Cajuns
 | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 1.2 million (2002 estimate)[1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| United States | |
| Louisiana | 815,259 |
| Texas | 56,000 |
| Languages | |
|
Cajun French Cajun English, American English, Standard French, Acadian French, Louisiana Creole | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Roman Catholicism | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| French, Québécois, Métis, Acadians, Louisiana Creoles, French Haitian | |
Cajuns (/ˈkeɪdʒən/; French: les Cadiens or Les Cadiens or les Acadiens, [le kadʒɛ̃, lez‿akadʒɛ̃])[2] are an ethnic group mainly living in the U.S. state of Louisiana, consisting of the descendants of Acadian exiles (French-speakers from Acadia in what are now The Maritimes of Eastern Canada). Today, the Cajuns make up a significant portion of south Louisiana's population and have exerted an enormous impact on the state's culture.[3]
While Lower Louisiana had been settled by French colonists since the late 17th century, the Cajuns trace their roots to the influx of Acadian settlers after the Great Expulsion from their homeland during the French and British hostilities prior to the Seven Years' War (1756 to 1763). The Acadia region to which modern Cajuns trace their origin consisted largely of what are now Nova Scotia and the other Maritime provinces, plus parts of eastern Quebec and northern Maine. Since their establishment in Louisiana, the Cajuns have developed their own dialect, Cajun French, and developed a vibrant culture including folkways, music, and cuisine. The Acadiana region is heavily associated with them.
Acadia
The origin of the designation Acadia is credited to the explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano, commissioned by the King Francis I of France, who on his 16th-century map applied the ancient Greek name "Arcadia" to the entire Atlantic coast north of Virginia. "Arcadia" derives from the Arcadia district in Greece which since classical antiquity had the extended meanings of "refuge" or "idyllic place". The Dictionary of Canadian Biography says: "In the 17th century Champlain fixed its present orthography, with the 'r' omitted, and (the Canadian historian) W.F.Ganong has shown its gradual progress northwards, in a succession of maps, to its resting place in the Atlantic Provinces."[4]
Ethnic group of national origin
The Cajuns retain a unique dialect of the French language and numerous other cultural traits that distinguish them as an ethnic group. Cajuns were officially recognized by the U.S. government as a national ethnic group in 1980 per a discrimination lawsuit filed in federal district court. Presided over by Judge Edwin Hunter, the case, known as Roach v. Dresser Industries Valve and Instrument Division (494 F.Supp. 215, D.C. La., 1980), hinged on the issue of the Cajuns' ethnicity:
We conclude that plaintiff is protected by Title VII's ban on national origin discrimination. The Louisiana Acadian (Cajun) is alive and well. He is "up front" and "mainstream." He is not asking for any special treatment. By affording coverage under the "national origin" clause of Title VII he is afforded no special privilege. He is given only the same protection as those with English, Spanish, French, Iranian, Portuguese, Mexican, Italian, Irish, et al., ancestors.[5]
History of Acadian ancestors
The British Conquest of French Acadia happened in 1710. Over the next 45 years, the Acadians refused to sign an unconditional oath of allegiance to Britain. During this period, Acadians participated in various militia operations against the British and maintained vital supply lines to the French fortress of Louisbourg and Fort Beausejour.[6] During the French and Indian War (part of the Seven Years' War and known by that name in Canada and Europe), the British sought to neutralize the Acadian military threat and to interrupt their vital supply lines to Louisbourg by deporting Acadians from Acadia.[7] During 1755-1763 Acadia consisted of parts of present-day Canada: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and the Gaspe Peninsula in the province of Quebec. The deportation of the Acadians has become known as the Great Upheaval or Le Grand Dérangement.
