Military history of Iran
With thousands of years of recorded history, and due to an unchanging geographic (and subsequently geopolitical) condition, Iran (previously known as Persia in the West until 1935) has had a long, varied, and checkered military culture and history, ranging from triumphant and unchallenged ancient military supremacy affording effective superpower status in its day, to a series of near catastrophic defeats (beginning with the destruction of Elam) at the hand of previously subdued and conquered peripheral nations (including Greece, Macedon, Arabia, and the Asiatic nomadic tribes at the Eastern boundary of the lands traditionally home to the Iranian people).
Elam
Medes

Achaemenid Era
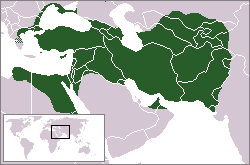


The Achaemenid Empire (559 BC–330 BC) was the first of the Persian Empires to rule over significant portions of Greater Iran. The empire possessed a “national army” of roughly 120.000-150.000 troops, plus several tens of thousands of troops from their allies.
The Persian army was divided into regiments of a thousand each, called hazarabam. Ten hazarabams formed a haivarabam, or division. The best known haivarabam were the Immortals, the King's personal guard division. The smallest unit was the ten man dathaba. Ten dathabas formed the hundred man sataba.
The royal army used a system of color uniforms to identify different units. A large variety of colors were used, some of the most common being yellow, purple, and blue. But this system was probably limited to native Persian troops and was not used for their numerous allies.
The usual tactic employed by the Persians in the early period of the empire, was to form a shield wall that archers could fire over. These troops (called sparabara, or shield-bearers) were equipped with a large rectangular wicker shield called a spara, and armed with a short spear, measuring around six feet long.
Though equipped and trained to conduct shock action (hand-to-hand combat with spears, axes and swords), this was a secondary capability and the Persians preferred to maintain their distance from the enemy in order to defeat him with superior missile-power. The bow was the preferred missile-weapon of the Persians. At maximum rate of fire a sparabara haivarabam of 10,000 men could launch approximately 100,000 arrows in a single minute and maintain this rate for a number of minutes. Typically the Persian cavalry would open the battle by harassing the enemy with hit and run attacks - shooting arrows and throwing small javelins - while the Persian sparabara formed up their battle-array. Then the Persian cavalry would move aside and attempt to harass the flanks of the enemy. Defending against the Persian cavalry required the enemy infantry to congregate in dense static formations, which were ideal targets for the Persian archers. Even heavily armoured infantry like the Greek hoplites would suffer heavy casualties in such conditions. Enemy infantry formations that scattered to reduce casualties from the dense volleys of Persian arrows, were exposed to a close-in shock assault by the Persian cavalry. Torn by the dilemma between exposure to a gradual attrition by the arrows or to being overwhelmed by a cavalry charge on their flanks, most armies faced by the Persians succumbed.
The major weaknesses of the typical Persian tactics were that proper application of these tactics required: a) A wide battlefield composed of fairly flat and smooth terrain that would not hinder the rapid movement of massed horses. b) Good coordination between the cavalry and the infantry. c) An enemy inferior in mobility. Most Persian defeats can be attributed to one or more of these requirements not being met. Thus, the Scythians evaded the Persian army time and again because they were all mounted and conducted only hit and run raids on the Persians; at Marathon the Athenians deployed on a rocky mountainous slope and only descended to the plain after the Persian cavalry had reboarded their transport-ships - charging through the arrow-shower to conduct close-combat with spears and swords - a form of combat for which the Athenians were better equipped and better trained; at Thermopylae the Greek army deliberately deployed in a location that negated the Persians ability to use cavalry and missile-power, again forcing them to fight in close-combat and was forced to retreat only after the Persians were informed of a bypass that enabled them to circumvent this defensive position; at Plataea the Persian attack was poorly coordinated and defeated piecemeal; Alexander the Great's Macedonian army that invaded the Persian empire was composed of a variety of infantry and cavalry types that enabled it, together with Alexander's superior tactical generalship, to negate the Persian capabilities and, once again, force them to fight close-combat.
Seleucid Empire (330 to 150 BCE)
The Seleucid Empire was a Hellenistic successor state of Alexander the Great's dominion, including central Anatolia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia, Turkmenistan, Pamir and the Indus valley.
Parthian Empire (250 BCE to 226 CE)
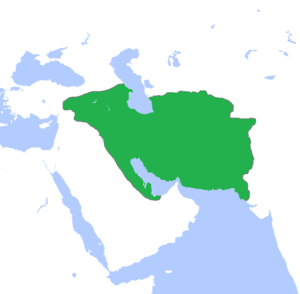
Parthia was an Iranian civilization situated in the northeastern part of modern Iran, but at the height of its power, the Parthian dynasty covered all of Iran proper, as well as Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iraq, Georgia, eastern Turkey, eastern Syria, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Pakistan, Kuwait, the Persian Gulf, the coast of Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and the UAE.[1]
The Parthian empire was led by the Arsacid dynasty, led by the Parni, a confederation of Scythians which reunited and ruled over the Iranian plateau, after defeating and disposing the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire, beginning in the late 3rd century BC, and intermittently controlled Mesopotamia between 150 BC and 224 AD. It was the third native dynasty of ancient Iran (after the Median and the Achaemenid dynasties). Parthia was the arch-enemy of the Roman Empire for nearly three centuries.[2]
After the Scythian-Parni nomads had settled in Parthia and built a small independent kingdom, they rose to power under king Mithridates the Great (171-138 BC).[3] Later, at the height of their power, Parthian influence reached as far as Ubar in Arabia, the nexus of the frankincense trade route, where Parthian-inspired ceramics have been found. The power of the early Parthian empire seems to have been overestimated by some ancient historians, who could not clearly separate the powerful later empire from its more humble obscure origins. The end of this long-lived empire came in 224 AD, when the empire was loosely organized and the last king was defeated by one of the empire's vassals, the Persians of the Sassanid dynasty.
Sassanid Era (224 CE to 651 CE)
.jpg)
The birth of the Sassanid army dates back to the rise of Ardashir I (r. 226–241), the founder of the Sassanid dynasty, to the throne. Ardashir aimed at the revival of the Persian Empire, and to further this aim, he reformed the military by forming a standing army which was under his personal command and whose officers were separate from satraps, local princes and nobility. He restored the Achaemenid military organizations, retained the Parthian cavalry model, and employed new types of armour and siege warfare techniques. This was the beginning for a military system which served him and his successors for over 400 years, during which the Sassanid Empire was, along with the Roman Empire and later the East Roman Empire, one of the two superpowers of Late Antiquity in Western Eurasia. The Sassanid army protected Eranshahr ("the realm of Iran") from the East against the incursions of central Asiatic nomads like the Hephthalites, Turks, while in the west it was engaged in a recurrent struggle against its rival, the Roman Empire and later the Byzantine Empire, setting on forth the conflict that had started since the time of their predecessors, the Parthians, and would end after around 720 years, making it the longest conflict in human history.[4][5]
Islamic conquest (637 to 651)

