Cerrado
| Cerrado (Cerrado) | |
| Savanna | |
 Vegetation in northwest Minas Gerais, Brazil. | |
| Countries | |
|---|---|
| Part of | South America |
| Area | 2,045,064 km2 (789,604 sq mi) |
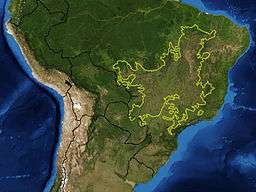 Map of the Cerrado biome as delineated by the WWF. Yellow line approximately encloses the Cerrado distribution.Satellite image from NASA.
| |
The Cerrado (pronounced: [sɨ.ˈʁa.du ~ sɛ'ʁa.du]) is a vast tropical savanna ecoregion of Brazil, particularly in the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Mato Grosso, Tocantins and Minas Gerais. The Cerrado biome core areas are the plateaus in the center of Brazil. The main habitat types of the Cerrado include: forest savanna, wooded savanna, park savanna and gramineous-woody savanna. Savanna wetlands and gallery forests are also included.[1] The second largest of Brazil's major habitat types, after the Amazonian rainforest, the Cerrado accounts for a full 21 percent of the country's land area (extending marginally into Paraguay and Bolivia).[2]
The first detailed account of the Brazilian cerrados was provided by Danish botanist Eugenius Warming (1892) in the book Lagoa Santa,[3] in which he describes the main features of the cerrado vegetation in the state of Minas Gerais.[4]
Since then vast amounts of research have proved that the Cerrado is one of the richest of all tropical savanna regions and has high levels of endemism. Characterized by enormous ranges of plant and animal biodiversity, World Wide Fund for Nature named it the biologically richest savanna in the world, with about 10,000 plant species and 10 endemic bird species.[2] There are nearly 200 species of mammal in the Cerrado, though only 14 are endemic.[2]
Climate
The Cerrado's climate is typical of the rather moister savanna regions of the world, with a semi-humid tropical climate. The Cerrado is limited to two dominant seasons throughout the year, wet and dry. Annual temperatures for the Cerrado average between 22 and 27 °C and average precipitation between 800–2000 mm for over 90% of the area.[5] This ecoregion has a very strong dry season during the southern winter (approx. April– September).[5]
Flora

The Cerrado is characterized by unique vegetation types.[5] It is composed of a shifting mosaic of habitats, with the savanna-like cerrado itself on well-drained areas between strips of gallery forest (closed canopy tall forest) which occur along streams.[5][6] Between the cerrado and the gallery forest is an area of vegetation known as the wet campo with distinct up- and downslope borders where tree growth is inhibited due to wide seasonal fluctuations in the water table.[5][6]
The savanna portion of the Cerrado is heterogeneous in terms of canopy cover. Goodland (1971) divided the Cerrado into four categories ranging from least to most canopy cover: campo sujo (herbaceous layer with occasional small trees about 3 m tall), campo cerrado (slightly higher density of trees about 4 m tall on average), cerrado sensu stricto (orchard-like vegetation with trees about 6 m high) and cerradao (canopy cover near 50% with general height 9 m).[7]
Probably around 800 species of trees are found in the Cerrado.[5] Among the most diverse families of trees in the Cerrado are the Leguminosae (153), Malpighiaceae (46), Myrtaceae (43), Melastomataceae (32) and Rubiaceae (30).[8] Much of the Cerrado is dominated by the Vochysiaceae (23 species in the Cerrado) due to the abundance of three species in the genus Qualea.[5] The herbaceous layer usually reaches about 60 cm in height and is composed mainly of the Poaceae, Cyperaceae, Leguminosae, Compositae, Myrtaceae and Rubiaceae.[5] Much of the vegetation in the gallery forests is similar to nearby rainforest; however, there are some endemic species found only in the Cerrado gallery forests.[5]
