State Great Khural
| State Great Khural Улсын Их Хурал Ulsyn Ikh hural | |
|---|---|
| 6th State Great Khural | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Chairman | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 76 (List) |
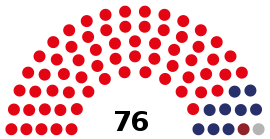 | |
Political groups |
Mongolian People's Party (65) |
| Elections | |
Last election | 29 June 2016 |
Next election | 2020 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Government Palace, Ulaanbaatar | |
| Website | |
| Parliament of Mongolia Website | |
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Mongolia |
|
Legislature |
|
Judiciary |
The State Great Khural (Mongolian: Улсын Их Хурал, Ulsyn Ikh Hural, also State Great Hural; English: State Great Assembly) is the unicameral parliament of Mongolia.[1] It is located in the Government Palace.
History
- 1924–1960
The first Ulsyn Ikh Hural was called to session in November 1924. This body was the legislature of the Mongolian People's Republic. It delegated much of its powers to an executive committee, the Ulsyn Baga Hural (Little Khural). The Great Khural held nine sessions between November 1924 and February 1949. Following electoral reforms in 1951, the numbering of its sessions began again. The first was held in July 1951 and the third in July 1957.[2]
- 1960–1992
In 1960 a new constitution was adopted and the body was renamed the "People's Great Khural" (Ardyn Ikh Hural), but the sessions were not renumbered. The fourth took place in July 1960 and the last in September 1992. In Russian and Mongolian historiography, the term "People's Great Khural" is frequently extended back to refer to the 1924–60 Khural to distinguish it from the post-1992 State Great Khural.[2]
The first free, democratic and multi-party election in Mongolia was held in 1990. Then the newly elected parliament changed the Constitution, established the State Baga Hural which replaced the People`s Great Hural as the highest legislative body. This elected the first Chairman, Radnaasumberel Gonghigdroj, and the first Chairman of the Secretariat, Byaraa Chimed.
The State Baga Hural had 5 standing committees. The Mongolian People`s Revolutionary Party (33), The Mongolian Democratic Party (13), The Mongolian Social Democratic Party (4), The Mongolian National Progressive Party (3) won seats in the parliament. The State Baga Hural adopted 27 new laws, ratified 17 international treaties and conventions as well as made amendments to 19 laws.
- 1992–1996
The State Great Hural had 10 standing committees (reduced to 6 in 1995). The Mongolian People`s Revolutionary Party (70), The Democratic Union Coalition of the Mongolian Democratic Party, The Mongolian National Progressive Party and the Green Party (4), The Mongolian Social Democratic Party (1) and one independent politician won seats. The elected Chairman was Natsag Bagabandi, and the Chairman of the Secretariat was Namsrai Rechnindorj. The State Great Hural adopted 137 laws, made amendments to 142 laws, and repealed 46 laws. The parliament also ratified 40 international treaties and conventions during its term.
- 1996–2000
The State Great Hural had 5 standing committees in 1996-1997. This increased to 7 standing committees in 1997-2000. The Democratic Union Coalition (50), The Mongolian People`s Revolutionary Party (25), The Mongolian Conservative United Party (1) won seats in the parliament. The elected Chairman was Radnaasumberel Gonghigdroj (for the second time), and the Chairman of the Secreteriat was Log Tsog until 1999. The next Chairman of the Secretariat was Baasanganobo Enebish. The State Great Hural adopted 173 new laws, made amendments to 255 laws and repealed 32 laws. The parliament also ratified 71 international treaties and conventions.
- 2000–2004
The State Great Hural had 7 standing committees. The Mongolian People`s Revolutionary Party (72), The Democratic Union Coalition (1), The Civil Will Party – The Mongolian Green Party (1), The Motherland – The Mongolian Democratic New Socialist Party (1), one independent won a seat in the parliament. The elected Chairman was Lkhamsurem Enebish till 2001, and the Chairman of the Secretariat was Baasanganobo Enebish till 2001. The next Chairman was Sanjbegz Yumur-Ochir, and the next Chairman of the Secretariat was Dagdankhuu Batbaatar till 2003. The third and final Chairman of the Secretariat during this term was Namsraijav Luvsanjav. The State Great Hural adopted 140 new laws, made amendments to 443 laws, and repealed 51 laws. The parliament also ratified 110 international treaties and conventions.
- 2004–2008
The State Great Hural had 11 standing committees as well as 8 subcommittees in 2004-2006. The number of standing committees was reduced to 7 in 2006. The seven political parties and a coalition of three parties participated in the election. The Mongolian People`s Revolutionary Party (37), the Motherland and Democracy Union (35), The Republican Party (1) and 3 independents won seats in the parliament. The elected Chairman was Nambar Enkhbayar till 2005, and the Chairman of the Secretariat continued to be Namsraijav Luvsanjav. The next Chairman was Tsend Nyamdorj till 2007. The third and final Chairman during this term was Danzan LundeejanstanThe State Great Hural adopted 89 new laws, made amendments to 336 laws. The parliament also ratified 38 international treaties and conventions as well as repealed 50 laws.