The Islamic conquest of Persia (633–656) led to the end of the Sassanid Empire and the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion in Persia. However, the achievements of the previous Persian civilizations were not lost, but were to a great extent absorbed by the new Islamic polity.
Most Muslim historians have long offered the idea that Persia, on the verge of the Arab invasion, was a society in decline and decay and thus it embraced the invading Arab armies with open arms. This view is not widely accepted however. Some authors have for example used mostly Arab sources to illustrate that "contrary to the claims, Iranians in fact fought long and hard against the invading Arabs."[6] This view further more holds that once politically conquered, the Persians began engaging in a culture war of resistance and succeeded in forcing their own ways on the victorious Arabs.[7][8]
Tahirid dynasty (821 to 873)
The Tahirid dynasty ruled the northeastern Persian Empire region of Khorasan (parts that are presently in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan). The Tahirid capital was Nishapur.
Although nominally subject to the Abbasid caliphate in Baghdad, the Tahirid rulers were effectively independent. The dynasty was founded by Tahir ibn Husayn, a leading general in the service of the Abbasid caliph al-Ma'mun. Tahir's military victories were rewarded with the gift of lands in the east of Persia, which were subsequently extended by his successors as far as the borders of India.
The Tahirid dynasty is considered to be the first independent dynasty from the Abbasid caliphate established in Khorasan. They were overthrown by the Saffarid dynasty, who annexed Khorasan to their own empire in eastern Persia.
Alavid dynasty (864 to 928)
The Alavids or Alavians were a Shia emirate based in Mazandaran of Iran. They were descendants of the second Shi'a Imam (Imam Hasan ibn Ali) and brought Islam to the south Caspian Sea region of Iran. Their reign was ended when they were defeated by the Samanid empire in 928 AD. After their defeat some of the soldiers and generals of the Alavids joined the Samanid dynasty. Mardavij the son of Ziar was one of the generals that joined the Samanids. He later founded the Ziyarid dynasty. Ali, Hassan and Ahmad the sons of Buye [bu:je] (that were founders of the Buyid or Buwayhid dynasty) were also among generals of the Alavid dynasty who joined the Samanid army.
Saffarid dynasty (861 to 1003)
The Saffarid dynasty ruled a short-lived empire in Sistan, which is a historical region now in southeastern Iran and southwestern Afghanistan. Their rule was between 861 and 1003.[9]
The Saffarid capital was Zaranj (now in Afghanistan). The dynasty was founded by – and took its name from – Ya'qub bin Laith as-Saffar, a man of humble origins who rose from an obscure beginning as a coppersmith (saffar) to become a warlord. He seized control of the Seistan region, conquering all of Afghanistan, modern-day eastern Iran, and parts of Pakistan. Using their capital (Zaranj) as base for an aggressive expansion eastwards and westwards, they overthrew the Tahirid dynasty and annexed Khorasan in 873. By the time of Ya'qub's death, he had conquered Kabul Valley, Sindh, Tocharistan, Makran (Baluchistan), Kerman, Fars, Khorasan, and nearly reaching Baghdad but then suffered defeat.[10]
The Saffarid empire did not last long after Ya'qub's death. His brother and successor Amr bin Laith was defeated in a battle with the Samanids in 900. Amr bin Laith was forced to surrender most of their territories to the new rulers. The Saffarids were subsequently confined to their heartland of Sistan, with their role reduced to that of vassals of the Samanids and their successors.
Samanid dynasty (819 to 999)
The Samanids (819–999)[11] were a Persian dynasty in Central Asia and Greater Khorasan, named after its founder Saman Khuda who converted to Sunni Islam[12] despite being from Zoroastrian theocratic nobility. It was among the first native Iranian dynasties in Greater Iran and Central Asia after the Arab conquest and the collapse of the Sassanid Persian empire.
Ziyarid dynasty (930 to 1090)
The Ziyarids, also spelled Zeyarids (زیاریان or آل زیار), were an Iranian dynasty that ruled in the Caspian sea provinces of Gorgan and Mazandaran from 930-1090 (also known as Tabaristan). The founder of the dynasty was Mardavij (from 930 to 935), who took advantage of a rebellion in the Samanid army of Iran to seize power in northern Iran. He soon expanded his domains and captured the cities of Hamadan and Isfahan.
Buwayhid dynasty (934 to 1062)
The Buyid dynasty[13] were a Shī‘ah Persian[14][15] dynasty that originated from Daylaman in Gilan. They founded a confederation that controlled most of modern-day Iran and Iraq in the 10th and 11th centuries.
Ghaznavid Empire (977 to 1186)
The Ghaznavids were a Muslim dynasty of Turkic slave origin[16] which existed from 975 to 1187 and ruled much of Persia, Transoxania, and the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent.[17]
The dynasty was founded by Sebuktigin upon his succession to rule of territories centered around the city of Ghazni from his father-in-law, Alp Tigin, a break-away ex-general of the Samanid sultans.[18] Sebuktigin's son, Shah Mahmoud, expanded the empire in the region that stretched from the Oxus river to the Indus Valley and the Indian Ocean; and in the west it reached Rey and Hamadan. Under the reign of Mas'ud I it experienced major territorial losses. It lost its western territories to the Seljuqs in the Battle of Dandanaqan resulting in a restriction of its holdings to what is now Afghanistan, as well as Balochistan and the Punjab. In 1151, Sultan Bahram Shah lost Ghazni to Ala al-Din Husayn of Ghur and the capital was moved to Lahore until its subsequent capture by the Ghurids in 1186.
Seljuq Empire (1037 to 1187)

