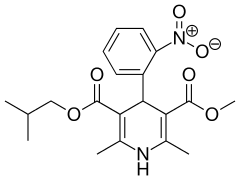
Nisoldipine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sular |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a696009 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | C08CA07 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Biological half-life | 7-12 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
63675-72-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 4499 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2524 |
| DrugBank |
DB00401 |
| ChemSpider |
4343 |
| UNII |
4I8HAB65SZ |
| KEGG |
D00618 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:7577 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1726 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.058.534 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H24N2O6 |
| Molar mass | 388.414 g/mol |
| | |
Nisoldipine (INN) is a calcium channel blocker of the dihydropyridine class. It sold in the United States under the proprietary name Sular. Nisoldipine has tropism for cardiac blood vessels.[1]
External links
- Mielcarek J, Grobelny P, Szamburska O (2005). "The effect of beta-carotene on the photostability of nisoldipine.". Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 27 (3): 167–71. doi:10.1358/mf.2005.27.3.890873. PMID 15834448.
- Missan S, Zhabyeyev P, Dyachok O, Jones SE, McDonald TF (November 2003). "Block of cardiac delayed-rectifier and inward-rectifier K+ currents by nisoldipine". Br. J. Pharmacol. 140 (5): 863–70. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705518. PMC 1574108
 . PMID 14530219.
. PMID 14530219. - Hamilton S, Houle L, Thadani U (1999). "Rapid-release and coat-core formulations of nisoldipine in treatment of hypertension, angina, and heart failure.". Heart Dis. 1 (5): 279–88. PMID 11720635.
References
- ↑ "Why is nisoldipine a specific agent in ischemic left ventricular dysfunction?". The American Journal of Cardiology. 75: E36–E40. doi:10.1016/S0002-9149(99)80446-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.