- 2008–2012
The State Great Hural had 7 standing committees and 11 subcommittees. The Mongolian People`s Revolutionary Party (46), The Democratic Party (27), The Civil Will Party (1)8 The Green Party (1) and 1 independent won the seats in the parliament. For 5 months (May to September, 2008), Danzan Sandang-Ochir was the Chairman of the Secretariat. The elected Chairman was Damdin Denberel, and the second Chairman of the Secretariat was Tserenkhuu Sharavdorj. The State Great Hural adopted 111 new laws and made amendments to 485 laws. The parliament also ratified 59 international treaties and conventions as well as repealed 70 laws.
- 2012–2016
The State Great Hural had 8 standing committees and 10 subcommittees. The Democratic Party (34), The Mongolian People`s Party (26), The Justice Coalition of the Mongolian People`s Revolutionary Party – The Mongolian National Democratic Party (11), The Civil Will Party – The Green Party (2), and 3 independents won seats in the parliament. For the first time, the legislative election was held on the mixed election system by the new law. 48 seats were elected directly from 26 constituencies and 28 seats were proportionally allocated based on the number votes which the political parties won. The elected Chairman was Zandaakhuu Enkhbold, and the Chairman of the Secretariat was Byambadorj Boldbaatar. For the first time in Mongolia, electronic voting machines were used for voter registration, vote counting and monitoring purposes.
- 2016–current
The Mongolian People's Party (65), The Democratic Party (9), The Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party (1), and 1 independent won seats in the parliament.
Structure

The State Great Khural is unicameral, and consists of 76 members. With mandate of no less than 57 of total members of the State Great Hural, the parliament shall be considered in existence of its powers. A member of the State Great Hural shall be an envoy of the people and shall represent and uphold the interests of all the citizens and the people. The mandate of a member of the State Great Hural shall begin with an oath taken before the State Emblem and expire when newly elected members of the State Great Hural are sworn in.
Chairman
Members of the Great State Hural elect the Chairman from among themselves in an open ballot. They serve a four-year term, but may be relieved or removed of the position, on grounds defined by law, before their term expiration. The Chairman executes the roles of the speaker and the deputy of the President. They automatically become a member of the National Security Council. The Chairman is responsible for the following duties:
- To ensure the compliance of the Constitution and other laws in every activities of the State Great Hural
- To declare regular, extraordinary and honorary sessions and ensures the preparations
- To define orders of plenary session agenda, considering the priority motions expressed from caucuses and Standing Committees
- To communicate with the President and the Cabinet on behalf of the State Great Hural
- To arrange the State Great Hural’s oversighting tasks on the Cabinet
- To coordinate activities of the State Great Hural’s subordinate organizations and arranges its scrutiny on those organizations
- To represent the State Great Hural both in foreign and domestic arena
- To authorize orders on issues permissible within the privileges enjoyed by the Chairman of the State Great Hural
Vice-Chairman
The Vice-Chairman is elected by each caucus formed by the result of an election. They serve a four-year term, but may be relieved or removed of the position, on grounds defined by law, before their term expiration. The Vice-Chairman is responsible for the following duties:
- To coordinate activities of the standing, temporary, sub committees and caucuses
- To ensure attendances of plenary sessions and Standing Committee sittings
- To scrutinize the State Great Hural’s procedures and compliance of ethic’s codes of the members
- To exercise other tasks and duties specified in the relevant laws and regulations
- To temporary exercises chairmanship’s tasks, by the assignment of the incumbent chairman of the State Great Hural during his or her absence
Chairman's Council
The Chairman's Council consists of the Vice-Chairman of the State Great Hural, Chairmen of the caucuses, leaders of parliamentary parties, and Chairmen of standing/temporary committees. The Chairman's Council is responsible for the following duties:
- To cohere and coordinate caucuses’ and Standing Committee activities to the oversighting functions of the State Great Hural
- To define orders of regular or extraordinary session agenda
- To approve weekly schedules and agendas of motions for sessions
- To submit motion on the State Great Hural’s budget proposal
- To confer other issues related with internal affairs of the State Great Hural
Functions
The State Great Hural has both legislative and oversighting power in Mongolia.
Its legislative functions are mainly preparing and carrying out plenary sessions or standing committee sittings, discussing drafts of laws or other decisions of the State Great Hural and adopting, passing and the resolving processes. The State Great Hural implements its oversighting powers by:
- Hearing reports, presentations and briefings from the Cabinet and other organizations directly accountable to the State Great Hural
- Enquiring the Prime Minister, cabinet members and executives of other organizations directly accountable to the State Great Hural and generate debate of the responses in its sessions
- Enquiring the Prime Minister, cabinet members and executives of other organizations directly accountable to the State Great Hural and demand responses
- Assessing implementation of laws and other resolutions of the State Great Hural at the cabinet and other organizations that directly accountable to the State Great Hural and generate debates at the Standing Committee sittings or if necessary at the plenary sessions
- Delivering verdict on professional or ethical offences committed by the Prime Minister, cabinet members and those who have been appointed by the State Great Hural or executives and members of other organizations directly accountable to the State Great Hural
Elections
Elections are held every four years to elect all 76 members of the State Great Hural. The election uses plurality-at-large voting in all 26 multi-member constituencies. To vote, a Mongolian citizen must be 18 years or older, and live in Mongolia. Any person over 25 is eligible to be elected. New elections are held if the Hural is dissolved, if two-thirds of members vote for dissolution, if the President dissolves the Hural, or if the President or half the Cabinet resigns.
