United States Senate election in Wisconsin, 2012
| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
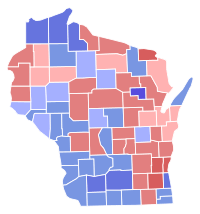
| U.S. Senate election results map. Blue denotes counties/districts won by Baldwin. Red denotes those won by Thompson. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Wisconsin |
|---|
 |
The 2012 United States Senate election in Wisconsin took place on November 6, 2012, alongside a U.S. presidential election as well as other elections to the United States Senate and House of Representatives and various state and local elections. Incumbent Democratic Senator Herb Kohl retired instead of running for re-election to a fifth term.
Primary elections were held on August 14, 2012. Democratic Congresswoman Tammy Baldwin of Wisconsin's 2nd congressional district ran unopposed for her party's nomination. The Republican nominee was former Governor of Wisconsin and former Secretary of Health and Human Services Tommy Thompson, who won with a plurality in a four-way race. In the general election, Baldwin defeated Thompson and won the open seat. She became the first woman elected to represent Wisconsin in the Senate and the first openly gay U.S. Senator in history. This is also the first time Thompson lost a statewide race.
Background
Incumbent Democratic Senator Herb Kohl was re-elected to a fourth term in 2006, beating Republican attorney Robert Lorge by 67% to 30%. Kohl's lack of fundraising suggested his potential retirement.[2] There was speculation that Kohl might decide to retire so as to allow Russ Feingold, who lost his re-election bid in 2010, to run again, although Mike Tate, chairman of the Wisconsin Democratic Party, dismissed speculation about Kohl's potential retirement.[3] Ultimately, Kohl announced in May 2011 that he would not run for re-election in 2012.
Democratic primary
Despite speculation that Kohl would retire to make way for his former Senate colleague Russ Feingold, Feingold did not enter the race. Other politicians thought to be likely candidates also declined to run, so Baldwin was unopposed in the Democratic primary.
Candidates
Declared
- Tammy Baldwin, U.S. Representative[4]
Declined
- Tom Barrett, Mayor of Milwaukee[5]
- Kathleen Falk, former Dane County Executive[6]
- Russ Feingold, former U.S. Senator[7]
- Steve Kagen, former U.S. Representative[8]
- Ron Kind, U.S. Representative[9]
- Herb Kohl, incumbent U.S. Senator[10][11]
- Gwen Moore, U.S. Representative[12]
- Tim Sullivan, businessman[13]
Polling
| Poll source | Date(s) administered | Sample size |
Margin of error |
Tammy Baldwin |
Jon Erpenbach |
Russ Feingold |
Kathleen Falk |
Steve Kagen |
Ron Kind |
Barbara Lawton |
Gwen Moore |
Other/ Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 387 | ± 5% | 48% | — | — | — | 19% | — | — | — | 33% |
| 37% | — | — | — | 15% | 21% | — | — | 27% | ||||
| Magellan Strategies | July 12–13, 2011 | 627 | ± 3.9% | 46% | — | — | — | 21% | — | — | — | 33% |
| 41% | — | — | — | — | 19% | — | — | 40% | ||||
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 783 | ± 3.5% | 12% | 5% | 70% | 1% | 3% | 4% | 1% | 2% | 3% |
| 30% | 13% | — | 4% | 17% | 16% | 3% | 6% | 12% |
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Tammy Baldwin | 185,265 | 99.77 | |
| Democratic | Write ins | 424 | 0.23 | |
| Total votes | 185,689 | 100 | ||
Republican primary

Congressman and House Budget Committee Chairman Paul Ryan had stated he would not run against Kohl if Kohl sought reelection, but would contemplate a run if Kohl retired.[15] Ryan later stated that he was "95 percent sure" that he would not run.[16]
Six candidates declared for the seat, although two later withdrew. The contest turned out to be a four-way fight and although a large majority of Republican primary voters consistently expressed a preference for a nominee "more conservative" than Tommy Thompson, Eric Hovde and Mark Neumann split the conservative vote and Thompson narrowly prevailed with a plurality of the vote.[17]