Soil fertility, fire regime and hydrology are thought to be most influential in determining Cerrado vegetation. Cerrado soils are always well-drained and most are oxisols with low pH and low calcium and magnesium.[5][9] The amount of potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus has been found to be positively correlated with tree trunk basal area in Cerrado habitats.[10] Much as in other grasslands and savannas, fire is important in maintaining and shaping the Cerrado's landscape; many plants in the Cerrado are fire-adapted, exhibiting characters like thick corky bark to withstand the heat.[5]
Cerrado vegetation is believed to be ancient, stretching back perhaps as far in a prototypic form during the Cretaceous before Africa and South America separated.[11] A dynamic expansion and contraction between cerrado and Amazonian rainforest has probably occurred historically, with expansion of the Cerrado during glacial periods like the Pleistocene.[12] These processes and the resulting fragmentation have probably contributed to the high species richness both of the Cerrado and of the Amazonian rainforest.[5]
Fauna
The insects of the Cerrado are relatively understudied.[13] A yearlong survey of the Cerrado at one reserve in Brazil found that the orders Coleoptera, Hymenoptera, Diptera and Isoptera accounted for 89.5% of all captures.[13] The Cerrado also supports high density of leaf cutter ant ("saúvas") nests (up to 4000 per hectare) which are also very diverse.[14] Along with termites, leaf cutter ants are the primary herbivores of the Cerrado and play an important role in consuming and decomposing organic matter, as well as constituting an important food source to many other animal species.[15] The highest diversity of galling insects (insects that build galls) in the world is also found in the Cerrado, with the most species (46) found at the base of the Serro do Cipó in southeast Brazil.[16]
The Cerrado has a high diversity of vertebrates; 150 amphibian species, 120 reptile species, 837 bird species, and 161 mammal species have been recorded.[17] Lizard diversity is generally thought to be relatively low in the Cerrado compared to other areas like caatinga or lowland rainforest[18] although one recent study found 57 species in one cerrado area with the high diversity driven by the availability of open habitat.[19] Ameiva ameiva is the largest lizard found in the Cerrado and is the most important lizard predator where it is found in the Cerrado.[18] There is a relatively high diversity of snakes in the Cerrado (22-61 species, depending on site) with Colubridae being the richest family.[20] The open nature of the cerrado vegetation most likely contributes to the high diversity of snakes.[20] Information about Cerrado amphibians is extremely limited, although the Cerrado probably has a unique assemblage of species with some endemic to the region.[21]

Most birds found in the Cerrado breed there although there are some Austral migrants (breed in temperate South America and winter in the Amazon basin) and Nearctic migrants (breed in temperate North America and winter in the Neotropics) that pass through.[22] Most breeding birds in the Cerrado are found in more closed canopy areas like gallery forests although 27% of the birds breed only in open habitats and 21% breed in either open or closed habitats.[22] Many of the birds in the Cerrado, especially those found in closed forest, are related to species from the Atlantic rainforest and also the Amazon rainforest.[23] The crowned solitary eagle, hyacinth macaw, toco toucan, buff-necked ibis, dwarf tinamou, and Brazilian merganser are examples of birds found in the Cerrado.
