Ukrainians in Kuban
The Ukrainians in Kuban in southern Russia constitute a national minority. The region as a whole shares many linguistic, cultural and historic ties with Ukraine.
Ukrainians first settled in the Kuban region in 1792. Until the mid-twentieth century the majority of the population there identified themselves as Little Russians or Ukrainians. Due to adverse Russian and Soviet national policies, including the Holodomor, most of the population came to self-identify as Russian, and the percentage of those who identified themselves as Ukrainians dropped from an official 65% (1926) to 0.9% (2002).
Ukrainian settlement
Ukrainian settlement of Kuban first started in 1792 when the Empress Catherine II gave the Black Sea Cossack Host the rights to these lands. Her decree of 30.6. and 1.7.1792 handed these lands over to the Black Sea Cossacks "for eternity". The territory involved included the Phanagorian peninsula and the lands on the right bank of the Kuban River.
Between 1792 and 1793 25,000 people settled the area, marking the first wave of Ukrainian settlement to the Kuban. The Cossack navy, consisting of 51 boats with 3247 people, landed on the shores of the Kuban on August 25, 1792. A second group of 600 people arrived with cattle overland. In October 1792 a third group arrived under the command of otaman Zakhary Chepiha. The final group arrived from Ukraine in 1793 under the command of Antin Holovaty.
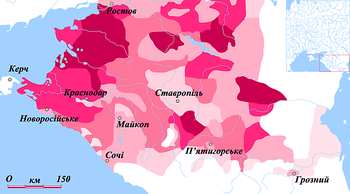
|
90-75%
75-50%
50-25%
|
25-10%
10-5%
5-2%
|
Between 1806 and 1809 about 562 Ukrainian Cossacks who had settled previously beyond the Danube were granted a pardon and arrived on the shores of the Taman Peninsula.
Between 1809 and 1811, 41,635 settlers arrived from Poltava and Chernihiv. This marked the second wave of settlers from Ukraine. During the 3rd wave in 1820-1825, 59,455 people of both genders migrated. The fourth wave of 11,949 people arrived from the Kharkiv, Chernihiv and Poltava regions in 1848-1849. In all, from 1792-1850 105 thousand people moved to Kuban from Ukraine.
The lands settled by the Ukrainians were known as the Lands of the Black Sea Host. 40 kurin settlements were allowed, which were not only administrative units, but encompassed specific territories. Settlers from Ukraine founded a town which became known as Yekaterinodar. In 1860 the Kuban oblast was formed.
After the February Revolution of 1905 a temporary Kuban Military government was formed. Two sides struggled to obtain supremacy: a pro-Ukrainian and a pro-Russian faction. The pro-Ukrainian faction supported autonomy for Kuban and the formation of a Union with Ukraine. Also Ukrainian cultural life flowered. Ukrainian-language schools opened and 6 newspapers began to publish in Ukrainian. In May 1918 a delegation headed by the head of the Kuban Rada M. Riabovol visited Kiev. Diplomatic ties were announced between the Kuban People's Republic and the Ukrainian People's Republic.
To cement its hold in Kuban, the Soviet government allowed a period of Ukrainianisation in the 1920s where Ukrainian cultural life was allowed to flourish. This was suddenly and brutally stopped in 1932.
Ukrainian demographics
- 1792-93 - 25,000 settled from Ukraine territories (first wave))
- 1806-09 -562 Danube Cossacks were resettled to the Kuban
- 1810 - 562 former Zaporozhian Cossacks were resettled from Bessarabia
- 1809-11 - 41,635 people from Poltava and Chernihiv regions (Second wave)
- 1820-25 - 59,455 people from Kharkiv, Poltava and Chernihiv regions (3rd wave)
- 1848-49 - 11,949 people Kharkiv, Poltava and Chernihiv regions (4th wave)
- From 1792-1850 over 105 thousand people resettled to the Kuban from central Ukrainian territories.
- The final major resettlement from Ukraine took place in 1862-66 with 1142 people.
In the census for 1926-7 there were 1,222,140 Ukrainians in the Kuban region, who made up 55% of the population of the area.
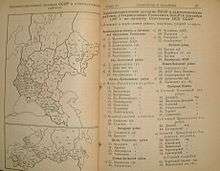

Russian census figures
The 1897 census combined both the Russian and Ukrainian population together. Together they made up 97.64% of the population. The number of Ukrainian language speakers was 859,122 (49.1%). The number of Russian language speakers was 732,283. (41.1%).[1] The ethnographer Pavlo Chubynsky stated that the number of Ukrainians in the Kuban was understated and that they also made up 60% of those who put down Russian as their language were of Ukrainian ethnicity. The ethnographer and statistician O. Rusov also noted a similar number in his writings.[1]
In the census for 1926 it was noted that there was a total population in the Kuban region of 3,343,893 of which 1,644.518 (49.2%) stated that they were Ukrainian, and 1,428,587 (42.7%) stated they were Russian. Other figures from the same census state that Ukrainian speakers made up 55% of the population of the area. In the 2002 Russian census it states that only 2% of the population speak Ukrainian and only 0.9% have been marked as being ethnically Ukrainian.