Candidates
Declared
- Jeff Fitzgerald, Speaker of the Wisconsin State Assembly[18]
- Eric Hovde, businessman[19]
- Mark Neumann, former U.S. Representative and nominee for the U.S. Senate in 1998[20][21]
- Tommy Thompson, former Governor of Wisconsin and former Secretary of Health and Human Services[22]
Withdrew
- Frank Lasee, State Senator[23] (endorsed Eric Hovde)
- Kip Smith, physical therapist[24]
Declined
- Mark Andrew Green, former U.S. Representative and former United States Ambassador to Tanzania[25]
- Theodore Kanavas, former State Senator[26]
- Paul Ryan, U.S. Representative[27]
- Tim Sullivan, businessman[13]
- J. B. Van Hollen, Wisconsin Attorney General[28]
Polling
| Poll source | Date(s) administered | Sample size |
Margin of error |
Jeff Fitzgerald |
Eric Hovde |
Mark Neumann |
Tommy Thompson |
Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | August 8–9, 2012 | 557 | ± 4.2% | 15% | 27% | 24% | 25% | 9% |
| Marquette University | August 2–5, 2012 | 519 | ± 4.4% | 13% | 20% | 18% | 28% | 7% |
| We Ask America | July 31, 2012 | 1,237 | ± 2.8% | 12.11% | 23.20% | 16.66% | 22.79% | 25.24% |
| Public Policy Polling | July 30–31, 2012 | 400 | ± 4.9% | 13% | 28% | 25% | 25% | 9% |
| — | 33% | 27% | 30% | 10% | ||||
| Marquette University | July 5–8, 2012 | 432 | ± 4.8% | 6% | 23% | 10% | 35% | 25% |
| Public Policy Polling | July 5–8, 2012 | 564 | ± 4.1% | 9% | 31% | 15% | 29% | 16% |
| OnMessage Inc.+ | June 26–27, 2012 | 600 | ± 4.0% | 7% | 29% | 16% | 34% | 14% |
| Marquette University | June 13–16, 2012 | 344 | ± 5.4% | 10% | 14% | 16% | 34% | 25% |
| Public Policy Polling | March 31–April 1, 2012 | 609 | ± 4.0% | 18% | — | 25% | 38% | 19% |
| Public Policy Polling | February 23–26, 2012 | 556 | ± 4.2% | 22% | — | 22% | 39% | 17% |
| 32% | — | 42% | — | 26% | ||||
| 37% | — | — | 46% | 17% | ||||
| — | — | 36% | 46% | 18% | ||||
| Public Policy Polling | October 20–23, 2011 | 650 | ± 3.8% | 21% | — | 29% | 35% | 11% |
| — | — | 39% | 43% | 17% | ||||
| 28% | — | 44% | — | 28% | ||||
| 35% | — | — | 47% | 17% | ||||
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 362 | ± 5.2% | — | — | 39% | 47% | 13% |
| Magellan Strategies | July 12–13, 2011 | 638 | ± 3.9% | 15% | — | 26% | 41% | 18% |
| — | — | 36% | 44% | 20% |
- + Commissioned by Eric Hovde
| Poll source | Date(s) administered | Sample size |
Margin of error |
Tommy Thompson |
Someone more conservative |
Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | July 30–31, 2012 | 400 | ± 4.9% | 29% | 58% | 13% |
| Public Policy Polling | July 5–8, 2012 | 564 | ± 4.1% | 34% | 50% | 17% |
| Public Policy Polling | February 23–26, 2012 | 556 | ± 4.2% | 37% | 47% | 17% |
| Public Policy Polling | October 20–23, 2011 | 650 | ± 3.8% | 35% | 51% | 14% |
Endorsements
| Endorsements for Jeff Fitzgerald |
|---|
|
| Endorsements for Eric Hovde |
|---|
|
| Endorsements for Mark Neumann |
|---|
|
| Endorsements for Tommy Thompson |
|---|
|
Politicians
Celebrities and political commentators[51]
Cabinet officials[51]
State legislators[51]
Political organization officials[51]
Law enforcement officials[51]
Organizations[51]
|
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Tommy Thompson | 197,928 | 34.0 | |
| Republican | Eric Hovde | 179,557 | 30.8 | |
| Republican | Mark Neumann | 132,786 | 22.8 | |
| Republican | Jeff Fitzgerald | 71,871 | 12.3 | |
| Republican | Write ins | 244 | 0.04 | |
| Total votes | 582,630 | 100 | ||
General election

Candidates
- Tammy Baldwin (Democratic), U.S. Representative
- Tommy Thompson (Republican), former Governor and former Secretary of Health and Human Services
- Joseph Kexel (Libertarian), IT consultant[57]
- Nimrod Allen III (Independent), consultant and former Marine[58]
Debates
Baldwin and Thompson agreed to three debates: September 28, October 18 and October 26, all broadcast statewide, and nationwide through C-SPAN.
