Hydrogen telluride
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
hydrogen telluride | |||
| Other names
hydrotelluric acid tellane tellurium hydride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 7783-09-7 | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.073 | ||
| PubChem | 21765 | ||
| UNII | 7F4735942K | ||
| Properties | |||
| H2Te | |||
| Molar mass | 129.6158 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless gas | ||
| Density | 3.310 g/cm3, gas 2.57 g/cm3 (−20 °C, liquid) | ||
| Melting point | −49 °C (−56 °F; 224 K)[1] | ||
| Boiling point | −2.2 °C (28.0 °F; 270.9 K) (unstable above −2 °C) | ||
| 0.70 g/100 mL | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.6 | ||
| Structure | |||
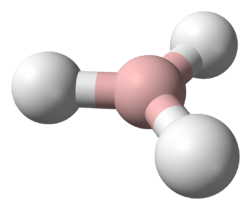
| bent | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
0.7684 kJ/g | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | toxic | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions |
H2O H2S H2Se H2Po | ||
| Other cations |
Na2Te Ag2Te K2Te Rb2Te Cs2Te | ||
| Related compounds |
telluric acid tellurous acid | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Hydrogen telluride (tellane) is the inorganic compound with the formula H2Te. A hydrogen chalcogenide and the simplest hydride of tellurium, it is rarely encountered because it decomposes rapidly to its constituent elements. However, the gas can exist at very low concentrations long enough to be readily detected by the odour of rotting garlic at extremely low concentrations; or by the revolting odour of rotting leeks at somewhat higher concentrations. Most compounds with Te–H bonds (tellurols) are unstable with respect to loss of H2. H2Te is chemically and structurally similar to hydrogen selenide, both are acidic. The H–Te–H angle is about 90°. Volatile tellurium compounds often have unpleasant odours, reminiscent of decayed leeks or garlic.[2]
Synthesis
H2Te is prepared by the acidification of salts of Te2−, such as Al2Te3 and Na2Te.[3] Na2Te can be generated by the reaction of Na and Te in anhydrous ammonia. The intermediate in the acidification, HTe−
, is a stable anion. Sodium hydrogen telluride, NaHTe, can be made by reducing tellurium with NaBH
4.[3]
Preparation
Tellurium hydrides is usually prepared in the laboratory by hydrolysis of the telluride derivatives of electropositive metals.[4] Typical is the hydrolysis of aluminum telluride:
- Al2Te3 + 6 H2O → 2 Al(OH)3 + 3 H2Te
Magnesium and alkali metal tellurides can also be hydrolyzed. Usually these procedures require acid since the H2Te is rather acidic. Electrolytic methods have been developed.[5]
Properties
H
2Te is an endothermic compound, unstable in air and easily oxidised to water and elemental tellurium:[6]
- 2 H
2Te + O
2 → 2 H
2O + 2 Te
It is almost as acidic as phosphoric acid (Ka = 8.1×10−3), having a Ka value of about 2.3×10−3.[6] It reacts with many metals to form tellurides.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Lide, David R., ed. (2006). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87th ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0487-3.
- ↑ Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
- 1 2 Nicola Petragnani; Hélio A. Stefani (2007). Tellurium in organic synthesis. Best synthetic methods (2nd ed.). Academic Press. p. 6. ISBN 0-08-045310-4.
- ↑ Shriver, Atkins. Inorganic Chemistry, Fifth Edition. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York, 2010; pp 407.
- ↑ F. Fehér, "Hydrogen Telluride" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. pp. 438.
- 1 2 Egon Wiberg; Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001). Nils Wiberg, ed. Inorganic chemistry. Translated by Mary Eagleson. Academic Press. p. 589. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ Henry Enfield Roscoe; Carl Schorlemmer (1878). A treatise on chemistry. 1. Appleton. pp. 367–368.