The Seljuqs were a Turco-Persian[20][21] Sunni Muslim dynasty that ruled parts of Central Asia and the Middle East from the 11th to 14th centuries. They set up an empire, the Great Seljuq Empire, which at its height stretched from Anatolia through Persia and which was the target of the First Crusade. The dynasty had its origins in the Turcoman tribal confederations of Central Asia and marked the beginning of Turkic power in the Middle East. After arriving in Persia, the Seljuqs adopted the Persian culture[22] and are regarded as the cultural ancestors of the Western Turks – the present-day inhabitants of Azerbaijan, Turkey, and Turkmenistan.
Khwarezmian Empire (1077 to 1231)
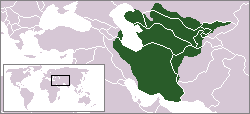
The Khwarezmian dynasty, also known as Khwarezmids or Khwarezm Shahs was a Persianate Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turkic mamluk origin.[23][24]
They ruled Greater Iran in the High Middle Ages, in the period of about 1077 to 1231, first as vassals of the Seljuqs, Kara-Khitan,[25] and later as independent rulers, up until the Mongol invasions of the 13th century. The dynasty was founded by Anush Tigin Gharchai, a former slave of the Seljuq sultans, who was appointed the governor of Khwarezm. His son, Qutb ud-Dīn Muhammad I, became the first hereditary Shah of Khwarezm.[26]
Ilkhanate (1256 to 1353)
The Ilkhanate was a Mongol khanate established in Persia in the 13th century, considered a part of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanate was based, originally, on Genghis Khan's campaigns in the Khwarezmid Empire in 1219–1224, and founded by Genghis's grandson, Hulagu, in what territories which today comprise most of Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Turkey, and western Pakistan. The Ilkhanate initially embraced many religions, but was particularly sympathetic to Buddhism and Christianity, and sought a Franco-Mongol alliance with the Crusaders in order to conquer Palestine. Later Ilkhanate rulers, beginning with Ghazan in 1295, embraced Islam.
Muzaffarid dynasty (1314 to 1393)
Chupanid dynasty (1337 to 1357)
Jalayerid dynasty (1339 to 1432)
The Jalayirids (آل جلایر) were a Mongol descendant dynasty which ruled over Iraq and western Persia[27] after the breakup of the Mongol Khanate of Persia (or Ilkhanate) in the 1330s.
The Jalayirid sultanate lasted about fifty years, until disrupted by Tamerlane's conquests and the revolts of the "Black sheep Turks" or Kara Koyunlu. After Tamerlane's death in 1405, there was a brief unsuccessful attempt to re-establish the Jalayirid sultanate and Jalayirid sultanate was ended by Kara Koyunlu in 1432.
Timurid Empire (1370 to 1506)
The Timurids were a Central Asian Sunni Muslim dynasty of originally Turko-Mongol descent whose empire included the whole of Central Asia, Iran, modern Afghanistan, as well as large parts of Pakistan, India, Mesopotamia, Anatolia and the Caucasus. It was founded by the militant conqueror Timur (Tamerlane) in the 14th century.
In the 16th century, Timurid prince Babur, the ruler of Ferghana, invaded India and founded the Mughal Empire, which ruled most of the Indian subcontinent until its decline after Aurangzeb in the early 18th century, and was formally dissolved by the British Raj after the Indian rebellion of 1857.
Qara Qoyunlu Turcomens (1407 to 1468)
Aq Qoyunlu Turcomans (1378 to 1508)

Safavid Era (1501 to 1736)

The Safavid rulers of Persia, like the Mamluks of Egypt, viewed firearms with distaste, and at first made little attempt to adopt them into their armed forces. Like the Mamluks they were taught the error of their ways by the powerful Ottoman armies. Unlike the Mamluks they lived to apply the lessons they had learnt on the battlefield. In the course of the sixteenth century, but still more in the seventeenth, the shahs of Iran took steps to acquire handguns and artillery pieces and to re-equip their forces with them. Initially, the principal sources of these weapons appears to have been Venice, Portugal, and England.
Despite their initial reluctance, the Persians very rapidly acquired the art of making and using handguns. A Venetian envoy, Vincenzo di Alessandri, in a report presented to the Council of Ten on 24 September 1572, observes:

"They used for arms, swords, lances, arquebuses, which all the soldiers carry and use; their arms are also superior and better tempered than those of any other nation. The barrels of the arquebuses are generally six spans long, and carry a ball little less than three ounces in weight. They use them with such facility that it does not hinder them drawing their bows nor handling their swords, keeping the latter hung at their saddle bows till occasion requires them. The arquebus is then put away behind the back so that one weapon does not impede the use of the other."
This picture of the Persian horseman, equipped for almost simultaneous use of the bow, sword, and firearm, aptly symbolized the dramatic and complexity of the scale of changes that the Persian Military was undergoing. While the use of personal firearms was becoming commonplace, the use of field artillery was limited and remained on the whole ineffective.