Sessions
The main organizational form of the State Great Hural is the session. According to the Article 27 of the Constitution, regular sessions of the State Great Hural convene in every six months for not less than 50 working days. Session consists of plenary sessions, exclusive or joint Standing Committee sittings and caucus meetings. The four types of sessions are:
- Inauguration session - Convenes, by the President’s convocation, within 30 days after the election.
- Regular session - Autumn session commences on the 1st of October, and the spring session commences on the 5th of April each year.
- Extra ordinary session - Convenes at the demand of greater than one third of the members of the State Great Hural, or on the initiative of either the President or the Chairman of the State Great Hural.
- Emergency session - Convenes within 72 hours of the President’s proclamation of state of emergency or war.
Committees
The State Great Hural shall have standing committees dealing with specific fields of public policy. The Standing committees are composed of 10-19 members and shall be convened on Tuesday and Wednesday each week. The subcommittee is affiliated with and deals with specific issues within the standing committee. The State Great Hural shall set up temporary committees for reviewing specific issues, making proposals and submitting reports to the plenary sessions.
Party caucuses
A party/coalition with 8 or more seats must establish a party caucus. Independents and members of several parties may choose to join a caucus, but may not establish their own. Each caucus must elect a leader, which is then reported to the Chairman. The decision to establish a caucus, along with its membership roster, must be submitted within 24 hours of the Chairman's election. The Chairman will then announce these decisions at the plenary session of the State Great Hural.
Legislation
Stage 1
The party caucuses or standing committees shall make draft legislation and decide whether to submit it for discussion at the plenary sessions of the State Great Hural. The State Great Hural will then decide whether to discuss the draft legislation. If they decide to discuss it, it shall send the drafts to standing committees to prepare for the first discussion. If they decide not to discuss legislation drafts, then it shall be sent back to its initiators.
Stage 2
The standing committee shall prepare a legislation draft for the first discussion and shall submit its proposal and conclusion to the State Great Hural. At this stage, party groups are allowed to make comments about the draft. Opinions and proposals of all parties shall be included in the standing committee conclusions. After the voting at the plenary session, drafts shall be sent back to the standing committees for the preparation of the final discussion.
Stage 3
The standing committees shall include conclusions from the first discussion to the original draft and shall make presentations about the first discussion. They shall also make the introduction of a draft to the State Great Hural. At this stage, the standing committees are allowed to request a re-voting regarding the draft. The draft shall be discussed, voted and fully adopted by the State Great Hural. If the draft is not fully adopted, it shall be sent back to the law initiators.
The standing committees shall prepare the final versions of the legislation drafts and other resolutions of the State Great Hural. The standing committees shall make the introduction of the final versions of the legislation and other resolutions to the State Great Hural. After the introduction of the final versions of the legislations and other resolutions at the State Great Hural, the Chairman of the State Great Hural shall sign the final versions within three working days. The signed legislations and other resolutions of the State Great shall be submitted to the President of Mongolia within 24 hours. If the president vetoes the legislations, the issue shall be discussed again at the State Great Hural. The legislation shall be considered valid after the publication of the legislations in the 'State Information' bulletin.
Most recent election
| Party | Seats | Votes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seats | +/− | Votes | % | +/− | |
| Mongolian People's Party | 65 | |
636,316 | 45.69% | |
| Democratic Party | 9 | |
467,341 | 33.55% | |
| Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party | 1 | |
113,103 | 8.12% | |
| Independents | 1 | |
67,220 | 4.83% | – |
| Others | 0 | |
122,143 | 7.81% | – |
| Totals | 76 | 1,406,123 | 100% | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 1,911,047 | 73.58% | – | ||
| Source: General Election Commission of Mongolia, Mongolian legislative election, 2016 | |||||
See also
- Baga Hural — Former lower house
- Politics of Mongolia
- List of political parties in Mongolia
- List of legislatures by country
References
- ↑ Montsame News Agency. Mongolia. 2006, Foreign Service office of Montsame News Agency, ISBN 99929-0-627-8, p. 40
- 1 2 Alan J. K. Sanders (ed.), "Hural, Little" and "Hural, State Little", in Historical Dictionary of Mongolia, 2nd ed. (Scarecrow Press, 2003), p. 161.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to State Great Khural. |
- (English) (Mongolian) Official website of The State Great Hural of Mongolia
- Official Website of the Government Organizations of Mongolia - Parliament websites