The first debate originated from the studios of Milwaukee Public Television and was coordinated by the Wisconsin Broadcasters Association. It aired on MPTV, Wisconsin Public Television, Wisconsin Public Radio and several commercial stations throughout the state.
The second debate originated from the Theater for Civic Engagement on the campus of the University of Wisconsin–Marathon County in Wausau and was coordinated by WPT/WPR, the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel and Milwaukee's WTMJ-TV. Again it was carried on MPTV, WPT/WPR, and several commercial stations, including WTMJ-TV.
The third debate originated from Eckstein Hall on the campus of Marquette University Law School and was coordinated by WISN-TV in Milwaukee. It aired on that station and across the state's other ABC affiliated stations.
- External links
- Complete video and transcript at C-SPAN, September 28, 2012
- Complete video and transcript at C-SPAN, October 18, 2012
- Complete video and transcript at C-SPAN, October 26, 2012
Fundraising
| Candidate (party) | Receipts | Disbursements | Cash on hand | Debt |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tammy Baldwin (D) | $14,643,869 | $15,204,940 | $143,852 | $0 |
| Tommy Thompson (R) | $9,585,823 | $9,582,888 | $2,934 | $0 |
| Source: Federal Election Commission[59] | ||||
Top contributors
| Tammy Baldwin | Contribution | Tommy Thompson | Contribution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMILY's List | $431,843 | Michael Best & Friedrich LLP | $36,825 | |
| MoveOn.org | $171,467 | ABC Supply | $28,500 | |
| University of Wisconsin | $117,600 | Akin Gump Strauss Hauer & Feld | $28,250 | |
| J Street PAC | $113,758 | Direct Supply | $27,500 | |
| League of Conservation Voters | $95,308 | Wisconsin Energy Corporation | $25,750 | |
| Democracy Engine | $81,330 | American Foods Group | $25,000 | |
| Council for a Livable World | $54,130 | Gilead Sciences | $23,000 | |
| Voices for Progress | $25,749 | Centene Corporation | $20,750 | |
| Marshfield Clinic | $21,800 | BGR Group | $20,500 | |
| Microsoft Corporation | $18,564 | C. R. Bard, Inc. | $20,000 | |
| Source: Center for Responsive Politics[60] | ||||
Top industries
| Tammy Baldwin | Contribution | Tommy Thompson | Contribution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women's Issues | $915,482 | Retired | $858,276 | |
| Retired | $791,756 | Leadership PACs | $244,804 | |
| Lawyers/Law Firms | $597,674 | Financial Institutions | $243,636 | |
| Democratic/Liberal | $555,792 | Lawyers/Law Firms | $228,379 | |
| Leadership PACs | $309,430 | Real Estate | $227,687 | |
| Universities | $298,298 | Pharmaceuticals/Health Products | $204,302 | |
| Human Rights Organisations | $215,539 | Insurance Industry | $202,654 | |
| Health Professionals | $202,654 | Manufacturing & Distributing | $169,104 | |
| Pro-Israel | $172,380 | Health Professionals | $150,149 | |
| Business Services | $163,238 | Lobbyists | $138,700 | |
| Source: Center for Responsive Politics[61] | ||||
Polling
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Tammy Baldwin (D) |
Tommy Thompson (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | November 2–3, 2012 | 1,256 | ± 2.8% | 51% | 48% | — | 2% |
| Angus Reid Public Opinion | November 1–3, 2012 | 482 | ± 4.5% | 50% | 48% | 2% | — |
| YouGov | October 31–November 3, 2012 | 1,225 | ± 3.1% | 48% | 47% | — | 5% |
| WeAskAmerica | October 31–November 1, 2012 | 1,210 | ± 3% | 49% | 46% | — | 5% |
| NBC/WSJ/Marist | October 31, 2012 | 1,065 | ± 3.0% | 48% | 47% | 4% | 1% |
| Rasmussen Reports | October 29, 2012 | 750 | ± 4.0% | 48% | 48% | 1% | 2% |
| St. Norbert College | October 25–29, 2012 | 402 | ± 5% | 43% | 46% | — | 11% |
| Marquette University | October 25–28, 2012 | 1,243 | ± 2.8% | 47% | 43% | — | 10% |
| Rasmussen Reports | October 25, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 47% | 48% | 2% | 4% |
| Angus Reid Public Opinion | October 18–20, 2012 | 502 | ± 4.5% | 45% | 42% | 3% | 11% |
| Rasmussen Reports | October 18, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 46% | 48% | 3% | 3% |
| Mason-Dixon | October 15–17, 2012 | 625 | ± 4% | 47% | 45% | — | 8% |
| NBC/WSJ/Marist Poll | October 15–17, 2012 | 1,013 | ± 3.1% | 49% | 45% | 1% | 5% |
