Economic history of Mexico

Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Mexico |
 |
|
Spanish rule |
| Timeline |
|
|
Mexico’s economic history has been characterized since the colonial era by resource extraction, agriculture, and a relatively underdeveloped industrial sector. Economic elites in the colonial period were predominantly Spanish born, active as transatlantic merchants and silver mine owners and diversifying their investments with the landed estates. The largest sector of the population was indigenous subsistence farmers, who lived mainly in the center and south.
New Spain was envisioned by the Spanish crown as a supplier of wealth to Iberia, which huge silver mines accomplished. A colonial economy to supply foodstuffs and products from ranching as well as a domestic textile industry meant that the economy supplied much of its own needs. Crown economic policy rattled American-born elites’ loyalty to Spain when in 1804 it instituted a policy to make mortgage holders pay immediately the principal on their loans, threatening the economic position of cash-strapped land owners.
Independence in Mexico in 1821 was economically difficult for the country, with Spanish merchants returning to Spain and many of the most productive silver mines not only damaged from the insurgency, but also the loss of its supply of mercury from Spain.[1]
Most of the patterns of wealth in the colonial era continued into the first half of the nineteenth century, with agriculture being the main economic activity with the labor of indigenous and mixed-race peasants. The mid-nineteenth-century Liberal Reforma (ca. 1850–1861; 1867–76) attempted to decrease the economic power of the Roman Catholic Church and to modernize and industrialize the Mexican economy. Following civil war and a foreign intervention, the late nineteenth century found political stability and economic prosperity during the presidential regime of General Porfirio Díaz (1876–1911). Mexico was opened to foreign investment and, to a lesser extent, foreign workers. Foreign capital built a railway network, one of the keys for transforming the Mexican economy, by linking regions of Mexico and major cities and ports. As the construction of the railway bridge over a deep canyon at Metlac demonstrates, Mexico's topography was a barrier to economic development. The mining industry revived in the north of Mexico and the petroleum industry developed in the north Gulf Coast states with foreign capital.
Regional civil wars broke out in 1910 and lasted until 1920, known generally as the Mexican Revolution. Following the military phase of the Revolution, Mexican regimes attempted to "transform a largely rural and backward country … into a middle-sized industrial power."[2] The Mexican Constitution of 1917 gave the Mexican government the power to expropriate property, which allowed for the distribution of land to peasants, but also the Mexican oil expropriation in 1938. Mexico benefited economically from its participation in World War II and the post-war years experienced what has been called the Mexican Miracle (ca. 1946–1970). This growth was fueled by import substitution industrialization. The Mexican economy experienced the limits of ISI and economic nationalism and Mexico sought a new model for economic growth. Huge oil reserves were discovered in the Gulf of Mexico in the late 1970s and Mexico borrowed heavily from foreign banks with loans denominated in U.S. dollars. When the price of oil dropped in the 1980s, Mexico experienced a severe financial crisis.
Under President Carlos Salinas de Gortari Mexico campaigned to join the North American Free Trade Agreement with the expanded treaty going into effect in Mexico, the U.S., and Canada on January 1, 1994. Mexico implemented neoliberal economic policies and changed significant articles of the Mexican Constitution of 1917 to ensure private property rights against future nationalization. In the twenty-first century, Mexico has strengthened its trade ties with China, but Chinese investment projects in Mexico have hit roadblocks in 2014–15. Mexico's continued dependence on oil revenues has had a deleterious impact when oil prices drop, as is happening 2014–15.[3]
Economy of New Spain, 1521–1821

Mexico's economy in the colonial period was based on resource extraction (mainly silver), on agriculture and ranching, and on trade, with manufacturing playing a minor role. In the immediate post-conquest period (1521–40), the dense indigenous and hierarchically organized central Mexican peoples were a ready labor supply and producers of tribute goods. Indian communities' tribute and labor (but not land)were awarded to individual conquerors in an arrangement called encomienda. Conquerors built private fortunes less from the plunder of the brief period of conquest than from the labor and tribute and the acquisition of land in areas where they held encomiendas, translating that into long-term sustainable wealth.[4][5]
The colonial landscape in central Mexico became a patchwork of different sized holdings by Spaniards and indigenous communities. As the crown began limiting the encomienda in the mid-sixteenth century to prevent the development of an independent seigneurial class, Spaniards who had become land owners acquired permanent and part-time labor from Indian and mixed-race workers. Although the encomienda was a major economic institution of the early period, in the end it was a transitory phase, due to the drop in the indigenous populations due to virgin land epidemics of diseases brought by Europeans, but also importantly rapid economic growth and the expansion of the number of Spaniards in New Spain.[6]
Mining
Silver became the motor of the Spanish colonial economy both in New Spain and in Peru. It was mined under license from the crown, with a fifth of the proceeds rendered to the crown.[7] Although Spaniards sought gold and there were some small mines were worked in Oaxaca and Michoacan, the big transformation in New Spain’s economy came in the mid-sixteenth century with discoveries of large deposits of silver.[8] Close to Mexico City, the Nahua settlement of Taxco was found in 1534 to have silver.[9]
But the biggest strikes were in the north outside the zone of dense indigenous communities and Spanish settlement. Zacatecas and later Guanajuato became the most important centers of silver production, but there were many others, including in Parral (Chihuahua) and later strikes in San Luis Potosí, optimistically named after the famous Potosí silver mine of Peru.[8] Spaniards established of cities in the mining region as well as agrarian enterprises supplying foodstuffs and material goods necessary for the mining economy. For Mexico, which did not have a vast supply of trees to use as fuel to extract silver from ore by high heat, the invention in 1554 of the patio process that used mercury to chemically extract the silver from ore was a break though.[10] Spain had a mercury mine in Almadén whose mercury was exported to Mexico. (Peru had its own local source of mercury at Huancavelica). The higher the proportion of mercury in the process meant the higher the extraction of silver.
.png)

The crown had a monopoly on mercury and set its price. During the Bourbon reforms of the eighteenth century, the crown increased mercury production at Almadén and lowered the price to miners by half resulting in a huge increase in Mexico's silver production.[11] As production costs dropped, mining became less risky so that there was a new surge of mine openings and improvements.[12] In the eighteenth century, mining was professionalized and elevated in social prestige with the establishment of the royal college of mining and a miners' guild (consulado), making mining more respectable. The crown promulgated a new mining code that limited liability and protected patents as technical improvements were developed.[13] Highly successful miners purchased titles of nobility in the eighteenth century, valorizing their status in society as well as bringing revenues to the crown.[14][15]
Wealth from Spanish mining fueled the transatlantic economy, with silver becoming the main precious metal in circulation worldwide. Although the northern mining did not itself become the main center of power in New Spain, the silver extracted there was the most important export from the colony.[16] The control that the royal mints exerted over the uniform weight and quality of silver bars and coins made Spanish silver the most accepted and trusted currency.
Labor in silver mines was paid labor of free workers. There was a brief period of mining in central and southern Mexico that mobilized indigenous men’s involuntary labor by the repartimiento, but Mexico’s mines developed in the north outside of the zone of dense indigenous settlement. They were ethnically mixed and mobile, becoming culturally part of the Hispanic sphere even if their origins were indigenous. Mine workers were generally well paid with a daily wage of 4 reales per day plus a share of the ore produced, the partido. In some cases, the partido was worth more than the daily wage. Mine owners sought to terminate the practice.[14] Mine workers pushed back against mine owners, particularly in a 1766 strike at the Real del Monte mine, owned by the Conde de Regla, in which they closed down the mine and murdered a royal official.[17] In the colonial period, mine workers were the elites of free workers,[18]
Agriculture and cattle ranching

Although pre-Hispanic Mexico produced surpluses of corn (maize) and other crops for tribute and subsistence use, Spaniards began commercial agriculture, cultivating wheat, sugar, fruit trees, and even for a period, mulberry trees for silk production in Mexico.[19][20] Areas that had never seen indigenous cultivation became important for commercial agriculture, particularly what has been called the "near North" of Mexico, just north of indigenous settlement in central Mexico. Wheat cultivation using oxen and Spanish plows was done in the Bajío, a region that includes a number of states of modern Mexico, Querétaro, Jalisco, and San Luis Potosí.
The system of land tenure has been cited as one of the reasons that Mexico failed to develop economically during the colonial period, with large estates inefficiently organized and run and the "concentration of land ownership per se caused waste and misallocation of resources."[21] These causes were posited before a plethora of studies of the hacienda and smaller agrarian enterprises as well as broader regional studies were done in the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. These meticulous studies of individual haciendas and regions over time demonstrates that hacienda owners were profit-seeking entrepreneurs. They had the advantage of economies of scale that smaller holders and Indian villages did not in cultivation of grains, pulque, sugar, and sisal and in ranching, with cattle and sheep.[22] Great haciendas did not completely dominate the agrarian sector, since there were products that could be efficiently produced by smaller holders and Indian villages, such as fruits and vegetables, cochineal red dye, and animals that could be raised in confined spaces, such as pigs and chickens.[23] Small holders also produced wine, cotton and tobacco.[23] In the eighteenth century, the crown created a tobacco monopoly on both cultivation and manufacturing of tobacco products.[24]

As Spanish agrarian enterprises developed, acquiring title to land became important. As the size of the indigenous labor force dropped and as the number of Spaniards seeking land and access to labor increased, a transitional labor institution called repartimiento ("allotment") developed, in which the crown allotted indigenous labor to Spaniards on a temporary basis. Many Spanish landowners found the system unsatisfactory since they could not count on receiving an allocation that suited their needs. The repartimiento for agriculture was abolished in 1632.[25] Large-scale landed estates or haciendas developed, and most needed both a small permanent labor force supplemented by temporary labor at peak times, such as planting and harvesting.[26][27]
Cattle ranching need far less labor than agriculture, but did need sufficient grazing land for their herds to increase. As more Spaniards settled in the central areas of Mexico where there were already large numbers of indigenous settlements, the number of ranching enterprises declined and ranching was pushed north. Northern Mexico was mainly dry and its indigenous population nomadic or semi-nomadic, allowing Spanish ranching activities to expand largely without competition. As mining areas developed in the north, Spanish haciendas and ranches supplied products from cattle, not just meat, but hides and tallow, for the silver mining areas. Spaniards also grazed sheep, which resulted in ecological decline since sheep cropped grass to its roots preventing regeneration.[28] Central Mexico attracted a larger proportion of Spanish settlement and landed enterprises there shifted from mixed agriculture and ranching to solely agriculture. Ranching was more widespread in the north, with its vast expanses and little access to water. Spaniards imported seeds for production of wheat for their own consumption.

