Shimonoseki Campaign
| Shimonoseki Campaign (下関戦争・馬関戦争) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Chōshū Rebellion | |||||||
Capture of a Choshu battery at Shimonoseki by British sailors and marines; picture taken by Felice Beato | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
Land: 2,000 Sea: 28 warships |
Land: 1,500 100 artillery pieces Sea: 6 warships 40 war-junks | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
72 killed or wounded 2 warships damaged | 47 killed or wounded | ||||||
The Shimonoseki Campaign (Japanese: 下関戦争/馬関戦争 Hepburn: Shimonoseki Sensō/Bakan Sensō) refers to a series of military engagements in 1863 and 1864, fought to control Shimonoseki Straits of Japan by joint naval forces from Great Britain, France, the Netherlands and the United States, against the Japanese feudal domain of Chōshū, which took place off and on the coast of Shimonoseki, Japan.
The Japanese term for this event translates to the Shimonoseki War.
Background
Despite efforts of appeasement by the Tokugawa shogunate to establish an atmosphere of peaceful solidarity, many feudal daimyos remained bitterly resentful of the shogunate's open-door policy to foreign trade. Belligerent opposition to European and American influence erupted into open conflict when the Emperor Kōmei, breaking with centuries of imperial tradition, began to take an active role in matters of state and issued on March 11 and April 11, 1863 his "Order to expel barbarians" (攘夷実行の勅命 – Jōi jikkō no chokumei).
The Chōshū clan, under Lord Mōri Takachika, began to take action to expel all foreigners after the deadline of the 10th day of the 5th month, by the traditional Japanese calendar. Openly defying the shogunate, Takachika ordered his forces to fire without warning on all foreign ships traversing Shimonoseki Strait. This strategic but treacherous 600-meter waterway separates the islands of Honshū and Kyūshū and provides a passage connecting the Inland Sea with the Sea of Japan.
Even before tensions escalated in Shimonoseki Strait, foreign diplomats and military experts, notably U.S. Foreign Minister to Japan Robert Pruyn and U.S. Navy Captain David McDougal had been aware of the precarious state of affairs in Japan. McDougal wrote a letter to the Secretary of the Navy, Gideon Welles, dated June 12, 1863, stating, "General opinion is that the government of Japan is on the eve of revolution, the principal object of which is the expulsion of foreigners."
"Revere the Emperor and expel the barbarians!"

The Chōshū clan was equipped with mostly antiquated cannons firing cannonballs, but also some modern armament, such as five 8-inch (200 mm) Dahlgren guns, which had been presented to Japan by the United States, and three steam warships of American construction: the bark Daniel Webster of six guns, the brig Lanrick, or Kosei, with ten guns, and the steamer Lancefield, or Koshin, of four guns.[1]
The first attack occurred on June 25, 1863, soon after the Imperial "Order to expel barbarians" came into effect. The U.S. merchant steamer SS Pembroke, under Captain Simon Cooper, was riding at anchor unsuspectingly outside Shimonoseki Strait when intercepted and fired upon by two European-built warships belonging to the rebel forces.
The crew of one enemy vessel taunted the frantic American seamen with a loud and unnerving cry: "Revere the Emperor and expel the barbarians!" (尊皇攘夷 sonnō jōi). Under incessant cannon fire, Pembroke managed to get underway and escape through the adjacent Bungo Strait, miraculously with only slight damage and no casualties.

Upon arrival in Shanghai, Cooper filed a report of the attack and dispatched it to the U.S. Consulate in Yokohama, Japan. The next day, the French naval dispatch steamer Kien Chan was also riding at anchor outside the strait, when rebel Japanese artillery atop the bluffs surrounding Shimonoseki opened fire on her. Kien Chan sustained damage to its engine and suffered four casualties before escaping to the open ocean.
On July 11, despite warnings from the crew of the Kien Chan, the 16-gun Dutch warship Medusa cruised into Shimonoseki Strait. Her skipper, Captain François de Casembroot, was convinced that Lord Mori would not dare fire on his vessel due to the strength of his ship and longstanding relations between the Netherlands and Japan.
But Takachika did just that, pounding Medusa with more than thirty shells and killing or wounding nine seamen. De Casembroot returned fire and ran the rebel gauntlet at full speed, fearful of endangering the life of the Dutch Consul General, who was on board. Within a short time, the Japanese warlord had managed to fire on the flags of most of the nations with consulates in Japan.
Battle of Shimonoseki Straits

