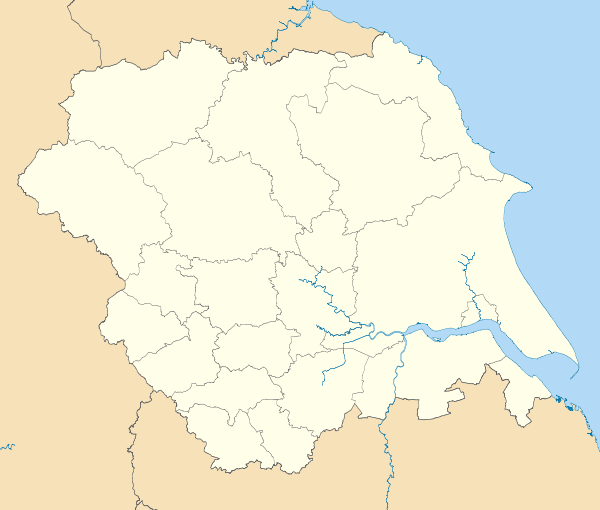
Kirklees
Coordinates: 53°35′35″N 1°48′04″W / 53.593°N 1.801°W
| Borough of Kirklees | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan borough | |
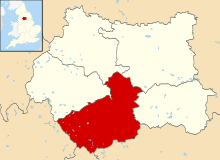 Kirklees shown within West Yorkshire | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | Yorkshire and the Humber |
| Ceremonial county | West Yorkshire |
| Founded | 1974 |
| Admin. HQ | Huddersfield |
| Government | |
| • Type | Kirklees Metropolitan Council |
| • Mayor: | Cllr. Ken Smith |
| • Chief Executive: | Adrian Lythgo |
| • Executive: | TBA (council NOC) |
| • MPs: |
Tracy Brabin, Jason McCartney, Paula Sherriff, Barry Sheerman |
| Area | |
| • Total | 157.8 sq mi (408.6 km2) |
| Area rank | 100th |
| Population (mid-2014 est.) | |
| • Total | 431,020 |
| • Rank | Ranked 11th |
| • Density | 2,700/sq mi (1,100/km2) |
| Time zone | Greenwich Mean Time (UTC+0) |
| • Summer (DST) | British Summer Time (UTC+1) |
| ONS code |
00CZ (ONS) E08000034 (GSS) |
| Ethnicity |
79.1% White 15% S. Asian 1.9% Black 2.3% Mixed Other 1.7%[1] |
| Website | kirklees.gov.uk |
The Metropolitan Borough of Kirklees is a metropolitan borough of West Yorkshire, England. It had a population of 422,500 in 2011[2] and includes the settlements of Batley, Birstall, Cleckheaton, Denby Dale, Dewsbury, Heckmondwike, Holmfirth, Huddersfield, Kirkburton, Marsden, Meltham, Mirfield and Slaithwaite. Huddersfield is the largest settlement of the district, and its centre of administration.
History
The borough was formed under the Local Government Act 1972 on 1 April 1974, by a merger of the county boroughs of Dewsbury and Huddersfield along with the municipal boroughs of Batley and Spenborough and the urban districts of Colne Valley, Denby Dale, Heckmondwike, Holmfirth, Kirkburton, Meltham and Mirfield.
The name "Kirklees" was chosen by the merging councils from more than fifty suggestions, including "Upper Agbrigg", "Brigantia" and "Wooldale".[3] It was named after Kirklees Priory, legendary burial place of Robin Hood.[3][4] The site of the priory is now Kirklees Park Estate, situated midway between Huddersfield and Dewsbury and the location of Kirklees Hall.[3] It is worth noting, however, that Robin Hood's Grave, Kirklees Priory and the majority of Kirklees Park Estate are, in fact, in the neighbouring borough of Calderdale.
