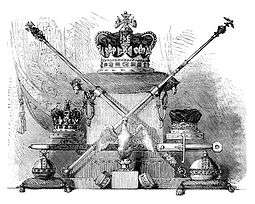
Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom
| Crown Jewels | |
|---|---|
|
St Edward's Crown (top) is used to crown the monarch. It is flanked by the sceptres. Also in this picture are the crown and diadem of Mary of Modena (wife of James II of England), the blunt Sword of Mercy, the eagle-shaped ampulla, the armills, and the orbs. | |
| Overview | |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Location | On public display in the Jewel House and the Martin Tower at the Tower of London, and the debating chambers at the Palace of Westminster |
| No. of objects |
|
| Oldest | Coronation Spoon (12th century) |
| Newest | Queen Elizabeth II's Armills (1953) |
| Precious stones | 23,578 |
| Owner | Queen Elizabeth II in right of the Crown |
| Managers |
Martin Swift (Crown Jeweller) Royal Collection Trust Historic Royal Palaces |
| Website |
www |
The Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom are 141 historic ceremonial objects, including the regalia and vestments worn by kings and queens of the country at their coronations, as well as processional and anointing objects, plate, and christening fonts.[lower-alpha 2]
A symbol of 800 years of monarchy,[3] the sovereign's coronation regalia is the only working collection in Europe – other present-day monarchies have abandoned coronations in favour of inauguration or enthronement ceremonies – and is the largest set of regalia in the world.[4] Objects used to invest and crown the monarch variously denote his or her roles as Head of State, Supreme Governor of the Church of England, and Commander-in-Chief of the British Armed Forces. Wives of kings are crowned as queen consort with a plainer set of regalia. Since 1831, a new crown has been made specially for each queen consort.
The use of regalia by monarchs in Britain can be traced back to its early history. Most of the present collection as a whole dates from around 350 years ago when King Charles II ascended the throne. The medieval coronation regalia and Tudor state regalia had been either sold or melted down by Oliver Cromwell, a republican who overthrew the monarchy in 1649, during the English Civil War. Notable among the precious stones which adorn the regalia are Cullinan I (the largest clear cut diamond in the world), Cullinan II (second-largest of the Cullinan diamonds), the Koh-i-Noor diamond with a history going back to the 13th century, the Stuart Sapphire, St Edward's Sapphire, and the Black Prince's Ruby – a large spinel worn by King Henry V at the Battle of Agincourt.
In addition to their use at coronations, a number of items are used at the annual State Opening of Parliament, royal christenings, weddings, and a few other state and religious occasions. Many pieces have fallen out of use, like the state trumpets and banqueting plate, and some were only designed to be used once, such as the bespoke ring made for Queen Victoria's coronation in 1838 and the Imperial Crown of India made for King George V to wear as Emperor of India at the Delhi Durbar in 1911.
When not in use, the Jewels are on public display, mainly in the Jewel House, a vault at the Tower of London where they are seen by around 2.5 million visitors from across the world every year. Although they are part of the Royal Collection and owned by the king or queen for the duration of his or her reign, the Crown Jewels do not belong to the monarch personally.
History
Early history
The earliest known use of regalia in England was discovered by archaeologists in 1988 in Deal, Kent and dates to between 200 and 150 BC;[5] a sword, brooch, ceremonial shield, and a bronze crown with one arch and La Tène-style patterns were found inside the tomb of the Mill Hill Warrior.[6] Following the Roman conquest of Britain in 43 AD, crowns and other symbols of authority continued to be used by the governors of Britain. A dig in a field at Hockwold cum Wilton, Norfolk in 1957 revealed a large number of circlets and a bronze crown with two arches and depictions of male faces, dating from the period of Roman occupation.[7]
Middle Ages
By the 5th century, the Romans had withdrawn from Britain, and the Angles and the Saxons settled. A series of new kingdoms began to emerge. One of the methods used by regional kings to solidify their authority over their territories was the use of ceremony and insignia.[8] The tomb of an unknown king – evidence suggests it may be Rædwald of East Anglia[9] – at Sutton Hoo provides a unique insight into the regalia of a pre-Christian Anglo-Saxon king. Inside the early 7th-century tomb discovered in 1939 was found an ornate helmet comprising an iron cap, neck guard, and face mask, decorated with images of animals and warriors in bronze, and set with garnets.[10] He was also buried with a heavy stone sceptre, on top of which is an iron ring surmounted by the figure of a stag; a decorated sword; and a ceremonial shield.[11]

In 597, a Benedictine monk had been sent by Pope Gregory I to start converting Pagan England to Christianity. The monk Augustine became the first Archbishop of Canterbury. Within two centuries, the ritual of anointing monarchs with holy oil and crowning them (initially with helmets rather than crowns) in a Christian ceremony had been established, and regalia took on a religious identity. There was still no permanent set of coronation regalia; each monarch generally had a new set made, with which he or she was usually buried upon death.[14]
Edward the Confessor is depicted on a throne and wearing a crown in the first scene of the Bayeux Tapestry. In 1066, Edward died without an heir, and William the Conqueror emerged as king of England following his victory over the English at the Battle of Hastings. Wearing a crown became an important part of William I's efforts to cement his authority over his new territory and subjects.[15] At his death in 1087, the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle reported:
[William] kept great state … He wore his crown three times a year as often as he was in England … On these occasions all the great men of England were assembled about him … He was so stern and relentless a man that no one dared do aught against his will … Among other things we must not forget the good order he kept in the land.[16]

