Mosquito Coast
| Mosquito Coast | ||||||||||
| English and British protectorate (1638–1787, 1844–1860) Spanish Colony (1787–1800, de jure 1819) Autonomous territory of Nicaragua (1860–1894) | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
 | ||||||||||
| Capital | Sandy Bay Bluefields (after 1787) | |||||||||
| Languages | Miskito English Spanish | |||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||
| King | ||||||||||
| • | c.1650–1687 | Oldman (first known) | ||||||||
| • | 1842–1860 | George Augustus Frederic II (last) | ||||||||
| Hereditary Chief | ||||||||||
| • | 1860–1865 | George Augustus Frederic II (first) | ||||||||
| • | 1890–1894 | Robert Henry Clarence (last) | ||||||||
| History | ||||||||||
| • | Established | Early 17th century | ||||||||
| • | Disestablished | 1894 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Today part of | | |||||||||
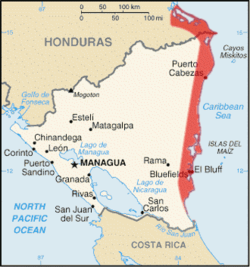
The Mosquito Coast, also known as the Miskito Coast, historically comprised an area along the eastern coast of present-day Nicaragua and Honduras. It formed part of the Western Caribbean Zone. It was named after the local Miskito Amerindians and was long dominated by British interests. The Mosquito Coast was incorporated into Nicaragua in 1894; however, in 1960, the northern part was granted to Honduras by the International Court of Justice.[1]
The Mosquito Coast was generally defined as the domain of the Mosquito or Miskito Kingdom and expanded or contracted with that domain. During the nineteenth century, the question of the kingdom's borders was a serious issue of international diplomacy between Britain, the United States, Nicaragua, and Honduras. Conflicting claims regarding both the kingdom's extent and arguable nonexistence were pursued in diplomatic exchanges.[2] The British and Miskito definition applied to the whole eastern seaboard of Nicaragua and even to La Mosquitia in Honduras: i.e., the coast region as far west as the Río Negro or Tinto. The Mosquito Coast in the later part of the century came to be considered as the narrow strip of territory, fronting the Caribbean Sea and extending from about 11°45’ to 14°10’ N. It stretched inland for an average distance of 60 kilometers (40 mi), and measured about 400 kilometers (225 mi) from north to south. In the north, its boundary skirted the Wawa River; in the west, it corresponded with the eastern limit of the Nicaraguan highlands; in the south, it followed the Río Rama. The chief modern towns are Bluefields, the largest town and capital of Nicaragua's South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region; Magdala on Pearl Cay; Prinzapolka on the river of that name; Wounta near the mouth of the Kukalaya; and Karata near the mouth of the Coco River.
History
Before the arrival of Europeans in the region, the area was divided into a large number of small, egalitarian groups, possibly speaking languages related to Sumu and Paya. Columbus visited the coast briefly in his fourth voyage. Detailed Spanish accounts of the region, however, only relate to the late 16th and early 17th centuries. According to their understanding of the geography, the region was divided between two "Provinces" Taguzgalpa and Tologalpa. Lists of "nations" left by Spanish missionaries include as many as 30 names, though careful analysis of them by Karl Offen suggests that many were duplicated and the regional geography included about a half dozen entities speaking related but distinct dialects occupying the various river basins of the region.[3]
Attempted Spanish settlement
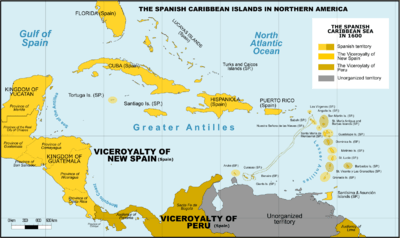
During the 16th century, Spanish authorities issued various licenses to conquer Taguzgalpa and Tologalpa in 1545, 1562, 1577 and 1594, but there is no evidence that any of these licenses resulted in even brief settlements or conquests. The Spanish were unable to conquer this region during the 16th century and in the 17th century sought to "reduce" the region through missionary efforts. These included several attempts by Franciscans between 1604 and 1612; another one led by Fray Cristóbal Martinez in 1622, and a third one between 1667 and 1675. None of these efforts resulted in any lasting success.[4]
Because the Spanish failed to have significant influence in the region, it remained independent of outside control. This allowed the indigenous people to continue their traditional way of life and to receive visitors from other regions. English and Dutch privateers who preyed on Spanish ships soon found refuge in the Mosquito Coast.
British contact and recognition of the Mosquito Kingdom
| Mosquito Kingdom | ||||||||||||
| Protectorate of the United Kingdom | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
| Anthem God Save the King/Queen | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Sandy Bay (King's residence) | |||||||||||
| Languages | Miskito English | |||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||||
| King | ||||||||||||
| • | c.1650-1687 | Oldman (first known) | ||||||||||
| • | 1776-1801 | George II Frederic (last) | ||||||||||
| Superintendent of the Shore | ||||||||||||
| • | 1749-1759[5] | Robert Hodgson, Sr. (first) | ||||||||||
| • | 1775-1787 | James Lawrie (last) | ||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||
| • | Arrival of the Providence Island Company | 1630 | ||||||||||
| • | British ally | 1638 | ||||||||||
| • | British protectorate | 1740 | ||||||||||
| • | Convention of London | 1786 | ||||||||||
| • | British evacuation | 1787 | ||||||||||
| Currency | Pound sterling | |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
Although the earliest accounts do not mention it, a political entity of uncertain organization, but probably not very stratified, which the English called the "Mosquito Kingdom" was present on the coast in the early seventeenth century. One of the kings of this polity visited England around 1638 at the behest of the Providence Island Company, and sealed an alliance with Great Britain.