The Acadians' migration from Canada was spurred by the Treaty of Paris (1763) which ended the war. The treaty terms provided 18 months for unrestrained emigration. Many Acadians moved to the region of the Atakapa in present-day Louisiana, often travelling via the French colony of Saint-Domingue (now Haiti).[8] Joseph Broussard led the first group of 200 Acadians to arrive in Louisiana on February 27, 1765, aboard the Santo Domingo.[9] On April 8, 1765, he was appointed militia captain and commander of the "Acadians of the Atakapas" region in St. Martinville.[10] Some of the settlers wrote to their family scattered around the Atlantic to encourage them to join them at New Orleans. For example, Jean-Baptiste Semer, wrote to his father in France:
My dear father [...] you can come here boldly with my dear mother and all the other Acadian families. They will always be better off than in France. There are neither duties nor taxes to pay and the more one works, the more one earns without doing harm to anyone.— Jean-Baptiste Semer, 1766[11]
The Acadians were scattered throughout the eastern seaboard. Families were split and put on ships with different destinations.[12] Many ended up west of the Mississippi River in what was then French-colonized Louisiana, including territory as far north as Dakota territory. France had ceded the colony to Spain in 1762, prior to their defeat by Britain and two years before the first Acadians began settling in Louisiana. The interim French officials provided land and supplies to the new settlers. The Spanish governor, Bernardo de Gálvez, later proved to be hospitable, permitting the Acadians to continue to speak their language, practice their native religion (Roman Catholicism – which was also the official religion of Spain), and otherwise pursue their livelihoods with minimal interference. Some families and individuals did travel north through the Louisiana territory to set up homes as far north as Wisconsin. Cajuns fought in the American Revolution. Although they fought for Spanish General Galvez, their contribution to the winning of the war has been recognized.[13]
"Galvez leaves New Orleans with an army of Spanish regulars and the Louisiana militia made up of 600 Cajun volunteers and captures the British strongholds of Fort Bute at Bayou Manchac, across from the Acadian settlement at St. Gabriel. And on September 21, they attack and capture Baton Rouge."[14]
A review of participating soldiers shows many common Cajun names among those who fought in the battles of Baton Rouge and West Florida. The Galvez Chapter of the Daughters of the American Revolution was formed in memory of those soldiers.[15] The Acadians' joining the fight against the British was partially a reaction to the British having evicted them from Acadia.
The Spanish colonial government settled the earliest group of Acadian exiles west of New Orleans, in what is now south-central Louisiana—an area known at the time as Attakapas, and later the center of the Acadiana region. As Brasseaux wrote, "The oldest of the pioneer communities . . . Fausse Point, was established near present-day Loreauville by late June 1765."[16] The Acadians shared the swamps, bayous and prairies with the Attakapa and Chitimacha Native American tribes.
After the end of the American Revolutionary War, about 1,500 more Acadians arrived in New Orleans. About 3,000 Acadians had been deported to France during the Great Upheaval. In 1785, about 1,500 were authorized to emigrate to Louisiana, often to be reunited with their families, or because they could not settle in France.[17] Living in a relatively isolated region until the early 20th century, Cajuns today are largely assimilated into the mainstream society and culture. Some Cajuns live in communities outside of Louisiana. Also, some people identify themselves as Cajun culturally despite lacking Acadian ancestry.
Ethnic mixing and alternate origins
Shriver estimates that 89% of Cajuns have no African or Native American ancestors, about 11% of Cajun people have at least 0.5% or 1% non-European ancestry. Not all Cajuns descend solely from Acadian exiles who settled in south Louisiana in the 18th century, as many have intermarried with other groups. Their members now include people with Irish and Spanish ancestry, as well as a lesser extent of Germans and Italians. Also, a lesser admixture exists of Native American Métis and African American Creole. Historian Carl A. Brasseaux asserted that this process of intermarriage created the Cajuns in the first place.[3]
Non-Acadian French Creoles in rural areas were absorbed into Cajun communities. Some Cajun parishes, such as Evangeline and Avoyelles, possess relatively few inhabitants of Acadian origin. Their populations descend in many cases from settlers who migrated to the region from Quebec, Mobile, or directly from France. Theirs is regarded as the purest dialect of French spoken within Acadiana. Regardless, Acadian influences are generally acknowledged to have prevailed in most sections of south Louisiana.
