Oral and maxillofacial pathology
| Oral and maxillofacial pathology | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | K00-K14 |
| ICD-9-CM | 520-529 |
| MeSH | D009057 |
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names | Oral and Maxillofacial Pathologist, Oral Pathologist |
Occupation type | Specialty |
Activity sectors | Pathology, Dentistry, Medicine |
| Description | |
Education required | Varies. Typically dental degree followed by specialist training |
Oral and maxillofacial pathology (also termed oral pathology, stomatognathic disease, dental disease, or mouth disease) refers to the diseases of the mouth ("oral cavity" or "stoma"), jaws ("maxillae" or "gnath") and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin (the skin around the mouth).[1][2] The mouth is an important organ with many different functions. It is also prone to a variety of medical and dental disorders.[3]
The specialty oral and maxillofacial pathology is concerned with diagnosis and study of the causes and effects of diseases affecting the oral and maxillofacial region. It is sometimes considered to be a specialty of dentistry and pathology.[4] Sometimes the term head and neck pathology is used instead, but this might imply that the pathologist deals with otorhinolaryngologic disorders (i.e. ear, nose and throat) in addition to maxillofacial disorders. In this role there is some overlap between the expertise of head and neck pathologists and that of endocrine pathologists.
Example pathologies
A great many diseases involve the mouth, jaws and orofacial skin. Some example pathologies which can involve the oral and maxillofacial region are listed. Some are more common than others, and this list is by no means complete. The examples are considered according to a surgical sieve.
Congenital
- Malocclusion
- Cleft lip and palate
- Macroglossia
- Ankyloglossia
- Stafne defect
- Torus palatinus
- Torus mandibularis
- Eagle syndrome
Acquired
Infective
Bacterial
- (Plaque-induced) gingivitis—A common periodontal (gum) disease is Gingivitis. Periodontal refers to the area the infection affects, which include the teeth, gums, and tissues surrounding the teeth. Bacteria cause inflammation of the gums which become red, swollen and can bleed easily. The bacteria along with mucus form a sticky colorless substance called plaque which harbours the bacteria. Plaque that is not removed by brushing and flossing hardens to form tartar that brushing doesn't clean. Smoking is a major risk factor.[5] Treatment of gingivitis is dependent on how severe and how far the disease has progressed. If the disease is not too severe it is possible to treat it with chlorhexidine rinse and brushing with fluoride toothpaste to kill the bacteria and remove the plaque, but once the infection has progressed antibiotics may be needed to kill the bacteria.[6]
- Periodontitis—When gingivitis is not treated it can advance to periodontitis, when the gums pull away from the teeth and form pockets that harbor the bacteria. Bacterial toxins and the body's natural defenses start to break down the bone and connective tissues. The tooth may eventually become loose and have to be removed.
- Scarlet fever is caused by streptococci species, and starts as tonsilitis and pharyngitis before involving the soft palate and the tongue. It usually occurs in children where a fever occurs and a rash develops on the skin. It is treated with penicillin and the prognosis is generally excellent.[4]
Viral
- Herpes simplex (infection with herpes simplex virus, or HSV) is very common in the mouth and lips. This virus can cause blisters and sores around the mouth (herpetic gingivostomatitis) and lips (herpes labialis). HSV infections tend to recur periodically. Although many people get infected with the virus, only 10% actually develop the sores. The sores may last anywhere from 3–10 days and are very infectious. Some people have recurrences either in the same location or at a nearby site. Unless the individual has an impaired immune system, e.g., owing to HIV or cancer-related immune suppression,[7] recurrent infections tend to be mild in nature and may be brought on by stress, sun, menstrual periods, trauma or physical stress.[8]
- Mumps of the salivary glands is a viral infection of the parotid glands. This results in painful swelling at the sides of the mouth in both adults and children. The infection is quite contagious. Today mumps is prevented by getting vaccinated in infancy. There is no specific treatment for mumps except for hydration and painkillers. Sometimes mumps can cause inflammation of the brain, testicular swelling or hearing loss.[9]
Fungal

- Oral candidiasis is by far the most common fungal infection that occurs in the mouth. It usually occurs in immunocompromised individuals. Individuals who have undergone a transplant, HIV, cancer or use corticosteroids commonly develop candida of the mouth and oral cavity. Other risk factors are dentures and tongue piercing. The typical signs are a white patch that may be associated with burning, soreness, irritation or a white cheesy like appearance. Once the diagnosis is made, candida can be treated with a variety of anti fungal drugs.[10]
Traumatic
- Chemical, thermal, mechanical or electrical trauma to the oral soft tissues can cause traumatic oral ulceration.