In subsequent years, the kingdom stood strongly against any Spanish incursions in their region, and were prepared to offer rest and asylum to any anti-Spanish groups that might come to their shores. At the very least English and French privateers and pirates did visit there, taking in water and food. A detailed account of the kingdom written by a buccaneer known only as M. W. describes its organization as being fundamentally egalitarian, with the king, and some officials (usually called "Captains" in that period but later being more elaborate) being primarily military leaders, but only in time of war.
Early British alliance
The first British contacts with the Mosquito region started around 1630, when the agents of the English chartered Providence Island Company—of which the Earl of Warwick was chairman and John Pym treasurer—occupied two small cays and established friendly relations with the local inhabitants. Providence Island, the company's main base and settlement, entered into regular correspondence with the coast during the decade of company occupation, 1631–41.[6]
The Providence Island Company sponsored the Miskito's "King's Son" visit to England during the reign of Charles I (1625–49). When his father died, this son returned home and placed his country under English protection.[7] Following the capture of Providence Island by Spain in 1641, England did not possess a base close to the coast. However, shortly after the English captured Jamaica in 1655, they recommenced relations with the coast, and Oldman went to visit England. According to the testimony of his son Jeremy, taken around 1699, he was received in audience by "his brother king," Charles II and was given a "lac'd hat" and a commission "to kindly use and relieve such straggling Englishmen as should chance to come that way."[8]
Emergence of the Mosquitos Zambos (Miskito Sambu)

While accounts vary, the Miskito Sambu appear to be descended from the survivors of a shipwrecked slave ship who reached this area in the mid-seventeenth century. These survivors intermarried with the local Miskito people and produced mixed-race offspring. They gradually adopted the language and much of the culture of their hosts. The Miskito Sambu settled near the Wanks (Coco) River. By the late 17th century, their leader held the office of General with jurisdiction over the northern portions of the Miskito Kingdom. In the early eighteenth century, they managed to take over the office of King, which they held for at least the rest of the century.
In the late 17th and early 18th centuries, Miskitos Zambos began a series of raids that attacked Spanish-held territories and still independent indigenous groups in the area. Miskito raiders reached as far north as the Yucatán, and as far south as Costa Rica. They sold many of the captives they took as slaves to English or other British merchants; the slaves were transported to Jamaica to work on sugar plantations.[9] Through such raiding, the Zambo gained a more dominant position and the king's domain was inhabited primarily by Zambos. They also assisted the government of Jamaica in hunting down Maroons in the 1720s.[10]
Sociopolitical system
Although English accounts referred to the area as a "kingdom," it was loosely organized. A description of the kingdom, written in 1699, notes that it occupied discontinuous areas along the coast. It probably did not include a number of settlements of English traders.[11] Although English accounts refer as well to various noble titles, Miskito social structure does not appear to have been particularly stratified. The 1699 description noted that people holding titles such as "king" and "governor" were only empowered as war leaders, and did not have the last word in judicial disputes. Otherwise, the author saw the population as living in an egalitarian state.[12]
M. W. mentioned titled officers in his account of 1699, but later sources define these superior offices to include the king, a Governor, and a General. In the early 18th century, the Miskito kingdom became organized into four distinct clusters of population, centered on the banks of the navigable rivers. They were integrated into a single, if loosely structured political entity. The northern portions were dominated by Sambus and the southern ones by Tawira Miskitos.[13] The King, whose domain lay from the Wanks River south to the Rio Kukalaya, including the king's residence near Sandy Bay, was a Sambu, as was the General, who ruled the northern portions of the kingdom, from the Wanks River to nearly Trujillo. The Governor, who was a Tawira, controlled the southern regions, from the Cucalaya River to Pearl Key Lagoon. In the later 18th century (post 1766), another title, Admiral, was recorded; this man was also a Tawira, controlling a region on the extreme south from Pearl Key Lagoon down to around Bluefields.[14]
British settlement
The Miskito king Edward I and the British concluded a formal Treaty of Friendship and Alliance in 1740, and Robert Hodgson, Senior was appointed as Superintendent of the Shore.[15] The language of the treaty includes what amounts to a surrender of sovereignty, and is often taken by historians as an indication that a British protectorate was established over the Miskito Kingdom.
Britain's primary motive and the most immediate result of the treaty was to secure an alliance between the Miskito and British for the War of Jenkin's Ear, and the Miskito and British cooperated in attacks on Spanish settlements during the war. This military cooperation would prove important as Miskito forces were vital to protecting not only British interests in the Miskito Kingdom, but also for British holdings in British Honduras (now Belize).
A more lasting result of this formal relation was that Edward I and other Miskito rulers who followed him allowed the British to establish settlements and plantations within his realm, and issued the first land grants to this effect in 1742. British settlement concentrated especially in the Black River area, Cape Gracias a Dios, and Bluefields. The British plantation owners used their estates to grow some export crops and as bases for the exploitation of timber resources, especially mahogany. Most of the labor on the estates was supplied by African slaves and by indigenous slaves captured in Miskito and British raids into Spanish territory. By 1786, there were several hundred British residents on the shore and several thousands slaves, mostly African.