In the morning of July 16, 1863, under sanction by Minister Pruyn, in an apparent swift response to the attack on the Pembroke, the U.S. frigate USS Wyoming, under Captain McDougal, sailed into the strait and single-handedly engaged the U.S.-built but poorly manned local fleet for almost two hours before withdrawing. McDougal sank two enemy vessels and severely damaged another one, along with inflicting some forty Japanese casualties, while the Wyoming suffered extensive damage, four crew dead and seven wounded, one later dying of his injuries. The two Japanese steamers sunk by the Wyoming were raised again by Chōshū in 1864 and attached to the harbor of Hagi.
Campaign
First Battle, July 20, 1863

On the heels of McDougal's engagement, on July 20, the French Navy retaliated for the attack on their merchant ship. The French force consisted of marines and two warships, the aviso Tancrède and the corvette Dupleix. With 250 men, under Captain Benjamin Jaurès, they swept into Shimonoseki and destroyed a small town, together with at least one artillery emplacement.
The intervention was supported by the French plenipotentiary in Japan, Duchesne de Bellecourt, but the French government, once informed, strongly criticized their representatives in Japan for taking such bellicose steps, for the reason that France had much more important military commitments to honour in other parts of the world, and could not afford a conflict in Japan.[2] Duchesne de Bellecourt would be relieved from his position in 1864.
Jaurès was also congratulated by the Shogunal government for taking such decisive steps against anti-foreign forces, and was awarded a special banner.[3]
Diplomatic negotiations
Meanwhile, the Americans, French, British and Dutch feverishly opened diplomatic channels in an effort to negotiate the reopening of the passage to the Inland Sea. Months dragged by with no end in sight to the growing dilemma. By May 1864, various bellicose Japanese factions had destroyed thousands of dollars in foreign property, including homes, churches and shipping. This wanton destruction included the U.S. Legation in Tokyo, which housed Minister Robert Pruyn.

Throughout the first half of 1864, as Shimonoseki Strait remained closed to foreign shipping, threats and rumors of war hung in the air, while diplomatic efforts remained deadlocked. Then the British Minister to Japan, Sir Rutherford Alcock, discussed with his treaty counterparts such as American Minister Robert Pruyn, the feasibility of a joint military strike against Takachika.
They were soon making preparations for a combined show of force. Under the wary eyes of the Japanese, fifteen British warships rode anchor alongside four Dutch vessels, while a British regiment from Hong Kong augmented their display of military might. The French maintained a minimal naval presence, with the bulk of their forces in Mexico trying to bolster Emperor Maximilian's unstable regime.
The U.S., engaged in its Civil War, limited itself to demonstrate diplomatic and minimal military support for the allies. In the meantime, Takachika procrastinated in negotiations by requesting additional time to respond to the allied demands, a response unacceptable to the treaty powers. The allies decided that the time for united action had arrived.
Despite retaliatory action from the treaty powers, another attack occurred in July 1864 when the rebel forces fired upon the U.S. steamer Monitor after she entered a harbor for coal and water. This provoked further outrage, even after a British squadron delivered a multi-national ultimatum to Takachika, threatening military force if the strait was not opened.
Final Battle, September 5–6, 1864
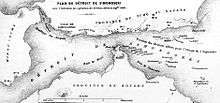