Gallery forests serve as primary habitat for most of the mammals in the Cerrado, having more water, being protected from fires that sweep the landscape and having a more highly structured habitat.[24] Eleven mammal species are endemic to the Cerrado.[24] Notable species include large herbivores like the Brazilian tapir and Pampas deer and large predators like the maned wolf, cougar, jaguar, giant otter, ocelot and jaguarundi. Although the diversity is much lower than in the adjacent Amazon and Atlantic Forest, several species of monkeys are present, including black-striped capuchin, black howler monkey and black-tufted marmoset.[25]
Human population
Before Europeans arrived in the 17th century, the Cerrado was the traditional home to native Brazilians (especially of the Macro-Jê groups). Beginning in the 1960s, a closer connection between the area and the more populated areas of Brazil has been built due to the construction of railways and roads. The native people had only a few cattle-grazing areas, small clearings for raising crops, and hunting and fishing to support their needs. The native vegetation provided them with the raw materials for their housing needs (timber, palm thatches, etc.). They could gather fruits, fibers, and firewood for the rural economy. During the last 25 years modern agriculture has been developed in the Cerrado to produce soya, maize, rice, etc. and huge numbers of cattle are raised in planted pastures.[26] Charcoal production for the Brazilian steel industry also causes great destruction of the Cerrado. By 1994, an estimated 695,000 km2[26] of cerrado (representing 35% of its area) had been converted to 'anthropic landscape'.[4]
Agriculture has grown so much because of various forms of subsidy, including very generous tax incentives and low interest loans, this has caused an enormous establishment of highly mechanized, capital intensive system of agriculture.[27]
Charcoal production
Charcoal production for Brazil’s steel industry comes in second to agriculture in the Cerrado.[8] They actually are quite intertwined. When land is being cleared to make more land for agriculture, the tree’s trunks and roots are often used in the production of charcoal, helping to make money for the clearing. The Brazilian steel industry has traditionally always used the trunks and roots from the Cerrado for charcoal but now that the steel mills in the state of Minas Gerais are the world’s largest, it has taken a much higher toll on the Cerrado.[8] However, recently because of the conservation efforts and the diminishing vegetation in the Cerrado, they now are receiving some charcoal from the eucalyptus plantations and these efforts are growing.[8]
History
Taking advantage of the sprouting of the herbaceous stratum that follows a burning in the Cerrado, the aboriginal inhabitants of these regions learned to use the fire as a tool, to increase the fodder to offer to their domesticated animals.
Until the mid-1960s, agricultural activities in the Cerrado were very limited, directed mainly at the extensive production of beef cattle for subsistence of the local market,[5] since cerrado soils are naturally infertile for agricultural production. After this period, however, the urban and industrial development of the Southeast Region has forced agriculture to the Central-West Region. The transfer of the country's capital to Brasília has been another focus of attraction of population to the central region. From 1975 until the beginning of the 1980s, many governmental programs have been launched with the intent of stimulating the development of the Cerrado region, through subsidies for agriculture.[26] As a result, there has been a significant increase in agricultural and cattle production. On the other hand, the urban pressure and the rapid establishment of agricultural activities in the region have been rapidly reducing the biodiversity of the ecosystems.
Agriculture

The Cerrado was thought worthless for agriculture until researchers at Brazil’s agricultural and livestock research agency, Embrapa, discovered that it could be made fertile by appropriate additions of phosphorus and lime. Researchers also developed tropical varieties of soybeans, until then a temperate crop.[28]