The Miskito kings received regular gifts from the British in the form of weapons and consumer goods, and provided security against slave revolts and capturing runaways.
British evacuation
Spain, which claimed the territory, suffered considerably from the Miskito attacks which continued during peacetime. When the American Revolutionary War broke out, Spanish forces attempted to eliminate the British presence, seizing the settlement at Black River, and driving British settlers from the isle of Roatán; however, this ultimately failed when armed settlers led by the Anglo-Irish soldier Edward Despard retook the settlements.
Although Spain had been unable to drive the British from the coast or occupy any position, in the course of the diplomatic negotiations following the war, Britain found itself making concessions to the Spanish. In the 1786 Convention of London, Britain agreed to evacuate British settlers and their slaves from the Mosquito Coast to their as yet informal colony in what was to become British Honduras (now Belize); later treaties recognized Britain's commercial, but never territorial rights in the region.[16] Some of the settlers and their slaves remained after they swore loyalty to the King of Spain, especially in Bluefields.[17]
Spanish interlude
Government reorganization and Spanish settlement
The Mosquito Coast was initially annexed (or from the Spanish point of view, re-annexed) to the Captaincy General of Guatemala. Since the beginning however, poor land communication with Guatemala City made easier for the Miskito elites to sail to Cartagena de Indias and swear fealty to Spain before the Viceroy of New Granada instead. Viceroy Francisco Gil de Taboada even suggested that government over the Mosquito Coast should be transferred to Havana, Cuba, mirroring the long-standing relation that the Mosquito Kingdom had earlier with British Jamaica, but this idea was rejected by the Spanish Crown. Guatemala protested the perceived unruliness of the Spanish appointed governor at Bluefields, who was none other but a former British Superintendent of the Mosquito Coast who had sworn recent fealty to Spain, Robert Hodgson Jr., but his loyalty and good work were defended by the New Granadan Viceroy José Manuel de Ezpeleta, who succeeded Taboada in 1789 and considered that Hodgson's influence among the Miskito was vital to avoid a revolt.[18] Hodgson Jr. was the son of Robert Hodgson Sr., the first British appointed Superintendent in 1749-1759, and he had occupied himself this post from 1767 to 1775, when his political enemies persuaded Lord George Germain to replace him with James Lawrie, the last British Superintendent before the evacuation and a declared adversary of Hodgson.[5]
The Spanish hoped to win over support of the Miskito elite by offering presents like the British had and educating their youth in Guatemala, as many Miskito had been educated previously in Jamaica. Catholic missionaries also travelled to the Coast with the aim of converting the native population in this period.[18] The acceptance of the new order was unequal and often influenced by the underlying tensions within the own Miskito elites, divided between the northern regions controlled by the Sambu, loyal to King George II Frederic who remained himself friendly to the British, and the Tawira southerners aligned with Admiral Briton, who developed closer ties with Spain and adopted the name Don Carlos Antonio Castilla after his own conversion.[18]
The Spanish also sought to occupy the positions formerly held by British settlers with their own colonists. Beginning in 1787, around 1,200 settlers were brought from the Iberian Peninsula and the Canary Islands. They settled in Sandy Bay, Cape Gracias a Dios and Black River, but not in the new capital Bluefields.[19]
Miskito revolt
The new colony suffered setbacks as a result of many of the settlers dying en route and the Miskito Crown showing its dissatisfaction with the gifts offered by the Spanish. The Miskito resumed trade with Jamaica and, when news of another Anglo-Spanish War arrived in 1797, George II raised an army to attack Bluefields, deposing Hodgson, and drove the Spanish out of the kingdom on September 4, 1800.[20][21] However, the king died suddenly in 1801. According to British George Henderson, who visited the Mosquito Coast in 1804, many in the kingdom believed that George II had been poisoned by his brother Stephen as part of a deal with the Spanish. In order to prevent Stephen from seizing power for himself, the General Robinson spirited George II's young heir George Frederic Augustus I to Jamaica by way of Belize and established a regency in his name.[22]
With Spanish power over the Mosquito Coast vanished and British influence rapidly returning, the Captaincy General of Guatemala sought full control of the shore to Spain. The Colombian Ricardo S. Pereira, writing in 1883, considered this act a miscalculation on the part of the Real Audiencia of Guatemala: had they simply raised an army and marched on the Mosquito Coast, nobody would have questioned that the area was part of the Captaincy General once Spanish power was fully restored. Instead, the Spanish government heeded the old advice exposed by Gil de Taboada and Ezpeleta, and decided against Guatemala's request on November 30, 1803, reaffirming the control of the Viceroyalty of New Granada over the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina (used by New Granadan coast guards as a base against British privateers, often coming from the Mosquito Coast itself) and transferring sovereignty over the Mosquito Coast to New Granada for considering the area dependent of San Andrés. While Spanish rule was never restored over the Mosquito Coast (instead, the British occupied the Archipelago itself in 1806, during the course of the war against Spain), the Royal Decree of 1803 became the reason for territorial disputes between the United Provinces of Central America and Gran Colombia after Latin American independence, and between Nicaragua and Colombia for the rest of the 19th century.[23]
In the mean time George II's brother Stephen made some overtures to Spain, who reciprocated by calling Stephen king and giving him the traditional gifts (albeit in less frequency than to George II),[17] but he later changed allegiances and raided Spanish held territory. In 1815 Stephen, styling himself "King Regent […] of the Shore", and 33 other Miskito notables gave their "consent, assent, and declaration to, for, and of" George Frederic Augustus I as their "Sovereign King".[24] His coronation in Belize on January 16, 1816,[25] in a deliberate move to secure British support, marked the end of the regency. Meanwhile, Spain lost rule over New Granada in 1819 and over Central America in 1821, when the First Mexican Empire was proclaimed.