Both Spaniards and Indians produced native products commercially, particular the color-fast red dye cochineal, as well as the fermented juice of the maguey cactus, pulque. In the early colonial period Mexico was briefly a silk producer. When the transpacific trade with Manila developed in the late sixteenth century, the finer quality Asian silks out-competed locally produced ones.[29] The bulk of luxury yard goods were imported from northern Europe via Spain. For rough cloth for the urban masses, cotton and wool were produced and woven in Mexico in small workshops called obrajes.[30]
Cities, trade and transportation routes
Cities were where crown officials, high ecclesiastical officials, merchants, and artisans were centered. Mexico City, the viceregal capital, was founded on the ruins of the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan and has never given up its primacy in Mexico. The history of Mexico City is deeply entwined in the development of the Mexican economy. Two main ports, Veracruz on the Caribbean coast the served the transatlantic trade and Acapulco on the Pacific coast, the terminus for the Asian trade via the Manila Galleon, allowed the crown to regulate trade. In Spain the House of Trade (Casa de Contratación) in Seville registered and regulated exports and imports as well as issuing licenses for Spaniards emigrating to the New World. Exports were silver and dyestuffs and imported were luxury goods from Europe, while a local economy of high bulk, low value products were produced in Mexico. Artisans and workers of various types provided goods and services to urban dwellers. In Mexico City and other Spanish settlements, the lack of a system of potable water meant that the services of water carriers supplied individual households.
A network of cities and towns developed, some were founded on previous indigenous city-states, (such as Mexico City) while secondary cities were established as provincial areas developed. The main axis was from Veracruz, via the well-situated city of Puebla, to Mexico City, the capital. Another axis connected Mexico City and Puebla to the mining areas of the north, centered on Guanajuato and Zacatecas. There was a road further north to New Mexico, but Mexico’s far north, except for a few mining centers such as Parral, were of little economic interest. California's rich deposits of gold were unknown in the colonial era and had they been discovered that whole region’s history would not be one of marginal importance.[31] To the south, trunk lines connected Mexico's center to Oaxaca and the port of Acapulco. Yucatán was more easily accessed from Cuba than Mexico City, but it had a dense Maya population so there was a labor force to produce products such as sugar, cacao, and later henequen (sisal).
Bad transportation was a major stumbling block to the movement of goods and people in Mexico, which had generally difficult topography. There were few paved roads and dirt tracks turned impassible during the rainy season. Rather than hauling goods by carts drawn by oxen or mules, the most common mode of transporting goods was via pack mules. Poor infrastructure was coupled with poor security, so that banditry was an impediment to the safe transport of people and goods. In the Northern area, the índios bárbaros or uncivilized Indians presented a threat to settlement and travel.

The eighteenth century saw New Spain increase the size and complexity of its economy. Silver remained the motor of the economy, and in fact production increased even though few new mines came into production. The key to the increased production was the lowering of the price of mercury, an essential element in refining silver. The larger the amount of mercury used in refining, the greater pure silver was extracted from ore. Another important element for the eighteenth-century economic boom was the number of wealthy Mexicans who were involved in multiple enterprises as owners, investors, or creditors. Mining is an expensive and uncertain extractive enterprise needed large capital investments for digging and shoring up shafts as well as draining water as mines got deeper.
Elites invested their fortunes in real estate, mainly in rural enterprises and to a lesser extent urban properties, with the Roman Catholic Church functioning as a mortgage bank. The Church itself accrued tremendous wealth, aided by the fact that as a corporation, its holdings were not broken up to distribute to heirs.
Crown policy and economic development
Crown policies generally impeded entrepreneurial activity in New Spain through laws and regulations that were disincentives to the creation of new enterprises.[32] There was no well-defined or enforceable set of property rights.[33][34] Lack of investment in a good system of paved roads made moving products to market insecure and expensive, so enterprises had a narrower reach for their products, particularly bulky agricultural products.[35] Although many enterprises, such as merchant houses and mining, were highly profitable, they were often family firms. The components of Roman Catholic Church had a considerable number of landed estates and the Church received income from the tithe, a ten percent tax on agricultural output. However, there were no laws that promoted "economies of scale through joint stock companies or corporations."[34] There were corporate entities, particularly the Church and indigenous communities, but also corporate groups with privileges (fueros), such as miners and merchants who had separate courts and exemptions.[36][37][38][39]
There was no equal standing before the law, given the exemptions of corporate entities (including indigenous communities) and legal distinctions between races. Only those defined as Spaniards, either peninsular- or American-born of legitimate birth had access to a variety of elite privileges such as civil office holding, ecclesiastical positions, but also entrance of women into convents, which necessitated a significant dowry. A convent for Indian women of "pure blood" was established in the eighteenth century. Indian men from the mid-sixteenth century had been barred from the priesthood, not only excluding them from empowerment in the spiritual realm, but also depriving them of the honor, prestige, and income that a priest could garner.

In the eighteenth century the Bourbon administrative reforms began restricting the number of American-born men appointed to office, which was not only a diminution of their own and their families’ status, but also excluded them from the revenues that flowed from office holding, not merely the salary but the networks of useful connections to do business.
The interventionist and pervasively arbitrary nature of the institutional environment forced every enterprise, urban or rural, to operate in a highly politicized manner, using kinship networks, political influence, and family prestige to gain privileged access to subsidized credit, to aid various stratagems for recruiting labor, to collect debts or enforce contracts, to evade taxes or circumvent courts, and to defend titles to land.[40]
The most closely controlled commodity from New Spain (and Peru) was the production and transportation of silver. Crown officials monitored each step of the process, from licensing on those who developed mines, to transportation, to minting of uniform size and quality silver bars and coins. |
| Silver 8 real coin of Charles III of Spain, 1776 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Obverse CAROLUS III DEI GRATIA 1776 "Charles III by the Grace of God, 1776" Right profile of Charles III in toga with laurel wreath. |
Reverse HISPAN[IARUM] ET IND[IARUM] REX M[EXICO] 8 R[EALES] F M "King of the Spains and the Indies, Mexico [City Mint], 8 reales" Crowned Spanish arms between the Pillars of Hercules adorned with PLVS VLTRA motto. |
The crown established monopolies in other commodities, most importantly mercury from Almadén, the key component in silver refining. But the crown also established monopolies over tobacco production and manufacturing. Guilds ("gremios") restricted the practice of certain professions, such as those engaged in painting, gilded framer makers, music instrument makers, and others. Indians and mixed–race castas were considered a threat, producing quality products far more cheaply.[41]
The crown sought to control trade and emigration to its overseas territories via the House of Trade (Casa de Contratación), based in Seville. Officials in Seville registered ships’ cargoes and passengers bound for the Indies (as the crown to the end of the colonial era called its territories) and upon arrival in New World ports, other crown officials inspected cargo and passengers. In Mexico, the Gulf Coast port of Veracruz, New Spain’s oldest Spanish city and main port, and the Pacific coast port of Acapulco, the terminus of the Manila Galleon were busy when ships were in port, but they did not have large numbers of Spanish settlers in large part due to their disagreeable tropical climate.
Restricting trade put big merchant houses, largely family businesses, in a privileged position. A consulado a great merchant families was established in Mexico City, which raised the status of merchants, and later consulados were established in Veracruz, Guadalajara, and Guatemala City indicating the growth of a core economic group in those cities.[42] Central regions could get imports those firms handled relatively easily, but with a bad transportation network, other regions became economic backwaters and smuggling and other non-sanctioned economic activity took place. The economic policy of comercio libre that was instituted in 1778, it was not full free trade but trade between ports in the Spanish empire and those in Spain; it was designed to stimulate trade. In Mexico, the big merchant families continued to dominate trade, with the main merchant house in Mexico City and smaller outlets staffed by junior members of the family in provincial cities.[43] For merchants in Guatemala City dealing in indigo, they had direct contact with merchants in Cádiz, the main port in Spain, indicating the level of importance of this dye stuff in trade as well as the strengthening of previously remote areas with larger trade networks, in this case by passing Mexico City merchant houses.[44] There was increased commercial traffic between New Spain, New Granada (northern South America), and Peru and during wartime, trade was permitted with neutral countries.[45]
Internal trade was hampered by taxes and levies, legal and otherwise, by officials. The alcabala or sales tax was established in Spain in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries, and was especially favored by the crown because in Spain it did not fall under the jurisdiction of the cortes or assembly.[46] Interestingly, goods produced by or for Indians were exempted from the alcabala.[47] In the eighteenth century, with more effective collection of the sales tax, the revenues increased significantly.[48] Other taxes included the tithe, which was a ten percent tax on agricultural production; tributes paid by non-whites (Indians, Blacks and mixed-race castas); and fees for licensing and other government regulation. Crown officials (with the exception of the viceroy) often purchased their offices, with the price recouped through fees and other means.[49] During the late eighteenth century with the Bourbon reforms, the crown established a new administrative system, the intendancy, with much better paid crown officials, with the hope that graft and other personal enrichment would not be so tempting.[50] In the eighteenth century, there were new and increased taxes including on maize, wheat flour, and wood.[51] Fluctuations in rainfall and harvests played havoc with the price of maize, which often resulted in civil unrest, such that the crown began establishing granaries (alhondigas) to moderate the fluctuations and to forestall rioting.

In a major move to tap what it thought was a major source of revenue, the crown in 1804 promulgated the Act of Consolidation (Consolidación de Vales Reales), in which the crown mandated that the church turn over its funds to the crown, which would in turn pay the church five percent on the principal.[52] Since the church was the major source of credit for hacendados, miners, and merchants, the new law meant that they had to pay the principal to the church immediately. For borrowers who counted on thirty or more year mortgages to repay the principal, the law was a threat to their economic survival. For conservative elements in New Spain that were loyal to the crown, this most recent change in policy was a blow. With the Napoleonic invasion of Iberia in 1808, which placed Napoleon’s brother Joseph on the Spanish throne, an impact in New Spain was to suspend the implementation on the deleterious Act of Consolidation.[53][54]
A Spanish intellectual Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos wrote a critique of the decline of Spain as an economic power in 1796 that contended the stagnation of Spanish agriculture was a major cause of Spain's economic problems. He recommended that the crown press for major changes in the agrarian sector, including the breakup of entailed estates, sale of common lands to individuals, and other instruments to make agriculture more profitable.[55] In New Spain, the bishop-elect of the diocese of Michoacan, Manuel Abad y Queipo, was influenced by Jovellanos's work and proposed similar measures in Mexico. The bishop-elect's proposal for agrarian land reform in Mexico in the early nineteenth century, influenced by Jovellanos's from the late eighteenth century, had a direct impact on Mexican liberals seeking to make the agrarian sector more profitable. Abad y Queipo “fixed upon the inequitable distribution of property as the chief cause of New Spain’s social squalor and advocated ownership of land as the chief remedy.”[56] At the end of the colonial era, land was concentrated in large haciendas and the vast number of peasants had insufficient land and the agrarian sector stagnated.
From the era of independence to the Mexican Revolution, 1800–1920
Late colonial era and independence, 1800–22
In the late colonial era, the Spanish crown had implemented what has been called a "revolution in government", which significantly realigned New Spain's administration with significant economic impacts.[57] When the Napoleonic invasion of Iberia ousted the Bourbon monarch, there was a significant period of political instability in Spain and Spain's overseas possessions, as many elements of society viewed Joseph Napoleon as an illegitimate usurper of the throne. In 1810, with the massive revolt led by secular cleric Miguel Hidalgo rapidly expanded into a social upheaval of Indians and mixed-race castas that targeted Spaniards (both peninsular-born and American-born) and their properties. American-born Spaniards who might have opted for political independence retrenched and supported to conservative elements and the insurgency for independence was a small regional struggle. In 1812, Spanish liberals adopted a written constitution that established the crown as a constitutional monarch and limited the power of the Roman Catholic Church.

