Uridine diphosphate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Uridine 5'-(trihydrogen diphosphate) | |
| Identifiers | |
| 58-98-0 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL130266 |
| ChemSpider | 19952429 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.372 |
| 1749 | |
| MeSH | Uridine+diphosphate |
| PubChem | 1158 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H14N2O12P2 | |
| Molar mass | 404.161 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
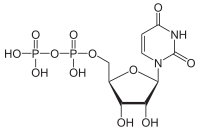
Uridine diphosphate, abbreviated UDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside uridine. UDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase uracil.
UDP is an important factor in glycogenesis. Before glucose can be stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, the enzyme UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase forms a UDP-glucose unit by combining glucose 1-phosphate with uridine triphosphate, cleaving a pyrophosphate ion in the process. Then, the enzyme glycogen synthase combines UDP-glucose units to form a glycogen chain. The UDP molecule is cleaved from the glucose ring during this process and can be reused by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase.[1][2]
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.