Renewed British presence
As internecine conflicts seized both Gran Colombia and Central America post-independence, the potential of any regional power to threaten the Miskito kingdom declined. Miskito Kings renewed their alliance with Great Britain, and Belize replaced Jamaica as the principal British connection to the kingdom. George Frederic Augustus I's 1816 coronation in Belize was imitated by his successor Robert Charles Frederic in 1845.
Economic expansion

The Miskito kings allowed the settlement of foreigners in their lands as long as their sovereignty was respected, opportunity that was seized by British merchants and Garifuna people from Trujillo, Honduras. Between 1820 and 1837 the Scottish con man Gregor MacGregor pretended to have been named "Cacique of Poyais" by George Frederic Augustus I and sold forged land rights to eager settlers and investors in Britain and France. Most settlers suffered from the lack of infrastructure and died from tropical diseases, MacGregor having led them to believe that the area was already developed and just in need of skilled workers. In the 1830s and 40s King Robert Charles Frederic also appointed small traders, notably William Hodgson and brothers Peter and Samuel Shepherd, as his agents to administer his claims to tribute and taxes from lands as far south as Panama.[26][27]

At the same time, the mahogany trade peaked in Europe, but the supply in Belize, a main exporter, was becoming scarce. The Miskito Kingdom became an alternative source to Belize-based traders and wood cutting companies, who acquired concessions and land grants from Robert Charles Frederic. In 1837 Britain formally recognized the Mosquito Kingdom as an independent state, and took diplomatic measures to prevent the new nations that left the imploding Federal Republic of Central America in 1838-1841 from interferring with the kingdom.[28][29]
The expansion of the economy attracted and benefitted from the arrival of capital from the United States, and immigrants from the States, the West Indies, Europe, Syria and China.[17] Especially abundant was the immigration of Afro-Caribbeans following the abolition of slavery in the British and French Caribbean in 1841, who settled mainly in and around Bluefields, merging with the descendants of the slaves that had not been evacuated in 1786 and giving origin to the Miskito Coast Creoles. Because of their greater knowledge of English, the Creoles soon became the workers most sought by foreign companies, occupying the intermediate levels in the businesses and relegating the native Miskitu to the worst paid occupations at the base.[17]
In August 1841, a British ship, without knowledge of London, carried the Miskito King Robert Charles Frederic and the British Governor of Belize, Alexander MacDonald, to occupy Nicaragua's only Caribbean port in San Juan del Norte, placed at the mouth of the San Juan River and likely endpoint of a possible future transoceanic canal through Nicaragua, and claimed it for the Mosquito Kingdom. The commander of the port was kidnapped and abandoned in a deserted beach, and the civilian population was told to leave the place by March 1842. The Nicaraguan government protested and the British did not carry on the threatened evacuation of the port, but neither did they take action against MacDonald for the incident.[16]
Second British protectorate and American opposition
| Mosquito Kingdom | ||||||||||||||
| Protectorate of the United Kingdom | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Anthem God Save the Queen | ||||||||||||||
| Capital | Bluefields[17] | |||||||||||||
| Languages | English Miskito | |||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||||||
| King | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1842-1860 | George Augustus Frederic II | ||||||||||||
| Consul-General[16] Consul (after 1851) |
||||||||||||||
| • | 1844-1848 | Patrick Walker (first)[16] | ||||||||||||
| • | 1849-1860 | James Green (last)[30] | ||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||
| • | Protectorate declared | 1844 | ||||||||||||
| • | Annexation of San Juan del Norte | 1848 | ||||||||||||
| • | Bombardment of San Juan del Norte | 1854 | ||||||||||||
| • | Treaty of Managua | January 28, 1860 | ||||||||||||
| Currency | Pound Sterling | |||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
In 1844 the British government declared a new protectorate over the Mosquito Kingdom and appointed a Consul-General of the Mosquito Coast, Patrick Walker with seat in Bluefields. The proclamation was motivated by the state of anarchy in the Mosquito Kingdom after the death of Robert Charles Frederic, but also by the impending American annexation of Texas and the British desire to build a canal through Central America before the United States did.[16]
The protectorate was claimed to extend from Cape Honduras in the north to the mouth of the San Juan River in the south, including San Juan del Norte. Nicaragua protested again and sent forces to San Juan del Norte, which the Miskito King George Augustus Frederic II replied to with an ultimatum demanding all Nicaraguan forces to leave before January 1, 1848. Nicaragua appealed to the United States, but the Americans, then at war with Mexico, did not answer. After the ultimatum expired, Miskito-British forces led by the King and Patrick Walker, and backed by two British warships, seized San Juan del Norte. They also destroyed Serapaqui, where the British prisoners captured during a first attempt on San Juan del Norte were interned, and advanced to Lake Nicaragua, during which Walker drowned. On March 7 Nicaragua signed a peace treaty where it ceded San Juan del Norte to the Mosquito Kingdom, who renamed it Greytown after Charles Edward Grey, governor of Jamaica.[16]
With the Mexican-American War concluded, the new US delegate in Central America, E. G. Squier, tried to get Nicaragua, El Salvador and Honduras to form a common front against the British, who were now threatening to annex Tiger Island (El Tigre) in Honduras' Pacific coast. After British and American forces nearly clashed in El Tigre, both governments reprimanded the commanders of their forces there and concluded the Clayton-Bulwer Treaty on April 18, 1850.[16] In this document the two powers pledged themselves to guarantee the neutrality and equal use of the proposed canal, and to not "occupy, or fortify, or colonize, or assume or exercise any dominion over Nicaragua, Costa Rica, the Mosquito Coast or any part of Central America", nor make use of any protectorate or alliance, present or future, to such ends.[31]