Shah Abbas (1587–1629) was instrumental in bringing about a 'modern' gunpowder era in the Persian army. Following the Ottoman Army model that had impressed him in combat the Shah set about to build his new army. He was much helped by two English brothers, Anthony and Robert Sherley, who went to Iran in 1598 with twenty-six followers and remained in the Persian service for a number of years. The brothers helped organize the army into an officer-paid and well-trained standing army similar to a European model. It was organized along three divisions: Ghilman ('crown servants or slaves' conscripted from hundreds of thousands of ethnic Circassians, Georgians, and Armenians), Tofongchis (musketeers), and Topchis (artillery-men)
Shah Abbas's new model army was massively successful and allowed him to re-unite parts of Greater Iran and expand his nations territories at a time of great external pressure and conflict.
The Safavid era also saw the mass integration of hundreds of thousands of ethnic Caucasians, notably Circassians, Georgians, Armenians, and other peoples of the Caucasus in Persian society, starting with the era of Shah Tahmasp I, and which would last all the way till the Qajar era. Originally only deployed for being fierce warriors and having beautiful women, this policy was notably significantly expanded under Shah Abbas I, who would use them as a complete new layer in Persian society, most notably to crush the power of the feudal Qizilbash. Under Abbas' own reign, some 200,000 Georgians, tens of thousands of Circassians, and 300,000 Armenians were deported to Iran. Many of them were, as above mentioned, put in the ghilman corps, but the larger masses were deployed in the regular armies, the civil administration, royal household, but also as labourers, farmers, and craftsmen. Many notorious Iranian generals and commanders were of Caucasian ancestry. Many of their descendants linger forth in Iran as the Iranian Georgians, Iranian Circassians, and Iranian Armenians (see Peoples of the Caucasus in Iran), and many millions of Iranians are estimated to have Caucasian ancestry as a following of this.
Upon the fall of the Safavid dynasty Persia entered into a period of uncertainty. The previously highly organized military fragmented and the pieces were left for the following dynasties to collect.
Afsharid Dynasty (1750 to 1794)
Following the decline of the Safavid state a brilliant general by the name of Nader Shah took the reins of the country. This period and the centuries following it were characterised by the rise in Russian power to Persia's north.
From the time of Peter The Great, the northern states of the Persian Empire were under threat of Russian annexation. In 1710, Tsar Peter formulated his foreign policy principles, the backbone of which was 'invasion and territorial expansion'. The first to suffer from the new Russian power was the Ottoman Empire. However, pressure was soon exerted on the Persian Empire as well. In May 1723, the first major Russo-Persian War occurred and the invasion came as far as the northern city of Rasht. At the Treaty of Bab-e Ali the Ottoman and Russian Empires divided up large portions of Persia between themselves. It was Nader Shah who, with great force, drove the Ottomans and Russians out of the occupied lands and eventually began expanding the borders of Greater Iran.
Following Nader Shah, many of the other leaders of the Afsharid dynasty were weak and the state they had built quickly gave way to the Qajars. As the control of the country de-centralised with the collapse of Nader Shah's rule, many of the peripheral territories of the Empire gained independence and only paid token homage to the Persian State.
Qajar Era (1794 to 1925)
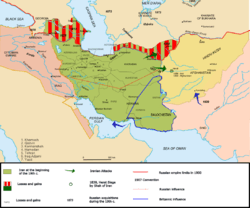