When the Bourbon monarchy was restored in 1814, Ferdinand VII swore allegiance to the constitution, but almost immediately reneged and returned to autocratic rule and asserted his rule being "by the grace of God" as the 8 real silver of coin minted in 1821 asserts.[58] Anti-French forces, particularly the British, had enabled the return of Ferdinand VII to the throne. Ferdinand's armed forces were to be sent to its overseas empire to reverse the gains that many colonial regions had gained. However, the troops mutinied and prevented a renewed assertion of royal control in the Indies.[59]
| Silver 8 real coin of Ferdinand VII of Spain, 1821 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Obverse FERDIN[ANDUS] VII DEI GRATIA 1821"Ferdinand VII by the Grace of God, 1821." Right profile of Ferdinand VII with cloak and laurel wreath. |
Reverse HISPAN[IARUM] ET IND[IARUM] REX M[EXICO] 8 R[EALES] I I"King of the Spains and the Indies, Mexico [City Mint], 8 reales." Crowned Spanish arms between the Pillars of Hercules adorned with PLVS VLTRA motto. |
In 1820, Spanish liberals staged a coup and forced Ferdinand to reinstate the Spanish Constitution of 1812 passed by the Cortes de Cadiz. For elites in New Spain, the specter of liberal policies that would have a deleterious impact on their social and economic position propelled former royalists to join the insurgent cause, thus bringing about Mexican independence in 1821. A pact between former royalist officer Agustín de Iturbide and insurgent Vicente Guerrero unified under the Plan de Iguala and the Army of the Three Guarantees brought about Mexican independence in September 1821. Rather than the insurgency being a social revolution, in the end it allowed conservative forces in now independent Mexico to remain at the top of the social and economic system.
Although independence might have brought about rapid economic growth in Mexico since the Spanish crown was no longer the sovereign, Mexico's economic position in 1800 was far better than it would be for over the next hundred years.[60] In many ways the colonial economic system remained largely in place, despite the transition to formal political independence.
At the end of the colonial era, there was no national market and only poorly developed regional markets. The largest proportion of the population was poor, both peasants, who worked small holdings for subsistence or worked for low wages, and urban dwellers, most of whom were underemployed or unemployed, with only a small artisan sector. Although New Spain had been the major producer of silver and the greatest source of income for the Spanish crown, Mexico ceased to produce silver in any significant amounts until the late nineteenth century. Poor transportation, the disappearance of a ready source of mercury from Spain, and deterioration and destruction of deep mining shafts meant that the motor of Mexico's economy ground to a halt. A brief period of monarchic rule in the First Mexican Empire ended with a military coup in 1822 and the formation of a weak federated republic under the Constitution of 1824.
Early republic to 1855
The early post-independence period in Mexican was organized as a federal republic under the Constitution of 1824. Mexican state was a weak institution, with regional struggles between those favoring federalism and a weak central government versus those favoring a strong central government with states subordinate to it. The weakness of the state contrasts with the strength of Roman Catholic Church in Mexico, which was the exclusive religious institution with spiritual power, but it was also a major holder of real estate and source of credit for Mexican elites. The Mexican military was also a stronger institution than the state, and intervened in politics on a regular basis. Local militias also continued to exist, with the potential for both enforcing order and creating disorder.

The new republic's situation did not promote economic growth and development.[61][62]

The early republic has often been called the "Age of Santa Anna," a military hero, participant in the coup ousting emperor Augustín I during Mexico's brief post-independence monarchy. He was president of Mexico on multiple occasions, seeming to prefer having the job rather than doing the job. Mexico in this period was characterized by the collapse of silver exports, political instability, and foreign invasions and conflicts that lost Mexico a huge area of its North.
The social hierarchy in Mexico was modified in the early independence era, such that racial distinctions were eliminated and the formal bars to non-whites' upward mobility were eliminated. When the Mexican republic was established in 1824, noble titles were eliminated, however, special privileges (fueros) of two corporate groups, churchmen and the military, remained in force so that there were differential legal rights and access to courts. Elite Mexicans dominated the agrarian sector, owning large estates. With the Roman Catholic Church still the only religion and its economic power as a source of credit for elites, conservative landowners and the Church held tremendous economic power. The largest percentage of the Mexican population was engaged in subsistence agriculture and many were only marginally engaged in market activities. Foreigners dominated commerce and trade.[63]

It was contended by Mexican liberals that the Roman Catholic Church was an obstacle to Mexico's development through its economic activities. The Church was the beneficiary of the tithe, a ten percent tax on agricultural production, until its abolition in 1833. Church properties and Indian villages produced a significant proportion of agricultural output and were outside tithe collection, while private agriculturalists' costs were higher due to the tithe. It has been argued that an impact of the tithe was in fact to keep more land in the hands of the Church and Indian villages.[64] As for the uses the Church put this ten percent of the agrarian output subject to it, it has been argued that rather being spent on "unproductive" activities that the Church had a greater liquidity that could be translated into credit for enterprises.[65]
In the first half of the nineteenth century, obstacles to industrialization were largely internal, while in the second half largely external.[66] Internal impediments to industrialization were due to Mexico's difficult topography and lack of secure and efficient transportation, remedied in the late nineteenth century by railroad construction. But the problems of entrepreneurship in the colonial period carried forward into the post-independence period. Internal tariffs, licensing for enterprises, special taxes, lack of legislation to promote joint-stock companies that protected investors, lack of enforcement to collect loans or enforce contracts, lack of patent protections, and the lack of a unified court system or legal framework to promote business made creating an enterprise a lengthy and fraught process.[67]
The Mexican government could not count on revenues from silver mining to fund its operations. The exit of Spanish merchants involved in the transatlantic trade was also a blow to the Mexican economy. The division of the former viceroyalty into separate states of a federal system, all needed a source of revenue to function meant that internal tariffs impeded trade.[68] For the weak federal government, a large source of revenue was the customs revenue on imports and exports. The Mexican government floated loans to foreign firms in the form of bonds. In 1824 the Mexican government floated a bond taken up by a London bank, B.A. Goldschmidt and Company; in 1825 Barclay, Herring, Richardson and Company of London not only loaned more money to the Mexican government, but opened a permanent office.[69] The establishment of a permanent branch of Barclay, Herring, Richardson and Co. in Mexico in 1825 and then establishment of the Banco de Londres y Sud América in Mexico set the framework for foreign loans and investment in Mexico. The Banco de Londres issued paper money for private not public debt. Paper money was a first for Mexico which had long used silver coinage.[70] After an extended civil war and foreign invasions, the late nineteenth century saw the more systematic growth of banking and foreign investment during the Porfiriato (1876–1911).

Faced with political disruptions, civil wars, unstable currency, and the constant threat of banditry in the countryside, most wealthy Mexicans invested their assets the only stable productive enterprises that remained viable: large agricultural estates with access to credit from the Catholic Church. These entrepreneurs were later accused of preferring the symbolic wealth of tangible, secure, and unproductive property to the riskier and more difficult but innovative and potentially more profitable work of investing in industry, but the fact is that agriculture was the only marginally safe investment in times of such uncertainty. Furthermore, with low per capita income and a stagnant, shallow market, agriculture was not very profitable. The Church could have loaned money for industrial enterprises, the costs and risks of starting one in the circumstances of bad transportation and lack of consumer spending power or demand meant that agriculture was a more prudent investment.[71]
However, conservative intellectual and government official Lucas Alamán founded the investment bank, Banco de Avío, in 1830 in an attempt to give direct government support to enterprise. The bank never achieved its purpose of providing capital for industrial investment and ceased to exist twelve years after its founding.[72]
Despite obstacles to industrialization in the early post-independence period, cotton textiles produced in factories owned by Mexicans date from the 1830s in the central region.[73] The Banco de Avío did loan money to cotton textile factories during its existence, so that in the 1840s, there were close to 60 factories in Puebla and Mexico City to supply the most robust consumer market in the capital.[74] In the colonial era, that region had seen the development of obrajes, small-scale workshops that wove cotton and woolen cloth.[75]
In the early republic, other industries developed on a modest scale, including glass, paper, and beer brewing. Other enterprises produced leather footwear, hats, wood-working, tailoring, and bakeries, all of which were small-scale and designed to serve domestic, urban consumers within a narrow market.[76] There were no factories to produce machines used in manufacturing, although there was a small iron and steel industry in the late 1870s before Porfirio Díaz's regime took hold after 1876.[77]
Interestingly, some of the factors that impeded Mexico's own industrial development were also barriers to penetration of British capital and goods in the early republic. Small-scale manufacturing in Mexico could make a modest profit in the regions where it existed, but with high transportation costs and protective import tariffs and internal transit tariffs, there was not enough profit for British to pursue that route.[78]
Era of the Liberal reform and French intervention, 1855–67


The Liberals' ouster of conservative Antonio López de Santa Anna in 1854 ushered in a major period of institutional and economic reform, but also one of civil war and foreign invasion. The Liberal Reforma via the lerdo law abolished corporations’ right to own property as corporations, a reform aimed at breaking the economic power of the Catholic Church and of Indian communities which held land as corporate communities. The Reform also mandated equality before the law, so that the special privileges or fueros that had allowed ecclesiastics and the military personnel to be tried by their own courts were abolished. The Liberals codified the Reform in the Constitution of 1857. A civil war between Liberals and Conservatives, known as the War of the Reform or the Three Years’ War was won by Liberals, but Mexico was plunged again in conflict with the government of Benito Juárez reneging on payment of foreign loans contracted by the rival conservative government. European powers prepared to intervene for repayment of the loans, but it was France with imperial ambitions that carried out an invasion and the installation of Maximilian of Habsburg as Emperor of Mexico.
Restored republic, 1867–76
The seeds of economic modernization were laid under the Restored Republic (1867–76), following the fall of the French-backed empire of Maximilian of Habsburg (1862–67). Mexican conservatives had invited Maximilian to be Mexico's monarch with the expectation that he would implement policies favorable to conservatives. Maximilian held liberal ideas and alienated his Mexican conservative supporters. The withdrawal of French military support for Maximilian, alienation of his conservative patrons, and post-Civil War support for Benito Juárez's republican government by the U.S. government precipitated Maximilian's fall. The conservatives' support for the foreign monarch destroyed their credibility and allowed the liberal republicans to implement economic policy as they saw fit after 1867 until the outbreak of the Mexican Revolution in 1910.
President Benito Juárez (1857–72) sought to attract foreign capital to finance Mexico's economic modernization. His government revised the tax and tariff structure to revitalize the mining industry, and it improved the transportation and communications infrastructure to allow fuller exploitation of the country's natural resources. The government issued contracts for construction of a new rail line northward to the United States, and in 1873 it finally completed the commercially vital Mexico City–Veracruz railroad, begun in 1837 but disrupted by civil wars and the French invasion from 1850 to 1868. Protected by high tariffs, Mexico's textile industry doubled its production of processed items between 1854 and 1877. Overall, manufacturing grew using domestic capital, though only modestly.
Mexican per capita income had fallen during the period 1800 until sometime in the 1860s, but began recovering during the Restored Republic. However, it was during the Porfiriato (the rule of General and President Porfirio Díaz (1876–1911)) that per capita incomes climbed, finally reaching again the level of the late colonial era. "Between 1877 and 1910 national income per capita grew at an annual rate of 2.3 percent—extremely rapid growth by world standards, so fast indeed that per capita income more than doubled in thirty-three years."[79]
Porfiriato, 1876–1911
During the Porfiriato, Mexico underwent rapid but highly unequal growth. The railway system expanded from a single line from Mexico City to the Gulf Coast port of Veracruz to create an entire network of railways that encompassed most regions of Mexico.[80] The industrial sector, mainly in textiles, in central Mexico that drew on Mexican capital and labor, vastly expanded in the late nineteenth century with the influx not only of foreign capital and entrepreneurs, but also foreign workers.[81]
Economic advisers of liberal politician and military hero from the Battle of Puebla, 1862, President Porfirio Díaz reversed the country's decades-long opposition to foreign investment, and by playing off British, French, and U.S. investors and governments against one another, was able to maintain a modicum of national independence. Taking "order and progress" as its watchwords, the Porfirian regime established political stability and at least an image of social peace and the rule of law. Other watchwords for Díaz's presidency were "less politics, more administration," which in practice meant the either the suppression or co-optation of political rivals, so that Díaz did not have to contend with uprisings or civil wars. Three-quarters of nineteenth-century Mexican history was plagued by internal political instability and foreign interventions.