Under the original draft of the Act, the area was set to include Ossett, which was part of the Dewsbury Parliamentary constituency at that time. However, once Huddersfield was chosen as the headquarters, it was decided that Ossett was too remote to be governed by Kirklees. After an appeal by the Ossett Labour Party, the town was moved into the Wakefield district.[5]
Governance
Borough council
The local authority for the Kirklees borough is Kirklees Metropolitan Borough Council
Election results
Borough status and mayoralty
The shadow Kirklees District Council petitioned the privy council for a royal charter under section 245 of the Local Government Act 1972 granting the status of a borough from 1 April 1974.[6] The grant of borough status entitled the chairman of the council to the title of "mayor", effectively continuing the mayoralties of the former boroughs of Dewsbury (1862), Huddersfield (1898), Batley (1869) and Spenborough (1955).[7] The mayor is elected from among the councillors for a one-year term (the "civic year") at the council's annual meeting.[8]
Kirklees is the most populated borough or district in England not to have city status. In 2001 it was announced that a grant of city status was to be made to an English town to mark the Golden Jubilee of Elizabeth II, and Kirklees council indicated that it was considering applying on behalf of Huddersfield. An unofficial telephone poll by the Huddersfield Examiner found a slim majority against the proposal, and the council did not proceed with the application.[9]
Freedom of the borough
Borough status also allows the council to confer the freedom of the borough on "persons of distinction". Since its formation Kirklees Borough Council has granted this right to two individuals and two groups:
- 3rd Battalion Yorkshire Volunteers - (25 March 1979)[10] On 25 March 1979 Kirklees Metropolitan Borough Council gave the Freedom of Kirklees to the 3rd Battalion of the Yorkshire Volunteers. The 3rd Battalion was at that time the Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding) Territorial Army unit. However the freedom given by Kirklees to the 3rd battalion of the Yorkshire Volunteers did not permit any transfer to heirs or successors and effectively that freedom ceased when the battalion was amalgamated into the East and West Riding Regiment on 1 July 1999. The East and West Riding Regiment ceased to exist on 6 June 2006, having been merged into the Yorkshire Regiment as its 4th Battalion. The Yorkshire Regiment requested the freedom to march to be transferred to them. On 25 October 2008 Kirklees Council transferred the Freedom of Huddersfield to the Yorkshire Regiment at a freedom parade held by the 3rd Battalion, formerly the Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding).
- Sir William Mallalieu MP (27 January 1980)[11]
- The Rt Hon Betty Boothroyd MP (20 November 1992)[11]
- Citizens of Besançon, France (7 October 2005)[11]
- The Yorkshire Regiment (25 October 2008)[12]
Twin towns
Kirklees is twinned with:
Coat of arms
Kirklees Borough Council was granted armorial bearings by the College of Arms by letters patent dated 24 June 1974. the blazon of the arms is as follows:
Vert on a bend Argent a bendlet wavy azure on a chief Or a pale between two cog-wheels azure on the pale a Paschal Lamb supporting a staff of the fourth flying therefrom a forked pennon argent charged with a cross gules; and for a Crest, On a wreath of the colours a ram's head affronty couped argent armed Or gorged with a mural crown sable masoned argent.Supporters: On either side a lion guardant purpure resting the inner hind leg on a cross crosslet Or embellished in each of the four angles with a fleur de lis azure. Badge or device: A roundel purpure charged with a Lacy Knot Or all within a circle of eleven roses argent barbed and seeded proper.[14]
The green colouring of the shield represents the fields, woods and moorland of the borough. The white stripe or bend represents the M62 motorway, while the blue wave upon it is for the many waterways of the area. On the chief or upper third of the shield is a paschal lamb, symbol of St John the Baptist. John was the patron saint of woolworkers, and the inclusion of the emblem represents the historic woollen industry. The cogwheels are for the modern engineering industries. The crest is a ram's head, found in the arms of the County Borough of Huddersfield and the Mirfield Urban District Council. The black mural crown stands for the district's status as a borough, recalling a city wall. The supporters are purple lions from the arms of the de Laci family, medieval lords of Huddersfield. For heraldic "difference" from other lion supporters a distinctive cross has been placed below their inner feet. This device, combining the symbols of Christ and the Virgin Mary, represents the priory from which the borough took its name.[14][15]
