Trisomy
| Trisomy | |
|---|---|
|
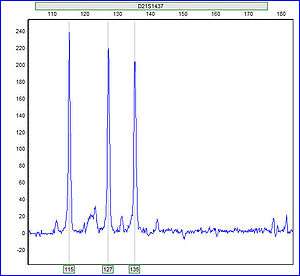
Example of Trisomy 21 detected via qPCR Short Tandem Repeat assay | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 |
Q90-Q92 Q97-Q98 |
| MeSH | D014314 |
| Orphanet | 3376 |
A trisomy is a type of polysomy in which there are three instances of a particular chromosome, instead of the normal two.[1] A trisomy is a type of aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes).
Description and causes
Most organisms that reproduce sexually have pairs of chromosomes in each cell, with one chromosome inherited from each parent. In such organisms, a process called meiosis creates cells called gametes (eggs or sperm) that have only one set of chromosomes. The number of chromosomes is different for different species. Humans have 46 chromosomes (i.e. 23 pairs of chromosomes). Human gametes have only 23 chromosomes.
If the chromosome pairs fail to separate properly during cell division, the egg or sperm may end up with a second copy of one of the chromosomes. (See non-disjunction.) If such a gamete results in fertilization and an embryo, the resulting embryo may also have an entire copy of the extra chromosome.
Terminology
The number of chromosomes in the cell where trisomy occurs is represented as, for example, 2n+1 if one chromosome shows trisomy, 2n+1+1 if two show trisomy, etc.[2]
- "Full trisomy", also called "primary trisomy",[2] means that an entire extra chromosome has been copied. *"Partial trisomy" means that there is an extra copy of part of a chromosome.
- "Secondary trisomy" - the extra chromosome has quadruplicated arms (the arms are identical; it is an "isochromosome").[2]
- "Tertiary trisomy" - the extra chromosome is made up of copies of arms from two other chromosomes.[2]
Trisomies are sometimes characterised as "autosomal trisomies" (trisomies of the non-sex chromosomes) and "sex-chromosome trisomies." Autosomal trisomies are described by referencing the specific chromosome that has an extra copy. Thus, for example, the presence of an extra chromosome 21, which is found in Down syndrome, is called trisomy 21.
Human trisomy
Trisomies can occur with any chromosome, but often result in miscarriage, rather than live birth. For example, Trisomy 16 is the most common trisomy in human pregnancies, occurring in more than 1% of pregnancies; only those pregnancies in which some normal cells occur in addition to the trisomic cells, or mosaic trisomy 16, survive.[3] This condition, however, usually results in spontaneous miscarriage in the first trimester.
The most common types of autosomal trisomy that survive to birth in humans are:
- Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)
- Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)
- Trisomy 9
- Trisomy 8 (Warkany syndrome 2)
- Trisomy 22
Of these, Trisomy 21 and Trisomy 18 are the most common. In rare cases, a fetus with Trisomy 13 can survive, giving rise to Patau syndrome. Autosomal trisomy can be associated with birth defects, intellectual disability and shortened life expectancy.
Trisomy of sex chromosomes can also occur and include:[4]
- XXX (Triple X syndrome)
- XXY (Klinefelter syndrome)
- XYY
Compared to trisomy of the autosomal chromosomes, trisomy of the sex chromosomes normally has less severe consequences. Individuals may show few or no symptoms and have a normal life expectancy.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "CRC - Glossary T". Retrieved 2007-12-23.
- 1 2 3 4 Rieger, R.; Michaelis, A.; Green, M.M. (1968). A glossary of genetics and cytogenetics: Classical and molecular. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 9780387076683.
- ↑ Hassold, T; Merrill, M; Adkins, K; Freeman, S; Sherman, S (1995). "Recombination and maternal age-dependent nondisjunction: molecular studies of trisomy 16". American Journal of Human Genetics. 57 (4): 867–74. PMC 1801507
 . PMID 7573048.
. PMID 7573048. - 1 2 O'Connor, Clare (2008). "Chromosomal Abnormalities: Aneuploidies". Nature Education. 1 (1): 172.