Autoimmune
Inflammatory
Neoplastic
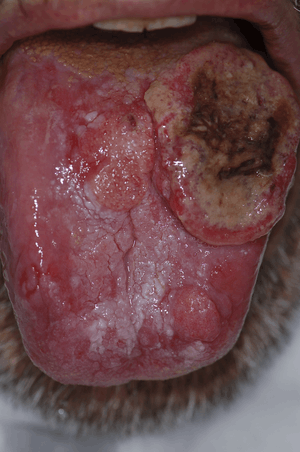
- Oral cancer may occur on the lips, tongue, gums, floor of the mouth or inside the cheeks. The majority of cancers of the mouth are squamous cell carcinoma. Oral cancers are usually painless in the initial stages or may appear like an ulcer. Causes of oral cancer include smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, exposure to sunlight (lip cancer), chewing tobacco, infection with human papillomavirus, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.[11] The earlier the oral cancer is diagnosed, the better the chances for full recovery. If you have a suspicious mass or ulcer on the mouth which has been persistent, then you should always get a dentist to look at it. Diagnosis is usually made with a biopsy and the treatment depends on the exact type of cancer, where it is situated, and extent of spreading.
Idiopathic
There are many oral and maxillofacial pathologies which are not fully understood.
- Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a disorder where there is a burning sensation in the mouth that has no identifiable medical or dental cause. The disorder can affect anyone but tends to occur most often in middle aged women. BMS has been hypothesized to be linked to a variety of factors such as the menopause, dry mouth (xerostomia) and allergies. BMS usually lasts for several years before disappearing for unknown reasons. Other features of this disorder include anxiety, depression and social isolation. There is no cure for this disorder and treatment includes use of hydrating agents, pain medications, vitamin supplements or the usage of antidepressants.[12]

- Aphthous stomatitis is a condition where ulcers (canker sores) appear on the inside of the mouth, lips and on tongue. Most small canker sores disappear within 10–14 days. Canker sores are most common in young and middle aged individuals. Sometimes individuals with allergies are more prone to these sores. Besides an awkward sensation, these sores can also cause pain or tingling or a burning sensation. Unlike herpes sores, canker sores are always found inside the mouth and are usually less painful. Good oral hygiene does help but sometime one may have to use a topical corticosteroid.[13]
.jpg)
- Migratory stomatitis is a condition that involves the tongue and other oral mucosa. The common migratory glossitis (geographic tongue) affects the anterior two thirds of the dorsal and lateral tongue mucosa of 1% to 2.5% of the population, with one report of up to 12.7% of the population. The tongue is often fissured, especially. in elderly individuals. In the American population, a lower prevalence was reported among Mexican Americans (compared with Caucasians and African Americans) and cigarette smokers. When other oral mucosa, beside the dorsal and lateral tongue, are involved, the term migratory stomatitis (or ectopic geographic tongue) is preferred. In this condition, lesions infrequently involve also the ventral tongue and buccal or labial mucosa. They are rarely reported on the soft palate and floor of the mouth.[14]
Oral and maxillofacial pathology as a specialty
Oral and maxillofacial pathology, previously termed oral pathology, is a speciality involved with the diagnosis and study of the causes and effects of diseases affecting the oral and maxillofacial regions (i.e. the mouth, the jaws and the face). It can be considered a speciality of dentistry and pathology.[4] Oral pathology is a closely allied speciality with oral and maxillofacial surgery and oral medicine.
