Airgíalla
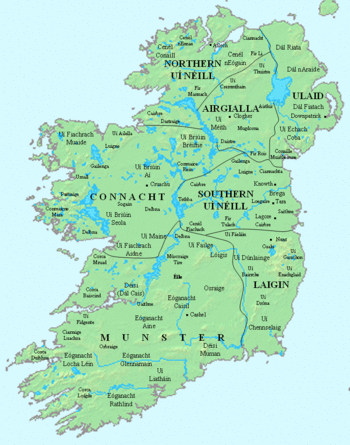

Airgíalla[1] (Modern Irish: Oirialla, English: Oriel[2]) is the name of a medieval Irish over-kingdom and the collective name for the confederation of tribes that formed it. The confederation consisted of nine minor-kingdoms, all independent of each other but paying nominal suzerainty to an overking, usually from the most powerful dynasty.[3] Airgíalla at its peak spanned the modern Irish counties of Londonderry, Monaghan, Tyrone, along with parts of Armagh, Fermanagh and Louth.[3] The later constricted kingdom of Airgíalla survived in Monaghan—which was known as Oirghialla and Oriel after the Norman Invasion of Ireland—until the end of the Gaelic order in Ireland.[3]
Airgíalla was according to legend founded by the Three Collas,[3] who conquered what is now central Ulster from the Ulaid. The decisive victory was the battle of Achadh Leithdheirg, said to have been fought around the year 331. The actual year and circumstances of how the Airgíalla confederation came into existence is however unknown.
Originally thought to have been under the dominance of the neighbouring Ulaid to the east, the territory of the Airgíalla from the 6th-century onwards was gradually eroded by the encroachment of their western neighbours, the Cenél nEógain of the Northern Uí Néill,[4] as well as the Southern Uí Néill to their south. From 735 they fell under the dominance of the Cenél nEógain, and by 827 had become their vassals.[4]
Etymology
Airgíalla may mean "those who give hostages" or "the hostage givers", and refers to both the Irish over-kingdom of Airgíalla, and the confederation of tribes that formed it.[3][5] It is commonly Anglicised as Oriel; however, archaic Angliciations include: Uriel, Orial, Orgialla, Orgiall, Oryallia, and Ergallia.[6]
After the Anglo-Norman invasion, the Anglicisation "Uriel" became the name of the part of Airgíalla that had extended into modern-day County Louth.[3] Similarly, the portion of Airgíalla that survived in modern-day County Monaghan, became known as Oirghialla,[3] from which derives the Anglicisation "Oriel".
In early manuscripts the Bishop of Clogher was styled Bishop of Oirialla.
Origins
According to legend
In the beginning of the 4th century, three warlike brothers, known as the Three Collas, made a conquest of a great part of Ulster, which they wrested from the Ulaid. It was the after the battle of Achadh Leithdheirg, fought c331, that they founded Airgialla.[7][8] In this battle the forces of the Three Collas defeated the forces of Fergus Foga, king of Ulster, who was slain, and the victors burned to the ground Emain Macha, the ancient capital of Ulaid.
However, in general it can be shown that the origin legend was written (or composed) in the second quarter of the 8th century to seal their alliance with the Northern Uí Néill.
Historical emergence
The earliest reference to the Airgíalla occurs in the Annals of Tigernach under the year 677, where the death of Dunchad mac Ultan, "Rí Oigriall", is noted. However, it is suspected of being a retrospective interpolation. On the other hand, the entry in the Annals of Ulster under the year 697 which lists Mael Fothataig mac Mael Dub as "Rex na nAirgialla" may indeed be genuine. Both Mael Fothatag and his son, Eochu Lemnae (died 704), are listed among the guarantors of the "Cáin Adomnáin" in 697. Thus it is believed that the Airgíalla were probably in existence as an entity by then, or certainly by the opening years of the 8th century.
Dynastic groups
Airgíalla was composed of nine minor-kingdoms, each named after their ruling dynasty. These were:[4]
- Uí Tuirtri, also spelt as Uí Tuirtre, meaning "descendants of Tort". They were based east of the Sperrin Mountains in eastern County Londonderry and Tyrone. From 776, the Uí Thuirtri had moved east of the River Bann and into the over-kingdom of Ulaid, and by 919 they had lost all links to the Airgíalla.[4]
- Uí Maic Cairthinn, meaning "descendants of Cairthend". Based south of Lough Foyle in north-western County Londonderry.
