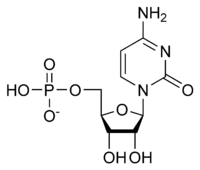
Cytidine monophosphate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-Amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
Cytidylic acid; 5'-Cytidylic acid; Cytidine 5'-monophosphate; Cytidine 5'-phosphate; Cytidylate; 5'-CMP | |
| Identifiers | |
| 63-37-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17361 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL307679 |
| ChemSpider | 5901 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.506 |
| PubChem | 6131 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H14N3O8P | |
| Molar mass | 323.20 g·mol−1 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.8, 4.5, 6.3 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Cytidine monophosphate, also known as 5'-cytidylic acid or simply cytidylate, and abbreviated CMP, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA.[1] It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside cytidine. CMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase cytosine; hence, a ribonucleoside monophosphate. As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix cytidylyl-.
Metabolism
CMP can be phosphorylated to cytidine diphosphate by the enzyme CMP kinase, with adenosine triphosphate or guanosine triphosphate donating the phosphate group. Since cytidine triphosphate is generated by amination of uridine triphosphate, the main source of CMP is from RNA being decomposed by RNAse.
See also
References
- ↑ Pascal JM (February 2008). "DNA and RNA ligases: structural variations and shared mechanisms". Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 18 (1): 96–105. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2007.12.008. PMID 18262407.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.