Although a major innovation in the late nineteenth century was large-scale foreign investment, Mexican entrepreneurs also created large enterprises, many of which were vertically integrated. Some of these include steel, cement, glass, explosives, cigarette, soap, cotton and wool textiles, and paper.[82] Yucatán underwent an agricultural boom with the creation of large-scale henequen (sisal) haciendas. Yucatán's capital of Mérida saw many elites build mansions based on the fortunes they made in henequen.
The financing of Mexican domestic industry was accomplished through a small group of merchant-financiers, who could raise the capital for high start up costs of domestic enterprises, which included the importation of machinery. Although industries were created, the national market was yet to be built so that enterprises ran inefficiently well below their capacity.[83] Overproduction was a problem since even a minor downturn in the economy meant the consumers with little buying power had to choose necessities over consumer-goods.
The apparent stability of the Porfiriato brought increased foreign capital investment to finance national development and modernization. His minister of finance, José Yves Limantour developed policies that forwarded both those aims.[84] Foreign investors clustered in export related sectors, such as petroleum and mining, but the earliest and most far reaching investment was in the creation of a railway network. Railroads dramatically decreased transportation costs so that heavy or bulky products could be exported to Mexico's Gulf Coast ports as well as rail links on the U.S. border. Railroads were initially owned almost exclusively by foreign investors, expanded from 1,000 kilometers to 19,000 kilometers of track between 1876 and 1910. Railways have been termed a "critical agent of capitalist penetration,"[85] Railways linked areas of the country that suffered from poor transportation previously. The Interoceanic Railway linked Mexico City to the port of Veracruz; the Monterrey and Mexican Railroad linked that northern city with the Gulf Coast port of Tampico; the Southern Pacific of Mexico linked west coast cities from Guaymas to Mazatlan; the Sonora Railway linked Nogales to the port of Guaymas; and the Mexican Central Railroad went north to the U.S. border at El Paso, Texas.[86]

Changes in fundamental legal principles of ownership during the Porfiriato had a positive effect on foreign investors. During Spanish rule, the crown controlled subsoil rights of its territory so that silver mining, the motor of the colonial economy, was controlled by the crown with licenses to mining entrepreneurs was a privilege not a right. The Mexican government changed the law to giving absolute subsoil rights to property owners. For foreign investors, protection of their property rights meant that mining and oil enterprises became much more attractive investments and consistent with liberal principles. The rush of foreign investment into the extractive industries and many Mexicans' sense that they national patrimony was being usurped by foreigners became the impetus during the framing of the Constitution of 1917 to return sovereignty to the nation via Article 27. In the realm of labor, in 1886, Mexico repealed laws requiring the registration of foreigners and bestowed equal rights as Mexicans held.[87]

Rural banditry, which had increased following the demobilization of republican forces in 1867 fighting Maximilian's supporters, was suppressed The rural police force, known as the rurales, was established under Juárez's government and increased in size and importance under Díaz. Other factors promoting a better economic situation were the elimination of local customs duties that had hindered domestic trade were abolished; increased foreign investment in mining; and communications and transportation facilities were modernized as the Mexican railroad system.
The economic growth of the Porfirian era was heavily concentrated in the north of the country—the region with the greatest concentration of mineral resources and, coincidentally, the region closest to the recently acquired Southwestern states of the United States. U.S. entrepreneurs invested heavily in mining, mineral refining operations, and the railroad system that connected northern Mexico with the U.S.[88] As the railroad system improved, and as the population grew in the western U.S., long-distance commercial agriculture became viable, and both U.S. and Mexican entrepreneurs began investing heavily in modernized large-scale agricultural estates along the railroad lines of the north. The bilingual son of a U.S. immigrant to Mexico and the niece of the powerful Creel family of Chihuahua, Enrique Creel became a banker and intermediary between foreign investors and the Mexican government. As a powerful politician and landowner, Creel "became one of the most hated symbols of the Porfirian regime."[89]

The North was also the region with the smallest indigenous populations and ones that were not engaged in subsistence agriculture, so that from the colonial period onward, the North developed huge landed estates devoted mainly to cattle ranching. With the expansion of the rail network northward, linking central Mexico with the United States, northern areas that could produce crops but which previously could not get crops to market cheaply could now develop. The family of Francisco Madero, who challenged Díaz for the presidency in 1910, made an agricultural fortune in Coahuila in the late nineteenth century due to the expansion of railroads. The linkage between the capital and the port of Veracruz was important for making travel and communication more efficient on the trunk line established immediately after the conquest in 1521. As the railway network increased, so too did the building of telegraph lines by the tracks, allowing for the first time rapid communication between the central government and regions of Mexico that had developed largely in isolation. If there was a telegraph report of an uprising, the rural police force and their horses could be put on trains to suppress it. The central government was thus able to effectively control its territory, and, with better security, foreign investors were more confident in putting their capital to work in Mexico by establishing businesses.



The development of the petroleum industry in Mexico on the Gulf Coast dates from the late nineteenth century. Two prominent foreign investors were Weetman Pearson, who was later knighted by the British crown, and Edward L. Doheny, a U.S. businessman. Oil has been an important contributor to the Mexican economy as well as an ongoing political issue, since early development was in the hands of foreigners. Economic nationalism played the key role in the Mexican oil expropriation of 1938.
Silver mining revived in Mexico during the Porfiriato and once again, silver coins from Mexico found their way to China as they had during the colonial transpacific trade of the Manila galleon.
The technocratic economic advisers, the científicos, of the late period Porfirio Díaz regime, as well as the foreign investors they invited into the country, were quite satisfied with the advances that the Mexican economy made between 1876 and 1910. Under the surface, however, popular discontent was reaching the boiling point. The economic-political elite scarcely noticed the country's widespread dissatisfaction with the political stagnation of the Porfiriato, the increased demands for worker productivity during a time of stagnating or decreasing wages and deteriorating work conditions, the repression of worker's unions by the police and army, and the highly unequal distribution of wealth. When a political opposition to the Porfirian regime developed in 1910, following Díaz's initial statement that he would not run again for the presidency in 1910 and then reneging, there was considerable unrest.
With the growth of industry in Mexico, an industrial work force was also created. Railways, mining, and petroleum were developed by foreign capital, but also brought U.S. workers from north of the border. Industrialists needed a docile, reliable workforce that showed up on time, did a full day's work, was skilled, sober, and honest. Many Mexicans willing to work for a wage continued to keep ties to their home communities, which meant they were not completely dependent on wage labor for their livelihood. Creating a skilled and loyal workforce entirely dependent on wage labor was more ideal for industrialists. Industrialists attempt to impose work discipline met considerable worker resistance, with laborers not putting in a full day or week, with Mondays notoriously a day of worker absence and termed tongue-in-cheek "San Lunes", St Monday, with workers extending the weekend a day. Workers drank, which affected their work. Wage labor, however, also created a market for beer in Mexico, produced in factories built by German or Austrian immigrants to Mexico.
Foreign enterprises employed significant numbers of foreign workers, especially in skilled, higher paying positions keeping Mexicans in semi-skilled positions with much lower pay. The foreign workers did not generally know Spanish, so business transactions were done in the foreign industrialists' language. The cultural divide extended to religious affiliation (many were Protestants) and different attitudes "about authority and justice."[90] There were few foreigners in the central Mexican textile industry, but many in mining and petroleum, where Mexicans had little or no experience with advanced technologies.[91]

Although there was a small sector of foreigners working in foreign owned industries, Mexico was not a destination for immigrants the way the United States, Argentina, and Canada were in the nineteenth century. Mexico's population in 1800 at 6 million was a million larger than that of the young U.S. republic, but in 1910 Mexico's population was 15 million while that of the U.S. was 92 million. Lack of slow natural increase and higher death rates coupled with lack of immigration meant that Mexico had a much smaller labor force in comparison.[92]
Era of the Mexican Revolution, 1910–20
The outbreak of the Mexican Revolution in 1910 began as a political crisis over presidential succession and exploded into civil wars in northern Mexico and the peasant center of the country near Mexico City. Political demands by the Mexican Liberal Party (PLM, Partido Liberal de Mexico) included many that set the political and economic agenda for the successful revolutionary faction that wrote the Constitution of 1917. That constitution had provisions that asserted the state's power over its land and subsoil rights (Article 27) that could be utilized for land reform benefiting peasants and economic nationalism that charted a course for Mexican industrialization. Labor was a big winner in the constitution, with Article 123 empowering labor to organize but more importantly put the government on the side of workers, guaranteeing an eight-day and other protections for labor. The power of the Catholic Church was curbed with even tighter restrictions on it. Although many areas that experienced warring factions' conflicts, the Gulf Coast petroleum sector escaped violence and oil revenues in fact helped fund the winning Constitutionalist faction. With the end of the armed conflict by 1920 and the new revolutionary constitution, twentieth-century presidential regimes worked to turn Mexico from a largely rural and economically stagnant country into a modern, urban, industrial power.