The second half of the 18th Century saw a new dynasty take hold in Iran. The new Qajar dynasty was founded on slaughter and plunder of Iranians, particularly Zoroasterian Iranians. The Qajars, under their dynasty founder, Agha Mohammad Khan plundered and slaughtered the aristocrats of the previous Zand Dynasty. Following this, Agha Mohammad Khan was determined to regain all lost territories following the death of Nadir Shah. First on his was the Caucasus, and most notably Georgia. Iran had intermittently ruled most of the Caucasus since 1555, since the early days of the Safavid Dynasty, but while Iran was in chaos and tumult, many of their subjects had declared themselves quasi-independent, or in the case of the Georgians, had plotted an alliance with the Russian Empire by the Treaty of Georgievsk. Agha Mohammad Khan, furious at his Georgian subjects, starting his expedition with 60,000 cavalry under his command, defeated the Russian garrisons stationed there and drove them back out of the entire Caucasus in several important battles, and completely sacked Tblisi, and carried of some 15,000 captives back to Iran. Following the capture of Georgia, Agha Mohammad Khan was murdered by two of his servants who feared they would be executed. The rise of the Qajars was very closely timed with Catherine the Great's order to invade Iran once again. During the Persian Expedition of 1796, Russian troops crossed the Aras River and invaded parts of Azarbaijan and Gilan, while they also moved to Lankaran with the aim of occupying Rasht again. His nephew and successor, Fath Ali Shah, after several successful campaigns of his own against the Afshars, with the help of Minister of War Mirza Assadolah Khan and Minister Amir Kabir created a new strong army, based on the latest European models, for the newly chosen Crown-Prince Abbas Mirza.
This period marked a serious decline in Persia's power and thus its military prowess. From here onwards the Qajar dynasty would face great difficulty in its efforts, due to the international policies mapped out by some western great powers and not Persia herself. Persia's efforts would also be weakened due to continual economic, political, and military pressure from outside of the country (see The Great Game), and social and political pressures from within would make matters worse.
With the consolidation of the Treaty of Georgievsk, Russia annexed eastern Georgia and Dagestan in 1801, dethroning the Bagrationi Dynasty. In 1803, Fath Ali Shah was determined to get Georgia and Dagestan back, and fearing Russia would march on more south towards Persia and the Ottoman Empire too, declared war on Russia. While starting with the upper hand, Russians were ultimately victorious in the Russo-Persian War (1806-1813). From the beginning, Russian troops had a great advantage over the Persians as they possessed much modern Artillery, the use of which had never sunk into the Persian army since the Safavid dynasty three centuries earlier. Nevertheless, the Persian army under the command of Abbas Mirza managed to win several victories over the Russians. Iran's inability to develop modern artillery during the preceding, and the Qajar, dynasty resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Gulistan in 1813. This marked a turning point in the Qajar attitude towards the military. Abbas Mirza sent a large number of Persians to England to study Western military technology and at the same time he invited British officers to Persia to train the Persian forces under his command. The army's transformation was phenomenal as can be seen from the Battle of Erzeroum (1821) where the new army routed an Ottoman army. This resulted in the Treaty of Erzurum whereby the Ottoman Empire acknowledged the existing frontier between the two empires. These efforts to continue the modernisation of the army through the training of officers in Europe continued until the end of the Qajar dynasty. With the exceptions of Russian and Imperial British armies, the Qajar army of the time was unquestionably the most powerful in the region.
With his new army, Abbas Mirza invaded Russia in 1826. While in the first year of the war Persia managed to regain almost all lost territories, reaching almost Georgia and Dagestan too, the Persian army ultimately proved no match for the significantly larger and equally capable Russian army. The following Treaty of Turkmenchay in 1828 crippled Persia through the ceding of much of Persia's northern territories and the payment of a colossal war indemnity. The scale of the damage done to Persia through the treaty was so severe that The Persian Army and state would not regain its former strength till the rise and creation of the Soviet Union and the latter's cancellation of the economic elements of the treaty as 'tsarist imperialistic policies'. After these periods of Russo-Persian Wars, Russian influence in Persia rose significantly too.
The reigns of both Mohammad Shah and Nasser al-Din Shah also saw attempts by Persia to bring the city of Herat, occupied by the Afghans, again under Persian rule. In this, though the Afghans were no match for the Persian Army, the Persians were not successful, this time because of British Intervention as part of The Great Game (See papers by Waibel and Esandari Qajar within the Qajar Studies source). Russia backed the Persian attacks, using Persia as a 'cat's paw' for expansion of its own interests. Britain feared the seizure of Herat would leave a route to attack India controlled by a power friendly to Russia, and threatened Persia with closure of the trade of the Persian Gulf. When Persia abandoned its designs on Herat, the British no longer felt India was threatened. This, combined with growing Persian fears about Russian designs on their own country, led to the later period of Anglo-Persian military co-operation.
Ultimately, under the Qajars Persia was shaped into its modern form. Initially, under the reign of Agha Mohammad Khan Persia won back many of its lost territories, notably in the Caucasus, only to be lost again through a series of bitter wars with Russia. In the west the Qajars effectively stopped enroachment of their Ottoman arch rival in the Ottoman–Persian War (1821–23) and in the east the situation remained fluid. Ultimately, through Qajar rule the military institution was further developed and a capable and regionally superior military force was developed. This was quashed by the then superpowers of the day: Russia and Britain.
For World War I, see the Persian Campaign.
Pahlavi Era (1925 to 1979)
When the Pahlavi dynasty came to power the Qajar dynasty was already weak from years of war with Russia. The standing Persian army was almost non-existent. The new king Reza Shah Pahlavi, was quick to develop a new military, the Imperial Iranian Armed Forces. In part, this involved sending hundreds of officers to European and American military academies. It also involved having foreigners re-train the existing army within Iran. In this period a national air force (the Imperial Iranian Air Force) was established and the foundation for a new navy (the Imperial Iranian Navy) was laid.
Following Germany's invasion of the USSR in June 1941, Britain and the Soviet Union became allies. Both saw the newly opened Trans-Iranian Railroad as a strategic route to transport supplies from the Persian Gulf to the Soviet Union. In August 1941, Britain and the USSR invaded Iran and deposed Reza Shah Pahlavi in favor of his son Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi. Following the end of the Second World War, both countries withdrew their military forces from Iran.
Following a number of clashes in April 1969, international relations with Iraq fell into a steep decline, mainly due to a dispute over the Shatt al-Arab waterway in the 1937 Algiers Accord. Iran abrogated the 1937 accord and demanded a renegotiation which ended completely in its favor. Furthermore, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi embarked on an unprecedented modernisation program for the Iranian armed forces. In many cases Iran was being supplied with advanced weaponry even before it was supplied to the armed forces of the countries that developed it. During this period of strength Iran protected its interests militarily in the region: in Oman, the Dhofar Rebellion was crushed. In November 1971, Iranian forces seized control of three uninhabited but strategic islands at the mouth of the Persian Gulf; Abu Musa and the Tunb islands.