Many Cajuns also have some ancestors who were not French. Many of the original settlers in Louisiana were Spanish Basques and Spanish Canary Islanders. A later migration included Irish and German immigrants who began to settle in Louisiana before and after the Louisiana Purchase, particularly on the German Coast along the Mississippi River north of New Orleans. People of Latin American origin; a number of early Filipino settlers (notably in Saint Malo, Louisiana) who were known as "Manilamen" from the annual cross-Pacific Galleon or Manila Galleon trade with neighboring Acapulco, Mexico; descendants of African American slaves; and some Cuban Americans have also settled along the Gulf Coast, and in some cases, intermarried into Cajun families.
One obvious result of this cultural mixture is the variety of surnames common among the Cajun population. Surnames of the original Acadian settlers (which are documented) have been augmented by French and non-French family names that have become part of Cajun communities. The spelling of many family names has changed over time. (See, for example, Eaux).
Modern preservation and renewed connections
During the early part of the 20th century, attempts were made to suppress Cajun culture by measures such as forbidding the use of the Cajun French language in schools. After the Compulsory Education Act forced Cajun children to attend formal schools, American teachers threatened, punished, and sometimes beat their Cajun students in an attempt to force them to use English (a language to which many of them had not been exposed before). During World War II, Cajuns often served as French interpreters for American forces in France; this helped to overcome prejudice.[18]
In 1968, the organization of Council for the Development of French in Louisiana was founded to preserve the French language in Louisiana. Besides advocating for their legal rights, Cajuns also recovered ethnic pride and appreciation for their ancestry. Since the mid-1950s, relations between the Cajuns of the U.S. Gulf Coast and Acadians in the Maritimes and New England have been renewed, forming an Acadian identity common to Louisiana, New England, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia.
State Senator Dudley LeBlanc ("Coozan Dud", a Cajun slang nickname for "Cousin Dudley") took a group of Cajuns to Nova Scotia in 1955 for the commemoration of the 200th anniversary of the expulsion. The Congrès Mondial Acadien, a large gathering of Acadians and Cajuns held every five years since 1994, is another example of continued unity.
Sociologists Jacques Henry and Carl L. Bankston III have maintained that the preservation of Cajun ethnic identity is a result of the social class of Cajuns. During the 18th and 19th centuries, "Cajuns" came to be identified as the French-speaking rural people of Southwestern Louisiana. Over the course of the 20th century, the descendants of these rural people became the working class of their region. This change in the social and economic circumstances of families in Southwestern Louisiana created nostalgia for an idealized version of the past. Henry and Bankston point out that "Cajun", which was formerly considered an insulting term, became a term of pride among Louisianans by the beginning of the 21st century.[19]

Edwin W. Edwards, Constitution of 1974
Perhaps the greatest proponent and catalyst for reclaiming Cajun and French history of Louisiana is four-term former Louisiana Governor Edwin Edwards. Selected to serve as honorary chair of the Eighteenth Century Louisiana panel of the 2014 academic Enlightenment Conference in Montréal,[20] the former Governor in a video address[21] said[22] "One of the legacies of which I am most proud is Louisiana’s 1974 Constitution and its provision that the 'right of the people to preserve, foster, and promote their respective historic linguistic and cultural origins is recognized.'"[23]
As the late LSU Law Center professor Lee Hargrave wrote, in reference to the protection of cultural heritage, "Proponents of the section were primarily Francophones concerned with the protection of the French Acadian culture. Representatives of the Council for the Development of French in Louisiana appeared before the committee several times to urge some recognition of cultural rights, and delegates from Lafayette and Lake Charles worked strongly for the proposal."[24]
Montréal panelist and New Orleans Créole historian Jari Honora explained that Edwards “is a perfect commentator for this panel given his advocacy for Louisiana’s Francophone cultural communities during his four terms as governor. After several decades of ‘Americanization’ and suppression of French language and culture in Louisiana, Governor Edwards’ conscious self -identification as an Acadian descendant marked a high-point for the Cajun/Creole cultural renaissance in this state.”[25]
Culture
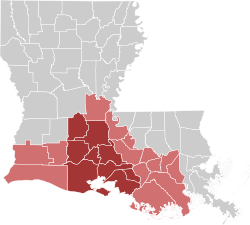
Geography
Geography had a strong correlation to Cajun lifestyles. Most Cajuns resided in Acadiana, where their descendants are still predominant. Cajun populations today are found also in the area southwest of New Orleans and scattered in areas adjacent to the French Louisiana region, such as to the north in Alexandria, Louisiana. Strong Cajun roots, influence, and culture can also be found in parts of Southern Mississippi. These areas include; Bay St. Louis, Pass Christian, “pass-chris-chee-anne”, Gulfport, Gautier, “go-shay”, Natchez, D'Iberville, "Dee-eye-burr-ville", and Biloxi, Mississippi. Over the years, many Cajuns and Creoles also migrated to the Houston, Beaumont and Port Arthur areas of Southeast Texas, in especially large numbers as they followed oil-related jobs in the 1970s and 1980s, when oil companies moved jobs from Louisiana to Texas. However, the city of Lafayette is referred to as "The Heart of Acadiana" because of its location, and it is a major center of Cajun culture.
