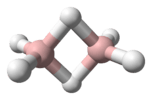Triphosphane
See also: triphos
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Triphosphane[1] | |||
| Other names
Triphosphine[2] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 13597-70-1 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:35893 | ||
| ChemSpider | 123032 | ||
| PubChem | 139510 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
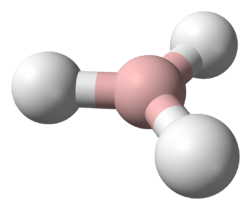
| P 3H 5 | |||
| Molar mass | 97.96099 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless gas | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions |
triazane | ||
| Related Binary phosphanes |
phosphane diphosphane | ||
| Related compounds |
triazene | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Triphosphane (IUPAC systematic name) or triphosphine is an inorganic compound having the chemical formula HP(PH2)2. It can be generated from diphosphine but is highly unstable at room temperature:[3]
- 2 P2H4 → P3H5 + PH3
Samples to date have been contaminated with P2H4 and P4H6 (both branched and linear isomers).[4]
References
- ↑ "triphosphane (CHEBI:35893)". Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI). UK: European Bioinformatics Institute. 7 June 2006. Main. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ↑ "Triphosphine". NIST Chemistry WebBook. USA: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-08-037941-9.
- ↑ Marianne Baudler, Klaus Glinka (1993). "Monocyclic and polycyclic phosphines". Chem. Rev. 93: 1623–1667. doi:10.1021/cr00020a010.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.