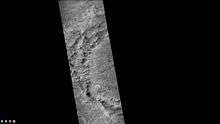 West side of Rossby Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
West side of Rossby Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Gullies in Rossby Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of previous image of west side of Rossby Crater.
Gullies in Rossby Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of previous image of west side of Rossby Crater. Martz Crater, as seen by CTXcamera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Martz Crater, as seen by CTXcamera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Gullies on central mound in Martz Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: This is an enlargement of the previous image of Martz Crater.
Gullies on central mound in Martz Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: This is an enlargement of the previous image of Martz Crater. Campbell Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Campbell Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).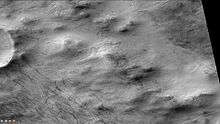 Dust devil tracks, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image of Campbell Crater.
Dust devil tracks, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image of Campbell Crater. Knobel Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Knobel Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Haldane Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Dark portions on the floor are dunes.
Haldane Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Dark portions on the floor are dunes. Vinogradsky Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Vinogradsky Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Priestly Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Priestly Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Latitude dependent mantle
Much of the Martian surface is covered with a thick ice-rich, mantle layer that has fallen from the sky a number of times in the past.[50] [51] [52] In some places a number of layers are visible in the mantle
 Mantle layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
Mantle layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.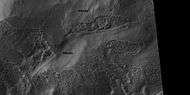 Close view of places covered and not covered by mantle layer which falls from the sky when climate changes.
Close view of places covered and not covered by mantle layer which falls from the sky when climate changes.
Other features in Eridania quadrangle
- Map of Eridania quadrangle, with major craters.
- Ariadne Colles Chaos, as seen by HiRISE. The original image displays many interesting details. The scale bar is 500 meters long.
- Hummocks in Ariadness Colles, as seen by HiRISE. Right picture is an enlargement of a portion of the other picture.
 Crater floor, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Rough surface was produced by ice leaving the ground. The crater has accumulated much ice that is covered by rocks and dirt.
Crater floor, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Rough surface was produced by ice leaving the ground. The crater has accumulated much ice that is covered by rocks and dirt. Crater floor showing brain terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Crater floor showing brain terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Channel on floor of crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Channel on floor of crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Ridges exposed from under a dark layer, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Ridges exposed from under a dark layer, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Channel cutting across trough, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program The trough and channel are labeled.
Channel cutting across trough, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program The trough and channel are labeled.
Other Mars quadrangles
Interactive Mars map
See also
References
- ↑ Davies, M.E.; Batson, R.M.; Wu, S.S.C. “Geodesy and Cartography” in Kieffer, H.H.; Jakosky, B.M.; Snyder, C.W.; Matthews, M.S., Eds. Mars. University of Arizona Press: Tucson, 1992.
- ↑ Grant, J. and P. Schultz. 1990. Gradational epochs on Mars: Evidence from west-northwest of Isidis Basin and Electric. Icarus: 84. 166-195.
- ↑ Edgett, K. et al. 2003. Polar-and middle-latitude martian gullies: A view from MGS MOC after 2 Mars years in the mapping orbit. Lunar Planet. Sci. 34. Abstract 1038.
- 1 2 http://www.planetary.brown.edu/pdfs/3138.pdf
- ↑ Dickson, J. et al. 2007. Martian gullies in the southern mid-latitudes of Mars Evidence for climate-controlled formation of young fluvial features based upon local and global topography. Icarus: 188. 315-323
- ↑ http://www.psrd.hawaii.edu/Aug03/MartianGullies.html
- ↑ Heldmann, J. and M. Mellon. Observations of martian gullies and constraints on potential formation mechanisms. 2004. Icarus. 168: 285-304.
- ↑ Forget, F. et al. 2006. Planet Mars Story of Another World. Praxis Publishing. Chichester, UK.
- ↑ Heldmann, J. and M. Mellon. 2004. Observations of martian gullies and constraints on potential formation mechanisms. Icarus. 168:285-304
- ↑ http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/mars_aquifer_041112.html
- ↑ Harris, A and E. Tuttle. 1990. Geology of National Parks. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. Dubuque, Iowa
- ↑ Malin, M. and K. Edgett. 2001. Mars Global Surveyor Mars Orbiter Camera: Interplanetary cruise through primary mission. J. Geophys. Res: 106> 23429-23570
- ↑ Mustard, J. et al. 2001. Evidence for recent climate change on Mars from the identification of youthful near-surface ground ice. Nature: 412. 411-414.
- ↑ Carr, M. 2001. Mars Global Surveyor observations of fretted terrain. J. Geophys. Res: 106. 23571-23595.
- ↑ http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/15702457?
- ↑ http://www.pnas.org/content/105/36/13258.full
- ↑ Head, J. et al. 2008. Formation of gullies on Mars: Link to recent climate history and insolation microenvironments implicate surface water flow origin. PNAS: 105. 13258-13263.
- ↑ Christensen, P. 2003. Formation of recent martian gullies through melting of extensive water-rich snow deposits. Nature: 422. 45-48.
- ↑ http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2008/03/080319-mars-gullies_2.html
- ↑ Jakosky B. and M. Carr. 1985. Possible precipitation of ice at low latitudes of Mars during periods of high obliquity. Nature: 315. 559-561.
