Morgan Park, Chicago
| Morgan Park | |
|---|---|
| Community area | |
| Community Area 75 - Morgan Park | |
|
Entrance to the George C. Walker Library. The building and many of the books the library contained when it opened were a gift of George C. Walker, then president of the Blue Island Land and Building Company (his predecessor being F.H. Winston, a prominent Chicago attorney[3]). The original portion of the building was designed by Charles Sumner Frost and cost $12,000. It opened on April 22nd, 1890, was expanded by an addition that quadrupled its space in 1929,[4] and received a major renovation in 1995. | |
 Location within the city of Chicago | |
| Coordinates: 41°41.4′N 87°40.2′W / 41.6900°N 87.6700°WCoordinates: 41°41.4′N 87°40.2′W / 41.6900°N 87.6700°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Illinois |
| County | Cook |
| City | Chicago |
| Neighborhoods |
list
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 3.19 sq mi (8.26 km2) |
| Population (2014) | |
| • Total | 23,204 |
| • Density | 7,300/sq mi (2,800/km2) |
| Demographics 2014[5] | |
| • White | 29.84% |
| • Black | 65.21% |
| • Hispanic | 2.68% |
| • Asian | 0.22% |
| • Other | 2.05% |
| Time zone | CST (UTC-6) |
| • Summer (DST) | CDT (UTC-5) |
| ZIP Codes | parts of 60643 and 60655 |
| Median income[6] | $56,886 |
| Source: U.S. Census, Record Information Services | |
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1930 | 12,747 | — | |
| 1940 | 15,645 | 22.7% | |
| 1950 | 22,618 | 44.6% | |
| 1960 | 27,912 | 23.4% | |
| 1970 | 31,047 | 11.2% | |
| 1980 | 29,315 | −5.6% | |
| 1990 | 26,740 | −8.8% | |
| 2000 | 25,226 | −5.7% | |
| 2010 | 22,544 | −10.6% | |
| [7] | |||
Morgan Park, located on the far south side of the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, is one of the city's 77 semi-official community areas.
Morgan Park
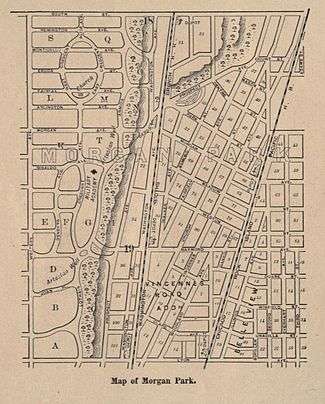
Comparing this with a modern map will show how the far northern ends of West Crescent and East Crescent (today Oakley and Bell Avenues, respectively) were vacated between Remington and Monticello Avenues (today 107th and 108th Places, respectively) to create Crescent Park.
Morgan Park is located south of the Beverly (properly Beverly Hills) neighborhood and shares a border at 107th St. with Beverly on the north, Halsted St. (north of 115th St.) and Ashland Ave. (south of 115th St.) on the east, 119th St. on the south, and (roughly) California Ave. on the west, and includes Mount Greenwood Cemetery. Beverly Hills and Morgan Park share the same ZIP code. The community was initially settled in the mid-19th century and known as North Blue Island because of its geographic relationship to the already established settlement of Blue Island to the south and because of its position on the blue island ridge. Thomas Morgan became the area's largest landholder [9] when he purchased all of the property between what is today 91st St. on the north, 119th St. on the south, Western Avenue on the west, and roughly Vincennes Ave. to the east. Morgan was born in Surrey, England, and came to the United States in 1843, briefly settling in Albany, New York. He was the son of a London banker and was left a large fortune by his father which he used to establish himself on the ridge in 1844. Here he cleared trees and operated a cattle and sheep ranch for the next quarter of a century. Morgan's son Henry was for a time the village president of Hyde Park before that community was annexed to the City of Chicago in 1889.[10] In 1869, the Blue Island Land and Building Company purchased three thousand acres of this property from the Morgan family and laid out streets, planted thousands of trees,[11] and built houses for those who were attracted to the bucolic atmosphere of the new community. The goal of the organization was to create a suburban community "..free from smoke and other nuisances that [were] becoming more and more intolerable in the city".[12]
Both the president and the treasurer of the Blue Island Land and Building Company were executives of the Rock Island Railroad at the time the former company was incorporated, and they immediately used their influence to have a spur line built to serve the new community.[13] This arrangement lasted until 1889, when the "Suburban Line" as it exists today was built between Gresham and the Vermont Street station in Blue Island, at which time the dummy line, as it was called, was removed, much to the consternation of those who lived immediately nearby.[14] At this point Morgan Park received three handsome passenger depots (at 107th St., 111th St., and 115th St.), with the 111th Street station being an elaborate Queen Ann structure [15] designed by John T. Long [16] that is sited immediately east of Bohn Park. Morgan Park (and especially the area of it depicted in western part of the map included with this article) is primarily an upper middle-class community, with a housing stock to reflect this demographic, although there are several estate-sized houses on the ridge at Longwood Drive. Many of the buildings in the neighborhood were designed by notable architects, including Dwight Perkins, Dankmar Adler, Murray Hetherington, John Hetherington, Palliser, Palliser & Co., Normand S. Patton and Harry H. Waterman. The community is home to the Beverly Arts Center.