Parish and town councils
In five areas of the borough there is a second tier of local government: the civil parish. Parish or town councils have limited powers of a purely local character, such as owning or maintaining allotments, burial grounds, footpaths and war memorials. Four of the parishes were formed as successor parishes to urban districts abolished in 1974.[16] The fifth was formed in 1988.[17] The five town or parish councils are:
| Council | Area covered | Number of councillors | Parish Wards | Formed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denby Dale Parish Council | Denby Dale, Upper and Lower Cumberworth, Upper and Lower Denby, Birdsedge and High Flatts, Scissett, Skelmanthorpe and the hamlet of Kitchenroyd, Emley and Emley Moor and Clayton West[16] | 17[18] | Clayton West, Denby & Cumberworth, Emley, Skelmanthorpe[18] | Successor to Denby Dale UDC 1973[19] |
| Holme Valley Parish Council | Holmfirth and Honley, Brockholes, Cinderhills, Hade Edge, Hepworth, Hinchliffe Mill, Holmbridge, Holme, Jackson Bridge, Netherthong, New Mill, Scholes, Thongsbridge, Upperthong, Wooldale[16] | 23[20] | Brockholes, Fulstone, Hepworth, Holmfirth Central, Honley Central and East, Honley South, Honley West, Netherthong, Scholes, Upper Holme Valley, Upperthong, Wooldale[20] | Successor to Holmfirth UDC 1973,[19] renamed Holme Valley 1975. |
| Kirkburton Parish Council | Farnley Tyas, Flockton, Grange Moor, Highburton, Kirkburton, Kirkheaton, Lepton, Shelley, Shepley and Thurston[16] | 25[21][22] | Flockton, Kirkburton, Kirkheaton, Lepton, Lepton & Whitley Upper, Shelley, Shepley, Thurstonland/Farnley Tyas[21][22] | Successor to Kirkburton UDC 1973[19] |
| Meltham Town Council | Crosland Edge, Meltham, Helme, Wilshaw[16] | 12[23] | None[23] | Successor to Meltham UDC 1973[19] |
| Mirfield Town Council | Battyeford, Mirfield, Northorpe, Lower Hopton and Upper Hopton[16] | 16[17] | Battyeford, Crossley, Eastthorpe, Hopton, Northorpe[17] | Formed 1988[17] |
The remainder of the borough is unparished, with the borough council exercising parish powers.
Parliamentary representation
1997 to date
Since 1997 Kirklees has been divided into five constituencies: four being entirely within the borough, while one ward (Wakefield) is included in the Wakefield Council borough.
The boundaries of two of the Colne Valley and Huddersfield constituencies were virtually unchanged from those defined in 1983. Denby Dale and Kirkburton wards were transferred from Dewsbury to Wakefield, with the former constituency receiving Heckmondwike ward from Batley and Spen.
The constituencies were first used at the 1997 general election, when the Labour Party came to power in a landslide, gaining all the seats in the borough. The party held the seats at the subsequent elections of 2001 and 2005.[24] The incumbent MP for Batley and Spen, Jo Cox, was murdered on 16 June 2016.[25] A constituency by-election took place on 20 October 2016 and Tracy Brabin was elected.[26]
| Constituency | Wards | Member of parliament | Party | Majority | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batley and Spen Borough Constituency |
The following wards continued to formulate the Batley seat from 1997-2005: At the 2010 general elections the boundary commission moved Heckmondwike from |
Jo Cox | Labour Party | 2015: 6,057 (over Conservatives)[27] | |
| Mike Wood | Labour Party | 2010: 4,406 (over Conservatives) | |||
| 2005: 5,788 (over Conservatives) | |||||
| 2001: 5,064 (over Conservatives)[28] | |||||
| 1997: 6,141 (over Conservatives)[28] | |||||
| Colne Valley County Constituency | Colne Valley West, Crosland Moor, Golcar, Holme Valley North, Holme Valley South and Lindley.[24] |
Jason McCartney | Conservative Party | 2015: 5,378 (over Labour) | |
| 2010: 4,837 (over Liberal Democrats) | |||||
| Kali Mountford | Labour Party | 2005: 1,501 (over Conservatives) | |||
| 2001: 4,639 (over Conservatives)[29] | |||||
| 1997: 4,840 (over Conservatives)[29] | |||||
| Dewsbury County Constituency | The following wards continued to formulate the Dewsbury seat from 1997-2005: Dewsbury East, Dewsbury West, Heckmondwike, Mirfield and Thornhill. At the 2010 general elections the boundary commission moved Heckmondwike from |