Consolidation of the Revolution and the Great Depression, 1920–40
During the ten-year military phase of the Mexican Revolution (1910–20), Mexico's social and economic problems erupted.[93] The conflict was regional, with the Constitutionalist faction of Mexico's North being the big winner. Organized labor in Mexico was mobilized against the peasant uprising in Morelos under Emiliano Zapata, since they had fundamental interests that contrasted urban labor's need for cheap food and desire for the expansion of the industrial sector versus subsistence peasant agriculture. A major outcome of the nearly decade-long conflict was the Constitution of 1917. Organized labor was a big winner, with Article 123 enshrining in the constitution basic worker rights, such as the right to organize and strike, the eight-hour day, and safe working conditions. Organized labor could no longer be simply suppressed by the industrialists or the Mexican state. Although Mexican and foreign industrialists now had to contend with a new legal framework, the Revolution did not, in fact, destroy the industrial sector, either its factories, extractive facilities, or its industrial entrepreneurs, so that once the fighting stopped in 1917, production resumed.[94]
An even more important provision of the constitution was Article 27, which empowered the state to expropriate private holdings if deemed in the national interest and returned subsoil rights to the state. Article 27 enshrined the right of the state could expropriate land and redistribute it to peasant cultivators, which was done in the 1920s and 1930s. The state's power regarding subsoil rights meant that the mining and petroleum industries that were developed and owned by foreign industrialists now had less secure title to their enterprises. The industrial sector of Mexico escaped the destruction of revolutionary violence and many Mexican and foreign industrialists remained in Mexico, but the uncertainty and risk of new investments in Mexican industry meant that it did not expand in the immediate post-Revolutionary period.[95] An empowered labor movement with constitutionally guaranteed rights was a new factor industrialists also had to deal with. However, despite the protections of organized labor's rights to fair wages and working conditions, the constitution restricted laborers' ability to emigrate to the U.S. to work. It "required each Mexican to have a labor contract signed by municipal authories and the consulate of the country where they intended to work."[96] Since "U.S. law prohibited offering contracts to foreign laborers before they entered the United States," Mexicans migrating without a permission from Mexico did so illegally.[97]

Concessions made to foreign oil during the Porfiriato were a particularly difficult matter in the post-Revolutionary period, but General and President Alvaro Obregón negotiated a settlement in 1923, the Bucareli Treaty, that guaranteed petroleum enterprises already built in Mexico. It also settled some claims between the U.S. and Mexico stemming from the Revolution. The treaty had an important impact for the Mexican government, since it paved the way for U.S. recognition of Obregón's government. The agreement not only normalized diplomatic relations, but also opened the way for U.S. military aid to the regime and gave Obregón the means to suppress a rebellion. As the Porfiriato had demonstrated, a strong government that could maintain order paved the way for other national benefits; however, the Constitution of 1917 sought to enshrine rights of groups that suffered under that authoritarian regime. . General and President Plutarco Elías Calles succeeded Obregón in the presidency; he was another of the revolutionary generals who then became president of Mexico. An important economic achievement of the Calles administration was the 1925 founding of the Banco de México, that became the first permanent government bank (following the nineteenth-century failure of the Banco de Avío). Although this was an important economic achievement, Calles enforced the anticlerical articles of the Constitution of 1917, prompting a major outbreak of violence in the Cristero rebellion of 1926–29. Such violence in the center of the country killed tens of thousands and prompted many living in the region to migrate to the United States. For the United States, the situation was worrisome, since U.S. industrialists continued to have significant investments in Mexico and the U.S. government had a long-term desire for peace along its long southern border with Mexico. The U.S. ambassador to Mexico, Dwight Morrow, a former Wall Street banker, brokered an agreement in 1929 between the Mexican government and the Roman Catholic Church, which restored better conditions for economic development.
The Mexican political system was again seen as fragile when in 1928 a religious fanatic assassinated president-elect Obregón, who would have returned to the presidency after a four-year hiatus. Calles stepped in to form in 1929 the Partido Nacional Revolucionario, the precursor to the Institutional Revolutionary Party, helped stabilize the political and economic system, creating a mechanism to manage conflicts and set the stage for more orderly presidential elections. Later that year, the U.S. stock market crashed and the Mexican economy suffered as the worldwide Great Depression took hold. It had already slowed in the 1920s, with investor pessimism and the fall of Mexican exports as well as capital flight. Even before the Great Crash of the U.S. stock market in 1929, Mexican export incomes fell between 1926 and 1928 from $334 million to $299 million (approximately 10%) and then fell even further as the Depression took hold, essentially collapsing.[98] In 1932, GDP dropped 16%, after drops in 1927 of 5.9%, in 1928 5.4%, and 7.7%, such that there was a drop in GDP of 30.9% in a six-year period.[99][100]
The Great Depression brought Mexico a sharp drop in national income and internal demand after 1929. A complicating factor for Mexico-United States relations in this period was forced Mexican repatriation to Mexico of undocumented Mexican workers in the U.S.[101][102] The largest sector of the Mexican economy remained subsistence agriculture so that these fluctuations in the world market and the Mexican industrial sector did not affect all sectors of Mexico equally.
In the mid-1930s, Mexico's economy started to recover under the General and President Lázaro Cárdenas (1934–40), which initiated a new phase of industrialization in Mexico.[103] In 1934, Cárdenas created the National Finance Bank(Nacional Financiera SA (Nafinsa)).[104] as a "semi-private finance company to sell rural real estate" but its mandate was expanded during the term of Cárdenas's successor, Manuel Avila Camacho term to include any enterprise in which the government had an interest.[105] An important achievement of the Cárdenas presidency was "the restoration of social peace"[106] achieved in part by not exacerbating the long simmering post-revolutionary conflict between the Mexican state and the Roman Catholic Church in Mexico, extensive redistribution of land to the peasantry, and re-organizing the party originally created by Plutarco Elías Calles into one with sectoral representation of workers, peasants, the popular sector, and the Mexican army. The Partido Revolucionario Mexicana created the mechanism to manage conflicting economic and political groups and manage national elections.
Education had always been a key factor in the nation's development, with liberals enshrining secular, public education in the Constitution of 1857 and the Constitution of 1917 to exclude and counter the Roman Catholic Church from its long-standing role in education. Cárdenas founded the Instituto Politécnico Nacional in 1936 in northern Mexico City, to train professional scientists and engineers to forward Mexico's economic development. The National Autonomous University of Mexico traditionally trained lawyers and doctors, and in its colonial incarnation, it was a religiously affiliated university. UNAM has continued to be the main university for aspiring politicians to attend, at least as undergraduates, but the National Polytechnic Institute marked a significant step in reforming Mexican higher education.
The railroads had been nationalized in 1929 and 1930 under Cárdenas's predecessors, but his nationalization of the Mexican petroleum industry was a major move in 1938, which created Petroleos Mexicanos or PEMEX. Cárdenas also nationalized the paper industry, whose best-selling product was newsprint. In Mexico the paper industry was controlled by a single firm, the San Rafael y Anexas paper company. Since there was no well-developed capital market in Mexico ca. 1900, a single company could dominate the market. But in 1936, Cárdenas considered newsprint a strategic company and nationalized it. By nationalizing it, a company with poor prospects for flourishing could continue via government support.[107] During the 1930s, agricultural production also rose steadily, and urban employment expanded in response to rising domestic demand. The government offered tax incentives for production directed toward the home market. Import-substitution industrialization began to make a slow advance during the 1930s, although it was not yet official government policy.
To foster industrial expansion, the administration of Manuel Ávila Camacho (1940–46) in 1941 reorganized the National Finance Bank. During his presidency, Mexico's economy recovered from the Depression and entered a period of sustained growth, known as the Mexican Miracle.
World War II and the Mexican miracle, 1940–1970

Mexico's inward-looking development strategy produced sustained economic growth of 3 to 4 percent and modest 3 percent inflation annually from the 1940s until the 1970s. This growth was sustained by the government's increasing commitment to primary education for the general population from the late 1920s through the 1940s. The enrollment rates of the country's youth increased threefold during this period;[108] consequently when this generation was employed by the 1940s their economic output was more productive. Additionally, the government fostered the development of consumer goods industries directed toward domestic markets by imposing high protective tariffs and other barriers to imports. The share of imports subject to licensing requirements rose from 28 percent in 1956 to an average of more than 60 percent during the 1960s and about 70 percent in the 1970s. Industry accounted for 22 percent of total output in 1950, 24 percent in 1960, and 29 percent in 1970. The share of total output arising from agriculture and other primary activities declined during the same period, while services stayed constant. The government promoted industrial expansion through public investment in agricultural, energy, and transportation infrastructure. Cities grew rapidly during these years, reflecting the shift of employment from agriculture to industry and services. The urban population increased at a high rate after 1940 (see Urban Society, ch. 2).
Although growth of the urban labor force exceeded even the growth rate of industrial employment, with surplus workers taking low-paying service jobs, many Mexican laborers migrated to the United States where wages were higher. During World War II, Mexico-United States relations had improved significantly from the previous three decades. The Bracero Program was set up with orderly migration flows were regulated by both governments. However. many Mexicans could not qualify for the program and migrated north illegally, without permission from their own government and without sanction from the U.S. authorities.[109] In the post-war period as the U.S. economy boomed and as Mexico's entered a phase of rapid industrialization, the U.S. and Mexico cooperated closely on illegal border crossings by Mexicans. For the Mexican government, this loss of labor was "a shameful exposure of the failure of the Mexican Revolution to provide economic well-being for many of Mexico's citizens, but it also drained the country of one of its greatest natural resources, a cheap and flexible labor supply."[110] The U.S. and Mexico cooperated closely to stop the flow, including the 1954 program called Operation Wetback.
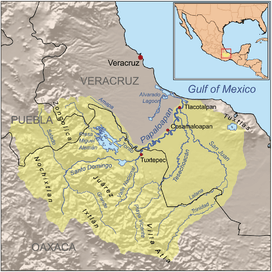
In the years following World War II, President Miguel Alemán Valdés's (1946–52) full-scale import-substitution program stimulated output by boosting internal demand. The government raised import controls on consumer goods but relaxed them on capital goods, which it purchased with international reserves accumulated during the war. The government spent heavily on infrastructure. By 1950 Mexico's road network had expanded to 21,000 kilometers, of which some 13,600 were paved. Large-scale dam building for hydroelectric power and flood control were initiated, most prominently the Papaloapan Project in southern Mexico.[111] In recent years, there has been a re-evaluation of such infrastructure projects, particularly their negative impact on the environment.[112]
Mexico's strong economic performance continued into the 1960s, when GDP growth averaged about 7 percent overall and about 3 percent per capita. Consumer price inflation averaged only 3 percent annually. Manufacturing remained the country's dominant growth sector, expanding 7 percent annually and attracting considerable foreign investment. Mining grew at an annual rate of nearly 4 percent, trade at 6 percent, and agriculture at 3 percent. By 1970 Mexico had diversified its export base and become largely self-sufficient in food crops, steel, and most consumer goods. Although its imports remained high, most were capital goods used to expand domestic production.
Deterioration in the 1970s
Although the Mexican economy maintained its rapid growth during most of the 1970s, it was progressively undermined by fiscal mismanagement and by a poor export industrial sector and a resulting sharp deterioration of the investment climate. The GDP grew more than 6 percent annually during the administration of President Luis Echeverría Álvarez (1970–76), and at about a 6 percent rate during that of his successor, José López Portillo y Pacheco (1976–82). But economic activity fluctuated wildly during the decade, with spurts of rapid growth followed by sharp depressions in 1976 and 1982.