Music
Cajun music is evolved from its roots in the music of the French-speaking Catholics of Canada. In earlier years, the fiddle was the predominant instrument, but gradually the accordion has come to share the limelight. Cajun music gained national attention in 2007, when the Grammy Award for Best Zydeco or Cajun Music Album category was created.[26]
Cuisine

Due to the Great Derangement, many Acadians were invited to settle in Louisiana by the Spanish Governor Galvez. Unfamiliar with the terrain, they assimilated Creole and Native American influences into their Acadian traditions.. Cajun cuisine focused on local ingredients and wild game (e.g., duck, rabbit), vegetables (e.g., okra, mirlitons), and grains. Coastal communities relied heavily on fish and shellfish. Seafood, especially shellfish, is still very popular in the region and remains a dominant feature of many classic Cajun dishes like seafood gumbo and court boullion.
Since many Cajuns were farmers and not especially wealthy, they were known for not wasting any part of a butchered animal. Many rural communities held a weekly boucherie, which is a communal butchering of an animal, often a pig. Each family received a share of the meat. Some high-profile foods like cracklins and boudin are examples of Cajun cuisine that are widely popular.[27]
Language
Cajun French is a misnomer for the French that was spoken before the Acadians arrived. It is a variety or dialect of the French language spoken primarily in Louisiana. At one time as many as seven dialects were spread across the Cajun heartland.
Recent documentation has been made of Cajun English, a French-influenced dialect of English spoken by Cajuns, either as a second language, in the case of the older members of the community, or as a first language by younger Cajuns.
Religious traditions
Cajuns are predominantly Roman Catholic. However, Protestant and Evangelical Christian denominations have made inroads among Cajuns, but not without controversy—some Cajuns frown upon family members converting to any form of Protestantism because of the extreme persecution the Cajuns were subjected to by Protestants during the Great Expulsion of 1755, and throughout their history for maintaining their Catholicism.
The 1992 cookbook, Who's Your Mama, Are You Catholic and Can You Make a Roux, by Cajun chef Marcelle Bienvenue, outlines long-standing beliefs that Cajun identity was rooted in community, cuisine, and very specifically, devout Roman Catholicism. Traditional Catholic religious observances such as Mardi Gras, Lent, and Holy Week are integral to many Cajun communities. Likewise, these traditional Catholic religious observances may further be understood from Cultural Catholicism in Cajun-Creole Louisiana by Marcia Gaudet[28] which tells that such traditional religious observances, although they may not be "strictly theological and liturgical forms", are still integral and necessary to many and remain religiously valid as "unofficial religious customs and traditions are certainly a part of Roman Catholicism as it is practiced".[29]
Mardi Gras

Mardi Gras, (French for "Fat Tuesday", also known as Shrove Tuesday), is the day before Ash Wednesday, which marks the beginning of Lent, a 40-day period of fasting and reflection in preparation for Easter Sunday. Mardi Gras was historically a time to use up the foods that were not to be used during Lent, including fat, eggs, and meat.