In the 1960s as Iran began to prosper from oil revenues, and diplomatic relations were established with many countries, Iran began to expand its military. In the 1960s it purchased Canada's fleet of 90 Canadair Sabre fighters armed with AIM-9 Sidewinder missiles. These aircraft were later sold to Pakistan.[28]
In the early 1970s the Iranian economy saw record years of growth thanks to booming oil prices. By 1976, the Iranian GDP was the largest in the Greater Middle East. The Shah (king) of Iran set about modernising the Iranian military, intent on purchasing billions of dollars worth of the most sophisticated and advanced equipment and weaponry through countries like the United States and the United Kingdom.[29]
Iran's purchases from the United States prior to the Iranian Revolution in 1979 included: 79 F-14 Tomcats, 400 M60 Patton tanks, 225 McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II fighter planes, including 16 RF-4E reconnaissance variants; 166 Northrop F-5 Tiger II fighters and 15 Northrop RF-5A reconnaissance planes; 12 Lockheed P-3 Orion maritime patrol aircraft and two decommissioned and modernised American destroyers, (USS Zellars and USS Stormes). As of 1976 Iran had acquired 500 M109 howitzers from the United States, 52 MIM-23 Hawk anti aircraft batteries with over 2000 missiles, over 2500 AGM-65 Maverick air to ground missiles and over 10,000 BGM-71 TOW missiles. Furthermore, Iran ordered hundreds of helicopters from the United States, notably 202 Bell AH-1J Sea Cobras, 100 Boeing CH-47C Chinooks and 287 Bell 214 helicopters.[30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37]
Iran's purchases from the United Kingdom prior to the 1979 revolution included 1 decommissioned and modernized British destroyer (HMS Sluys), 4 British-built frigates (Alvand-class frigate) and a vast array of missiles such as the Rapier and Seacat missile systems. Additionally Iran purchased several dozen hovercraft in the SR.N6 variety, 250 FV101 Scorpion light tanks and 790 Chieftain tanks.[36][38][39][40]
Iran also notably received much of there ground armored equipment from the Soviet Union. These deals were usually bartered using cheap oil and natural gas from the Iranian side in exchange for Russian expertise, training and equipment. In regards to military equipment Iran ordered ZSU-23-4 artillery vehicles, BTR 300 BTR-60's along with 270 BTR-50s and 300 BM-21 Grad multiple rocket launchers.[41]
The Imperial Iranian Army maintained the largest fleet of operational attack hovercraft in the world. These hovercraft's were obtained from various British and American companies and were later retrofitted with weaponry. In having this fleet the Iranian Army would be able to patrol shallow areas or the gulf and avoid minefields.[42]
The Iranian military never received many of the orders placed in the late 1970s due to the Iranian Revolution occurring in February 1979. The list below seeks to highlight some of the major orders that were placed prior the Iranian revolution but never were completed or delivered.
In the late 1970s, Iran accelerated it's orders from the United States in an attempt to outpace British, French and Chinese military orders. The Shah of Iran believed the Iran was destined to become a world super power, proudly led by one of the strongest militaries in the world. In regards to the Imperial Iranian Air Force from the USA in 1976 Iran placed for 300 F-16 Fighting Falcons, a further 71 Grumman F-14 Tomcats on top of the 79 that had arrived. All of these orders were due in 1980. In September 1976 Iran formally requested the purchase 250 F-18 Hornet, however this order would not have arrived until 1985. In addition to this in late 1977 Iran ordered 7 Boeing E-3 AWACS command and control aircraft and 12 Boeing 707 jets designed to refuel planes in midair.[43][44][45]
A massive order was made by the Iranian government in an attempt to modernize the Iranian Imperial Navy and give it capability to patrol the Caspian Sea, Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. The Iranian Navy had placed an order for 4 Kidd-class destroyers equipped with Standard missiles, Harpoon missiles, Phalanx CIWSs and Mark 46 torpedoes, 3 used retrofitted Tang-class submarines (these were transferred rather than sold to Iran from the American military) equipped with sub Harpoon missiles. In addition the navy sought to acquire 39 Lockheed P-3 Orion maritime reconnaissance planes for ocean surveillance and anti-submarine warfare.[46][47] Unlike the air force the Imperial Iranian Navy did not solely rely on American equipment and used a wide variety of suppliers. From Germany, Iran ordered 6 diesel type 209 submarines due to arrive in 1980 designed to protect Iran in the Indian Ocean.[48] From Italy, Iran ordered 6 Lupo-class frigates, capable of anti-submarine warfare and outfitted with Otomat missiles.[49] In 1978 Iran ordered 8 Kortenaer-class frigates from the Dutch, each one equipped with Mk. 46 torpedoes, Harpoon missiles and Sea Sparrow anti-aircraft missiles. In the same year Iran sought to order a further four Bremen-class frigates (similar in design to the Korteaer class).[50] Iran had entered discussions with Great Britain as early as the late 1960s to purchase a nuclear powered aircraft carrier that would give Iran amphibious attack capabilities in the Indian Ocean. While initially interested in purchasing one CVA-01 aircraft carrier, which was later on cancelled by the British, Iran expressed interest in the Invincible-class aircraft carriers.[51] Talks were in place for Iran to purchase 3 modified versions of these carriers however no official record stands to prove that such an order was placed.[52] From France, Iran ordered 12 La Combattante IIa-class fast attack craft equipped with Harpoon missiles. Of this order, approximately 6 were delivered and the subsequent 6 cancelled.
During this same time-frame in the 1970s the Imperial Iranian Army was making several advancements and placing massive orders to keep up with other divisions of the military. To reinforce the ground troops the Iranians ordered 500 M109 howitzer's, 400 M60 Patton A3 tanks were ordered from the Americans. The largest order was placed from the British for 2000 Chieftain tanks, which had been specifically designed for the Iranian Army.[52] Some other major equipment on order included hundreds of Russian BMP-1 outfitted with anti-tank missiles.[40] In addition the Iranians sought to strengthen their position in the Strait of Hormuz by setting up missile sites in the close vicinity.
When the Carter administration turned down Iran's request for nuclear capable missiles, they turned to the Israelis. They were working on the Project Flower ballistic missiles with Israel.[53]
In addition to these developments, the government of Iran had begun alongside American and British corporations to enter the licensed manufacturing of several different types of military equipment. Iran was very active in manufacturing Bell Helicopters, Boeing Helicopters and TOW missiles. As well many bases were under construction to house all of the military equipment. Two very notable and large bases that were to be built were in Abadan, where a massive infantry unit and airforce would serve to protect Iran from any Iraqi aggression, while the other in Chabahar was to house a port capable of housing submarines and aircraft carriers which would serve to allow Iran to patrol the Indian Ocean.[52]
At this time Iran was investing over $10bn in the construction of nuclear stations, 8 locations would be built by the Americans, 2 by the Germans and 2 by the French, for its 23,000 MW nuclear project which could produce enough uranium for 500-600 warheads.[54][55]
Iran contributed to United Nations peacekeeping operations. It joined the United Nations Operation in the Congo (ONUC) in the 1960s, and ten years later, Iranian troops joined the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF) on the Golan Heights.
-