Ukrainian cultures in the Kuban
Ukrainian language
%2C_ethnic_groups.jpg)
The rise of a Ukrainian self-awareness produced an anti-Ukrainian sentiment within the some layers of the Russian empire. To curtail this movement, the use of Ukrainian (Little Russian) language within the Russian empire was initially restricted by the Valuev Circular and later banned completely by the Ems ukaz. Some restrictions were relaxed in 1905 and others ceased to be policed for a short period of time after the Revolution in 1917.
In Kuban, with the repealing of formal restrictions by the Russian government on the use of Ukrainian language, the official use of the Ukrainian language began to blossom. During the brief period of Kuban independence some 1391 beginning school, 180 middle schools, 151 high schools, 2 seminaries 124 professional tertiary establishments included education in the Ukrainian language.[2]
By 1922 there were 33 schools that taught primarily in the Ukrainian language.
In 1927 there were 746 Ukrainian language schools. Ukrainian textbooks began to be published in Krasnodar in 1926 with the crossing over of most institutes of higher learning to Ukrainian language instruction.
In 1920 in Krasnodar the first Institute of Folk Education (later renamed the Krasnodar Pedagogical Institute) was established. To better serve the local population, the medical institute was also Ukrainianised. A teachers' college for the preparation of Ukrainian language teachers was also opened in 1922.
By 1927 there were 6 Institutes of higher learning that taught in Ukrainian.
Мost Ukrainians speakers speak a Ukrainian dialect, which differs only slightly from standard literary Ukrainian.
Local Publishing
The sending of Ukrainian language publications to Kuban had been kept in check by the Russian post office. It wasn’t until 1923 that people in the Kuban could subscribe to a Ukrainian language newspaper from Ukraine.
In 1921 the first Ukrainian language magazine “Zoria” was published. Ukrainian language newspapers such as “Novy shliakh”, “Chornomorets”, “Chornomorsky krai” were soon established. In the 1920s close to 150 Ukrainian language writers lived in Kuban. All were repressed after 1932 either being shot or exiled.
Ukrainian music of the Kuban



Music was one of the most important loves of the Ukrainians in Kuban. There many Ukrainian folk songs sung in the Kuban region. Many of the songs are about Cossack heroes from Ukraine such as Morozenko, Baida (Cossack), Doroshenko, Sahaidachny, Bohdan Khmelnytsky, Maksym Kryvonis, and Danylo Nechay. A characteristic of Ukrainian folk songs of Kuban is the replacement of particular words to better reflect the local history and conditions. Where the word "Dunai" (the Danube) is used as a generic word for river, it is replaced by the word Kuban. Particularly popular are songs by the Sich Riflemen from Galicia, composed in the early 20th century, which juxtapose the word "rifleman" (Strilets) with the word "Cossack" (Kozak).
In 1886 A. Bihdai published 14 books containing 556 Ukrainian folk songs. A similar publication named Malorusski pesni (Little-Russian (Ukrainian) songs) containing over 200 Ukrainian folk songs was collected by H. Kontsevych from singers of the Kuban Army choir. Close to 3,000 Ukrainian folk songs were recorded in Kuban by Oleksander Koshetz, who spent 3 years collecting materials.
In 1966 a collection of songs of the Kuban Cossacks published in Krasnodar included the text of "Shche ne vmerla Ukraina", the Ukrainian Nationalist Anthem, which at that time was banned in Ukraine.[3]
In the early 20th century a significant movement was organised for the support of people learning to play the Ukrainian folk instrument known as the bandura. The bandura movement became quite significant until it was repressed in the 1930s. A number of Kuban bandurists were founding members of the first professional bandurist capella organized in Kiev in 1918 under Vasyl Yemetz. Kuban bandurists were also prominent in the formation of the second bandurist capella in Prague in 1923.
In recent times there has been a revival in the singing of Ukrainian folk songs led by the Kuban Cossack Choir and its director, Viktor Zakharchenko. In a concert at the Ukraina Palace in Kiev in 1990, the Kuban Cossack Choir was the first to sing the Ukrainian National Anthem, which they announced as a Kuban folk song. Ukrainian folk instruments are no longer officially banned and are returning to use, being taught at the Krasnodar Music college.