On August 17, 1864, a squadron consisting of nine British (Euryalus, Conqueror, Tartar, Leopard, Barrosa, Perseus, Argus, Coquette, and Bouncer), four Dutch (Amsterdam, Medusa, Metalen-Kruis, and D'Jambi), and three French warships (Tancrède, Sémiramis, and Dupleix), together with 2,000 soldiers, marines and sailors, all under the command of Admiral Sir Augustus Leopold Kuper of the Royal Navy, steamed out of Yokohama to open Shimonoseki Strait.
The U.S. chartered steamer Ta-Kiang accompanied the operation in a token show of support. The two-day battle that followed on September 5 and 6 did what the previous operations could not; it destroyed the Chōshū Domain's ability to wage war on the western powers. Unable to match the firepower of the international fleet, and amid mounting casualties, Chōshū forces finally surrendered two days later on September 8, 1864.
Allied casualties included 72 killed or wounded and two severely damaged British ships. A full account of the battle is contained in Ernest Satow's A Diplomat in Japan. Satow was present as a young interpreter for the British admiral, Augustus Kuper on the British flagship HMS Euryalus, commanded by Captain J. H. I. Alexander. It was also the action at which Duncan Gordon Boyes won his Victoria Cross (VC) at the age of seventeen. Satow described Boyes as receiving the award "for conduct very plucky in one so young." Another VC winner at Shimonoseki was Thomas Pride, and the third was the first American to win the medal, William Seeley. De Casembroot wrote his account of the events in De Medusa in de wateren van Japan, in 1863 en 1864.
The stringent accord, drawn up in the wake of the ceasefire and negotiated by U.S. Minister Pruyn, included an indemnity of $3,000,000 from the Japanese, an amount equivalent to the cost of about 30 steamships at that time.[4] The Tokugawa shogunate proved unable to pay such an amount, and this failure became the basis of further foreign pressure to have the treaties ratified by the Emperor, the harbor of Hyōgo opened to foreign trade, and customs tariffs lowered uniformly to 5%.[5] In 1883, twenty years after the first battle to reopen the strait, the United States quietly returned $750,000 to Japan, which represented its share of the reparation payment.
Aftermath

Right after the foreign interventions, the Shogunal government also launched its own preparations for a punitive expedition against Chōshū, the First Chōshū expedition. The expedition was aimed at punishing the 1864 Kinmon Incident in which Chōshū forces attacked Shogunal forces in Kyōto. The expedition was however cancelled after a compromise was brokered, involving the beheading of the leaders of the rebellion.
At the same time as this campaign, the British Royal Navy engaged Satsuma samurai at the Bombardment of Kagoshima, one of the several engagements of the Japanese conflict of 1863 and 1864.
Historical significance
Closely resembling the series of little conflicts fought by the European powers in Asia, Africa and elsewhere during the nineteenth century, the troubles in Japan seemed to exemplify their gunboat diplomacy, a prevalent tool in imperialism. Bitter resentment against foreign influence made the Chōshū clan feel justified in engaging in foolish acts of military provocation in defiance of their own government.
The same nationalistic anger directed against foreigners would later flare up in the Chinese Boxer Rebellion. The U.S. and its European allies then felt compelled to use military force to uphold the treaty with Japan. For the U.S., July 1863 was a momentous month, with the battles of Gettysburg and Vicksburg.

While it was bitterly embroiled in the American Civil War, President Abraham Lincoln's government was carefully watched by the world for signs of weakness and indecision. The actions of USS Wyoming made it the first foreign warship to offensively uphold treaty rights with Japan; this fact coupled with the possibility that the events would mire the U.S. in a foreign war made the battle of Shimonoseki a significant engagement.
While the battles of Shimonoseki Strait were mere footnotes in the histories of the European powers, an interesting aspect of the affair was the resourcefulness displayed by the Japanese, something another generation of Europeans and Americans would come to appreciate eighty years later. The feudal Japanese had not set eyes on a steam-powered ship until Commodore Perry's arrival only a decade before USS Wyoming's battle. Yet they had rapidly learned the ways of the Europeans within that brief span, purchasing foreign vessels and arming them with foreign weaponry. The quality and abundance of these armaments in 1860s Japan shocked the world.
The Shimonoseki city government in 2004, in recognition of the importance of the bombardment in Japanese history, placed several life-size replicas of the guns used by Chōshū where they were captured. The replicas are made of hollow steel and include coin-operated sound effects and smoke from the barrels.
See also
Notes
References
- "A Diplomat in Japan", Ernest Satow, 2006 Stone Bridge Press, ISBN 978-1-933330-16-7
- Polak, Christian. (2001). Soie et lumières: L'âge d'or des échanges franco-japonais (des origines aux années 1950). Tokyo: Chambre de Commerce et d'Industrie Française du Japon, Hachette Fujin Gahōsha (アシェット婦人画報社).
- __________. (2002). 絹と光: 知られざる日仏交流100年の歴史 (江戶時代-1950年代) Kinu to hikariō: shirarezaru Nichi-Futsu kōryū 100-nen no rekishi (Edo jidai-1950-nendai). Tokyo: Ashetto Fujin Gahōsha, 2002. ISBN 978-4-573-06210-8; OCLC 50875162
- Denney, John. Respect and Consideration: Britain in Japan 1853–1868 and beyond. Radiance Press (2011). ISBN 978-0-9568798-0-6
This article incorporates text from OpenHistory.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bombardment of Shimonoseki. |