Imperial Iranian Ministry of War
-

Imperial Iranian Ground Force (IIGF)
-

Imperial Iranian Navy (IIN)
-

Imperial Iranian Air Force (IIAF)
-
.svg.png)
Imperial Iranian Gendarmerie (IIG)
-

Shahrbani
-

Imperial Guard
Islamic Republic of Iran (1979 to present)
In 1979, the year of the Shah's departure and the revolution, the Iranian military experienced a 60% desertion from its ranks. Following the ideological principles of the Islamic revolution in Iran, the new revolutionary government sought to strengthen its domestic situation by conducting a purge of senior military personnel closely associated with the Pahlavi Dynasty. It is still unclear how many were dismissed or executed. The purge encouraged the dictator of Iraq, Saddam Hussein to view Iran as disorganised and weak, leading to the Iran–Iraq War. The indecisive eight-year war wreaked havoc on the region and the Iranian military, only coming to an end in 1988 after it expanded into the Persian Gulf and led to clashes between the United States Navy and Iranian military forces between 1987-1988. Following the Iran–Iraq War an ambitious military rebuilding program was set into motion with the intention to create a fully fledged military industry.
Regionally, since the Islamic Revolution, Iran has sought to exert its influence by supporting various groups (militarily and politically). It openly supports Hezbollah in Lebanon in order to influence Lebanon. Various Kurdish groups are also supported as needed in order to maintain control of its Kurdish regions. In neighbouring Afghanistan, Iran supported the Northern Alliance for over a decade against the Taliban, and nearly went to war against the Taliban in 1998.[56]
-