See also
- Kuban bandurists
- Balachka – Ukrainian Cossack dialect
Forced Russification of Kuban Ukrainians
In 1930 the Ukrainian People’s Komissar Mykola Skrypnyk as one of those involved in solving the nationalities question within the USSR put forward suggestions to Joseph Stalin:
- 1) That the Constitution of the Ukrainian SSR be valid on the territory of the whole USSR
- 2) That the territories of Voronezh, Kursk, Chornomoriya, Azov, Kuban regions be administered by the government of the Ukrainian SSR
- 3) That Ukrainian colonies in the Russian SFSR and other Soviet Republics be given national-political autonomy (VS. p 36)
However, the Ukrainization policies of Kuban were abruptly reversed at the end of 1932. The December 14, 1932 publication of the grain procurement resolution of CK VKP(b) and the Council of People's Commissars demanded the immediate transfer of all official paperwork and publishing of the "ukrainized" districts of Kuban into Russian language "more intelligible for the people of Kuban".[4]
In 1932-33, the policies of forced collectivization of the Ukrainian population of the Soviet Union, which caused a devastating famine that greatly affected the Ukrainian population of the Kuban.
The mass repressions of the 1930s also resulted in the arrest and execution of over 1500 Ukrainian speaking intellectuals from Krasnodar. Many teachers of Ukrainian language were arrested and exiled from the region. By 1932 all Ukrainian language education establishments were closed. The professional Ukrainian theatre in Krasnodar was closed. All Ukrainian toponyms in the Kuban, which reflected the areas from which the first Ukrainians settlers had moved, were changed. The names of Stanytsias such as Kiev was changed to "Krasnoartilyevskaya", and Uman to "Leningrad", and Poltavska to "Krasnoarmieiskaya". The physical destruction of all aspects of Ukrainian culture and the Ukrainian population, and the resultant ethnic cleansing of the population, the terrorist tactics of Russification, the Holodomor of 1932-33 and 1946-7 and other tactics used by the Union government lead to the catastrophic fall in population that associated themselves with Ukrainian ethnicity in the Kuban. Official Soviet Union statistics of 1959 state that Ukrainians made up 4% of the population, in 1989 – 3%.
The number of self-identified Ukrainians in Kuban fell between 1927 and 2002 from 1,222,140 (55% of the 1927 total) to 61,867 (0.9% of the 2002 total).
Prominent Ukrainians from Kuban

- Mykhailo Teliha – bandurist
- Anton Chorny – bandurist
- Fedir Shcherbyna – historian
- Mykola Riabovol – politician
- Vasyl Ivanys – Otoman, historian
- Hryhory Kontsevych – Composer, conductor
- Yakiv Kukharenko – Historian, ethnograher, otaman of the Kuban Cossack Army
- Viktor Zakharchenko – Artistic director of the Kuban Cossack Choir
- Yuri Bulavin – bandurist, concertmaster of the Kuban Cossack Choir
Prominent Ukrainians associated with the Kuban
- Vasyl Yemetz – bandurist
- Mykola Mikhnovsky – historian, lawyer
- Symon Petliura – politician, journalist, military leader
- Hnat Khotkevych – writer, composer, bandurist
- Oleksander Koshetz – Composer, conductor
- Antin Holovaty – Cossack politician, bandurist
- Mykhailo Hrushevskyi – politician, historian, ethnograph
See also
References
- 1 2 (Польовий Р. Кубанська Україна К. Дiокор 2003 p. 28)
- ↑ (Сергійчук В. Українізація Росії К. 2000 p. 141)
- ↑ Песни Казаков Кубани – Краснодарскоe книжное издательство, 1966, p.256
- ↑ С. Кульчицький, "Національна політика більшовиків в Україні під час створення комуністичного ладу" (pdf), Проблеми Історіїї України: факти, судження, пошуки, №13, 2005, сс. 3-56
Sources
- Українське козацтво – Енциклопедія – Kiev, 2006.
- Serhiy Z. Zaremba. З національно-культурного життя українців на Кубані (20-30-і роки ХХ ст.). Київська старовина – 1993 #1, с. 94-104.
- Evhen D. Petrenko. Українське козацтво. Київська старовина – 1993 #1, с. 114-119.
- Renat Pol'ovyy. Кубанська Україна. К. Дiокор 2003.
- Valeriy N. Ratushnyak. Очерки истории Кубани с древнейших времен по 1920 г. – Krasnodar, 1996.
- Volodymyr I. Serhiychuk. Українізація Росії. К. 2000.