Fiscal profligacy combined with the 1973 oil shock to exacerbate inflation and upset the balance of payments. Moreover, President Echeverría's leftist rhetoric and actions—such as abetting illegal land seizures by peasants—eroded investor confidence and alienated the private sector. The balance of payments disequilibrium became unmanageable as capital flight intensified, forcing the government in 1976 to devalue the peso by 58 percent. The action ended Mexico's twenty-year fixed exchange rate.
Although significant oil discoveries in 1976 allowed a temporary recovery, the windfall from petroleum sales also allowed continuation of Echeverría's destructive fiscal policies. In the mid-1970s, Mexico went from being a net importer of oil and petroleum products to a significant exporter. Oil and petrochemicals became the economy's most dynamic growth sector. Rising oil income allowed the government to continue its expansionary fiscal policy, partially financed by higher foreign borrowing. Between 1978 and 1981, the economy grew more than 8 percent annually, as the government spent heavily on energy, transportation, and basic industries. Manufacturing output expanded modestly during these years, growing by 8.2 percent in 1978, 9.3 percent in 1979, and 8.2 percent in 1980.
This renewed growth rested on shaky foundations. Mexico's external indebtedness mounted, and the peso became increasingly overvalued, hurting non-oil exports in the late 1970s and forcing a second peso devaluation in 1980. Production of basic food crops stagnated and the population increase was skyrocketing, forcing Mexico in the early 1980s to become a net importer of foodstuffs. The portion of import categories subject to controls rose from 20 percent of the total in 1977 to 24 percent in 1979. The government raised tariffs concurrently to shield domestic producers from foreign competition, further hampering the modernization and competitiveness of Mexican industry.
Peso–US dollar exchange 1970–2016
Since 1910 to this day, the Mexican peso has devalued 7,500%
| President | Party | Years | Exchange rate at beginning | at end | Difference | % devaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lic. Luis Echeverría Alvarez | PRI | 1970–1976 | $12.50 | $22.69 | $10.19 | 82% |
| Lic. José Lopez Portillo | PRI | 1976–1982 | $22.69 | $150.29 | $127.60 | 562% |
| Lic. Miguel de la Madrid Hurtado | PRI | 1982–1988 | $150.29 | $2,289.58 | $2,132.71 | 1552% |
| Dr. Carlos Salinas de Gortari | PRI | 1988–1994 | $2,289.58 | $3,410 | $892.00 | 36% |
| Dr. Ernesto Zedillo Ponce de León | PRI | 1994–2000 | $3,410 | $9.360 | $6.08 | 180% |
| Lic. Vicente Fox Quezada | PAN | 2000–2006 | $9.360 | $10.880 | $1.45 | 15% |
| Lic. Felipe Calderón Hinojosa | PAN | (2006–2012) | $10.900 | $12.50 | $1.60 | 15% |
| Lic. Enrique Peña Nieto | PRI | (2012–present) | $12.50 | $18.4350 Mid-market rates: 2016-02-02 | - | - |
Note: During Calderón's government, the peso reached an exchange rate of $15.10. Source: Devaluación del peso mexicano (Spanish)
1982 crisis and recovery
The macroeconomic policies of the 1970s left Mexico's economy highly vulnerable to external conditions. These turned sharply against Mexico in the early 1980s, and caused the worst recession since the 1930s, with the period known in Mexico as La Década Perdida, "the lost decade", i.e., of economic growth. By mid-1981, Mexico was beset by falling oil prices, higher world interest rates, rising inflation, a chronically overvalued peso, and a deteriorating balance of payments that spurred massive capital flight. This disequilibrium, along with the virtual disappearance of Mexico's international reserves—by the end of 1982 they were insufficient to cover three weeks' imports—forced the government to devalue the peso three times during 1982. The devaluation further fueled inflation and prevented short-term recovery. The devaluations depressed real wages and increased the private sector's burden in servicing its dollar-denominated debt. Interest payments on long-term debt alone were equal to 28 percent of export revenue. Cut off from additional credit, the government declared an involuntary moratorium on debt payments in August 1982, and the following month it announced the nationalization of Mexico's private banking system.

By late 1982, incoming President Miguel de la Madrid reduced public spending drastically, stimulated exports, and fostered economic growth to balance the national accounts. Recovery was slow to materialize, however. The economy stagnated throughout the 1980s as a result of continuing negative terms of trade, high domestic interest rates, and scarce credit. Widespread fears that the government might fail to achieve fiscal balance and have to expand the money supply and raise taxes deterred private investment and encouraged massive capital flight that further increased inflationary pressures. The resulting reduction in domestic savings impeded growth, as did the government's rapid and drastic reductions in public investment and its raising of real domestic interest rates to deter capital flight.
Mexico's GDP grew at an average rate of just 0.1 percent per year between 1983 and 1988, while inflation on an average of 100%. Public consumption grew at an average annual rate of less than 2 percent, and private consumption not at all. Total investment fell at an average annual rate of 4 percent and public investment at an 11 percent pace. Throughout the 1980s, the productive sectors of the economy contributed a decreasing share to GDP, while the services sectors expanded their share, reflecting the rapid growth of the informal economy and the change from good jobs to bad ones (services jobs). De la Madrid's stabilization strategy imposed high social costs: real disposable income per capita fell 5 percent each year between 1983 and 1988. High levels of unemployment and underemployment, especially in rural areas, stimulated migration to Mexico City and to the United States.
By 1988 (de la Madrid's final year as President) inflation was at last under control, fiscal and monetary discipline attained, relative price adjustment achieved, structural reform in trade and public-sector management underway, and the economy was bound for recovery. But these positive developments were inadequate to attract foreign investment and return capital in sufficient quantities for sustained recovery. A shift in development strategy became necessary, predicated on the need to generate a net capital inflow.
In April 1989, President Carlos Salinas de Gortari announced his government's national development plan for 1989–94, which called for annual GDP growth of 6 percent and an inflation rate similar to those of Mexico's main trading partners. Salinas planned to achieve this sustained growth by boosting the investment share of GDP and by encouraging private investment through denationalization of state enterprises and deregulation of the economy. His first priority was to reduce Mexico's external debt; in mid-1989 the government reached agreement with its commercial bank creditors to reduce its medium- and long-term debt. The following year, Salinas took his next step toward higher capital inflows by lowering domestic borrowing costs, reprivatizing the banking system, and broaching the idea of a free-trade agreement with the United States. These announcements were soon followed by increased levels of capital repatriation and foreign investment.
Due to the financial crisis that took place in 1982, the total public investment on infrastructure plummeted from 12.5% of GDP to 3.5% in 1989. After rising during the early years of Salinas' presidency, the growth rate of real GDP began to slow during the early 1990s. During 1993 the economy grew by a negligible amount, but growth rebounded to almost 4 percent during 1994, as fiscal and monetary policy were relaxed and foreign investment was bolstered by United States ratification of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). In 1994 the commerce and services sectors accounted for 22 percent of Mexico's total GDP. Manufacturing followed at 20 percent; transport and communications at 10 percent; agriculture, forestry, and fishing at 8 percent; construction at 5 percent; mining at 2 percent; and electricity, gas, and water at 2 percent (services 80%, industry and mining 12%, agriculture 8%). Some two-thirds of GDP in 1994 (67 percent) was spent on private consumption, 11 percent on public consumption, and 22 percent on fixed investment. During 1994 private consumption rose by 4 percent, public consumption by 2 percent, public investment by 9 percent, and private investment by 8 percent.
1993: Hyperinflation and the Nuevo Peso
The nuevo peso (new peso) was the result of hyperinflation in Mexico. In 1993, President Carlos Salinas de Gortari stripped three zeros from the peso, creating a parity of $1 new peso for $1000 of the old ones.
1994, NAFTA, crisis, and recovery
January 1, 1994, the North American Free Trade Agreement, signed by Mexico, the United States, and Canada went into effect.