The cerrado was regarded as unfit for farming before the 1960s because the soil was too acidic and poor in nutrients, according to Nobel Peace Prize winner Norman Borlaug, an American plant scientist referred to as the father of the Green Revolution. However, from the 1960s, vast quantities of lime (pulverised chalk or limestone) were poured on the soil to reduce acidity. The effort went on and in the late 1990s between 14 million and 16 million tonnes of lime were being spread on Brazilian fields each year. The quantity rose to 25 million tonnes in 2003 and 2004, equalling around five tonnes of lime per hectare. As a result, Brazil has become the world's second biggest soyabeans exporter and, thanks to the boom in animal feed production, Brazil is now the biggest exporter of beef and poultry in the world.[29]
Today the Cerrado region contributes more than 70% of the beef cattle production in the country ("Pecuária de Corte no Brasil Central"; Beef Cattle Production in Central Brazil, Corrêa, 1989), and thanks to irrigation and soil correcting techniques it is also an important production centre of grains, mainly soya, beans, maize and rice. Great extensions of the Cerrado are also utilised in the production of cellulose pulp for the paper industry, with the cultivation of several species of Eucalyptus and Pinus, but still as a secondary activity. Coffee produced in the Cerrado is now an important export.[30]
The region is increasingly threatened by single-crop monoculture plantations (particularly soybeans), the expansion of agriculture in general, and the burning of the vegetation for charcoal. Current knowledge on changes in carbon stocks upon land use conversion in the Brazilian Cerrado have been reviewed by Battle-Bayer et al.[31]
Nobel Peace Prize laureate Norman Borlaug described the Cerrado as one of Earth's last remaining arable frontiers for the expansion of agriculture.[32] The 2006 World Food Prize was awarded to former Brazilian Minister of Agriculture Alysson Paolinelli, soil scientist Edson Lobato (also of Brazil), and American soil scientist A. Colin McClung for their leadership in soil science and policy implementation that opened the Cerrado to agricultural and food production.[33]
In total, 37.3% of the Cerrado has already been totally converted to human use, while an additional 41.4% is used for pasture and charcoal production. The gallery forests in the region have been among the most heavily affected. It is estimated that about 432,814 km2, or 21.3% of the original vegetation, remains intact today.[34]
Conservation
While the Cerrado is a major, species rich habitat, it is not currently recognized by the Brazilian Constitution as a National Heritage.[5] The government has protected 1.5% of the Cerrado biome in Federal Reserves.[2] One issue with expanding this reserve is that research needs to be done to choose the location of these reserves because the Cerrado biome is floristically very heterogeneous and constitutes a biological mosaic.[26] Teams from the University of Brasília, CPAC and the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh have been collaborating on this project for a number of years funded by Brazilian, European Community and British funds. The project has recently been expanded into a major Anglo-Brazilian initiative, Conservation and Management of the Biodiversity of the Cerrado Biome, with UK Overseas Development Administration funding1. Its aim is to survey the floristic patterns of Cerrado vegetation and to discover representative areas and biodiversity `hot-spots'.[5]
The industrial farming of the Cerrado, with the clearing of land for Eucalyptus and Soya plantation and the development of dams to provide irrigation are drawing criticisms and have been identified as potential threats to several Brazilian rivers.[35]
See also
References
- ↑ " VASCONCELOS, Vitor Vieira; VASCONCELOS, Caio Vieira; VASCONCELOS, Davi Mourão Phyto-Environmental Characterization of Brazilian Savanna (Cerrado) and Brazilian Atlantic Forest, with the Research of Stone Lines and Paleosols Geografia. Ensino & Pesquisa (UFSM), v. 14, p. 3, 2010."
- 1 2 3 4 Conservation International. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2008-05-09.. Access date: May 5, 2011