The clinical evaluation and diagnosis of oral mucosal diseases are in the scope of oral & maxillofacial pathology specialists and oral medicine practitioners,[15] both disciplines of dentistry. When a microscopic evaluation is needed, a biopsy is taken, and microscopically observed by a pathologist. The American Dental Association uses the term oral and maxillofacial pathology, and describes it as "the specialty of dentistry and pathology which deals with the nature, identification, and management of diseases affecting the oral and maxillofacial regions. It is a science that investigates the causes, processes and effects of these diseases."[16]
In some parts of the world, oral and maxillofacial pathologists take on responsibilities in forensic odontology.
Geographic variation
United Kingdom
There are fewer than 30 consultant oral and maxillofacial pathologists in the UK. A dental degree is mandatory, but a medical degree is not. The shortest pathway to becoming an oral pathologist in the UK is completion of 2 years' general professional training and then 5 years in a diagnostic histopathology training course. After passing the required exams and gaining a Certificate of Completion of Specialist Training, the trainee is entitled to apply for registration as a specialist.[17] Many oral and maxillofacial pathologists in the UK are clinical academics, having undertaken a PhD either prior to or during training. Generally, oral and maxillofacial pathologists in the UK are employed by dentals or medical schools and undertake their clinical work at university hospital departments.
New Zealand
There are 5 practising Oral Pathologists in New Zealand (as of May 2013).[18] Oral pathologists in New Zealand also take part in forensic evaluations.[18]
See also
References
- ↑ "gnath(o)-". TheFreeDictionary.com.
- ↑ "ICD-10:".
- ↑ Mouth Disease Information Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- 1 2 3 Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CA, Bouquot JE (2002). Oral & maxillofacial pathology (2nd ed.). Philadelphia?page=ix (preface): W.B. Saunders. ISBN 0721690033.
- ↑ "Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments". National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. Retrieved 2013-12-27.
- ↑ "Gingivitis". Emedicine. Retrieved 2013-12-25.
- ↑ Elad S, Zadik Y, Hewson I, et al. (August 2010). "A systematic review of viral infections associated with oral involvement in cancer patients: a spotlight on Herpesviridea". Support Care Cancer. 18 (8): 993–1006. doi:10.1007/s00520-010-0900-3. PMID 20544224.
- ↑ Herpes Guide: How do I know if I have herpes Canadian Herpes Information portal. Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- ↑ What are Mumps Ministry of health and long term care portal. Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- ↑ Women's Oral Health and Overall
- ↑ Elad S, Zadik Y, Zeevi I, et al. (December 2010). "Oral cancer in patients after hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: long-term follow-up suggests an increased risk for recurrence". Transplantation. 90 (11): 1243–4. doi:10.1097/TP.0b013e3181f9caaa. PMID 21119507.
- ↑ Burning Mouth Syndrome American Academy of Family Physicians. Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- ↑ Diseases of the Digestive System The oral cavity FAQ's Health Portal. Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- ↑ Zadik Y, Drucker S, Pallmon S (Aug 2011). "Migratory stomatitis (ectopic geographic tongue) on the floor of the mouth". J Am Acad Dermatol. 65 (2): 459–60. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.016. PMID 21763590.
- ↑ Zadik, Yehuda; Orbach Hadas; Panzok Amy; Smith Yoav; Czerninski Rakefet (2011). "Evaluation of oral mucosal diseases: inter- and intra-observer analyses". J Oral Pathol Med. 41 (1): 68–72. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.2011.01070.x. PMID 21883487. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- ↑ "ADA.org: Dentistry Definitions".
- ↑ "The British Society of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathologists". Retrieved 25 April 2013.
- 1 2 "Specialisation". New Zealand Dental Association. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
External links
| Wikiversity has learning materials about Oral pathology |
- British Society of Oral & Maxillo-facial Pathologists Website
- Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Website