Corydon, Indiana
| Town of Corydon, Indiana | |
|---|---|
| Town | |
|
Downtown Corydon Indiana viewed from the Pilot Knob in the Hayswood Nature Reserve | |
 Location in the state of Indiana | |
| Coordinates: 38°12′46″N 86°7′31″W / 38.21278°N 86.12528°WCoordinates: 38°12′46″N 86°7′31″W / 38.21278°N 86.12528°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Indiana |
| County | Harrison |
| Township | Harrison |
| Area[1] | |
| • Total | 1.65 sq mi (4.27 km2) |
| • Land | 1.65 sq mi (4.27 km2) |
| • Water | 0 sq mi (0 km2) |
| Elevation | 587 ft (179 m) |
| Population (2010)[2] | |
| • Total | 3,122 |
| • Estimate (2012[3]) | 3,108 |
| • Density | 1,892.1/sq mi (730.5/km2) |
| Time zone | EST (UTC-5) |
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) |
| ZIP code | 47112 |
| Area code(s) | 812 |
| FIPS code | 18-15256[4] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0433003[5] |
| Website |
www |
Corydon is a town in Harrison Township, Harrison County, Indiana. Located north of the Ohio River in the extreme southern part of the U.S. state of Indiana, it is the seat of government for Harrison County. Corydon was founded in 1808 and served as the capital of the Indiana Territory from 1813 to 1816. It was the site of Indiana's first constitutional convention, which was held June 10–29, 1816. Forty-three convened to consider statehood for Indiana and drafted its first state constitution. Under Article XI, Section 11, of the Indiana 1816 constitution, Corydon was designated as the capital of the state until 1825, when the seat of state government was moved to Indianapolis. During the American Civil War, Corydon was the site of the Battle of Corydon, the only official pitched battle waged in Indiana. More recently, the town's numerous historic sites have helped it become a tourist destination. A portion of its downtown area is listed in the National Register of Historic Places as the Corydon Historic District. As of the 2010 census, Corydon had a population of 3,122.
History
Early settlement
During the American Revolution George Rogers Clark captured the surrounding area of what became the town of Corydon from the British, bringing it under the control of the fledgling United States government.
In the early 1800s Edward Smith brought his family to settle at the edge of a fertile valley near a large spring, the site of the present-day Harrison County fairgrounds. William Henry Harrison, the first governor of the Indiana Territory and a future president of the United States, often stopped to rest at their home while travelling to and from Vincennes, the territorial capital. In 1804 Harrison purchased a tract of land where Big Indian Creek and Little Indian Creek join to become Indian Creek and decided to build a town on the site.
The town gets its name from "The Pastoral Elegy," a hymn that celebrates the death of a shepherd named Corydon.[6] Tradition says that Harrison asked Edward Smith's daughter, Jenny, to name the town and he chose the name from Harrison's favorite hymn, "The Pastoral Elegy."[7] Harrison sold the town site to Harvey Heth in 1807.[6]
Corydon's official founding date of 1808 commemorates the year when Heth, a U.S. government surveyor and landowner, platted the town. Heth donated the town square for public use and sold individual lots to settlers and the territorial government.[7] When Harrison County was established in 1808, Corydon became its county seat of government. In 1809 Corydon was connected by road to Doup's Ferry, 15 miles (24 km) to the south at Mauck's Port, providing access to the Ohio River for trade.
During the War of 1812 Corydon sent a mounted militia company nicknamed the Yellow Jackets to support the territorial army. The company fought in the Battle of Tippecanoe, where it suffered more casualties than any other unit engaged on there.