Mardi Gras celebrations in rural Acadiana are distinct from the more widely known celebrations in New Orleans and other metropolitan areas. A distinct feature of the Cajun celebration centers on the Courir de Mardi Gras (translated: fat Tuesday run).[30] A group of people, usually on horseback and wearing capuchons (a cone-shaped ceremonial hat) and traditional costumes, approach a farmhouse and ask for something for the community gumbo pot. Often, the farmer or his wife allows the riders to have a chicken, if they can catch it. The group then puts on a show, comically attempting to catch the chicken set out in a large open area. Songs are sung, jokes are told, and skits are acted out. When the chicken is caught, it is added to the pot at the end of the day.[30] The courir held in the small town of Mamou has become well known. This tradition has much in common with the observance of La Chandeleur, or Candlemas (February 2), by Acadians in Nova Scotia.
Easter
On Pâques (French for Easter), a game called pâquer, or pâque-pâque was played. Contestants selected hard-boiled eggs, paired off, and tapped the eggs together — the player whose egg did not crack was declared the winner. This is an old European tradition that has survived in Acadia until today. Today, Easter is still celebrated by Cajuns with the traditional game of paque, but is now also celebrated in the same fashion as Christians throughout the United States with candy-filled baskets, "Easter bunny" stories, dyed eggs, and Easter egg hunts.
Folk beliefs
One folk custom is belief in a traiteur, or healer, whose primary method of treatment involves the laying on of hands and of prayers. An important part of this folk religion, the traiteur combines Catholic prayer and medicinal remedies to treat a variety of ailments, including earaches, toothaches, warts, tumors, angina, and bleeding. Another is in the rougarou, a version of a loup garou (French for werewolf), that will hunt down and kill Catholics who do not follow the rules of Lent. In some communities, the loup garou of legend have taken on an almost protective role. Children are warned that loup garou can read souls, and that they only hunt and kill evil men and women and misbehaved horses.
Celebrations and gatherings
Cajuns, along with other Cajun Country residents, have a reputation for a joie de vivre (French for "joy of living"), in which hard work is appreciated as much as "passing a good time".
Community gatherings
In the culture, a coup de main (French for "to give a hand") is an occasion when the community gathers to assist one of their members with time-consuming or arduous tasks. Examples might include a barn raising, harvests, or assistance for the elderly or sick.
Festivals

The majority of Cajun festivals include a fais do-do ("go to sleep" in French, originating from encouraging children to fall asleep in the rafters of the dance hall as the parents danced late into the night) or street dance, usually to a live local band. Crowds at these festivals can range from a few hundred to more than 100,000.
Other festivals outside of Louisiana
- In Texas, the Winnie Rice Festival and other celebrations often highlight the Cajun influence in Southeast Texas.
- Major Cajun/Zydeco festivals are held annually in Rhode Island, which does not have a sizable Cajun population, but is home to many Franco-Americans of Québécois and Acadian descent. It features Cajun culture and food, as well as authentic Louisiana musical acts both famous and unknown, drawing attendance not only from the strong Cajun/Zydeco music scene in Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York City, and California, but also from all over the world. In recent years, the festival became so popular, now several such large summer festivals are held near the Connecticut-Rhode Island border: The Great Connecticut Cajun and Zydeco Music & Arts Festival, The Blast From The Bayou Cajun and Zydeco Festival, also in California the Cajun/Zydeco Festival; Bay Area Ardenwood Historic Farm, Fremont, Calif. and The Simi Valley Cajun and Blues Music Festival.
In media

Documentary films
- Spend it All (1971, color) director: Les Blank with Skip Gerson
- The Good Times Are Killing Me (1975, color)
- Hot Pepper (1975, color) director: Les Blank
- J'ai Été Au Bal (English: I Went to the Dance), by Les Blank, Chris Strachwitz & Maureen Gosling; narrated by Barry Jean Ancelet and Michael Doucet (Brazos Films). Louisiana French and Zydeco music documentary.
- Louisiana Story (1948, black and white) director: Robert Flaherty. Further addressed in 2006 documentary Revisiting Flaherty's Louisiana Story, by a group at Louisiana State University.
Film
- Southern Comfort (1981 film) (1981, color) director: Walter Hill, starring Powers Boothe
- Belizaire the Cajun (1986, color) director: Glen Pitre, starring Armand Assante
- Little Chenier (2006, color) director: Bethany Ashton, starring Johnathon Schaech
- The Curious Case of Benjamin Button (film) (2008, color) director: David Fincher, starring Brad Pitt
Literature
- Evangeline (1847), an epic poem by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, is loosely based on the events surrounding the 1755 deportation. It became an American classic, and also contributed to a rebirth of Acadian identity in both Maritime Canada and in Louisiana.