The United States assumed that this meant the immediate British evacuation of the Mosquito Coast, while the British argued that it only bound them to not expand further in Central America and that both the 1844 protectorate and the 1848 peace treaty were still valid. On November 21, the American steamer Prometheus was fired upon by a British warship for not paying port tariffs at Greytown. One of the passengers was Cornelius Vanderbilt, business magnate and one of the richest people in the United States. The British government apologized after the United States sent two armed sloops to the area.[16]
More incidents happened in the following years. In 1852, Britain occupied the Bay Islands off the coast of Honduras and rebuffed the American protests claiming that they had been part of Belize before the treaty. The American representative in Nicaragua, Solon Borland, considered the treaty breached and argued openly for the US annexation of Nicaragua and the rest of Central America, for which he was forced to resign. In 1853 the buildings of the US-owned Accessory Transit Company in Greytown were looted and destroyed by the locals. In 1854, an American steamer captain killed a Greytown Creole, and Borland, who had remained in Greytown after his resignation, stopped the arrest for murder by threatening the marshal and his men with a rifle, arguing that they had no power to arrest an American citizen. Though he held no office, Borland ordered 50 American passengers bound for New York to remain on land and "protect US interests" while he sailed to the United States for help. In an example of gunboat diplomacy, the Americans sent then the USS Cyane and demanded 24,000 dollars in damages, an apology and a pledge of good behavior in the future. When the terms weren't met, the crew bombarded Greytown, then landed and burnt the town to the ground. Damage was extensive but no one was killed. With its attention seized by the ongoing Crimean War and the firm opposition of Britain's merchant class to a war with the United States, the British government only protested and demanded an apology that was never received.[16]
By 1859 British opinion was no longer supportive of their nation's presence in the Mosquito Coast. The British government returned the Bay Islands and ceded the northern part of the Mosquito Coast to Honduras, negotiating with Guatemala to enlarge the British territory in Belize as compensation. The next year, Britain signed the Treaty of Managua, ceding the rest of the Mosquito Coast to Nicaragua.[16]
Arrival of the Moravian Church
In the 1840s, two British citizens who travelled Europe advertizing the sale of land in Cabo Gracias a Dios attracted the interest of Prince Charles of Prussia. Charles' first plan was to establish a Prussian settlement in the area and sent three German merchants to study this possibility on the ground. Their dictamen was against colonization, but their suggestion to evangelize the Mosquito Coast was taken up by the Prince of Schönburg-Waldenburg, who delegated the task in the Moravian Church. The first missionaries arrived in 1848 with a letter of recommendation from Lord Palmerston and began to work in 1849 in Bluefields, targeting the royal family and the Creoles before expanding to the rest of the Kingdom.[17]
Treaty of Managua
| Mosquito Reserve | ||||||||||
| Reserva Mosquitia | ||||||||||
| Autonomous territory of Nicaragua | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Anthem Hermosa Soberana | ||||||||||
| Capital | Bluefields | |||||||||
| Languages | Spanish Miskito | |||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||
| Hereditary Chief | ||||||||||
| • | 1860-1865 | George Augustus Frederic II (first) | ||||||||
| • | 1890-1894 | Robert Henry Clarence (last) | ||||||||
| History | ||||||||||
| • | Treaty of Managua | January 28, 1860 | ||||||||
| • | Annexation to Nicaragua | 1894 | ||||||||
| Currency | Nicaraguan peso Pound sterling | |||||||||
| ||||||||||
Britain and Nicaragua signed the Treaty of Managua in January 28, 1860, which transferred suzerainty over the Caribbean coast between Cabo Gracias a Dios and Greytown to Nicaragua. Attempts to decide the sovereignty over the northern bank of the Wanks/Coco River which cuts Cabo Gracias a Dios in half, began in 1869, but wouldn't be settled until ninety-one years later when the International Court of Justice decided in favor of Honduras.[32]
The 1860 treaty also recognized that the Mosquito Kingdom, now reduced to the territory around Bluefields, would become an autonomous Miskito reserve. The municipal constitution of the reserve, signed on September 13, 1861, confirmed George Augustus Frederic II as ruler of the territory and its inhabitants, but only as Hereditary Chief and not King, title that, along the ones of General, Admiral and Governor, was abolished; and that the Hereditary Chief would be advised by a council of 41 members elected for a period of eight years. The composition of this council was not limited to Miskito: instead, the first council included a number of Moravian missionaries and its first session started with an oration in this denomination. In compensation for his loses, George Augustus Frederic II would be paid £1000 yearly and until 1870 by the Nicaraguan government.[17]
The death of George Augustus Frederic II in 1865, after only half that time had passed, led to a dispute between Nicaragua and the reserve's government. As indicated in its name, the position of Hereditary Chief was not completely elective like the title of King that preceded it, but had to be occupied by a member of George Augustus Frederic II's lineage of full Miskito ancestry. The council argued that none of George Augustus Frederic II's wives was Miskito and that none of their children was eligible as a result.[17] The election of William Henry Clarence as new chief, George Augustus Frederic II's nephew by his second sister, was not recognized by Nicaragua. William Henry Clarence asked for support to Great Britain, accusing Nicaragua of not abiding to the terms of the 1860 treaty and threatening the Miskitu's autonomy, and complaining both about increasing Nicaraguan immigration and the political instability in Nicaragua proper, which threatened the peace within the reserve.[17]
In 1881 Nicaragua and Britain agreed to subject the most disputed points of the 1860 treaty to the arbitration of the Emperor Francis Joseph I of Austria-Hungary. His decision, released on June 2, agreed largely with the interests of the Miskito - and by extension, the British. The arbitration decided that:[33]
- Sovereignty over the Mosquito Coast belonged to Nicaragua, but it was largely limited by the autonomy of the Miskito, as recognized in the 1860 treaty.