Territorial capitol (1813–1816)

Corydon became the second capital of the Indiana Territory on May 1, 1813, when it was relocated from Vincennes in Knox County. Opponents of William Henry Harrison, the former territorial governor, wanted to move the capital away from his political stronghold in Knox County. Supporters of the move felt that relocation of the territorial capital to the east would provide a more centralized location for its citizens, especially after its western portion was reorganized to form the Illinois Territory in 1809.[6][7][8]
Corydon competed with Charlestown, Clarksville, Lawrenceburg, Madison, and Jeffersonville to become the new territorial capital.[9] Dennis Pennington, a Harrison County representative and the speaker of the territorial legislature's lower house, helped secure the town's selection during the 1813 session of the Indiana Territory's general assembly. Pennington pointed out that Corydon would be an ideal location. The Harrison County court had approved a design for a new county courthouse on Corydon's public square in 1811 and it could be used as an assembly building for the territorial legislature. Pennington supervised construction of limestone courthouse, which was nearly completed when Indiana's first state legislature convened at Corydon in 1816.[6][10][11]
Constitutional convention, 1816
On April 19, 1816, President James Madison signed an Enabling Act that provided for the election of delegates to a convention at Corydon to consider statehood for Indiana. Forty-three delegates, including five men from Harrison County, convened June 10–29, 1816, to draft Indiana's first state constitution.[12][13] The preamble of the constitution acknowledges the site of the historic gathering: "We the Representatives of the people of the Territory of Indiana, in Convention met, at Corydon, on Monday the tenth day of June in the year of our Lord eighteen hundred and sixteen,..."[14]
The delegates met in an unfinished log cabin near the Harrison County courthouse, which had not yet been completed, but due to cramped conditions and the summer heat, the men often sought refuge outside, under a giant elm tree.[15] (The tree was later named the Constitution Elm. A portion of its trunk has been preserved, surrounded by a sandstone memorial.)[16][17] The delegates completed their work in nineteen days, adjourning on June 29, 1816, when the newly signed state constitution went into effect.[18] As outlined in Article XI, Section 11, of the constitution of 1816: "Corydon, in Harrison County shall be the seat of Government of the state of Indiana, until the year eighteen hundred and twenty-five, and until removed by law."[19]
State capital (1816–1825)
On November 4, 1816, the Indiana General Assembly met for the first time at Corydon under the new constitution and state government.[20] President James Madison signed the congressional resolution admitting Indiana as the nineteenth state in the Union on December 11, 1816,[21] and Corydon began a new era as the first state capital of Indiana.[6][22]
The Harrison County courthouse, now known as the Old Capitol, served as Indiana's first state capitol building. It housed state government offices from 1816 until 1825.[6] Several other historic structures in Corydon date from the early statehood era, including the Governor's Mansion and the Old Treasury Building (Indiana's first state office building), which were built in 1817, and the Colonel Thomas Lloyd Posey home, among others.[23][24] Cordon's Grand Masonic Lodge, the first in the state, was built in 1819.
During the eleven years that Corydon served as a territorial and state capital, it was a center of politics. Notable residents during this time included Davis Floyd, a prominent local politician; two governors of Indiana, Jonathan Jennings and Ratliff Boon (the state's first and second governors, respectively); Dennis Pennington, the first Speaker of the Indiana Senate; and William Hendricks, Indiana's first U. S. Representative, its third governor, and a U.S. Senator.
The state constitution's provision making Corydon the seat of state government was not a popular one, especially among the citizens of rival towns. Others expressed concern that the town's geographical location in the extreme southern part of Indiana would become inconvenient as the state's population center shifted northward; however, Dennis Pennington and other Harrison County representatives to the Indiana General Assembly successfully resisted attempts to move the seat of government from Corydon until 1825.[21][25][26] Governor Hendricks signed a legislative bill in 1824 to move the state capital to Indianapolis,[27] effective January 10, 1825.[28]
Post-capital period
After the seat of state government moved to Indianapolis in 1825, Corydon continued its role as the seat of county government and a market town for the surrounding agricultural area.[29] On September 11–14, 1860, the first annual county fair was held on Corydon's 36-acre (15 ha) fairgrounds. It has been an annual event since 1860, making it the longest, consecutive-running annual county fair in the state.[30] The fairgrounds, established in the southwest corner of town, is bordered on the south and west by a large ridge that served as a natural grandstand until the first grandstand was built, circa 1910.[31]
Battle of Corydon (1863)

During the Civil War, Corydon was the site of the only "official pitched battle" fought in Indiana. On July 9, 1863, Confederate brigadier general John Hunt Morgan's cavalry of more than 2,000 men crossed the Ohio River into Indiana to begin what is known as "Morgan's Raid". The Confederate troops opposed about 450 members of a hastily-assembled home guard at the Battle of Corydon outside of town, but the Union forces were quickly defeated and the town surrendered.[32]
Corydon was sacked in retaliation for Union looting in Kentucky, the town's treasury of $690 was seized, and the inmates of the local jail were released. General Morgan demanded $600 to $700 in ransom from each mill and shop owner to keep their buildings from being burned. Tradition says one Corydon miller overpaid by $200; Morgan promptly returned it to him.[33][34]
Later development
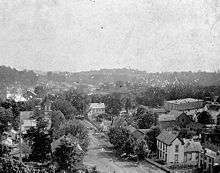
Beginning in 1882 the Louisville, New Albany and Corydon Railroad, an 8-mile (13 km) spur of the Southern Railway, connected Corydon to other towns in the region.[29] Southern Railroad's main line ran across northern Harrison County at Crandall, and remained open to passenger traffic until 1996. As of 2008, the line was owned by Lucas Oil.