| Marquette University | October 11–14, 2012 | 870 | ± 3.3% | 45% | 46% | — | 7% |
| YouGov | October 4–11, 2012 | 639 | ± 4.9% | 48% | 43% | — | 9% |
| Rasmussen Reports | October 9, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 51% | 47% | 1% | 2% |
| CBS/NYT/Quinnipiac | October 4–9, 2012 | 1,327 | ± 2.7% | 48% | 46% | — | 5% |
| Public Policy Polling | October 4–6, 2012 | 979 | ± 3.1% | 49% | 46% | — | 6% |
| Marquette University | September 27–30, 2012 | 894 | ± 3.3% | 48% | 44% | — | 6% |
| We Ask America | September 20–23, 2012 | 1,238 | ± 2.8% | 52% | 40% | — | 8% |
| Public Policy Polling | September 18–19, 2012 | 842 | ± 3.4% | 49% | 45% | — | 6% |
| NBC/WSJ/Marist Poll | September 16–18, 2012 | 968 | ± 3.2% | 48% | 46% | — | 5% |
| CBS/NYT/Quinnipiac | September 11–17, 2012 | 1,485 | ± 2.5% | 47% | 47% | — | 6% |
| Marquette University | September 13–16, 2012 | 705 | ± 3.8% | 50% | 41% | — | 5% |
| Public Policy Polling | September 12–13, 2012 | 959 | ± n/a | 48% | 45% | — | 6% |
| YouGov | September 4–11, 2012 | 772 | ± n/a | 42% | 48% | — | 10% |
| CBS/NYT/Quinnipiac | August 15–21, 2012 | 1,190 | ± 3.0% | 44% | 50% | 1% | 4% |
| Marquette University | August 16–19, 2012 | 576 | ± 4.2% | 41% | 50% | — | 9% |
| Public Policy Polling | August 16–19, 2012 | 1,308 | ± 2.7% | 44% | 49% | — | 7% |
| Rasmussen Reports | August 15, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 43% | 54% | 1% | 3% |
| Quinnipiac | July 31–August 6, 2012 | 1,428 | ± 2.6% | 47% | 47% | 1% | 5% |
| Marquette University | August 2–5, 2012 | 1,400 | ± 2.6% | 43% | 48% | — | 5% |
| Rasmussen Reports | July 25, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 48% | 41% | 5% | 6% |
| Marquette University | July 5–8, 2012 | 810 | ± 3.5% | 41% | 45% | — | 14% |
| Public Policy Polling | July 5–8, 2012 | 1,057 | ± 3.0% | 45% | 45% | — | 11% |
| Marquette University | June 13–16, 2012 | 707 | ± 3.8% | 41% | 49% | — | 10% |
| Rasmussen Reports | June 12, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 36% | 52% | 6% | 6% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 11–13, 2012 | 851 | ± 3.4% | 42% | 47% | — | 11% |
| Rasmussen Reports | May 9, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 38% | 50% | 5% | 7% |
| Public Policy Polling | April 13–15, 2012 | 1,136 | ± 2.9% | 45% | 47% | — | 8% |
| Rasmussen Reports | March 27, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 44% | 48% | 4% | 4% |
| Rasmussen Reports | February 27, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 36% | 50% | 4% | 10% |
| Public Policy Polling | February 23–26, 2012 | 900 | ± 3.3% | 46% | 45% | — | 9% |
| Marquette University | February 16–19, 2012 | 716 | ± 3.7% | 42% | 48% | 1% | 9% |
| Rasmussen Reports | October 26, 2011 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 42% | 49% | 4% | 6% |
| Public Policy Polling | October 20–23, 2011 | 1,170 | ± 2.9% | 44% | 46% | — | 10% |
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 830 | ± 3.4% | 42% | 50% | — | 8% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 44% | 45% | — | 11% |
- with Baldwin
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Tammy Baldwin (D) |
Jeff Fitzgerald (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinnipiac | July 31–August 6, 2012 | 1,428 | ± 2.6% | 51% | 39% | — | 9% |
| Marquette University | August 2–5, 2012 | 1,400 | ± 2.6% | 45% | 40% | — | 7% |
| Rasmussen Reports | July 25, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 47% | 37% | 6% | 10% |
| Marquette University | July 5–8, 2012 | 810 | ± 3.5% | 43% | 37% | — | 20% |
| Public Policy Polling | July 5–8, 2012 | 1,057 | ± 3.0% | 46% | 42% | — | 13% |
| Marquette University | June 13–16, 2012 | 707 | ± 3.8% | 45% | 39% | — | 16% |
| Rasmussen Reports | June 12, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 44% | 43% | 5% | 8% |
| Rasmussen Reports | May 9, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 45% | 41% | 4% | 9% |
| Public Policy Polling | April 13–15, 2012 | 1,136 | ± 2.9% | 47% | 40% | — | 13% |
| Rasmussen Reports | March 27, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 48% | 40% | 4% | 7% |
| Rasmussen Reports | February 27, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 40% | 41% | 4% | 15% |