Because of its ecclesiastical associations (George Walker's father was affiliated with the old University of Chicago and Walker himself would play an influential role in the creation of the present University of Chicago, both of which were founded by organizations with Baptist connections) Morgan Park prohibited the sale of alcohol east of Western Avenue when it was incorporated as a village in 1882 - a ban which stands to this day. The suburb became a city neighborhood when it was annexed in 1914.[17]
Rotary International
Rotary International was formed in Morgan Park at the home of Paul P. Harris at 10856 Longwood Drive, and today the house is owned and maintained by that organization as a memorial to him.[18]
Government and infrastructure
The United States Postal Service operates the Morgan Park Post Office.[19]
Education




There was a serious attempt made by the Blue Island Land and Building Company to have Morgan Park become a great center of learning, an effort which was successful to a degree in that it brought to the community Morgan Park Academy (founded in 1873 as Mt Vernon Military & Classical Academy), the Chicago Female College (established 1875), Baptist Union Theological Seminary (which relocated to Morgan Park from Chicago in 1877 and where the noted educator William Rainey Harper was granted a professorship at the age of twenty-three[22]), and the American Institute of Hebrew.[23]
There was also an effort made in 1888 to bring the new University of Chicago to the community, although that project developed in another direction when its primary benefactor, John D. Rockefeller, indicated a preference for the significantly larger site at 57th Street and Ellis Avenue in Hyde Park that was donated by Marshall Field.[24] It was thought by virtue of its size and its location in what was then the city proper that that property would allow for a much grander vision, and the "proposals (in Morgan Park) were at once laid aside in view of the greater plan".[25] When the university opened in 1892, it absorbed the Chicago Female College and the Baptist Union Theological Seminary (the latter then becoming the university's divinity school[26]), and for the next fifteen years Morgan Park Academy became a preparatory school for the university (at which time it was known as Morgan Park Academy of the University of Chicago) until the death of U of C president William Rainey Harper in 1906 ended the university's sponsorship and it passed into other hands.[27] The school continues to operate today serving a highly diverse student body. It was recently ranked among the top private schools in Chicago.[28]
Morgan Park High School, Clissold School, St. Walter Elementary School, and Esmond Elementary School (one of the Chicago Public School's oldest school buildings, having been being built in the 1890s, and added to in the early years of the 20th century and again in the 1970s) represent the educational institutions that today call Morgan Park home.
In 1988 the Walgreen family donated their home on the ridge at 116th & Longwood Drive to the Mercy Home for Girls.[29]
Horse Thief Hollow
In the early 1840s, a small section of what was to become southern Morgan Park had an unsavory reputation with the settlers in the region.[30] What follows are the recollections of Isaac T. Greenacre, an early 19th century resident who settled at the north end of the ridge. The area he describes below is today what is roughly the stretch of Vincennes Road from 115th Street to 121st St.:
"On the edge of the hill on which Morgan Park is situated, and a little south, is a deep and exceedingly steep ravine. This in early times was covered with long grass and thick underbrush, and was not only a very discreet hiding place, but a very formidable fortress for horse thieves. These notable gentry were rather nocturnal in their habits, as they traveled during the night and by day were wont to refresh themselves in Horse Thief Hollow. I imagine it must have been a solitary place as the long grass, thick underbrush, and the forest overhead must have entirely excluded the sunlight from it. The farmers are confident of the character of this den, having found in it bags of oats and other commodities which proved the use of the ravine for horse stealing. The bottom of the ravine was trampled into a mire by horses' hoofs, and once in a while they would find a horse shoe. The farmers have watched these gentry and proved to themselves the purpose of their frequent visitations. The horse thieves generally traveled by the aid of a buggy, in which they kept all the utensils necessary for their business."[31]
References
- ↑ "Advertisement for the Blue Island Land and Building Company". Chicago Daily Tribune: 1. September 27, 1872.
- ↑ "Citizens to Hail Library Jubilee at Morgan Park - Branch's History Partly that of Whole Area". Chicago Daily Tribune: SW2. April 21, 1940.