In 1889 Corydon was shocked by an attempted murder, the first in the town's history. A quiet, orderly mob of 200 men led by twenty masked Indiana White Caps removed the two alleged assailants named Devin and Tennyson from the county jail. The two were hanged from the old Western Bridge.[35][36] Although their identities were known, the members of the lynching mob were never prosecuted.
In 1917 the state of Indiana purchased the historic Old Capital with the goal of restoring it. The Federal-style building opened as a state memorial in 1929–30; it is a part of the Corydon Capitol State Historic Site. The Harrison County government also used the former statehouse until a new, three-story county courthouse was completed in 1929.[24][37][38]
In 1960 a fire destroyed much of the Harrison County Fairgrounds, including its grandstand. A replacement grandstand was acquired from the minor league baseball team at Parkway Field in Louisville, Kentucky, is still in use.
In 1969 Corydon-born environmental historian Samuel P. Hays donated the 311-acre (126-hectare) Hayswood Nature Reserve to the county. Known as Hayswood Park, it is the county's second largest nature reserve.
In 1973 a portion of Corydon's downtown area was listed on the National Register of Historic Places as the Corydon Historic District. Initially, the district included major sites dating from the period when Corydon was a territorial and state capital: the Old Capitol/Harrison County Courthouse building, the Governor Hendricks' Headquarters, Constitution Elm, the first state office building, the Kintner-McGrain House (Cedar Glade), and the Posey House, among others. In 1989 the historic district's boundary was increased to include The Kintner House Inn, among other commercial and residential buildings.[29][39][40]
In 2008 Corydon celebrated its bicentennial anniversary with a year-long series of events that included the unveiling of a $200,000 bronze statue of Honorable Frank O'Bannon, the late governor of Indiana and a former citizen of Corydon.[41]
Government
Corydon remains the county seat of Harrison County.[42] The current town board president is Fred Cammack, who has served in this position since 1975.
Geography
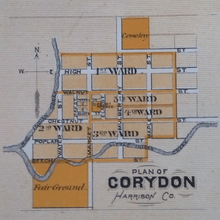
Corydon is located near the center of Harrison County. Indiana State Road 62 passes through the town from east to west; Interstate 64 passes in the same direction less than a mile north of the town. The state capitol of Indianapolis is about 120 miles (190 km) to the north, and the city of Louisville, Kentucky is about 25 miles (40 km) to the east. Indian Creek passes through the town; the creek continues to the southwest where it empties into the Ohio River.[43]
According to the 2010 census, Corydon has a total area of 1.65 square miles (4.27 km2), all land.[1]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1850 | 462 | — | |
| 1870 | 747 | — | |
| 1880 | 763 | 2.1% | |
| 1890 | 880 | 15.3% | |
| 1900 | 1,610 | 83.0% | |
| 1910 | 1,703 | 5.8% | |
| 1920 | 1,785 | 4.8% | |
| 1930 | 2,009 | 12.5% | |
| 1940 | 1,865 | −7.2% | |
| 1950 | 1,944 | 4.2% | |
| 1960 | 2,701 | 38.9% | |
| 1970 | 2,719 | 0.7% | |
| 1980 | 2,724 | 0.2% | |
| 1990 | 2,661 | −2.3% | |
| 2000 | 2,715 | 2.0% | |
| 2010 | 3,122 | 15.0% | |
| Est. 2015 | 3,144 | [44] | 0.7% |
2010 census
As of the census[2] of 2010, there were 3,122 people, 1,341 households, and 716 families residing in the town. The population density was 1,892.1 inhabitants per square mile (730.5/km2). There were 1,491 housing units at an average density of 903.6 per square mile (348.9/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 96.7% White, 0.7% African American, 0.2% Native American, 0.2% Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 0.9% from other races, and 1.2% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2.6% of the population.