| Public Policy Polling | February 23–26, 2012 | 900 | ± 3.3% | 47% | 39% | — | 14% |
| Marquette University | February 16–19, 2012 | 716 | ± 3.7% | 45% | 37% | 3% | 15% |
| Rasmussen Reports | October 26, 2011 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 46% | 39% | 4% | 6% |
| Public Policy Polling | October 20–23, 2011 | 1,170 | ± 2.9% | 44% | 40% | — | 16% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 48% | 37% | — | 15% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Tammy Baldwin (D) |
Eric Hovde (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinnipiac | July 31–August 6, 2012 | 1,428 | ± 2.6% | 47% | 43% | 1% | 8% |
| Marquette University | August 2–5, 2012 | 1,400 | ± 2.6% | 44% | 41% | — | 9% |
| Rasmussen Reports | July 25, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 45% | 42% | 5% | 8% |
| Marquette University | July 5–8, 2012 | 810 | ± 3.5% | 44% | 38% | — | 18% |
| Public Policy Polling | July 5–8, 2012 | 1,057 | ± 3.0% | 44% | 45% | — | 11% |
| Marquette University | June 13–16, 2012 | 707 | ± 3.8% | 45% | 36% | — | 19% |
| Rasmussen Reports | June 12, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 42% | 44% | 4% | 10% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 11–13, 2012 | 851 | ± 3.4% | 41% | 45% | — | 14% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Tammy Baldwin (D) |
Mark Neumann (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinnipiac | July 31–August 6, 2012 | 1,428 | ± 2.6% | 48% | 45% | 1% | 6% |
| Marquette University | August 2–5, 2012 | 1,400 | ± 2.6% | 44% | 44% | — | 6% |
| Rasmussen Reports | July 25, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 48% | 42% | 3% | 8% |
| Marquette University | July 5–8, 2012 | 810 | ± 3.5% | 43% | 40% | — | 17% |
| Public Policy Polling | July 5–8, 2012 | 1,057 | ± 3.0% | 45% | 41% | — | 13% |
| Marquette University | June 13–16, 2012 | 707 | ± 3.8% | 44% | 44% | — | 12% |
| Rasmussen Reports | June 12, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 43% | 45% | 5% | 7% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 11–13, 2012 | 851 | ± 3.4% | 42% | 46% | — | 12% |
| Rasmussen Reports | May 9, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 42% | 44% | 4% | 9% |
| Public Policy Polling | April 13–15, 2012 | 1,136 | ± 2.9% | 46% | 45% | — | 9% |
| Rasmussen Reports | March 27, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 48% | 40% | 4% | 8% |
| Rasmussen Reports | February 27, 2012 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 37% | 46% | 4% | 13% |
| Public Policy Polling | February 23–26, 2012 | 900 | ± 3.3% | 47% | 41% | — | 12% |
| Marquette University | February 16–19, 2012 | 716 | ± 3.7% | 44% | 40% | 2% | 14% |
| Rasmussen Reports | October 26, 2011 | 500 | ± 4.5% | 44% | 43% | 4% | 9% |
| Public Policy Polling | October 20–23, 2011 | 1,170 | ± 2.9% | 44% | 43% | — | 13% |
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 830 | ± 3.4% | 40% | 44% | — | 15% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 46% | 41% | — | 13% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Tammy Baldwin (D) |
J. B. Van Hollen (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 46% | 39% | — | 15% |
- with Feingold
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Russ Feingold (D) |
Jeff Fitzgerald (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 55% | 39% | — | 7% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Russ Feingold (D) |
Mark Neumann (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 830 | ± 3.4% | 51% | 44% | — | 5% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 53% | 41% | — | 6% |
| Public Policy Polling | February 24–27, 2011 | 768 | ± 3.5% | 50% | 40% | — | 10% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Russ Feingold (D) |
Paul Ryan (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | February 24–27, 2011 | 768 | ± 3.5% | 49% | 42% | — | 9% |
| Public Policy Polling | December 10–12, 2010 | 702 | ± 3.7% | 50% | 43% | — | 7% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Russ Feingold (D) |
Tommy Thompson (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 830 | ± 3.4% | 48% | 47% | — | 5% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 52% | 42% | — | 6% |