- ↑ Warming, E. (1892) Lagoa Santa: Et Bidrag til den biologiske Plantegeografi med en Fortegnelse over Lagoa Santas Hvirveldyr. Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskabs Skrifter - Naturvidenskabelig og Mathematisk Afdeling, 6. Rk. vol. 6 (3): 153-488. Later French and Portuguese translations
- 1 2 Oliveira S., Paulo, and Robert Marquis J. The Cerrados of Brazil : Ecology and Natural History of a Neotropical Savanna. Columbia University Press, 2002. eBook.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 RATTER, J.A.; RIBEIRO,J.F. & BRIDGEWATER, S. (1997) The Brazilian Cerrado vegetation and Threats to its Biodiversity. Annals of Botany, 80: pp. 223-230
- 1 2 VIERRA, E.M. & MARINHO-FILHO, J. (1998). Pre- and Post-Fire Habitat Utilization by Rodents of Cerrado from Central Brazil. Biotropica, 30: pp. 491-496
- ↑ GOODLAND, R. 1971. A physiognomic analysis of the 'cerrado' vegetation of central Brazil. Journal of Ecology, 59: 411- 419
- 1 2 3 4 HERRINGER, E.P.; BARROSO, G.M.; RIZZO J.A. & RIZZINI C.T. 1977. A Flora do Cerrado. In FERRI M.G. ed. IV SimpoUsio sobre o cerrado. São Paulo, Brazil. 211-232
- ↑ FURLEY P.A. & RATTER, J.A. 1988. Soil resources and plant communities of the Central Brazilian cerrado and their development. Journal of Biogeography 15: 97-108
- ↑ GOODLAND, R & POLLARD, R. 1973. The Brazilian Cerrado Vegetation: A Fertility Gradient. Journal of Ecology 61: 219-224
- ↑ RATTER, J.A. & RIBEIRO, J.F. 1996. Biodiversity of the flora of the cerrado. In: PEREIRA, R.C. & NASSER L.C.B., eds. Anais/Proceedings of the VIII Simpósio sobre o cerrado 1st Internet. Symposium on Tropical Savannas. Planaltina, DF, Brazil. EMBRAPA/CPAC: 3-6
- ↑ MAYLE, F.E.; BURBRIDGE, R. & KILLEEN T.J. 2000. Millennial-Scale Dynamics of Southern Amazonian Rain Forests. Science 290: 2291-2294
- 1 2 PINHEIRO, F.; DINIZ, I.R.; COELHO, D. & BANDEIRA, M.P.S. 2002. Seasonal pattern of insect abundance in the Brazilian cerrado. Austral Ecology 27: 132-136
- ↑ LEAL, I.R. & OLIVEIRA, P.S. 2000. Foraging ecology of attine ants in a Neotropical savanna: seasonal use of fungal substrate in the cerrado vegetation of Brazil. Insectes Sociaux 47: 376-382
- ↑ OLIVEIRA, P.S. & FREITAS, A.V.L. 2004. Ant-plant-herbivore interactions in the neotropical cerrado savanna. Naturwissenschaften 91: 557-570
- ↑ LARA, A.C.F. & FERNANDES, G.W. 1996. The highest diversity of galling insects: Serra dó Cipo, Brazil. Biodiversity Letters 3: 111-114
- ↑ MYERS, N.; MITTERMEIER, R.A.; MITTERMEIER, C.G.; DA FONESCA, G.A.B. & KENT, J. 2000. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 403: 853-858
- 1 2 VITT, L. 1991. An Introduction to the Ecology of Cerrado Lizards. Journal of Herpetology 25:79-90
- ↑ NOGUEIRA, C.; COLLI, G.R. & MARTINS, M. 2009. Local richness and distribution of the lizard fauna in natural habitat mosaics of the Brazilian Cerrado. Austral Ecology 34:83-96
- 1 2 FRANC, F.G.R.; MESQUITA, D.O.; NOGUEIRA, C.C. & ARAUJO, A.F. 2008. Phylogeny and ecology determine morphological structure in a snake assemblage in the central Brazilian Cerrado. Copeia 1:23-38
- 1 2 BRASILEIRO, C.A.; SAWAYA, R.J.; KIEFER, M.C. & MARTINS, M. 2005. Amphibians of an open cerrado fragment in southeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica 5
- 1 2 DA SILVA, J.S.C. 1997. Endemic birds species and conservation in the Cerrado region, South America. Biodiversity and Conservation 6: 435-450
- ↑ DA SILVA, J.S.C. 1996. Distribution of Amazonian and Atlantic birds in gallery forests of the cerrado region, South America. Ornitologia Neotropical 7: 1-18
- 1 2 REDFORD, K.H. 1986. The role of gallery forests in the zoogeography of the Cerrado’s non-volant mammalian fauna. Biotropica 18: 126-135
- ↑ HENRIQUES, R.P.B. & CAVALCANTE, R.J. 2004. Survey of a gallery forest orimate community in the cerrado of the Distrito Federal, central Brazil. 12: 78-83
- 1 2 3 4 A Disappearing Biome? Reconsidering Land-Cover Change in the Brazilian Savanna Wendy Jepson, The Geographical Journal. Vol. 171, No. 2 (Jun., 2005), pp. 99-111
- ↑ Carlos Klink and Ricardo Machado (2005). "Conservation of the Brazilian Cerrado". Conservation Biology, Volume 19 #3.
- ↑ Rohter, Larry (October 2, 2007). "Scientists Are Making Brazil's Savannah Bloom". The New York Times. Retrieved December 7, 2015.