Paula Sherriff | Labour Party | 2015: 1,451 (over Conservatives) | |
| Simon Reevell | Conservative Party | 2010: 1,526 (over Labour) | |||
| Shahid Malik | Labour Party | 2005: 4,615 (over Conservatives) | |||
| Ann Taylor | 2001: 8,323 (over Conservatives)[30] | ||||
| 1997: 4,840 (over Conservatives)[30] | |||||
| Huddersfield Borough Constituency | Almondbury, Birkby, Dalton, Deighton, Newsome and Paddock.[24] |
Barry Sheerman | Labour Co-op | 2015: 7,345 (over Conservatives) | |
| 2010: 4,472 (over Conservatives) | |||||
| 2005: 8,351 (over Conservatives) | |||||
| 2001: 10,046 (over Conservatives)[31] | |||||
| 1997: 15,848 (over Conservatives)[31] | |||||
| Wakefield County Constituency | At the 2010 general elections the boundary commission moved Denby Dale and Kirkburton wards out of Wakefield seat and into the Dewsbury seat |
Mary Creagh | Labour Party | 2015: 2,613 (over Conservatives) | |
| 2010: 1,613 (over Conservatives) | |||||
| 2005: 5,154 (over Conservatives) | |||||
| David Hinchliffe | 2001: 7,954 (over Conservatives)[32] | ||||
| 1997: 14,604 (over Conservatives)[32] | |||||
1983 to 1997
The 1983 general election was the first at which constituencies based on the administrative areas created in 1974 were used. Kirklees was divided into four constituencies.[33] The Conservative Party polled well in the 1983 election, and took two of the borough's constituencies. Labour held Huddersfield, while the Liberals, running in an alliance with the Social Democrats, held Colne Valley. In the following election in 1987 the Labour vote increased slightly, and they gained Dewsbury from the Conservatives. At the same time the Alliance vote fell, and the Conservatives took Colne Valley. The four MPs elected in 1992 were all returned in 1997.
| Constituency | Wards | Member of parliament | Party | Majority | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batley and Spen Borough Constituency | Batley East, Batley West, Birstall and Birkenshaw, Cleckheaton, Heckmondwike and Spen[33] |
Elizabeth Peacock | Conservative Party | 1992: 1,408 (over Labour)[34] | |
| 1987: 1,362 (over Labour)[35] | |||||
| 1983: 870 (over Labour)[36] | |||||
| Colne Valley County Constituency | Colne Valley West, Crosland Moor, Golcar, Holme Valley North, Holme Valley South and Lindley.[33] |
Graham Riddick | Conservative Party | 1992: 7,225 (over Labour)[37] | |
| 1987: 1,677 (over Liberal / Alliance)[38] | |||||
| Richard Wainwright | Liberal / Alliance | 1983: 3,146 (over Conservatives)[39] | |||
| Dewsbury County Constituency | Denby Dale, Dewsbury East, Dewsbury West, Kirkburton, Mirfield and Thornhill.[33] |
Ann Taylor | Labour Party | 1992: 634 (over Conservatives))[40] | |
| 1987: 445 (over Conservatives)[41] | |||||
| John Whitfield | Conservative Party | 1983: 2,068 (over Labour)[42] | |||
| Huddersfield Borough Constituency | Almondbury, Birkby, Dalton, Deighton, Newsome and Paddock.[33] |
Barry Sheerman | Labour Party | 1992: 7,258 (over Conservatives)[43] | |
| 1987: 7,278 (over Conservatives)[44] | |||||
| 1983: 3,955 (over Conservatives)[43] | |||||
1974 to 1983
Parliamentary constituencies in England and Wales continued to be defined in terms of the boroughs and districts abolished in 1974 until a general redistribution of seats in 1983. Accordingly, Kirklees was divided between seven constituencies, which had first been used in the 1950 general election.[45]
| Constituency | Former administrative areas | Member of parliament | Party | Majority | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batley and Morley Borough Constituency | Municipal Borough of Batley Also included the former Municipal Borough of Morley in the City of Leeds. |
Kenneth Woolmer | Labour Party | 1979: 5,352 (over Conservatives)[46] | |
| A D D Broughton | October 1974: 8,248 (over Conservatives)[47] | ||||
| February 1974: 7,091 (over Conservatives)[48] | |||||
| Brighouse and Spenborough Borough Constituency | Municipal Borough of Spenborough Also included the former Municipal Borough of Brighouse in the Metropolitan Borough of Calderdale. |
Gary Waller | Conservative Party | 1979: 1,734 (over Labour)[49] | |
| Colin Jackson | Labour Party | October 1974: 2,177 (over Conservatives)[50] | |||
| February 1974: 1,546 (over Conservatives)[51] | |||||
| Colne Valley County Constituency | Colne Valley Urban District, Holmfirth Urban District, Kirkburton Urban District, Meltham Urban District Also included the former Saddleworth Urban District in the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham. |