| Public Policy Polling | December 10–12, 2010 | 702 | ± 3.7% | 49% | 40% | — | 11% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Russ Feingold (D) |
J. B. Van Hollen (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 53% | 38% | — | 9% |
| Public Policy Polling | February 24–27, 2011 | 768 | ± 3.5% | 51% | 39% | — | 10% |
| Public Policy Polling | December 10–12, 2010 | 702 | ± 3.7% | 52% | 41% | — | 7% |
- with Steve Kagen
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Steve Kagen (D) |
Jeff Fitzgerald (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 43% | 38% | — | 19% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Steve Kagen (D) |
Mark Neumann (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 830 | ± 3.4% | 38% | 45% | — | 17% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 42% | 41% | — | 17% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Steve Kagen (D) |
Tommy Thompson (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 830 | ± 3.4% | 41% | 49% | — | 10% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 42% | 45% | — | 13% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Steve Kagen (D) |
J. B. Van Hollen (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 43% | 38% | — | 19% |
- with Ron Kind
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Ron Kind (D) |
Jeff Fitzgerald (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 45% | 37% | — | 18% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Ron Kind (D) |
Mark Neumann (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 830 | ± 3.4% | 40% | 43% | — | 17% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 44% | 40% | — | 16% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Ron Kind (D) |
Tommy Thompson (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | August 12–14, 2011 | 830 | ± 3.4% | 41% | 48% | — | 11% |
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 44% | 44% | — | 12% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Ron Kind (D) |
J. B. Van Hollen (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | May 19–22, 2011 | 1,636 | ± 2.4% | 44% | 38% | — | 17% |
- with Herb Kohl
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Herb Kohl (D) |
Mark Neumann (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | February 24–27, 2011 | 768 | ± 3.5% | 51% | 37% | — | 12% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Herb Kohl (D) |
Paul Ryan (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | February 24–27, 2011 | 768 | ± 3.5% | 49% | 42% | — | 10% |
| Public Policy Polling | December 10–12, 2010 | 702 | ± 3.7% | 48% | 42% | — | 11% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Herb Kohl (D) |
Tommy Thompson (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | December 10–12, 2010 | 702 | ± 3.7% | 49% | 40% | — | 11% |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Herb Kohl (D) |
J. B. Van Hollen (R) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Policy Polling | February 24–27, 2011 | 768 | ± 3.5% | 52% | 37% | — | 11% |
| Public Policy Polling | December 10–12, 2010 | 702 | ± 3.7% | 51% | 38% | — | 11% |
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Tammy Baldwin | 1,547,104 | 51.41% | -15.9 | |
| Republican | Tommy Thompson | 1,380,126 | 45.86% | +16.4 | |
| Libertarian | Joseph Kexel | 62,240 | 2.07% | +2.1 | |
| Independent | Nimrod Allen, III | 16,455 | 0.55% | n/a | |
| Other | Scattered | 3,486 | 0.12% | +0.1 | |
| Majority | 166,978 | 5.55% | |||
| Turnout | 3,009,411 | 72.5% | |||
| Democratic hold | Swing | ||||
Aftermath
Brian Schimming, the Vice Chairman of the Wisconsin Republican Party, partly blamed Thompson's defeat on the fact that he had to face a competitive primary whereas Baldwin was unopposed for the Democratic nomination: "[Thompson] blew all his money going through the primary. So when he gets through the primary, it was like three weeks before he was up on the air. [Baldwin] piled on immediately." He claimed "If [Thompson] hadn't had as ugly a primary, we could have won that seat."[63]
See also
- United States Senate elections, 2012
- United States House of Representatives elections in Wisconsin, 2012
References
- ↑ Dr. Michael McDonald (February 9, 2013). "2012 General Election Turnout Rates". George Mason University. Retrieved April 3, 2013.