- Bayou Folk (1894) by Kate Chopin, who wrote about the Creoles and Cajuns (Acadiens)
- Children's book author Mary Alice Fontenot wrote several volumes on Cajun culture and history.
- Acadian Waltz (2013) by Alexandrea Weis, who wrote about the Cajun culture
Songs
- "Jambalaya (On the Bayou)" (1952) is credited to Hank Williams, about life, parties, and stereotypical Cajun cuisine. The music is taken from the Cajun song "Grand Texas".
- "Acadian Driftwood" (1975), a popular song based on the Acadian Expulsion by Robbie Robertson, appeared on The Band's album Northern Lights - Southern Cross.
- "Louisiana Man", an autobiographical song written and performed by Doug Kershaw, became the first song broadcast back to Earth from the Moon by the astronauts of Apollo 12. Over the years, the song has been recorded by hundreds of artists, sold millions of copies and become a standard of modern Cajun music.
- "Jolie Blonde"(or "Jolie Blon", "Jole Blon", or "Joli Blon"), with lyrics and song history of the traditional Cajun waltz, is often referred to as "the Cajun national anthem".
- "Mississippi Queen" is a 1970 song by Mountain about a Cajun woman visiting from Mississippi.
- "Elvis Presley was a Cajun" is a song from the 1991 Irish film The Commitments, in which a two-piece band plays along to the lyric "Elvis was a Cajun, he had a Cajun heart."
- "Amos Moses", a song by Jerry Reed, is about a fictional one-armed alligator-hunting Cajun man.
- "Perfect Day", a song by Lady Antebellum, starts off with the singer seeing "a Cajun man with a red guitar singing on the side of the street" and throwing "a handful of change in his beat-up case and [saying] play me a country beat".
- "Cajun Hell", a song by american thrash metal band Exodus, from 1989 album Fabulous Disaster.
See also
- Cajun cuisine
- French Americans
- French Canadians
- Expulsion of the Acadians
- List of Cajuns
- Louisiana Creole people
- French language in the United States
- Boudreaux and Thibodeaux, traditional Cajun jokes
References
Footnotes
- ↑ James Minahan (2002-01-01). Encyclopedia of the Stateless Nations: A-C. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 355. ISBN 978-0-313-32109-2.
- ↑ Valdman, Albert; Kevin J. Rottet, eds. (2009). Dictionary of Louisiana French: As Spoken in Cajun, Creole, and American Indian Communities. University Press of Mississippi. p. 98. ISBN 978-1-60473-404-1.
- 1 2 Carl A. Brasseaux, Acadian to Cajun: Transformation of a People. Jackson, Miss.: University Press of House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary, 2nd edition
- ↑ Morley, William F. E. (1979) [1966]. "Verrazzano, Giovanni da". In Brown, George Williams. Dictionary of Canadian Biography. I (1000–1700) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- ↑ http://www.leagle.com/decision/1980709494FSupp215_1669/ROACH%20v.%20DRESSER%20IND.%20VALVE%20&%20INSTRUMENT%20DIVISION
- ↑ John Grenier, Far Reaches of Empire: War in Nova Scotia 1710-1760, Oklahoma Press. 2008
- ↑ Stephen E. Patterson. "Indian-White Relations in Nova Scotia, 1749-61: A Study in Political Interaction." Buckner, P, Campbell, G. and Frank, D. (eds). The Acadiensis Reader Vol 1: Atlantic Canada Before Confederation, 1998. pp.105-106.; Also see Stephen Patterson, Colonial Wars and Aboriginal Peoples, p. 144.
- ↑ Gabriel Debien, "The Acadians in Santo-Domingo, 1764-1789" in: Glenn R. Conrad, ed., The Cajuns: Essays on their History and Culture, Lafayette, La., 1978, 21-96.