Richard Wainwright | Liberal Party | 1979: 2,352 (over Labour)[52] | |
| October 1974: 1,666 (over Labour)[53] | |||||
| February 1974: 719 (over Labour)[54] | |||||
| Dewsbury Borough Constituency | Municipal Borough of Dewsbury, Heckmondwike Urban District, Mirfield Urban District Also included the former Municipal Borough of Ossett in the City of Wakefield. |
David Ginsburg | Labour Party (Defected to the |
1979: 4,381 (over Conservatives)[56] | |
| October 1974: 6,901 (over Conservatives)[57] | |||||
| February 1974: 5,412 (over Conservatives)[58] | |||||
| Huddersfield East Borough Constituency | Seven wards of the County Borough of Huddersfield: Almondbury, Dalton, Deighton, Fartown, Newsome, North Central, South Central |
Barry Sheerman | Labour Party | 1979: 3,095 (over Conservatives)[59] | |
| J. P. W. Mallalieu | October 1974: 8,414 (over Conservatives)[60] | ||||
| February 1974: 7,304 (over Conservatives)[61] | |||||
| Huddersfield West Borough Constituency | Eight wards of the County Borough of Huddersfield: Birkby, Crosland Moor, Lindley, Lockwood, Longwood, Marsh, Milnsbridge, Paddock |
Geoffrey Dickens | Conservative Party | 1979: 1,508 (over Labour)[59] | |
| Kenneth Lomas | Labour Party | October 1974: 1,364 (over Conservatives)[60] | |||
| February 1974: 630 (over Conservatives)[61] | |||||
| Penistone County Constituency | Denby Dale Urban District Remainder of constituency consisted of former urban and rural districts in the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley and the City of Sheffield |
Allen McKay | Labour Party | 1979: 9,701 (over Conservatives)[62] | |
| 1978 by-election: 5,371 (over Conservatives) | |||||
| John Mendelson | October 1974: 1,364 (over Conservatives)[63] | ||||
| February 1974: 630 (over Conservatives)[64] | |||||
Geography
Most of Kirklees consists of old mill towns although there are a few country villages, such as Denby Dale and Emley. The combination of the two county boroughs (which only happened in three other metropolitan districts: Wirral, Sefton and Sandwell) resulted in a borough with no clear centre. Graham Riddick, MP for Colne Valley, campaigned in the early 1990s for it to be split into two.[65][66] A similar ambition was mentioned by Elizabeth Peacock, MP for Batley and Spen in 1991.[67] The boundaries of metropolitan boroughs were outside the remit of the Banham Commission appointed to review local government structures in 1992 or its successors, and only minor boundary changes were made with neighbouring districts in 1994.[68][69][70]
The district includes areas of three postal codes. Birkenshaw, Cleckheaton and Gomersal lie within the BD Bradford area. The Huddersfield HD postcode also includes the rural south area of the district, while Batley, Dewsbury, Heckmondwike and Mirfield lie within the Wakefield WF postcode. Similarly, the telephone dialling codes are split, with Kirklees residents being split between 01484 Huddersfield, 01274 Bradford and 01924 Wakefield. A small number of residents fall within 01422 Halifax (Birchencliffe village) and 0113 (part of Birkenshaw).
Demography
Religion
The stated religion of the population of Kirklees, as recorded at the 2001 census of population was as follows:[71]
- Christian 261,128 (67.2%)
- No religion 54,445 (14%)
- Muslim 39,312 (10.1%)
- Religion not stated 28,394 (7.3%)
- Sikh 2,726 (0.7%)
- Hindu 1,222 (0.3%)
- Other Religions 772 (0.2%)
- Buddhist 397 (0.1%)
- Jewish 171 (0.0%)
Notable features
One attraction in Kirklees is Kirklees Light Railway. The border of Kirklees borough with Derbyshire (High Peak district) runs across the summit of the significant hill named Black Hill.
Dewsbury and Batley have been made into a special E.U. transformation area to address their problems of deprivation.
See also
References
- ↑ "Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales 2011". National Statistics Online. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 2015-04-29.
- ↑ Kirklees MBC website - Community statistics, 2011 Census
- 1 2 3 O'Leary, Patrick (8 August 1974). "Kirklees: Robin Hood brings the communities together". The Times. p. 12.
- ↑ "In the footsteps of Robin Hood". History. Channel 4. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- ↑ Ossett Town Hall, Ossett Historical Society, 2008, page 104
- ↑ Local government in England and Wales: A Guide to the New System. London: HMSO. 1974. p. 25. ISBN 0-11-750847-0.