- ↑ "Advertisement for the Blue Island Land and Building Company". Chicago Daily Tribune: 1. September 27, 1872.
- ↑ "Citizens to Hail Library Jubilee at Morgan Park - Branch's History Partly that of Whole Area". Chicago Daily Tribune: SW2. April 21, 1940.
- ↑ Biasco, Paul. "Logan Square Hispanics Vanishing As Neighborhood Becomes More White". Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ Paral, Rob. "Chicago Census Data". Retrieved 21 September 2012.
- ↑ Paral, Rob. "Chicago Community Areas Historical Data". Retrieved 3 September 2012.
- ↑ Sinkevitch, Alice and Laurie McGovern Petersen, editors (2004). AIA Guide to Chicago. Fort Washington: Harvest Books. p. 473. ISBN 0156029081.
- ↑ Keating, Ann Durkin (2008). Chicago Neighborhoods and Suburbs: A Historical Guide. Chicago, London: University of Chicago Press. p. 216. ISBN 0226428834.
- ↑ "Washington Heights". Chicago Daily Tribune: 1. April 29, 1869.
- ↑ Maloney, Cathy Jean (2008). Chicago Gardens - The Early History. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. p. 175. ISBN 0-226-50234-1.
- ↑ The Blue Island Land & Building Company (1886). Suburban Homes - Morgan Park. Chicago: American Publication Society of Hebrew. p. 3.
- ↑ "Death Claims James Morgan - Millionaire Pioneer of Hyde Park Expires at his home in East End Avenue - TO BE BURIED TOMORROW - Half a Century of his Life Devoted to Business Activity in Chicago". Chicago Daily Tribune: 13. November 27, 1898.
- ↑ "EXCITED SUBURBANITES - WASHINGTON HEIGHTS OBJECTS TO FOOTING IT TO THE STATION - Rock Island Proposes to Moving the Dummy Tracks a Half a Mile West - Residents Say it is a Real Estate Scheme and Get an Injunction". Chicago Daily Tribune: 2. December 4, 1888.
- ↑ "Metra Rock Island District - 111th St. Morgan Park". Commuter Rail Division of the Regional Transportation Authority. Retrieved 2013-08-29.
- ↑ Sinkevitch, Alice (2004). AIA Guide to Chicago - Second edition. Orlando: HarcourtBooks. p. 474. ISBN 0-15-602908-1.
- ↑ "Morgan Park". The Newberry Library. Retrieved 2013-09-02.
- ↑ Anderson, Jon (July 14, 2005). "Hilltop mansion holds history of a fellowship; Century-old Rotary International took shape in gatherings at a picturesque and inviting home on the Far South Side, now preserved as a legacy to its founder". Chicago Tribune: Section 2c p.3.
- ↑ "Post Office™ Location - MORGAN PARK." United States Postal Service. Retrieved on April 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Palliser's Cottage Home No. 35". City of Chicago Department of Planning and Development, Landmarks Division. 2003. Retrieved 2013-09-01.
- ↑ Palliser, Palliser Company, Architects (1878). Palliser's American Cottage Homes. Bridgeport: Palliser, Palliser & Co. pp. Design 35.
- ↑ "The University of Chicago Centennial Catalogues - The Presidents of the University of Chicago - a Centennial View - William Rainey Harper". Retrieved 5 September 2013.
- ↑ The Blue Island Land & Building Company (1886). Suburban Homes - Morgan Park. Chicago: American Publication Society of Hebrew. pp. 8–11.
- ↑ "SITE FOR CHICAGO'S UNIVERSITY - A Tract of Land Donated by Marshall Field - Money That Was Collected". Chicago Daily Tribune: 6. January 19, 1890.
- ↑ Goodspeed, Thomas Wakefield (1916). A History of the University of Chicago - The First Quarter-Century. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. p. 46.
- ↑ Harper, William Rainey (1903). The President's Report - Administration - The Dicennial Publications - First Series Volume 1. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 215.
- ↑ Judson, Harry Pratt (1908). The President's Report - July 1906-July 1907 - With Publications of Members of the University. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 11.
- ↑ Johnson, Geoffrey and Kaitlin Peterson (November 11, 2011). "The Top Private Schools in Chicago and the Suburbs". Chicago.
- ↑ Mullen, William (August 12, 1990). "Mission of Mercy - A home away from harm for boys and girls who want a second chance". Chicago Tribune: 14.
- ↑ Schapper, Ferdinand (1917). Southern Cook County and History of Blue Island before the Civil War. Manuscript. p. 104.
- ↑ Volp, John Henry (1938). The First Hundred Years - 1835-1935, an Historical Review of Blue Island, Illinois. Blue Island: Blue Island Publishing. pp. 38–39.



