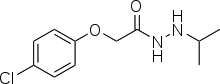
Iproclozide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | N06AF06 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
3544-35-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 19063 |
| ChemSpider |
17998 |
| UNII |
1II9D6CB3J |
| KEGG |
D07338 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL91238 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.536 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15ClN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 242.70 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Iproclozide (trade names Sursum, Sinderesin) is an irreversible and selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was used as an antidepressant, but has since been discontinued.[1] It has been known to cause fulminant hepatitis and there have been at least three reported fatalities due to administration of the drug.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ Suerinck A, Suerinck E (1966). "[Depressive states in a sanatorium milieu and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. (Therapeutic results by the combination of iproclozide and chlordiazepoxide). Apropos of 146 cases]". Journal de médecine de Lyon. 47 (96): 573–586. PMID 5930723.
- ↑ Pessayre D, de Saint-Louvent P, Degott C, Bernuau J, Rueff B, Benhamou JP (1978). "Iproclozide fulminant hepatitis. Possible role of enzyme induction.". Gastroenterology. 75 (3): 492–496. PMID 680506.
- ↑ Neil Kaplowitz; Laurie D. DeLeve (2003). Drug-induced liver disease. Informa Health Care. p. 455. ISBN 0-8247-0811-3. ISBN 9780824708115.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.