- ↑ "Former Mayors". Kirklees Council. August 2008. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- ↑ "The Mayor's Role". Kirklees Council. May 2006. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- ↑ "Huddersfield people undecided on city status bid". Huddersfield Examiner. 9 August 2001. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- ↑ "The Dukes and The West Riding". Regimental History. The Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding)Regimental Association. 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- 1 2 3 "Freedom of Kirklees ...for a French town!". Huddersfield Examiner. 1 April 2005. Retrieved 14 February 2009.
- ↑ Hirst, Andrew (16 October 2008). "Special Huddersfield parade to honour Yorkshire Regiment". Huddersfield Examiner. Retrieved 14 February 2009.
- ↑ "British towns twinned with French towns". Archant Community Media Ltd. Retrieved 2013-07-11.
- 1 2 "Kirklees Metropolitan Borough Council". Civic Heraldry of England and Wales. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- ↑ Kirklees Borough Guide, c.1974
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Parish and Town Councils". Kirklees Council. January 2006. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 3 4 "About the Council". Mirfield Town Council. 9 February 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 "The Councillors". Denby Dale Parish Council. 2007. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 3 4 The Local Government (Successor Parishes) (No. 2) Order 1973 (S.I. 1973/1939)
- 1 2 "Members of the Council". Holme Valley Parish Council. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 "Kirkburton Parish Council". Kirklees Council. July 2007. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 "Parish Councillors' Contact Details". Kirkburton Parish Council. 2007. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 "Your members of the council". Meltham Town Council. 2008. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "The Parliamentary Constituencies (England) Order 1995 (S.I. 1995/1626)". Office of Public Sector Information. 1995. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "Labour MP Jo Cox dies after being shot and stabbed in her constituency near Leeds". The Daily Telegraph. 16 June 2016. Retrieved 16 June 2016.
- ↑ "Batley and Spen by-election: Tracy Brabin victory for 'hope and unity'". BBC News. 21 October 2016. Retrieved 20 November 2016.
- ↑ "Batley & Spen". BBC News. Retrieved 13 May 2015.
- 1 2 "Batley & Spen". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- 1 2 "Colne Valley". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- 1 2 "Dewsbury". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- 1 2 "Huddersfield". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- 1 2 "Wakefield". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- 1 2 3 4 5 The Parliamentary Constituencies (England) Order 1983 (S.I. 1983/417)
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1992". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1987". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1983". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1992". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1987". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1983". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1992". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1987". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1983". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 "United Kingdom General Election Results 1983". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1987". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ Representation of the People Act 1948, (c.65), Schedule I
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1979". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results October 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results February 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1979". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results October 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results February 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1979". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results October 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results February 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ Crewe, Ivor; King, Anthony (1995). SDP: The Birth, Life and Death of the Social Democratic Party. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 109. ISBN 0-19-828050-5.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1979". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results October 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results February 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 "United Kingdom General Election Results 1979". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 "United Kingdom General Election Results October 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- 1 2 "United Kingdom General Election Results February 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results 1979". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results October 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ "United Kingdom General Election Results February 1974". Political Science Resources. University of Keele. Retrieved 2009-02-16.
- ↑ http://www.parliament.the-stationery-office.co.uk/pa/cm199192/cmhansrd/1992-03-09/Debate-6.html
|chapter-url=missing title (help). Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). House of Commons. 3 March 1992. col. 717. - ↑ http://www.parliament.the-stationery-office.co.uk/pa/cm199394/cmhansrd/1993-11-22/Debate-8.html
|chapter-url=missing title (help). Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). House of Commons. 22 November 1993. col. 277. - ↑ http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm199091/cmhansrd/1991-05-08/Orals-1.html
|chapter-url=missing title (help). Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). House of Collomons. 8 May 1991. col. 711. - ↑ http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm199596/cmhansrd/vo951204/debtext/51204-31.htm
|chapter-url=missing title (help). Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). House of Commons. 4 December 1995. col. 118. - ↑ "The Bradford, Kirklees and Leeds (City and Metropolitan Borough Boundaries) Order 1993". Office of Public Sector Information. 1993. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- ↑ "The Calderdale and Kirklees (Metropolitan Borough Boundaries) Order 1993". Office of Public Sector Information. 1993. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- ↑ "Table KS07 religion" (PDF). Statistics. Kirklees Council. Retrieved 2009-02-14.