There were 1,341 households of which 26.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 35.6% were married couples living together, 11.9% had a female householder with no husband present, 5.9% had a male householder with no wife present, and 46.6% were non-families. 41.6% of all households were made up of individuals and 20.5% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.14 and the average family size was 2.88.
The median age in the town was 40.8 years. 20.5% of residents were under the age of 18; 8.7% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 24.9% were from 25 to 44; 22.4% were from 45 to 64; and 23.4% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the town was 45.6% male and 54.4% female.
2000 census
As of the census[4] of 2000, there were 2,715 people, 1,171 households, and 674 families residing in the town. The population density was 1,708.1 people per square mile (659.3/km²). There were 1,271 housing units at an average density of 799.6 per square mile (308.6/km²). The racial makeup of the town was 97.27% White, 1.14% African American, 0.41% Native American, 0.11% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 0.85% from other races, and 0.18% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.88% of the population.
There were 1,171 households out of which 25.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 40.4% were married couples living together, 13.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 42.4% were non-families. 37.0% of all households were made up of individuals and 19.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.17 and the average family size was 2.81.
In the town the population was spread out with 20.1% under the age of 18, 10.2% from 18 to 24, 24.3% from 25 to 44, 20.7% from 45 to 64, and 24.8% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 41 years. For every 100 females there were 83.1 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 80.2 males.
The median income for a household in the town was $33,823, and the median income for a family was $41,630. Males had a median income of $29,159 versus $21,699 for females. The per capita income for the town was $20,740. About 9.8% of families and 10.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.2% of those under age 18 and 14.3% of those age 65 or over.
Culture

Because of its historic sites and the historic events that took place at Corydon, it has become a southern Indiana tourist destination. The town hosts weekly events from early spring until late fall, usually centered on its historic town square. Local events include an annual Halloween Parade, the Harrison County Fair, Friday night band concerts during the summer, and an annual reenactment of the Battle of Corydon, as well as country and bluegrass music performances. A weeklong county fair is held the last week of July at the Harrison County fairgrounds. It is one of Corydon's more popular events, with attendance usually exceeding 3,000 each night. The fair includes 4-H exhibits, a midway, demolition derbies, harness racing, and musical entertainment.[46]
Historic sites
- Old Capitol, Indiana's first state capitol building[24]
- Governor Hendricks' Headquarters, a former residence of William Hendricks[24]
- Constitution Elm Memorial[37]
- Old Treasury Building, Indiana's first state office building[37]
- Coburn-Porter Law Office, the former law office of Judge William Porter, who served as a speaker of the Indiana House of Representatives[24]
- Posey House[39]
- Battle of Corydon Memorial Park[47]
- The Kintner House Inn[39]
- Branham Tavern, built in 1800, a tavern began operating on the site in 1821.[48]
- Westfall House, the town's oldest extant home[49]
- Kintner-McGrain House (Cedar Glade)][49]
- Leora Brown School[50]
- Heth House
- Cedar Hill Cemetery[49]
- Flags Over Corydon[51]
- Harrison County Fairgrounds
Media
The Corydon Democrat, a weekly newspaper,has served the local area since 1856.[52] It is owned by O'Bannon Publishing Company. Former Indiana governor Frank O'Bannon once owned the publishing company.
Notable people
- James Best, born in Kentucky in 1926 and orphaned at the age of three, was adopted and raised in Corydon. Best joined the U.S. Army after World War II and became an actor in the 1950s. He first appeared in a western and later, a variety of other film genres. Best was also a guest star on television shows such as The Andy Griffith Show and The Twilight Zone. He is best known for his role as Sheriff Rosco P. Coltrane on The Dukes of Hazzard.[53]
- Arville Funk was born in Harrison County in 1929. He attended school in Corydon and beginning in 1955 taught high school history for ten years. Funk studied law in New Albany, Indiana, and returned to Corydon to practice law. In 1965 he formed a law partnership with Frank O'Bannon. Funk was also active in Indiana historical and genealogical societies and wrote many several about Indiana history. Funk died in 1990; he is buried at Corydon.[54]
- Samuel P. Hays was born in Corydon in 1924 to a sixth-generation Corydon family. He attended Swarthmore College and Harvard University. Hays became a professor at the University of Pittsburgh and a pioneer in research the history of the U.S. conservation movement.[55][56][57]
- Frank O'Bannon was born in 1930 and was raised in Corydon. He earned degrees in government and law from Indiana University and served two years in the U.S. Air Force. O'Bannon also served as a state senator for eighteen years and as Indiana's lieutenant governor for eight years, before becoming Indiana's governor in 1997. O'Bannon died in Chicago in 2003 of complications from a stroke prior to the end of his second term as governor. He was 73 years old.[58]
- Spier Spencer, born in Virginia circa 1770, was married in Kentucky before he moved to Vincennes. In 1809 Spencer was appointed the first sheriff of Harrison County and moved to Corydon. He fought in the Battle of Tippecanoe and was killed in action on November 7, 1811. Spencer, Indiana, as well as Spencer County, Indiana, and Spencer County, Kentucky, were named for him.