- Uí Fiachrach Arda Sratha, meaning "descendants of Fiachrach of Ard Straw". Based at Ardstraw in modern-day County Tyrone. They became subject to the Cenél nEógain by the 12th-century, and expanded southwards into Fir Luírg, in County Fermanagh.[9]
- Uí Cremthainn, based in what is now parts of modern-day County Fermanagh, Monaghan, and Tyrone.
- Uí Méith, based in modern-day County Monaghan.
- Airthir, meaning "Easterners".[4] They were based around the city of Armagh, and held control of the offices of the church in Armagh, which had preeminence in Ireland.[4]
- Mugdorna, based in County Monaghan, however by the 12th-century had settled the territory of Bairrche, located in southern County Down, and named it after themselves.[10] Their name lives on as "Mourne", the present-day name for the area and the Mourne Mountains.[10]
- Fir Chraíbe, also known as the Fir na Chraíbe,[11] meaning "men of the branch". They were located west of the River Bann in north-eastern County Londonderry. By the 9th-century they were a subject-people of the Cenél nEógain.[11]
- Fir Lí, also known as the Fir Lee, meaning "people of Lí". They were located west of the River Bann in mid-eastern County Londonderry. By the 9th-century they were a subject-people of the Cenél nEógain.[11]
Uí Moccu Úais
The Uí Tuirtri, Uí Maic Cairthinn, and Uí Fiachrach Arda Sratha, were collectively known as the Uí Moccu Úais as they claimed descent from Colla Uais.[4] The pedigrees in the Book of Leinster states that Colla Uais had two sons, Erc and Fiachra Tort. From Fiachra Tort came the Uí Tuirtri. From Erc, came Cairthend and Fiachrach, who were respectively the ancestors of the Uí Maic Cairthinn and the Uí Fiachrach Arda Sratha. The Fir Lí are also claimed as being decended from Fiachra Tort, though other sources claim they descend from another son of Colla Uais called Faradach.
The Uí Moccu Uais were also found in counties Meath and Westmeath.[4] They were known as Uí Moccu Uais Midi and Uí Moccu Uais Breg, meaning the Uí Moccu Uais of Meath and Brega, respectively.
See also
References
- ↑ pronunciation: http://forvo.com/word/airg%C3%ADalla_%28old_irish%29/#ga
- ↑ Ulster Irish to English Dictionary
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Connolly, p. 12.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Duffy, p. 14.
- ↑ Duffy, p. 13.
- ↑ cf. Airgialla, Uriel, Orial, Orgialla, Orgiall, Oryallia, Ergallia, srl.
- ↑ John O'Donovan (1856). Annala Rioghachta Éireann: Introductory remarks. Annals, to A.D. 902. Hodges, Smith, and Company. pp. 124–.
- ↑ Michael O'Cleary (1 March 2003). The Annals of Ireland by the Four Masters Translated Into English by Owen Connellan. Irish Roots Cafe. pp. 3–. ISBN 978-0-940134-77-5.
- ↑ Cosgrove, p. .
- 1 2 Magoo - The Mughdorna
- 1 2 3 Warner, p. 60.
Bibliography
- Connolly, S.J., ed. (2007). Oxford Companion to Irish History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-923483-7.
- Cosgrove, Art, ed. (2008). A New History of Ireland, II Medieval Ireland 1169-1534. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-019-953970-3.
- Duffy, Seán (2005). Medieval Ireland an Encyclopedia. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-4159-4052-8.
- Warner, R. The Re-Provenancing of Two Important Penannular Brooches of the Viking Period. Ulster Journal of Archaeology, Third Series, Vol. 36/37 (1973/1974), pp. 58-70. Ulster Archaeological Society.
External links
- Pronunciation of Airgíalla
- Coloniation and Conquest in Medieval Ireland:The English in Louth, 1170–1330, Brendan Smith, Cambridge, 1999
- The Kingship and Landscape of Tara, ed. Edel Bhreathnach, 2005; ISBN 1-85182-954-7
- "A Hidden Ulster" by Pádraigín Ní Ullacháin, 2003, Four Courts Press 1-85182-685-8 & 1-85182-738-2.
- "Songs From A Hidden Ulster", broadcast by RTÉ Radio 1 in 2006, presented by Pádraigín Ní Ullacháin.
- Early Modern Ireland
- The Three Collas