Ground Force of Iran
See also
References
- ↑ Parthia (2): the empire
- ↑ Ancient Syria:A Three Thousand Year History. Retrieved 5 June 2014.
- ↑ George Rawlinson, The Seven Great Monarchies of the Ancient Eastern World, 2002, Gorgias Press LLC ISBN 1-931956-48-0
- ↑ "Sassanids". Retrieved 5 June 2014.
- ↑ The Huns, Rome and the birth of Europe. Retrieved 5 June 2014.
- ↑ Milani A. Lost Wisdom. 2004 ISBN 0-934211-90-6 p.15
- ↑ Mohammad Mohammadi Malayeri, Tarikh-i Farhang-i Iran (Iran's Cultural History). 4 volumes. Tehran. 1982.
- ↑ ʻAbd al-Ḥusayn Zarrīnʹkūb (1379 (2000)). Dū qarn-i sukūt : sarguz̲asht-i ḥavādis̲ va awz̤āʻ-i tārīkhī dar dū qarn-i avval-i Islām (Two Centuries of Silence). Tihrān: Sukhan. OCLC 46632917. ISBN 964-5983-33-6. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Hatch Dupree, Nancy. "Sites in Perspective". An Historical Guide To Afghanistan.
- ↑ Britannica, Saffarid dynasty
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica, Online Edition, 2007, "Samanid Dynasty", LINK
- ↑ Daniel, Elton L. The History of Iran. p. 74.
- ↑ Busse, Heribert (1975), "Iran Under the Buyids", in Frye, R. N., The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs., Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, page 270: "Aleppo remained a buffer between the Buyid empire and Byzantium".
- ↑ "BUYIDS". Retrieved 10 November 2014.
- ↑ "Encyclopedia Iranica: "Deylamites"". Retrieved 10 November 2014.
- ↑ Islamic Central Asia: an anthology of historical sources, Ed. Scott Cameron Levi and Ron Sela, (Indiana University Press, 2010), 83; "The Ghaznavids were a dynasty of Turkic slave-soldiers..."
- ↑ C.E. Bosworth: The Ghaznavids. Edinburgh, 1963
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica, "Ghaznavid Dynasty", Online Edition 2007
- ↑ Black, Jeremy (2005). The Atlas of World History. American Edition, New York: Covent Garden Books. pp. 65, 228. ISBN 978-0-7566-1861-2. This map varies from other maps which are slightly different in scope, especially along the Mediterranean and the Black Sea.
- ↑ Grousset, Rene, The Empire of the Steppes, (New Brunswick:Rutgers University Press, 1988), 147.
- ↑ Grousset, Rene, The Empire of the Steppes, (Rutgers University Press, 1991)
- ↑ John Perry, "The Historical Role of Turkish in Relation to Persian of Iran", Iran & the Caucasus, Vol. 5, (2001), pp. 193-200.
- ↑ Bosworth in Camb. Hist. of Iran, Vol. V, pp. 66 & 93; B.G. Gafurov & D. Kaushik, "Central Asia: Pre-Historic to Pre-Modern Times"; Delhi, 2005; ISBN 81-7541-246-1
- ↑ C. E. Bosworth, "CHORASMIA ii. In Islamic times" in: Encyclopaedia Iranica (reference to Turkish scholar Kafesoğlu), v, p. 140, Online Edition: "The governors were often Turkish slave commanders of the Saljuqs; one of them was Anūštigin Ḡaṛčaʾī, whose son Qoṭb-al-Dīn Moḥammad began in 490/1097 what became in effect a hereditary and largely independent line of ḵǰᵛārazmšāhs." (LINK)
- ↑ Biran, Michel, The Empire of the Qara Khitai in Eurasian history, (Cambridge University Press, 2005), 44.
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica, "Khwarezm-Shah-Dynasty", (LINK)
- ↑ The History Files Rulers of Persia
- ↑ Cached
- ↑ Nixon, Kissinger, and the Shah: the origins of Iranian primacy in the Persian Gulf
- ↑ history.navy.mil: USS Stormes
- ↑ 2.^ navsource.org USS Zellars
- ↑ "Thirty minutes to choose your fighter jet: how the Shah of Iran chose the F-14 Tomcat over the F-15 Eagle". The Aviationist. Retrieved 2015-09-02.
- ↑ "The Imperial Iranian Ground Force..". aryamehr.org. Retrieved 2015-09-02.
- ↑ "IIAF - F-5". www.iiaf.net. Retrieved 2015-09-02.
- ↑ "Phantom with Iran". www.joebaugher.com. Retrieved 2015-09-02.
- 1 2 "LiveLeak.com - A brief history of Iran missile technology". Retrieved 2015-09-09.
- ↑ "[2.0] Second-Generation Cobras". www.airvectors.net. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
- ↑ "HMS Sluys, destroyer". www.naval-history.net. Retrieved 2015-09-02.
- ↑ Pike, John. "Alvand Class". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2015-09-02.
- 1 2 "The Imperial Iranian Ground Force..". aryamehr.org. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
- ↑ register http://armstrade.sipri.org/armstrade/page/trade register Check
|url=value (help). Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ "WRMEA - Iran's Alarming Military Buildup Transfixes Wary Gulf Neighbors". Retrieved 2015-09-09.
- ↑ "F-16 Air Forces - Cancelled Orders". www.f-16.net. Retrieved 2015-09-09.
- ↑ McGlinchey, Stephen (2014-06-05). US Arms Policies Towards the Shah's Iran. Routledge. ISBN 9781317697091.
- ↑ Tessmer, Arnold L. (1995-09-01). Politics of Compromise: NATO and AWACS. DIANE Publishing. ISBN 9780788121548.
- ↑ "DDG-993 KIDD-class - Navy Ships". fas.org. Retrieved 2015-09-09.
- ↑ Pike, John. "Iran Navy Modernization". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2015-09-09.
- ↑ Tan, Andrew T. H. (2014-05-22). The Global Arms Trade: A Handbook. Routledge. ISBN 9781136969546.
- ↑ "The ascendance of Iran : a study of the emergence of an assertive Iranian foreign policy and its impact on Iranian-Soviet relations. : Williams, James Harlon;Magnus, Ralph H. : Free Download & Streaming". Internet Archive. Retrieved 2015-09-09.
- ↑ CIA (23 March 1978). "National Intelligence Daily Cable" (PDF). Central Intelligence Agency.
- ↑ "THE HARRIER AIRCRAFT (Hansard, 24 April 1975)". hansard.millbanksystems.com. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
- 1 2 3 "The Iranian deals | The Guardian BAE investigation | guardian.co.uk". www.theguardian.com. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
- ↑ Times, Elaine Sciolino, Special To The New York (1986-04-01). "DOCUMENTS DETAIL ISRAELI MISSILE DEAL WITH THE SHAH". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
- ↑ Nuclear Iran: The Birth of an Atomic State By David Patrikarakos
- ↑ "This Page Has Been Deleted or Moved form Iran Map". Retrieved 10 November 2014.
- ↑ "Iran's gulf of misunderstanding with US". BBC News. 2006-09-25. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
Further reading
- Moshtagh Khorasani, Manouchehr (2006). Arms and Armor from Iran: The Bronze Age to the End of the Qajar Period. Legat Verlag. ISBN 978-3-932942-22-8.
- The Middle East: 2000 Years of History From The Rise of Christianity to the Present Day, Bernard Lewis, London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1995.
- Qajar Studies: War and Peace in the Qajar Era, Journal of the Qajar Studies Association, London: 2005.
- Moshtagh Khorasani, Manouchehr (March 2009). "Las Técnicas de la Esgrima Persa". Revista de Artes Marciales Asiáticas (in Spanish). 4 (1): 20–49.
- Moshtagh Khorasani, Manouchehr (2009). "Persian Firearms Part One: The Matchlocks". Classic Arms and Militaria. XVI (1): 42–47.
- Moshtagh Khorasani, Manouchehr (2009). "Persian Firearms Part Two: The Flintlock". Classic Arms and Militaria. XVI (2): 22–26.