- William T. Zenor, born near Corydon, studied law in New Albany, Indiana, and returned to Corydon to practice law. From 1885 to 1897 Zenor served as a judge. He was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives, where he served from 1897 to 1907, then returned to his law practice in Corydon. Zenor died in 1916; he is buried at Corydon.
See also
Notes
- 1 2 "G001 - Geographic Identifiers - 2010 Census Summary File 1". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 16, 2015.
- 1 2 "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved December 11, 2012.
- ↑ "Population Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 17, 2013. Retrieved June 25, 2013.
- 1 2 "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on September 11, 2013. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ↑ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. October 25, 2007. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Robert M. Taylor Jr., Errol Wayne Stevens, Mary Ann Ponder, and Paul Brockman (1992). Indiana: A New Historical Guide. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Society. p. 169. ISBN 0871950499.
- 1 2 3 Works Project Administration, Federal Writers' Project (1947). Indiana. A Guide to the Hoosier State. American Guide Series. US History Publishers. p. 181. ISBN 1-60354-013-X.
- ↑ John D. Barnhart and Dorothy L. Riker, eds. (1971). Indiana to 1816: The Colonial Period. The History of Indiana. I. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau and the Indiana Historical Society. p. 355.
- ↑ Ray E. Boomhower (2000). Destination Indiana: Travels Through Hoosier History. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Society. p. 15. ISBN 0871951479.
- ↑ Boomhower, p. 17.
- ↑ The limestone for the courthouse came from a nearby quarry. See D. F. Lemmon (1891). The Ancient Capital of the State of Indiana, Corydon, Harrison County. New Albany, IN: Ledger Company. p. 7.
- ↑ "The Setting for the Convention, " in Pamela J. Bennett, ed. (September 1999). "Indiana Statehood". The Indiana Historian. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau: 6.
- ↑ Harrison County's delegates were John Boone, Davis Floyd, Daniel C. Lane, Dennis Pennington, and Patrick Shields. See Barnhart and Riker, pp. 441–42.
- ↑ "Full Text Of The 1816 Constitution". State of Indiana. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- ↑ Earl L. Conn (2006). My Indiana: 101 Places to See. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Society. p. 204. ISBN 978-0-87195-195-3.
- ↑ Frederick P. Griffin (1974). The Story of Indiana's Constitution Elm, Corydon, Indiana, June 1816. Corydon, IN: General Print Company. pp. 10–13. OCLC 3901490. See also William P. McLauchlan (1996). The Indiana State Constitution: A Reference Guide. Reference Guides to the State Constitutions of the United States. 26. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-313-29208-8.
- ↑ "Indiana History: Indiana, the Nineteenth State (1816)". Center for History. Archived from the original on October 27, 2012.
- ↑ Barnhart and Riker, p. 460.
- ↑ "Constitution of 1816: Article XI". Indiana Historical Bureau. Retrieved August 3, 2016.
- ↑ "The Final Steps to Statehood," Bennett, The Indiana Historian, pp. 10–11.
- 1 2 Barnhart and Riker, p. 461–63.
- ↑ Lemmon, p. 5.
- ↑ Colonel Posey was the son of Thomas Posey, the governor of the Indiana Territory from 1813 until 1816. See Griffin, pp. 19–21.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Corydon Capitol: About Corydon Capitol State Historic Site". Indiana State Museum and Historic Sites. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ↑ "The Constitution of 1816," Bennett, The Indiana Historian, p. 12.
- ↑ Charles Kettleborough (1930). Constitution Making in Indiana: A Source Book of Constitutional Documents, with Historical Introduction and Critical Notes. Indiana Historical Collections. 1. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Commission. pp. 118, 138–39. OCLC 3654268.