The collapse of the new peso in December 1994 and the ensuing economic crisis caused the economy to contract by an estimated 7 percent during 1995. Investment and consumption both fell sharply, the latter by some 10 percent. Agriculture, livestock, and fishing contracted by 4 percent; mining by 1 percent; manufacturing by 6 percent; construction by 22 percent; and transport, storage, and communications by 2 percent. The only sector to register positive growth was utilities, which expanded by 3 percent.
By 1996 Mexican government and independent analysts saw signs that the country had begun to emerge from its economic recession. The economy contracted by 1 percent during the first quarter of 1996. The Mexican government reported growth of 7 percent for the second quarter, and the Union Bank of Switzerland forecast economic growth of 4 percent for all of 1996.
2011: 40 years of lag in income
Data by the Encuesta Nacional Ingreso Gasto de los Hogares (ENIGH) revealed that one minimum wage in 1970 equals 3 minimum wages in 2010. That is expressed in real salaries, which means the real buying power of salaries.[113][114]
Mexico and China
China has attempted to expand its investment and trade in Mexico in recent years, similar to China’s moves elsewhere in Latin America and Africa.[115] China was set to construct a $200 million, 1,400-acre mega-mall, Dragon Mart, near the beach resort of Cancún. The mall would have been not only a major emporium of Chinese goods, but also a gateway for Chinese goods elsewhere in the hemisphere. Mexican environmentalists have opposed the project on the grounds of environmental degradation of sensitive wetlands. The city of Cancún initially turned down the permit for the Chinese to build, but they appealed to the state of Quintana Roo and the federal government, which granted the permit. The government of Enrique Peña Nieto reversed that decision in January 2015. Mexico’s environmental protection agency’s head, Guillermo Haro, has cancelled the contract and imposed a fine of $1.5 million for damage already done. The mega-mall was likened to a permanent trade show, with booths for 3,000 exhibitors. Mexican industrialists were pleased with the government’s decision because the mega-mall was expected to flood the Mexican market with Chinese goods. Environmentalists hailed the decision as a victory and a precedent for evaluating future projects. In November 2014, the Mexican government cancelled a contract for China to build a bullet train in Mexico. One of the successful bidders on that contract "sold a mansion to the wife of the president on favorable terms".[116] The award was rescinded and a new bidding was to take place in 2015, but the government has "indefinitely suspended" the project.[117]
Impacts of drop in oil prices, 2014–15
Mexico has again felt the negative impact of the drop in oil prices, with the government cutting planned spending in 2015 and likely 2016 as well. Estimates are the one-third of Mexico's revenues come from petroleum, so that with oil prices going from $100/barrel in mid-2014 to $38/barrel in January 2015, the government is squeezed financially.[117] The Minister of Finance, Luis Videgaray, moved to curtail spending by cancelling a rail project in Yucatán, shelving indefinitely a joint China-Mexico bullet train project, and there were to be cutbacks in the Mexican state oil company, Pemex, and in the education ministry.[117] Gas prices for Mexicans have risen, and the U.S. dollar is strengthening against the peso, so that Mexican consumers are under pressure.[117]
See also
Further reading
Colonial economy
- Altman, Ida. Transatlantic Ties in the Spanish Empire. Brihuega, Spain and Puebla, Mexico, 1560–1620. Stanford: Stanford University Press 2000.
- Altman, Ida and James Lockhart. Provinces of Early Mexico. Los Angeles: UCLA Latin American Center 1976.
- Altman, Ida, Sarah Cline, and Javier Pescador. The Early History of Greater Mexico. Pearson 2003.
- Bakewell, Peter. Silver Mining and Society in Colonial Mexico: Zacatecas, 1546–1700. New York: Cambridge University Press 1971.
- Barrett, Ward. The Sugar Haciendas of the Marqueses del Valle. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press 1970.
- Baskes, Jeremy. Indians, Merchants, and Markets: A Reinterpretation of the Repartimiento and Spanish-Indian Economic Relations in Colonial Oaxaca, 1750–1821. Stanford: Stanford University Press 2000.
- Booker, Jackie R. Veracruz Merchants, 1770–1829: A Mercantile Elite in Late Bourbon and Early Independent Mexico. Tucson: University of Arizona Press 1988.
- Borah, Woodrow. Early Colonial Trade and Navigation between Mexico and Peru. Berkeley: University of California Press 1954.
- Borah, Woodrow. Silk Raising in Colonial Mexico. Berkeley: University of California Press 1943.
- D.A. Brading, Haciendas and Ranchos in the Mexican Bajío: León, 1700–1860. New York: Cambridge University Press 1987.
- D.A. Brading Miners and Merchants in Bourbon Mexico, 1763–1810. New York: Cambridge University Press 1971.
- D.A. Brading "Mexican Silver Minig in the Eighteenth Century: The Revival of Zacatecas." Hispanic American Historical Review 50(2)1970: 665–81.
- D.A. Brading and Harry Cross. "Colonial Silver Mining: Mexico and Peru," Hispanic American Historical Review, 52:4(1972): 545–79.
- Chowning, Margaret. "The Consolidación de Vales Reales in the Bishopric of Michoacan," Hispanic American Historical Review 69:3(1989) 451–78.
- Cline, Sarah.The Book of Tributes. Los Angeles: UCLA Latin American Center Publications 1993
- Costeloe, Michael P. Church Wealth in Mexico: A Study of the "Juzgado de Capellanías" in the Archbishopric of Mexico, 1800–1856. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1967.
- Deans-Smith, Susan. Bureaucrats, Planters, and Workers: The Making of the Tobacco Monopoly in Bourbon Mexico. Austin: University of Texas Press 1992.
- Garner, Richard and Spiro E. Stafanou. Economic Growth and Change in Bourbon Mexico. Gainesville: University of Florida Press 1993.
- Gibson, Charles. Aztecs Under Spanish Rule. Stanford: Stanford University Press 1964.
- Gutierrez Brockington, Lolita. The Leverage of Labor. Managing the Cortés Haciendas in Tehuantepec, 1588–1688. Durham: Duke University Press 1989.
- Hamnett, Brian R. Politics and Trade in Southern Mexico, 1750–1812. New York: Cambridge University Press 1971.
- Haskett, Robert S. "Our Suffering with the Taxco Tribute": Involuntary Mine Labor and Indigenous Society in Central New Spain," Hispanic American Historical Review 71:3(1991) 447–75.
- Himmerich y Valencia, Robert. The Encomenderos of New Spain, 1521–1555. Austin: University of Texas Press 1991.
- Hoberman, Louisa Schell. Mexico's Merchant Elite, 1590–1660. Durham: Duke University Press 1991.
- Kicza, John E. Colonial Entrepreneus: Families and Business in Bourbon Mexico City. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press 1983.
- Ladd, Doris M. The Making of a Strike: Mexican Silver Workers' Struggles in Real del Monte, 1766–1775. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press 1988.
- Lavrin, Asunción “The Execution of the Law of Consolidacion in New Spain: Economic Aims and Results.” Hispanic American Historical Review Vol. 53, No. 1 (Feb., 1973), pp. 27-49 Stable URL: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2512521
- Martin, Cheryl English. Rural Society in Colonial Morelos. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press 1985.
- Melville, Elinor G.K. A Plague of Sheep: Environmental Consequences of the Conquest of Mexico. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1997.
- Ouweneel, Arij. Shadows over Anahuac: An Ecological Interpretation of Crisis and Development in Central Mexico, 1730–1800. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press 1997.
- Patch, Robert W. "Agrarian Change in Eighteenth-Century Yucatan," Hispanic American Historical Review 65:1(1985)21-49.
- Riley, G. Michael. Fernando Cortés and the Marquesado in Morelos, 1522–1547. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press 1973.
- Salvucci, Richard J. Textiles and Capitalism in Mexico: an Economic History of the Obrajes, 1539–1840. Princeton: Princeton University Press 1987.
- Sampat Assadourian, Carlos. "The Colonial Economy: The Transfer of the European System of Production to New Spain and Peru," Journal of Latin American Studies Vol. 24, Quincentenary Supplement. (1992), pp. 55–68.
- Schurz, William Lytle. The Manila Galleon. New York: E.P. Dutton & Co. 1959.
- Schwaller, John Frederick. The Origins of Church Wealth in Mexico. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press 1985.
- Super, John C. "Querétaro Obrajes: Industry and Society in Provincial Mexico, 1600–1810," Hispanic American Historical Review 56 (1976): 197–216.
- Swann, Michael M. Migrants in the Mexican North. Mobility, Economy, and Society in a Colonial World. Boulder: Westview Press 1989.
- Taylor, William B. Landlord and Peasant in Colonial Oaxaca. Stanford: Stanford University Press 1979.
- Thomson, Guy P.C. Puebla de los Angeles. Industry and Society in a Mexican City, 1700–1850. Boulder: Westview Press 1989.
- Tutino, John. "Life and Labor in North Mexican Haciendas: The Querétaro-San Luis Potosí Region, 1775-1810," in Elsa Cecilia Frost, Michael C. Meyer, and Josefina Zoraida Vázquez, Labor and Laborers in Mexican History. Mexico and Tucson: El Colegio de México and University of Arizona Press 1979.
- Van Young, Eric. Hacienda and Market in Eighteenth-Century Mexico: The Rural Economy of the Guadalajara Region, 1675–1820. Berkeley: University of California Press 1981.
- West, Robert C. The Mining Community in Northern New Spain: The Parral Mining District. Berkeley: University of California Press 1949.
Post-independence economy
- Alegre, Robert F. Railroad Radicals in Cold War Mexico: Gender, Class, and Memory. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press 2014.
- Babb, Sarah. Managing Mexico: Economists from Nationalism to Neoliberalism. Princeton: Princeton University Press 2001.
- Bernstein, Marvin D. The Mexican Mining Industry, 1890–1950: A Study of the Interaction of Politics, Economics, and Technology. Albany 1964.
- Anderson, Rodney. Outcasts in Their Own Land: Mexican Industrial workers, 1906–1911. DeKalb: Northern Illinois University 1976.
- Armstrong, Christopher and H.V. Nelles. "A Curious Capital Flow: Canadian Investment in Mexico, 1902–1910," Business History Review 58(1984).
- Brown, Jonathan C. "Foreign and Native-Born Workers in Porfirian Mexico," American Historical Review vol. 98(June 1993), pp. 786–818.
- Brown, Jonathan C. "Foreign Investment and Domestic Politics: British Development of Mexican Petroleum during the Porfiriato," Business History Review 61(1987), 387–416.
- Brown, Jonathan C. Oil and Revolution in Mexico. Berkeley: University of California Press 1992.
- Coatsworth, John H. Growth Against Development: The Economic Impact of Railroads in Porfirian Mexico. DeKalb: Northern Illinois University Press 1981.
- Coatsworth, John H. "Obstacles to Economic Growth in Nineteenth-Century Mexico", American Historical Review, 83 (February 1978).
- Coatsworth, John H. "Economic and Institutional Trajectories in Nineteenth-Century Latin America," in Latin America and the World Economy since 1800, John H. Coatsworth and Alan M. Taylor, eds. Cambridge, MA: David Rockefeller Center for Latin American Studies, Harvard University 1998.
- Conant, Charles A. The Banking System of Mexico. Washington, D.C., Government Printing Office 1910.
- Cosío Villegas, Daniel, et al. Historia Moderna de México, 7 vols. El Porfiriato: La vida económica, 2 parts. Mexico 1965.
- Fowler-Salamini, Heather. Working Women, Entrepreneurs, and the Mexican Revolution: The Coffee Culture of Córdoba, Veracruz. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press 2013.
- González Navarro, Moisés. Las huelgas textiles en el porfiriato. Puebla, Mexico 1970.
- Haber, Stephen H. "Assessing the Obstacles to Industrialisation: The Mexican Economy, 1830–1940," Journal of Latin American Studies 24(1992).
- Haber, Stephen H. Industry and Underdevelopment: The Industrialization of Mexico, 1890–1940. Stanford: Stanford University Press 1989.
- Hamilton, Nora. The Limits of State Autonomy: Post-Revolutionary Mexico. Princeton: Princeton University Press 1982.
- Hamilton, Nora. "Banking and Finance, 1910–40" in Encyclopedia of Mexico, vol. 1 pp. 135–138. Chicago: Fitzroy and Dearborn, 1996.
- Knight, Alan. "The Working Class and the Mexican Revolution, c. 1900-1920," Journal of Latin American Studies, 16 (1984).
- Ludlow, Leonor and Carlos Marichal, eds. Banco y Poder en México, 1800–1925. Mexico: Grijalbo 1986.
- Maxfield, Sylvia. Governing Capital: International Finance and Mexican Politics. Ithaca: Cornell University Press 1990.
- McCaleb, Walter Flavius (1920). Present and Past Banking in Mexico. Harper & Brothers.
- McCaleb, Walter F. The Public Finances of Mexico. New York: Harper 1921.
- Miller, Richard Ulric. "American Railroad Unions and the National Railways of Mexico: An Exercise in Nineteenth-Century Manifest Destiny," Labor History 15(1974).
- Moore, O. Ernesto. Evolución de las instituciones financieras en México. Mexico: Centro de Estudios Monetarios Latinomericanos 1963.
- Pletcher, David M. "Mexico Opens the Door to American Capital, 1877–1880", The Americas XVI (1959) 1–14.
- Pletcher, David M. Rails, Mines, and Progress: Seven American Promoters in Mexico, 1867–1911. Ithaca: Cornell University Press 1958.
- Potash, Robert A. Mexican Government and Industrial Development: The Banco de Avío. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press 1983.