- ↑ "Carencro High School- Preparing Students for Life". Carencro High School- Preparing Students for Life. Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- ↑ "History:1755-Joseph Broussard dit Beausoleil (c. 1702-1765)". Retrieved 2009-03-14.
- ↑ "Letter by Jean-Baptiste Semer, an Acadian in New Orleans, to His Father in Le Havre, April 20, 1766." Transl. Bey Grieve. Louisiana History 48 (spring 2007): 219-26 Link to full transcription of the Letter by Jean-Baptist Semer
- ↑ John Mack Faragher (2005). A Great and Noble Scheme: The Tragic Story of the Expulsion of the French Acadians from their American Homeland, New York: W.W. Norton, 562 pages ISBN 0-393-05135-8 Online excerpt
- ↑ "Acadia:Acadians:American Revolution:Acadian & French Canadian Ancestral Home". Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- ↑ Haarmann, Albert (October 1960). "The Spanish Conquest of British West Florida, 1779–1781". The Florida Historical Quarterly. 39 (2): 112. JSTOR 30150253.
- ↑ Broussard, Karen (2004-03-11). "History of the Galvez Chapter". Lafayette, LA: National Society of the American Revolution, Galvez Chapter. Archived from the original on 2009-10-26. Retrieved 2011-03-17.
- ↑ Brasseaux, Carl A. (1987). The Founding of New Acadia: The Beginnings of Acadian Life in Louisiana, 1765-1803. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. pp. 91–92.
- ↑ Jean-Francois Mouhot (2009), Les Réfugiés Acadiens en France (1758-1785): L'Impossible Réintégration? Quebec: Septentrion, 456p.
- ↑ Tidwell, Michael. Bayou Farewell:The Rich Life and Tragic Death of Louisiana's Cajun Coast. Vintage Departures: New York, 2004.
- ↑ "Blue Collar Bayou: Louisiana Cajuns in the New Economy of Ethnicity". greenwood.com. Archived from the original on 14 November 2006.
- ↑ Desrosiers, Nicolas. "UQAM - Société canadienne d'étude du dix-huitième siècle - Programme". Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- ↑ Edwin W. Edwards Honorary Chair, Enlightenment Conference, Montreal, 18 Oct. 2014. 21 October 2014. Retrieved 3 May 2016 – via YouTube.
- ↑ https://www.academia.edu/8919778/Introductory_remarks_by_former_four-term_Louisiana_Governor_Edwin_W._Edwards_Honorary_Chair_Montreal_Enlightenment_Conference_October_18_2014
- ↑ Art. XII, Sec. 4, Louisiana Constitution, 1974 http://senate.legis.state.la.us/documents/constitution/Article12.htm
- ↑ Hargrave, Lee. "Statutory and Hortatory Provisions of the Louisiana Constitution of 1974." La. L. Rev. 43 (1982): 647. http://digitalcommons.law.lsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4729&context=lalrev
- ↑ Fernin Eaton. "Edwin W. Edwards, four-term former Governor of Louisiana, to chair Enlightenment panel in Montreal". Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- ↑ Grammy Awards
- ↑ Michael Stern. 500 Things to Eat Before It's Too Late: And the Very Best Places to Eat Them. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2009. ISBN 978-0-547-05907-5. Retrieved 2009-11-24.
- ↑ article from Louisiana Division of the Arts | Department of Culture, Recreation & Tourism - Louisiana Folklife Festival program books, the Louisiana Folklore Miscellany, the Smithsonian Folklife Festival program book
- ↑ Gaudet, Marcia. "Cultural Catholicism in Cajun-Creole Louisiana". Louisiana Folk Life.
- 1 2 Hoyt-Goldsmith, Diane; Migdale, Lawrence (September 1995). Mardi Gras: a Cajun country celebration. Holiday House. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-8234-1184-9.
Sources
- Maria Hebert-Leiter, Becoming Cajun, Becoming American: The Acadian in American Literature from Longfellow to James Lee Burke. Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University Press, 2009. ISBN 978-0-8071-3435-1.
- Dean Jobb, The Cajuns: A People's Story of Exile and Triumph, John Wiley & Sons, 2005 (published in Canada as The Acadians: A People's Story of Exile and Triumph)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cajuns. |