- ↑ Linda C. Gugin and James E. St. Clair, eds. (2006). The Governors of Indiana. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau and Indiana Historical Society Press. p. 57. ISBN 0871951967.
- ↑ Donald F. Carmony (1998). Indiana, 1816–1850: The Pioneer Era. The History of Indiana. I. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau and the Indiana Historical Society. pp. 112–13. ISBN 0871951258.
- 1 2 3 "Indiana State Historic Architectural and Archaeological Research Database (SHAARD)" (Searchable database). Department of Natural Resources, Division of Historic Preservation and Archaeology. Retrieved April 1, 2016. Includes Mary Ellen Gadsky (June 1988). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory Nomination Form: Corydon Historic District (Boundary Increase)" (PDF). Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ↑ "154th Harrison County Fair begins Sunday". Clarion News. July 10, 2013. Retrieved October 24, 2014. See also Alan Stewart. "Fair A-Buzz With Activities". The Corydon Democrat.
- ↑ Works Projects Administration, Federal Writers' Project, p. 184.
- ↑ Taylor, et. al, pp. 169, 171.
- ↑ Shelby Foote (1974). The Civil War: A Narrative, Red River to Appomattox. III. New York: Random House. ISBN 0-394-46512-1.
- ↑ Works Project Administration, Federal Writers' Project, pp. 181–82.
- ↑ William H. Roose (1911). Indiana's Birthplace: A History of Harrison County, Indiana. New Albany, Indiana: The Tribune Company, Printers. p. 62.
- ↑ "Strung to the Bridge, Corydon's MurderersLynched". Indiana State Sentinel. June 19, 1889. Retrieved April 17, 2016.
- 1 2 3 Taylor, et. al., p. 170.
- ↑ Boomhower, p. 21.
- 1 2 3 "Indiana State Historic Architectural and Archaeological Research Database (SHAARD)" (Searchable database). Department of Natural Resources, Division of Historic Preservation and Archaeology. Retrieved August 8, 2016. Includes Frederick Porter Griffin (December 1972). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory Nomination Form: Corydon Historic District" (PDF). Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ↑ National Park Service (2010-07-09). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- ↑ Jo Ann Spieth-Saylor (June 11, 2008). "Corydon celebrates 200 years". Clarion News. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 10, 2015. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ↑ Google (October 24, 2014). "Corydon, Indiana" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015". Retrieved July 2, 2016.
- ↑ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Archived from the original on May 11, 2015. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- ↑ Alan Stewart. "Fair a-buzz with activities". The Corydon Democrat.
- ↑ "Corydon Battle Site". State Historic Architectural and Archaeological Research Database (SHAARD). Indiana Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ↑ Conn, p. 205.
- 1 2 3 Taylor, et. al., p. 171.
- ↑ "Leora Brown School". Indiana Historical Bureau. Retrieved August 11, 2016. See also: "Leora Brown School". State Historic Architectural and Archaeological Research Database (SHAARD). Indiana Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ↑ "History and Heritage: Flags Over Corydon". Historic Corydon and Harrison County. Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- ↑ "About Us". The Corydon Democrat. August 3, 2016. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ↑ "Bio for James Best". Retrieved January 21, 2012.
- ↑ Donald E. Thompson, ed. (1974). Indiana Authors and their Books, 1917–1966. Crawfordsville, IN: Wabash College. p. 225.
- ↑ J. Morgan Kousser (Fall 1981). "History as Past Sociology in the Work of Samuel P. Hays: A Review Essay" (PDF). Historical Methods. California Institute of Technology. 14 (4): 181–86. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ↑ "A History of Environmental Politics Since 1945". University of Pittsburgh Press. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- ↑ "Samuel P Hays b1924 Corydon Harrison I". Mocavo.(subscription required)
- ↑ "Indiana Governor Frank O'Bannon (1930-2003)". Indiana Historical Bureau. Retrieved January 21, 2012.
References
- "154th Harrison County Fair begins Sunday". Clarion News. July 10, 2013. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- "A History of Environmental Politics Since 1945". University of Pittsburgh Press. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- "About Us". The Corydon Democrat. August 3, 2016. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- Barnhart, John D., and Dorothy L. Riker, eds. (1971). Indiana to 1816: The Colonial Period. The History of Indiana. I. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau and the Indiana Historical Society.
- "Bio for James Best". Retrieved January 21, 2012.