- Ramos Escandón, Carmen. La industria textil y el movimiento obrero en México. Mexico city 1988.
- Schell, William, Jr. "Money as Commodity: Mexico's Conversion to the Gold Standard, 1905." Mexican Studies/Estudios Mexicanos 12:1 (1996).
- Schoonover, Thomas. "Dollars Over Dominion: United State Economic Interests in Mexico, 1861-67," Pacific Historical Review vol 45, No. 1 (Feb. 1976), pp. 23–45.
- Smith, Robert Freeman. "The Formation and Development of the International Bankers Committee in Mexico." Journal of Economic History 23 (December 1963).
- Topik, Steven. "the Economic Role of the State in Liberal Regimes: Brazil and Mexico Compared, 1888–1910," in Guiding the Invisible Hand: Economic Liberalism and the State in Latin American History, Joseph L. Love and Nils Jacobsen, eds. New York 1988, 117–44.
- Wionczek, Miguel S. "Industrialization, Foreign Capital, and Technology Transfer: The Mexican Experience 1930–85," Development and Change (SAGE, London, Beverly Hills, and New Delhi) Vol. 17 (1986), 283–302.
- Zebadúa, Emilio. Banqueros y revolucionarios: La soberania financiera de México. Mexico: Fondo de Cultura Económico 1994.
References
- ↑ John H. Coatsworth, "Obstacles of Economic Growth in Nineteenth-Century Mexico", American Historical Review, vol. 83, no. 1 (Feb. 1978) p. 86.
- ↑ Miguel S. Woinczek. "Industrialization, Foreign Capital, and Technology Transfer: The Mexican Experience, 1930–1985." Development and Change (SAGE. London, Beverly Hills, and New Delhi). Vol 17 (1986), 283–302.
- ↑ Tracy Wilkinson, "Mexico, buffeted by low oil prices, cuts spending", Los Angeles Times, January 31, 2015, p. A7
- ↑ James Lockhart, "Encomienda and Hacienda: The Evolution of the Great Estate in the Indies," Hispanic American Historical Review 49:3(1969) 411–29
- ↑ Ida Altman, Sarah Cline, and Javier Pescador, The Early History of Greater Mexico, Pearson 2003, 163–64.
- ↑ Ida Altman, Sarah Cline, Javier Pescador, The Early History of Greater Mexico, Pearson 2003, p. 162.
- ↑ D.A. Brading and Harry E. Cross, "Colonial Silver Mining: Mexico and Peru," Hispanic American Historical Review 52:4(1972): 545–79.
- 1 2 Altman et al, Early History of Greater Mexico p. 169.
- ↑ Robert S. Haskett, "Our Suffering with the Taxco Tribute: Involuntary Mine Labor and Indigenous Society in Central New Spain," Hispanic American Historical Review 71:3(1991): 447–75.
- ↑ Alan Probert, "Bartolomé de Medina: The Patio Process and the Sixteenth Century Silver Crisis" in Bakewell, Peter, ed. Mines of Silver and Gold in the Americas. Variorum: Brookfield, 1997.
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico p. 290.
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 291.
- ↑ Altman et al., The Early History of Greater Mexico p. 291.
- 1 2 Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico p. 292.
- ↑ Doris M. Ladd, The Mexican Nobility at Independence, 1780–1826. Austin: University of Texas Institute of Latin American Studies 1976.
- ↑ Peter Bakewell, Silver Mining and Society in Colonial Mexico: Zacatecas 1546–1700. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1971.
- ↑ Doris M. Ladd, The Making of a Strike: Mexican Workers’ Struggles in Real del Monte, 1766–1775. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press 1988.
- ↑ Altman et al., The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 293.
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico, pp. 163–168.
- ↑ Woodrow Borah, Silk Raising in Colonial Mexico. Berkeley: University of California Press 1943.
- ↑ Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth," p. 86.
- ↑ Coatsworth, "Obstacles of Economic Growth", p. 87.
- 1 2 Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth," p. 87.
- ↑ Susan Deans-Smith, Bureaucrats, Planters, and Workers: The Making of the Tobacco Monopoly in Bourbon Mexico. Austin: University of Texas Press 1992.
- ↑ Altman et al, Early History of Greater Mexico p. 166.
- ↑ Altman et al, ‘’Early History of Greater Mexico’’, p. 166.
- ↑ James Lockhart and Stuart Schwartz, Early Latin America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1983.
- ↑ Elinor G.K. Melville, A plague of sheep : environmental consequences of the conquest of Mexico. New York: Cambridge University Press 1994.
- ↑ Woodrow W. Borah, Silk Raising in Colonial Mexico. Berkeley: University of California Press 1943.
- ↑ Richard J. Salvucci, Textiles and Capitalism in Mexico: An Economic History of Obrajes, 1539–1840. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1987.
- ↑ James Lockhart, "Trunk Lines and Feeder Lines," in Of Things of the Indies: Essays Old and New in Early Latin American History. Stanford: Stanford University Press 1999, 120–157.
- ↑ Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Development", p. 92.
- ↑ John T. Vance, A Guide to the Law and Legal Literature of Mexico. Washington, D.C. 1945.
- 1 2 Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth", p. 93.
- ↑ Bruce A. Castleman, Building the King's Highway: Labor, Society, and Family on Mexico's Caminos Reales, 1757–1804. Tucson: University of Arizona Press 2005
- ↑ N.M. Farriss, Crown and Clergy in Colonial Mexico, 1759–1821: The Crisis of Ecclesiastical Privilege. London: Athlone 1968.
- ↑ D.A. Brading, Miners and Merchants in Bourbon Mexico. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1971.
- ↑ Lyle McAlister, "The Fuero Militar" in New Spain, 1764–1800. Gaineville: University of Florida Press 1952.
- ↑ Woodrow Borah, Justice by Insurance: The General Indian Court of Mexico and the Legal Aides of the Half-Real. Berkeley: University of California Press 1983.
- ↑ Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth" p. 94.
- ↑ Manel Carrera Stampa, Los gremios mexicanos: La organización en Nueva España, 1521–1861. Mexico: Edición y Distribución Ibero Americana Publicaciones 1954.
- ↑ Altman et al. The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 296.
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 296.
- ↑ Altman et al., The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 297.
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 301
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 36.
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 153.
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 306.
- ↑ J.H. Parry, The Sale of Public Office in the Indies Under the Hapsburgs. Berkeley: University of California Press 1953.
- ↑ Altman et al, Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 306.
- ↑ Altman et al., The Early History of Greater Mexico, p. 310.
- ↑ Asunción Lavrin, “The Execution of the Law of Consolidacion in New Spain: Economic Aims and Results.” Hispanic American Historical Review Vol. 53, No. 1 (Feb., 1973), pp. 27-49 Stable URL: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2512521
- ↑ Altman et al, The Early History of Greater Mexico, pp. 311–12.
- ↑ Margaret Chowning, "The Consolidación de Vales Reales in the Bishopric of Michoacan," Hispanic American Historical Review 69(3)(1989) 451–78.
- ↑ D.A. Brading, The First America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1991, pp. 510–12.
- ↑ D.A. Brading, The First America, p. 568.
- ↑ D.A. Brading, Miners and Merchants in Bourbon Mexico. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1971.
- ↑ image of Ferdinand VII of Spain on the eight real coin.
- ↑ James Lockhart and Stuart Schwartz, Early Latin America. New York and Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1983, p. 415.
- ↑ John H. Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth in Nineteenth-Century Mexico"
- ↑ John H. Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth in Nineteenth-Century Mexico," American Historical Review vol. 83, No. 1 (Feb. 1978), pp. 80–100
- ↑ Stephen Haber, "Assessing the Obstacles to Industrialisation: The Mexican Economy, 1830–1940," Journal of Latin American Studies, vol. 24, No. 1 (Feb. 1992), pp. 1–32
- ↑ William Schell, Jr. "Banking and Finance: 1821–1910" in Encyclopedia of Mexico, vol. 1, p. 131. Chicago: Fitzroy and Dearborn 1993.
- ↑ Coatsworth, Obstacles to Economic Growth, p. 89.
- ↑ Coatsworth, Obstacles to Economic Growth, p. 90.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialisation", pp. 1–2.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing the Obstacles to Industrialisation", p. 6.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialisation," p. 1
- ↑ Schell, "Banking and Finance", p. 131.
- ↑ Schell, "Banking and Finance" p. 131.
- ↑ Coatsworth, Obstacles to Economic Growth in Nineteenth-Century Mexico.
- ↑ Robert A. Potash, Mexican Government and Industrial Development: The Banco de Avío. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press 1983.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialization", p. 2.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialisation," p. 7.
- ↑ Richard J. Salvucci, Textiles and Capitalism in Mexico: an Economic History of the Obrajes, 1539–1840. Princeton: Princeton University Press 1987.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialisation," p. 9.
- ↑ Haber, Assessing Obstacles to Industrialisation," p. 9.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing the Obstacles to Industrialisation," p. 7.
- ↑ John H. Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth in Nineteenth-Century Mexico," American Historical Review vol. 83, no. 1 (Feb. 1978) p. 81
- ↑ John H. Coatsworth, Growth Against Development: The Economic Impact of Railroads in Porfirian Mexico. DeKalb: Northern Illinois University 1981.
- ↑ John H. Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth in Nineteenth-Century Mexico," American Historical Review, vol. 83 (1978).
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialization", 2.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing the Obstacles of Industrialisation," 19.
- ↑ Arthur Schmidt, "José Ives Limantour" in Encyclopedia of Mexico, vol. 1, pp. 746–49. Fitzroy and Dearborn 1997.
- ↑ Brown, Foreign and Native-Born Workers, p. 811.
- ↑ Brown, "Foreign and Native-Born Workers", map. p. 788
- ↑ Jonathan C. Brown, "Foreign and Native-Born Workers in Porfirian Mexico", American Historical Review 98 (June 993) 786–818.
- ↑ Jonathan C. Brown, "Foreign and Native-Born Workers in Porfirian Mexico".
- ↑ Mark Wasserman, "Enrique Clay Creel" in Encyclopedia of Mexico, vol. 1, p. 369. Chicago: Fitzroy and Dearborn 1997.
- ↑ Brown, "Foreign and Native-Born Workers", p. 789.
- ↑ Brown, "Foreign and Native-Born Workers," p. 790.
- ↑ Coatsworth, "Obstacles to Economic Growth," p. 83.
- ↑ "Mexico". State.gov. 2012-06-25. Retrieved 2012-10-17.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing the Obstacles to Industrialisation: the Mexican Economy, 1830–1940," p. 27
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing the Obstacles to Industrialisation", p. 27–28.
- ↑ Kelly Lytle Hernández, "The Crimes and Consequences of Illegal Immigration: A Cross-Border Examination of Operation Wetback, 1943–1954." The Western Historical Quarterly, vol. 37. no. 4 (Winter, 2006), p.423.
- ↑ Hernández, "The Crimes and Consequences", p. 424.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialisation," p. 28.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing the Obstacles to Industrialisation", pp. 28-29.
- ↑ Enrique Cárdenas, La industrialización mexicana durante la Gran Depresión. Mexico 1987.
- ↑ Abraham Hoffman, Unwanted Mexican Americans in the Great Depression: Repatriation Pressures, 1929–1939. Tucson: University of Arizona Press, 1974.
- ↑ Francisco Balderrama and Raymond Rodríguez, Decade of Betrayal: Mexican Repatriation in the 1930s. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 1995.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialisation," p. 29.
- ↑ es:Nacional Financiera (México)
- ↑ Howard F. Cline, Mexico: Revolution to Evolution: 1940–1960. New York: Oxford University Press 1963, p. 244.
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing Obstacles to Industrialisation," p. 29
- ↑ Haber, "Assessing the Obstacles to Industrialisation," pp. 25–26.
- ↑ Easterlin, R. "Why Isn't the Whole World Developed?", Appendix Table 1. The Journal of Economic History Vol. 41 No. 1, 1981
- ↑ Hernández, "The Crimes and Consequences of Illegal Immigration," p. 423.
- ↑ Hernández, "The Crimes and Consequences of Immigration," p. 425.
- ↑ Howard F. Cline, The United States and Mexico, revised and enlarged edition. New York: Atheneum 1963, (originally published by Harvard University Press 1953, pp. 374–75, 382–85.
- ↑ Patrick H. Cosby, "Leviathan in the Tropics: A postcolonial environmental history of the Papaloapan Projects in Mexico." PhD diss. University of Florida 2011.
- ↑ Ixel Yutzil González; Mónica Rodriguez Sosa; Mario Benítez Rétiz (9 May 2011). "El deterioro salarial suma 40 años en México". El Universal (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 May 2013.
- ↑ Ixchel Yutzil González (9 May 2011). "El deterioro salarial suma 40 años en México" (in Spanish). Retrieved 21 May 2013.
Wages lag 40 years in Mexico
- ↑ Kevin P Gallagher (27 January 2015). "Why Latin America should not squander the China boom". BBC News. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ↑ Cecilia Sanchez and Tracy Wilkinson (29 January 2015). "Mexico Halts Massive Chinese Project". Los Angeles Times. p. A1.
- 1 2 3 4 Tracy Wilkinson, "Mexico, buffeted by low oil prices, cuts spending," Los Angeles Times, Saturday, January 31, 2015, p. A7.
External links
- Mexican Economic Crisis (80s) from the Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
- Products of Mexico and Central America from the early mid-20th century