- ↑ The Economist. Brazilian agriculture: The miracle of the cerrado. August 26, 2010. http://www.economist.com/node/16886442
- ↑ Lopes, A. Scheid. "Soils under Cerrado: A Success Story in Soil Management." Better Crops International. 10.2 (1996): n. page. Print.
- ↑ Batlle-Bayer; et al. (2010). "Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 137, p 47-58 Changes in organic carbon stocks upon land use conversion in the Brazilian Cerrado: A review". doi:10.1016/j.agee.2010.02.003.
- ↑ Borlaug, N.E. and C.R. Dowswell. Fertilizer: to nourish infertile soil that feeds a fertile population that crowds a fragile world. Keynote address at the 61st Annual Conference, International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA), May 24–27, 1993, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 18 p.
- ↑ Borlaug, N.E. and C.R. Dowswell. Fertilizer: to nourish infertile soil that feeds a fertile population that crowds a frag- ile world. Keynote address at the 61st Annual Conference, International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA), May 24–27, 1993, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 18 p.
- ↑ Conservation International. http://www.biodiversityhotspots.org/xp/hotspots/cerrado/pages/impacts.aspx Access date: 31/08/2011
- ↑ Hilaire, Eric (December 22, 2011). "Disappearing Cerrado: 'Brazil's great untold environmental disaster' - audio slideshow | Environment | guardian.co.uk". London: Guardian. Retrieved 2011-12-22.
- Oliveira, Paulo S.; Marquis, Robert J. The Cerrados of Brazil: Ecology and Natural History of a Neotropical Savanna (2002) New York City: Columbia University Press ISBN 0-231-12043-5
- (Portuguese) BRANDÃO, M.; GAVILANES, M. L. (1992). Espécies árboreas padronizadoras do Cerrado mineiro e sua distribuição no Estado. Informe Agropecuário 16 (173): 5-11.
- (Portuguese) BRANDÃO, M.; CARVALHO, P. G. S.; JESUÉ, G. (1992). Guia Ilustrado de Plantas do Cerrado. CEMIG.
- CASTRO, A. A. J. F., MARTINS F. R., TAMASHIRO, J. Y., SHEPHERD G. J. (1999). How rich is the flora of Brazilian Cerrados? Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 86 (1): 192-224.
- (Portuguese) COUTINHO, L. M. Cerrado São Paulo: University of São Paulo.
- RATTER, J.A.; RIBEIRO,J.F. & BRIDGEWATER, S. (1997) The Brazilian Cerrado vegetation and Threats to its Biodiversity. Annals of Botany, 80: pp. 223–230.
- (Portuguese) LEITÃO FILHO, H.F. (1992). A flora arbórea dos Cerrados do Estado de São Paulo. Hoehnea 19 (1/2): 151-163.
- (Portuguese) MENDONÇA, R. C.; FELFILI, J. M.; WALTER, B. M. T.; SILVA, M. C.; REZENDE, FILGUEIRAS, T. S.; NOGUEIRA, P. E. Flora vascular do bioma Cerrado. ("Vascular flora of Cerrado biome") IBGE
- GOTTSBERGER, G.; SILBERBAUER-GOTTSBERGER, I. (2006): Life in the Cerrado Reta Verlag, Ulm 2006, ISBN 3-00-017928-3 Volume 1, ISBN 3-00-017929-1 Volume 2
Further reading
- Cerrado biodiversity Hotspot (Conservation International)
- The miracle of the cerrado
- "2006 World Food Prize winners opened Brazil's 'closed lands'" - press release
- The Chapada dos Veadeiros, Cerrado de Altitude
- (Portuguese) EMBRAPA (Brazilian Government): Bioma Cerrado
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cerrado. |
- Nature Conservancy in Brazil - The Cerrado
- The Biodiversity of the Brazilian Cerrado
- Cerrado - Brazilian Government
- "Cerrado". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- Guardians of the Cerrado Photo Story by Peter Caton
Coordinates: 14°0′20.5″S 47°41′4.6″W / 14.005694°S 47.684611°W