- Nicaragua had the right to fly its flag in any part of the Mosquito Coast.
- Nicaragua could maintain a Commissioner on the Mosquito Coast to defend her national interests.
- The Miskito could also fly their own flag on the Mosquito Coast, so long as said flag included some sign of Nicaraguan suzerainty. A compromise was reached by using the flag used during the British protectorate (designed by Patrick Walker),[16] but with the Union Flag on the canton replaced by the flag of Nicaragua.
- Nicaragua could not make concessions to the exploitation of natural resources in the Mosquito Coast. That right alone corresponded to the Miskito government.
- Nicaragua could not regulate the Miskito's trade, nor tax importations to or exportations from the Mosquito Coast.
- Nicaragua had to pay the money overdue to the Miskito king.
- Nicaragua could not limit the goods imported or exported through the port of San Juan del Norte (Greytown), unless these goods went to or came from Nicaraguan territory outside the reserve.
From 1883, the land and capital in the reserve began to be aglutinated by an increasingly small number of US citizens.[17]
Annexation to Nicaragua
When, in 1894, Rigoberto Cabezas led a campaign to annex the reserve, natives responded with vigorous protest, an appeal to Britain to protect them, and more militant resistance[34] – to little avail. The situation was such that, from July 6 to August 7, the US occupied Bluefields to 'protect US interests'. After enjoying almost complete autonomy for fourteen years, on 20 November 1894 their territory formally became incorporated into that of the republic of Nicaragua by Nicaraguan president José Santos Zelaya. The former Mosquito Coast was established as the Nicaraguan department of Zelaya. During the 1980s, the department was dissolved and substituted by the North Atlantic Autonomous Region (RAAN) and South Atlantic Autonomous Region (RAAS), autonomous regions with a certain degree of self-government. Those regions were renamed the North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region (RACCN) and the South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region (RACCS) in 2014.
Miskito under Nicaragua
The Miskito continued to enjoy a certain autonomy under Nicaragua, though there was considerable tension between the claims of the government and those of the indigenous people. This tension was expressed openly during Sandinista rule, which sought greater state control. The Miskito were strong supporters of U.S. efforts to undermine the Sandinistas and were important allies of the Contras.
Miskito separatism
Miskito dissidents declared the independence of the unrecognized Communitarian Nation of Moskitia in 2009.[35][36] The movement is led by Reverend Hector Williams, who was elected as "Wihta Tara" (Great Judge) of Moskitia by the Council of Elders, its governing body[37] composed of traditional leaders from within the Miskito community. The council advocates for independence and has considered a referendum, seeking international recognition. It also addresses the needs of the impoverished Moskitian communities, such as drug addiction among youth as the coast is slowly gaining influence as a corridor for drug trafficking.[37] However, the allure of possible Narco funding might be a tempting method of supporting independence should the movement find no support.[38]
The movement was backed by a 400-man "indigenous army" made up of veterans of the contras, which captured the YAMATA party headquarters in 2009.[39]
Miskito Kings
- c 1650–c 1687 Oldman
- c 1687–1718 Jeremy I
- 1718–1729 H.M. Jeremy II
- 1729–1739 H.M. Peter I
- 1739–1755 H.M. Edward I
- 1755–1776 H.M. George I
- 1776–1801 H.M. George II Frederic
- 1801–1824 H.M. George Frederic Augustus I
- 1824–1842 H.M. Robert Charles Frederic
- 1842–1865 H.M. George Augustus Frederic II
- 1865–1879 H.E. William Henry Clarence, Hereditary Chief of Miskito
- 1879–1888 H.E. George William Albert Hendy, Hereditary Chief of Miskito
- 1888–1889 H.E. Andrew Hendy, Hereditary Chief of Miskito
- 1889–1890 H.E. Jonathan Charles Frederick, Hereditary Chief of Miskito
- 1890–1908 H.E. Robert Henry Clarence, Hereditary Chief of Miskito
Inhabitants
The Mosquito Coast of Nicaragua has a population of 118,000 inhabitants, consisting of 57% Miskito, 22% Creoles (Afro-Europeans) 15% Ladinos, 4% Sumu (Amerindian), 1% Garifuna (Afro-Indians), 0.5% Chinese and 0.5% Rama (Amerindian).[40]
| Miskito | Creole | Ladino | Sumo | Garifuna | Chinese | Rama |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 57% | 22% | 15% | 4% | 1% | .5% | .5% |
See also
Footnotes
- ↑ "Mosquito Coast". Encyclopædia Britannica. Britannica Concise Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2007-08-03.