- ↑ Glauber, Bill (November 3, 2010). "Kohl says he'll work with Johnson". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Retrieved November 29, 2010.
- ↑ Hall, Dee (November 4, 2010). "Feingold won't seek office in 2012, official says". Chippewa Herald. Retrieved November 29, 2010.
- ↑ http://www.jsonline.com/news/statepolitics/129281483.html
- ↑ Burns, Alexander (May 17, 2011). "Barrett closes door on Senate speculation". Politico. Retrieved May 17, 2011.
- ↑ Sullivan, Sean (January 18, 2012). "Falk Announces Candidacy in Wisconsin Gubernatorial Race". National Journal. Retrieved January 28, 2012.
- ↑ Thompson, Krissah (August 19, 2011). "Russ Feingold not running in 2012". The Washington Post.
- ↑ "Baldwin kicks off jobs tour; receives Kagen endorsement". Wispolitics.com. January 5, 2012. Retrieved January 28, 2012.
- ↑ Catanese, David (September 15, 2011). "Rep. Kind says no to Senate run". Politico. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ↑ http://www.rollcall.com/news/Herb-Kohl-Retiring-Senate-Wisconsin-2012-205591-1.html
- ↑ http://www.politico.com/blogs/davidcatanese/0511/Herb_Kohl_wont_seek_reelection.html?showall
- ↑ http://www.wispolitics.com/index.iml?Article=250796
- 1 2 "Former Bucyrus head unlikely to jump into races next year". WisPolitics.com. November 18, 2011. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- 1 2 "Canvass Results for 2012 PARTISAN PRIMARY - 8/14/2012" (PDF). Wisconsin Government Accountability Board. Retrieved September 22, 2012.
- ↑ Gilbert, Craig (April 25, 2009). "Ryan shines as GOP seeks vision". JSOnline. Retrieved June 29, 2010.
- ↑ Catanese, David (May 16, 2011). "Ryan telling GOPers he's unlikely to run". Politico. Retrieved May 17, 2011.
- ↑ Our Campaigns - WI US Senate - R Primary Race - Aug 14, 2012
- ↑ Marley, Patrick (October 11, 2011). "Jeff Fitzgerald announces Senate bid". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ↑ Hovde emerges as new Senate candidate - Leader-Telegram: Front Page
- ↑ Republican Neumann announces Senate run WBAY-TV. August 29, 2011. Accessed August 29, 2011
- ↑ Roll Call. August 29, 2011. Accessed August 29, 2011
- ↑ "Tommy Thompson Makes Wisconsin Senate Bid Official". September 19, 2011. Retrieved September 19, 2011.
- ↑ State Senator Lasee Drops Out Of U.S. Senate Race | News - Channel3000.com
- ↑ Kip Smith enters U.S. Senate race | Wisconsin | onPolitix
- 1 2 3 4 "Green backs Thompson for Senate". WLUK-TV. Associated Press. September 16, 2011. Retrieved December 18, 2011.