- ↑ Jakosky, B. et al. 1995. Chaotic obliquity and the nature of the Martian climate. J. Geophys. Res: 100. 1579-1584.
- ↑ MLA NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory (2003, December 18). Mars May Be Emerging From An Ice Age. ScienceDaily. Retrieved February 19, 2009, from http://www.sciencedaily.com /releases/2003/12/031218075443.htmAds by GoogleAdvertise
- ↑ Dickson, J. et al. 2007. Martian gullies in the southern mid-latitudes of Mars Evidence for climate-controlled formation of young fluvial features based upon local and global topography. Icarus: 188. 315-323.
- ↑ Hecht, M. 2002. Metastability of liquid water on Mars. Icarus: 156. 373-386.
- ↑ Peulvast, J. Physio-Geo. 18. 87-105.
- ↑ Costard, F. et al. 2001. Debris Flows on Mars: Analogy with Terrestrial Periglacial Environment and Climatic Implications. Lunar and Planetary Science XXXII (2001). 1534.pdf
- ↑ http://www.spaceref.com:16090/news/viewpr.html?pid=7124,
- ↑ Clow, G. 1987. Generation of liquid water on Mars through the melting of a dusty snowpack. Icarus: 72. 93-127.
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_006736_1325
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_00481_2410
- ↑ http://marsrovers.jpl.nasa.gov/gallery/press/spirit/20070412a.html
- ↑ http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/spotlight/KenEdgett.html
- ↑ Reiss, D. et al. 2011. Multitemporal observations of identical active dust devils on Mars with High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC). Icarus. 215:358-369.
- ↑ Barlow, N. 2008. Mars: An Introduction to its Interior, Surface and Atmosphere. Cambridge University Press
- ↑ ISBN 978-0-387-48925-4
- ↑ ISBN 978-0-521-82956-4
- ↑ http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/mars-plate-tectonics-recent-past-110103.html
- ↑ Connerney, J. et al. 1999. Magnetic lineations in the ancient crust of Mars. Science: 284. 794-798.
- ↑ Langlais, B. et al. 2004. Crustal magnetic field of Mars. Journal of Geophysical Research. 109: EO2008
- ↑ Connerney, J. et al. 2005. Tectonic implications of Mars crustal magnetism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 102: 14970-14975
- ↑ Acuna, M. et al. 1999. Global distribution of crustal magnetization discovered by the Mars Global Surveyor MAG/ER Experiment. Science. 284: 790-793.
- ↑ http://sci.esa.int/science-e/www/object/index.cfm?fobjectid=31028&fbodylongid=645
- ↑ Pye, Kenneth; Haim Tsoar (2008). Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes. Springer. p. 138. ISBN 9783540859109.
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/53068/barchan
- ↑ Mellon, J. T.; Feldman, W. C.; Prettyman, T. H. (2003). "The presence and stability of ground ice in the southern hemisphere of Mars". Icarus. 169 (2): 324–340. Bibcode:2004Icar..169..324M. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2003.10.022.
- ↑ Irwin, R., et al. 200). J. Geophys. Res., 109, E12009.
- 1 2 Michalski, J., E. Noe Dobrea1, C. Weitz. 2015. MG-RICH CLAYS AND SILICA-BEARING DEPOSITS IN ERIDANIA BASIN: POSSIBLE EVIDENCE FOR ANCIENT SEA DEPOSITS ON MARS. 46th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference. 2754.pdf
- ↑ Baker, D., J. Head. 2014. 44th LPSC, abstract #1252
- ↑ Cuadros, J., et al. 2013. Chem. Geol. 360-361, 142-158.
- ↑ Hecht, M. 2002. Metastability of water on Mars. Icarus 156, 373–386
- ↑ Mustard, J., et al. 2001. Evidence for recent climate change on Mars from the identification of youthful near-surface ground ice. Nature 412 (6845), 411–414.
- ↑ Pollack, J., D. Colburn, F. Flaser, R. Kahn, C. Carson, and D. Pidek. 1979. Properties and effects of dust suspended in the martian atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 2929-2945.
- 1 2 Morton, Oliver (2002). Mapping Mars: Science, Imagination, and the Birth of a World. New York: Picador USA. p. 98. ISBN 0-312-24551-3.
- ↑ "Online Atlas of Mars". Ralphaeschliman.com. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ↑ "PIA03467: The MGS MOC Wide Angle Map of Mars". Photojournal. NASA / Jet Propulsion Laboratory. February 16, 2002. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ↑ "Online Atlas of Mars". Ralphaeschliman.com. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ↑ "PIA03467: The MGS MOC Wide Angle Map of Mars". Photojournal. NASA / Jet Propulsion Laboratory. February 16, 2002. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
Further reading
- Lorenz, R. 2014. The Dune Whisperers. The Planetary Report: 34, 1, 8-14
- Lorenz, R., J. Zimbelman. 2014. Dune Worlds: How Windblown Sand Shapes Planetary Landscapes. Springer Praxis Books / Geophysical Sciences.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eridania quadrangle. |
- General review of many of the theories involving the origin of gullies.
- Good review of the history of the discovery of gullies.
- Martian Ice - Jim Secosky - 16th Annual International Mars Society Convention
| Quadrangles on Mars | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||