- ↑ Naylor, Robert A.; Penny Ante Imperialism: The Mosquito Shore and the Bay of Honduras, 1600–1914: A Case Study in British Informal Empire, Fairleigh Dickinson University Press, London, 1989, pp. 95–102, 110–112, 144–57
- ↑ Offen, Karl (2002). "The Sambo and Tawira Miskitu: The Colonial Origins and Geography of Intra-Miskitu Differentiation in Eastern Nicaragua and Honduras". Ethnohistory. 49 (2): 319–372 [pp. 328–333]. doi:10.1215/00141801-49-2-319.
- ↑ Añoveros, Jesus Maria Garcia (1988). "La presencia franciscana en la Taguzgalpa y la Tologalpa (La Mosquitia)". Mesoamérica (in Spanish). 9: 58–63.
- 1 2 Sorsby, William Shuman; The British Superintendency of the Mosquito Shore, 1749–1787, Ph.D. thesis, Faculty of Arts, University College, London, 1969
- ↑ Kupperman, Karen Ordal; Providence Island: The Other Puritan Colony, 1631–41, Cambridge University Press, 1993
- ↑ Sloane, Hans; A Voyage to the Islands of Madera, Barbados, Nieves, S. Christophers and Jamaica […], B. M., London, 1707, pp. lxxvi–lxxvii. According to a conversation held with Jeremy, the future king in about 1688.
- ↑ M. W.; "The Mosqueto Indian and his Golden River," in Churchill, Ansham; A Collection of Voyages and Travels, London, 1732, vol. 6, p. 288
- ↑ Helms, Mary (1983). "Miskito Slaving and Culture Contact: Ethnicity and Opportunity in an Expanding Population". Journal of Anthropological Research. 39 (2): 179–197. JSTOR 3629966.
- ↑ Romero Vargas, German; Las Sociedades del Atlántico de Nicaragua en los siglos XVII y XVIII, Banco Nicaraguënse, Managua, 1995, p. 165
- ↑ M. W.; "The Mosqueto Indian and His Golden River," in Churchill, Anshaw; A Collection of Voyages and Travels, London, 1728, vol. 6, pp. 285–290
- ↑ M. W.; "Mosketo Indian", p. 293
- ↑ Offen, Karl (2002). "The Sambo and Tawira Miskitu: The Colonial Origins and Geography of Intra-Miskitu Differentiation in Eastern Nicaragua and Honduras". Ethnohistory. 49 (2): 319–372. doi:10.1215/00141801-49-2-319.
- ↑ Olien, Michael (1998). "General, Governor and Admiral: Three Miskito Lines of Succession". Ethnohistory. 45 (2): 278–318. doi:10.2307/483061. JSTOR 483061.
- ↑ Floyd, Troy S.; The Anglo-Spanish Struggle for Mosquitia, University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque (NM), 1967, pp. 68–69
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Scheina, Robert L.; Latin America's Wars, vol. 1, The Age of the caudillo, 1791–1899, Potomac Books, Inc., Washington (DC), 2003
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 García, Claudia; Etnogénesis, hibridación y consolidación de la identidad del pueblo miskitu CSIC Press, 2007
- 1 2 3 Ezpeleta, Joseph de; Nota del Virrey Ezpeleta sobre Pacificación de la Costa de Mosquitos, 1790, in Pereira, Ricardo S.; Documentos sobre límites de los Estados-Unidos de Colombia: copiados de los originales que se encuentran en el Archivo de Indias de Sevilla, y acompañados de breves consideraciones sobre el verdadero Uti possidetis juris de 1810, Camacho Roldan y Tamayo, Bogotá, Colombia, 1883, ISBN 9781141811274 Cap. XII
- ↑ Pedrote, Enrique S.; El Coronel Hodgson y la Expedición a la Costa de Mosquitos, Anuario de Estudios Americanos, vol. 23, 1967, pp. 1205–1235
- ↑ Sorsby, William Shuman; Spanish Colonization of the Mosquito Coast, 1787–1800, Revista de Historia de América, vol. 73/74, 1972, pp. 145–153
- ↑ Dawson, Frank; The Evacuation of the Mosquito Shore and the English Who Stayed Behind, 1786–1800, The Americas, vol. 55, no. 1, 1998, pp. 63–89
- ↑ Henderson, George; An Account of the British Settlement of Honduras […], R. Baldwin, London, 1811 (2nd ed.), p. 219
- ↑ Pereira, Ricardo S.; Documentos sobre límites de los Estados-Unidos de Colombia: copiados de los originales que se encuentran en el Archivo de Indias de Sevilla, y acompañados de breves consideraciones sobre el verdadero Uti possidetis juris de 1810, Camacho Roldan y Tamayo, Bogotá, Colombia, 1883, ISBN 9781141811274 Cap. XII
- ↑ Correspondence Respecting the Mosquito Shore […], House of Commons of Great Britain, London, 1848, p. 46. The names of the signatories are printed on pp. 46-47.