- ↑ http://www.jsonline.com/blogs/news/130773358.html
- ↑ http://www.rollcall.com/news/Ryan-Out-Thompson-In-Wisconsin-Senate-205679-1.html?pos=hln
- ↑ http://www.jsonline.com/news/statepolitics/127969353.html?wpisrc=nl_fix
- 1 2 3 4 5 Fitzgerald gets key endorsements - Sun Prairie Star - Sun Prairie, WI
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Fitzgerald announces Waukesha endorsements - Sun Prairie Star - Sun Prairie, WI
- ↑ http://thehill.com/blogs/ballot-box/senate-races/237743-freedomworks-endorses-hovde-in-wisconsin The Hill
- ↑ CFG PAC endorses Kevin Cramer in North Dakota
- ↑ FRC Action PAC
- ↑ Blumenthal, Paul (November 11, 2011). "HUFFPOST FUNDRACE -- Perry Spends Big". Huffington Post.
- ↑ Sen. Coburn endorses Neumann in Wis. Senate race - The Hill's Ballot Box
- ↑ Jim DeMint Backs Wisconsin Senate Hopeful Over Tommy Thompson : Roll Call Politics
- ↑ Utah senator endorses Neumann - JSOnline
- 1 2 http://wispolitics.com/1006/120126_Neumann_100B.pdf
- ↑ Mark Neumann Wins Two Key Endorsements For Senate Race
- ↑ Primary Targets | RedState
- ↑ Neumann endorsed by Sen. Toomey - JSOnline
- ↑ http://wrtl.org/mec/
- ↑ http://impeachobamatoday.blogspot.com/2012/08/mark-levin-endorses-mark-neumann-for-us.html
- ↑ http://waukesha.patch.com/articles/herman-cain-stumps-for-tommy-thompson-at-waukesha-rally
- ↑ http://www.tommyforwisconsin.com/category/endorsements/
- 1 2 Endorsements
- ↑ Rudy Giuliani, Milwaukee Police Association backing Tommy Thompson - JSOnline
- 1 2 3 4 Tommy Thompson Picks Up Senate Endorsements : Roll Call Politics
- ↑ Walker, Don (December 15, 2011). "Huckabee endorses Thompson, slams Club for Growth". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Retrieved December 18, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Seven former governors endorse Thompson - JSOnline
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 http://www.tommyforwisconsin.com/2012/06/21/see-the-full-list/
- ↑ 'The Nuge' endorses Tommy Thompson - JSOnline
- ↑ The Coveted Dick Morris Endorsement
- ↑ http://shorewood.patch.com/articles/joe-the-plumber-supports-thompson-because-he-gets-stuff-done
- ↑ Lewis, Matt K. (September 30, 2011). "(Updated) NRA president backs Tommy Thompson, who opposed concealed carry". The Daily Caller. Retrieved November 17, 2011.
- ↑ GOProud Announces U.S. House Endorsements
- ↑ "Kexel Announces Run for US Senate" (PDF). Wispolitics.com. April 20, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2012.
- ↑ "NIMROD ALLEN III INDEPENDENT CANDIDATE FOR U.S. SENATE" (PDF). Wispolitics.com. July 20, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2012.
- ↑ "2012 House and Senate Campaign Finance for Wisconsin". fec.gov. November 26, 2012. Retrieved December 19, 2012.
- ↑ Center for Responsive Politics (March 25, 2013). "Top Contributors 2012 Race: Wisconsin Senate". opensecrets.org.
- ↑ Center for Responsive Politics (March 25, 2013). "Top Industries 2012 Race: Wisconsin Senate". opensecrets.org.
- ↑ http://gab.wi.gov/sites/default/files/County%20by%20County_11.6.12%20Gen%20Election_U.S.%20Senate.pdf
- ↑ Alex Roarty (September 26, 2013). "Can Republicans Avoid the Next Todd Akin?". National Journal. Retrieved September 30, 2013.
External links
- Elections & Voting at the Wisconsin Government Accountability Board
- Campaign contributions at OpenSecrets.org
- Outside spending at Sunlight Foundation
- Candidate issue positions at On the Issues
- Official candidate sites
- Tammy Baldwin for U.S. Senate
- Tommy Thompson for U.S. Senate
- Joe Kexel for U.S. Senate
- Nimrod Allen III for U.S. Senate