PRKACB
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
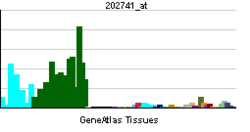
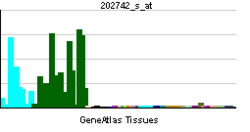
cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKACB gene.[4]
cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the protein kinase A (PKA), which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive holoenzyme of PKA is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits of PKA have been identified in humans. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family and is a catalytic subunit of PKA. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed.[4]
Interactions
PRKACB has been shown to interact with Ryanodine receptor 2[5] and Low affinity nerve growth factor receptor.[6]
References
- ↑ "Drugs that physically interact with cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta view/edit references on wikidata".
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: PRKACB protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, beta".
- ↑ Marx, S O; Reiken S; Hisamatsu Y; Jayaraman T; Burkhoff D; Rosemblit N; Marks A R (May 2000). "PKA phosphorylation dissociates FKBP12.6 from the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor): defective regulation in failing hearts". Cell. UNITED STATES. 101 (4): 365–76. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80847-8. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 10830164.
- ↑ Higuchi, Haruhisa; Yamashita Toshihide; Yoshikawa Hideki; Tohyama Masaya (April 2003). "PKA phosphorylates the p75 receptor and regulates its localization to lipid rafts". EMBO J. England. 22 (8): 1790–800. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg177. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 154469
 . PMID 12682012.
. PMID 12682012.
Further reading
- Simard J, Bérubé D, Sandberg M, et al. (1992). "Assignment of the gene encoding the catalytic subunit C beta of cAMP-dependent protein kinase to the p36 band on chromosome 1.". Hum. Genet. 88 (6): 653–7. doi:10.1007/BF02265292. PMID 1551670.
- Hofmann B, Nishanian P, Baldwin RL, et al. (1991). "HIV inhibits the early steps of lymphocyte activation, including initiation of inositol phospholipid metabolism.". J. Immunol. 145 (11): 3699–705. PMID 1978848.
- Beebe SJ, Oyen O, Sandberg M, et al. (1990). "Molecular cloning of a tissue-specific protein kinase (C gamma) from human testis--representing a third isoform for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase.". Mol. Endocrinol. 4 (3): 465–75. doi:10.1210/mend-4-3-465. PMID 2342480.
- Scarpetta MA, Uhler MD (1993). "Evidence for two additional isoforms of the endogenous protein kinase inhibitor of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in mouse.". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (15): 10927–31. PMID 7684369.
- Hofmann B, Nishanian P, Nguyen T, et al. (1993). "Human immunodeficiency virus proteins induce the inhibitory cAMP/protein kinase A pathway in normal lymphocytes.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90 (14): 6676–80. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.14.6676. PMC 46995
 . PMID 7688126.
. PMID 7688126. - Hofmann B, Nishanian P, Fan J, et al. (1994). "HIV Gag p17 protein impairs proliferation of normal lymphocytes in vitro.". AIDS. 8 (7): 1016–7. doi:10.1097/00002030-199407000-00025. PMID 7946090.
- Gamm DM, Baude EJ, Uhler MD (1996). "The major catalytic subunit isoforms of cAMP-dependent protein kinase have distinct biochemical properties in vitro and in vivo.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (26): 15736–42. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.26.15736. PMID 8662989.
- Swingler S, Gallay P, Camaur D, et al. (1997). "The Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhances serine phosphorylation of the viral matrix.". J. Virol. 71 (6): 4372–7. PMC 191654
 . PMID 9151826.
. PMID 9151826. - Chen P, Mayne M, Power C, Nath A (1997). "The Tat protein of HIV-1 induces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production. Implications for HIV-1-associated neurological diseases.". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (36): 22385–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.36.22385. PMID 9278385.
- Liapi C, Takahashi N, Raynaud F, et al. (1998). "Effects of [D-Ala1] peptide T-NH2 and HIV envelope glycoprotein gp120 on cyclic AMP dependent protein kinases in normal and psoriatic human fibroblasts.". J. Invest. Dermatol. 110 (4): 332–7. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00149.x. PMID 9540970.
- Rabbi MF, al-Harthi L, Saifuddin M, Roebuck KA (1998). "The cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and protein kinase C-beta pathways synergistically interact to activate HIV-1 transcription in latently infected cells of monocyte/macrophage lineage.". Virology. 245 (2): 257–69. doi:10.1006/viro.1998.9158. PMID 9636365.
- Zidovetzki R, Wang JL, Chen P, et al. (1998). "Human immunodeficiency virus Tat protein induces interleukin 6 mRNA expression in human brain endothelial cells via protein kinase C- and cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathways.". AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 14 (10): 825–33. doi:10.1089/aid.1998.14.825. PMID 9671211.
- Mayne M, Bratanich AC, Chen P, et al. (1998). "HIV-1 tat molecular diversity and induction of TNF-alpha: implications for HIV-induced neurological disease.". Neuroimmunomodulation. 5 (3-4): 184–92. doi:10.1159/000026336. PMID 9730685.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination.". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948
 . PMID 11076863.
. PMID 11076863. - Jiang CH, Tsien JZ, Schultz PG, Hu Y (2001). "The effects of aging on gene expression in the hypothalamus and cortex of mice.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (4): 1930–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.98.4.1930. PMC 29359
 . PMID 11172053.
. PMID 11172053. - Ørstavik S, Reinton N, Frengen E, et al. (2001). "Identification of novel splice variants of the human catalytic subunit Cbeta of cAMP-dependent protein kinase.". Eur. J. Biochem. 268 (19): 5066–73. doi:10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02429.x. PMID 11589697.
- Wu KJ, Mattioli M, Morse HC, Dalla-Favera R (2002). "c-MYC activates protein kinase A (PKA) by direct transcriptional activation of the PKA catalytic subunit beta (PKA-Cbeta) gene.". Oncogene. 21 (51): 7872–82. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205986. PMID 12420224.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Higuchi H, Yamashita T, Yoshikawa H, Tohyama M (2003). "PKA phosphorylates the p75 receptor and regulates its localization to lipid rafts.". EMBO J. 22 (8): 1790–800. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg177. PMC 154469
 . PMID 12682012.
. PMID 12682012. - Gassel M, Breitenlechner CB, Rüger P, et al. (2003). "Mutants of protein kinase A that mimic the ATP-binding site of protein kinase B (AKT).". J. Mol. Biol. 329 (5): 1021–34. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00518-7. PMID 12798691.