- ↑ The Honduras Almanack for the year of our Lord 1829, Legislative Assembly, Belize, p. 56
- ↑ Naylor, Robert A.; Penny Ante Imperialism: The Mosquito Shore and the Bay of Honduras, 1600–1914: A Case Study in British Informal Empire, Fairleigh Dickinson University Press, London, 1989, pp. 99–100
- ↑ His grants to them are found in British and Foreign State Papers (1849–50), vol. 38, London, 1862, pp. 687 and 689
- ↑ Naylor, Robert A. (1967). "The Mahogany Trade as a Factor in the British Return to the Mosquito Shore in the Second Quarter of the Nineteenth Century". Jamaica Historical Journal. 7: 63–64.
- ↑ Naylor, Robert A.; Penny Ante Imperialism: The Mosquito Shore and the Bay of Honduras, 1600–1914: A Case Study in British Informal Empire, Fairleigh Dickinson University Press, London, 1989, pp. 103–117; 122–123 on the concessions
- ↑ http://www.worldstatesmen.org/Nicaragua.htm
- ↑ Pletcher, David M.; The diplomacy of trade and investment: American economic expansion in the Hemisphere, 1865-1900, University of Missouri Press, 1998
- ↑ Memorial Submitted by the Government of Nicaragua, vol. I: Maritime delimitation between Nicaragua and Honduras in the Caribbean Sea (Nicaragua v. Honduras), International Court of Justice, 21 March 2001
- ↑ Varela, Raúl; Jefes Hereditarios Miskitos, Pueblos Originarios de América: Biografías
- ↑ Hale, Charles R. (1994). "Resistance and Contradiction: Miskitu Indians and the Nicaraguan State, 1894-1987". Stanford (CA): Stanford University. p. 37. Retrieved 2014-10-01.
- ↑ Gibbs, Stephen (3 August 2009). "Nicaragua's Miskitos seek independence". BBC News. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- ↑ "Mosquito Coast Bites Nicaragua's Ortega". Time. 1 May 2009.
- 1 2 Rogers, Tim (2011-05-10). "Drugs dilemma on Nicaragua's Mosquito coast". BBC News.
- ↑ Rogers, Tim (2011-04-14). "Narco-Dividends: White Lobsters on the Mosquito Coast". Time.
- ↑ Mosquito bite as a swarm of Miskitos takes over the coast of Nicaragua, SchNEWS, no. 677, 2009-05-29
- ↑ "Lenguas indigenas" (PDF). Salamanca: El Rincón del Vago. Retrieved 2014-10-01.
Sources and references
Internet resources
- http://www.flag.de/FOTW/flags/ni-mc.html – Mosquito Coast flag
- RoyalArk-Mosquitos
- Douglas, James (1867). "Account of the attempt to form a settlement in 1823, on the Mosquito Shore". Transactions, New Series. Literary and Historical Society of Quebec (5). Retrieved 2013-04-27.
Printed sources
- Dozier, Craig; Nicaragua's Mosquito Shore: The Years of British and American Presence, University of Alabama Press, 1985
- Floyd, Troy S.; The Anglo-Spanish Struggle for Mosquitia, University of New Mexico Press, Albuquerque (NM), 1967
- Hale, Charles R. (1994). "Resistance and Contradiction: Miskitu Indians and the Nicaraguan State, 1894-1987". Stanford (CA): Stanford University.
- Helms, Mary (1969). "The Cultural Ecology of a Colonial Tribe". Ethnology. 8 (1): 76–84. doi:10.2307/3772938.
- Helms, Mary (1983). "Miskito Slaving and Culture Contact: Ethnicity and Opportunity in an Expanding Population". Journal of Anthropological Research. 39 (2): 179–197. JSTOR 3629966.
- Helms, Mary (1986). "Of Kings and Contexts: Ethnohistorical Interpretations of Miskito Political Structure and Function". American Ethnologist. 13 (3): 506–523. doi:10.1525/ae.1986.13.3.02a00070.
- Ibarra Rojas, Eugenia; Del arco y la flecha a las armas de fuego. Los indios mosquitos y la historia centroamericana, Editorial Universidad de Costa Rica, San Jose, 2011
- Naylor, Robert A.; Penny Ante Imperialism: The Mosquito Shore and the Bay of Honduras, 1600–1914: A Case Study in British Informal Empire, Fairleigh Dickinson University Press, London, 1989
- Offen, Karl (2002). "The Sambo and Tawira Miskitu: The Colonial Origins and Geography of Intra-Miskitu Differentiation in Eastern Nicaragua and Honduras". Ethnohistory. 49 (2): 319–372. doi:10.1215/00141801-49-2-319.
- Olien, Michael; The Miskito Kings and the Line of Succession, Journal of Anthropological Research, vol. 39, no. 2, 1983, pp. 198–241
- Olien, Michael; Micro/Macro-Level Linkages: Regional Political Structure on the Mosquito Coast, 1845–1864, Ethnohistory, vol. 34, no. 3, 1987, pp. 256–287
- Olien, Michael; General, Governor and Admiral: Three Miskito Lines of Succession, Ethnohistory, vol. 45, no. 2, 1998, pp. 278–318
- Potthast, Barbara; Die Mosquitoküste im Spannungsfeld Britischer und Spanischer Politik, 1502–1821, Bölau., Cologne, 1988
- Romero Vargas, Germán; Las Sociedades del Atlántico de Nicaragua en los siglos XVII y XVIII, Banco Nicaraguënse, Managua, 1995
Coordinates: 13°22′44″N 83°35′02″W / 13.379°N 83.584°W


.svg.png)