- Bennett, Pamela J., ed. (September 1999). "Indiana Statehood". The Indiana Historian. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau.
- Boomhower, Ray E. (2000). Destination Indiana: Travels Through Hoosier History. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Society. ISBN 0871951479.
- Carmony, Donald F. (1998). Indiana, 1816–1850: The Pioneer Era. The History of Indiana. I. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau and the Indiana Historical Society. ISBN 0871951258.
- Conn, Earl L. (2006). My Indiana: 101 Places to See. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Society. ISBN 978-0-87195-195-3.
- "Constitution of 1816: Article XI". Indiana Historical Bureau. Retrieved August 2, 2016.
- "Corydon Battle Site". State Historic Architectural and Archaeological Research Database (SHAARD). Indiana Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- "Corydon Capitol: About Corydon Capitol State Historic Site". Indiana State Museum and Historic Sites. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 10, 2015. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Foote, Shelby (1974). The Civil War: A Narrative, Red River to Appomattox. III. New York: Random House. ISBN 0-394-46512-1.
- "Full Text of the 1816 Constitution". State of Indiana. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- Gadsky, Mary Ellen (June 1988). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory Nomination Form: Corydon Historic District (Boundary Increase)" (PDF). Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- Griffin, Frederick Porter (December 1972). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory Nomination Form: Corydon Historic District" (PDF). Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- Griffin, Frederick P. (1974). The Story of Indiana's Constitution Elm, Corydon, Indiana, June 1816. Corydon, IN: General Print Company. OCLC 3901490.
- Gugin, Linda C., and James E. St. Clair, eds. (2006). The Governors of Indiana. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Bureau and Indiana Historical Society Press. ISBN 0871951967.
- "History and Heritage: Flags Over Corydon". Historic Corydon and Harrison County. Retrieved August 12, 2016.
- "Indiana Governor Frank O'Bannon (1930-2003)". Indiana Historical Bureau. Retrieved January 21, 2012.
- "Indiana State Historic Architectural and Archaeological Research Database (SHAARD)" (Searchable database). Department of Natural Resources, Division of Historic Preservation and Archaeology. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- Kettleborough, Charles (1930). Constitution Making in Indiana: A Source Book of Constitutional Documents, with Historical Introduction and Critical Notes. Indiana Historical Collections. 1. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Commission. OCLC 3654268.
- Kousser, J. Morgan (Fall 1981). "History as Past Sociology in the Work of Samuel P. Hays: A Review Essay" (PDF). Historical Methods. California Institute of Technology. 14 (4): 181–86. Retrieved August 8, 2016.
- Lemmon, D. F. (1891). The Ancient Capital of the State of Indiana, Corydon, Harrison County. New Albany, IN: Ledger Company, Printers.
- "Leora Brown School". Indiana Historical Bureau. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- "Leora Brown School". State Historic Architectural and Archaeological Research Database (SHAARD). Indiana Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- McLauchlan, William P. (1996). The Indiana State Constitution: A Reference Guide. Reference Guides to the State Constitutions of the United States. 26. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-313-29208-8.
- Roose, William H. (1911). Indiana's Birthplace: A History of Harrison County, Indiana. New Albany, IN: The Tribune Company, Printers.
- "Samuel P Hays b1924 Corydon Harrison I". Mocavo. (subscription required)
- Spieth-Saylor, Jo Ann (June 11, 2008). "Corydon Celebrates 200 Years". Clarion News. Retrieved October 24, 2014.
- Stewart, Alan. "Fair A-Buzz With Activities". The Corydon Democrat.
- "Strung to the Bridge, Corydon's Murderers Lynched". Indiana State Sentinel. June 19, 1889. Retrieved April 17, 2016.
- Taylor Jr., Robert M., Errol Wayne Stevens, Mary Ann Ponder, and Paul Brockman (1992). Indiana: A New Historical Guide. Indianapolis: Indiana Historical Society. ISBN 0871950499.
- Thompson, Donald E., ed. (1974). Indiana Authors and Their Books, 1917–1966. Crawfordsville, IN: Wabash College.
- Works Project Administration, Federal Writers' Project (1947). Indiana. A Guide to the Hoosier State. American Guide Series. US History Publishers. ISBN 1-60354-013-X.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Corydon. |
- Corydon and Harrison County, Indiana, tourism website
- The Corydon Democrat
- Corydon Central High School