In 1161, Edward the Confessor was made a saint, and objects connected with his reign became holy relics. The monks at his burial place Westminster Abbey claimed that Edward had asked them to look after his regalia in perpetuity and that they were to be used at the coronations of all future kings of England.[15] A note to this effect is contained in an inventory of relics drawn up by Richard Sporley, a monk at the abbey from 1430 until 1480, recording a tunicle (and other vestments), a golden crown, comb and spoon, for the queen's coronation a crown and two rods, and for the communion a chalice of onyx and a golden paten.[17] Although the claim was likely an exercise in self-promotion on the part of the abbey, and some of the regalia had probably been taken from Edward's grave when he was reinterred there, it became accepted as a fact, thereby establishing the concept of hereditary coronation regalia.[15]
A crown referred to as St Edward's Crown is first recorded as having been used for the coronation of Henry III in 1220, and it appears to be the same crown worn by Edward.[18] Being crowned and invested with regalia owned by a previous monarch who was also a saint reinforced the king's authority.[19] The crown would be used in many subsequent coronations until its eventual destruction 400 years later. One of the few descriptions of St Edward's Crown to survive, from Henry III's time, is a "gold crown with diverse stones".[18] Also in the Crown Jewels in this period was an item called a state crown. Together with other crowns, rings, and swords, it comprised the monarch's non-hereditary state regalia that was kept separate from the coronation regalia, mostly at the royal palaces.[20]
.jpg)
Following the defeat in 1282 of the Welsh prince Llewelyn ap Gruffydd by Edward I, the Welsh regalia, including the crown of the legendary King Arthur, were surrendered to England. According to the Chronicle of Aberconwy Abbey, "and so the glory of Wales and the Welsh was handed over to the kings of England".[21] After the invasion of Scotland in 1296, the Stone of Scone was sent to the Tower of London "in recognition", as the chronicler Walter of Guisborough put it, "of a kingdom surrendered and conquered".[22] It was fitted into a wooden chair – then known as King Edward's Chair – which came to be used for the investiture of kings of England, earning its reputation as the Coronation Chair.[23] The Scottish regalia were also taken to London;[24] Scotland eventually regained its independence.[25]
In Edward II's treasury in 1324 there were no fewer than 10 crowns.[26] At some point in the 14th century, the state regalia were moved to the White Tower at the Tower of London due to a series of successful and attempted thefts in a part of Westminster Abbey,[lower-alpha 4] where the holy relics of the coronation regalia stayed behind intact.[27] Arches topped with a monde and cross were added to St Edward's Crown by the time of Henry IV and to the state crown during the reign of his successor Henry V.[28] Known as a closed or imperial crown, the arches symbolised the king's pretensions of being an emperor of his own domain, subservient to no one but God, unlike some continental rulers who owed fealty to more powerful kings or the Holy Roman Emperor.[29]
Early modern period
The traditions established in the medieval period continued later.[30] By the middle of the 15th century, a crown was formally worn on six religious feasts every year: Christmas, Epiphany, Easter, Whitsun, All Saints and one or both feasts of St Edward.[31] A crown was also displayed and worn at the annual State Opening of Parliament.[32] Around this time, swords – symbols of kingship since ancient times – were introduced into the coronation ceremony. Three swords were used to represent the king's powers in the administration of justice: the Sword of Spiritual Justice, Sword of Temporal Justice and Sword of Mercy.[33] Another emerging item of state regalia was the orb, described in Tudor inventories as a round ball with a cross of gold,[34] which underlined the monarch's sovereignty. Orbs had been pictorial emblems of royal authority in Britain since the early Middle Ages but a real orb was not used at any British coronation until that of Henry VIII in 1509; it would be added to the coronation regalia in the 17th century.[35]
State regalia were increasingly passed from one king to the next. The first example of this was Henry VIII's Crown. Its date of manufacture is unknown but it was probably created at the beginning of the Tudor dynasty.[34] The gold crown was covered in pearls, rubies, sapphires and diamonds, and its rim was decorated with alternating crosses pattée and fleurs-de-lis. The centre petals of the fleurs-de-lis had images of Christ, the Virgin Mary and St George in an effort by Henry VIII to secure his position as head of the new Church of England.[36] Although some English monarchs laid claim to the French throne, the fleurs-de-lis on their crowns had evolved from the trefoil introduced by King Canute and were purely decorative.[37] The concept of hereditary state regalia was enshrined in law after the Union of the Crowns when James VI and I decreed in 1606: "the Imperial Diadem and Crown, and other royal and princely ornaments and jewels [are] to be individually and inseparably for ever hereafter annexed to the kingdom of this realm".[38]
Interregnum
Following the death of James I in 1625, Charles I succeeded the throne. His many conflicts with Parliament, stemming from his belief in the divine right of kings and the many religious conflicts that pervaded his reign, triggered the English Civil War. After six years of war, Charles was defeated and executed by the Roundheads in 1649. Less than a week after the king's execution, the Rump Parliament voted to abolish the monarchy, and Oliver Cromwell would become Lord Protector of England. The newly created English Republic found itself short of money. In order to raise funds, the 'Act for the Sale of the Goods and Personal Estate of the Late King, Queen and Prince' was brought into law, and trustees were appointed to value the Jewels – regarded by Cromwell as symbolic of the "detestable rule of kings"[39] – and sell them to the highest bidder.[40] The most valuable object was Henry VIII's Crown, valued at £1,100.[41] Stripped of their gemstones and pearls, the coronation regalia and state regalia were melted down and turned into coins by the Royal Mint.[42]
Restoration to present day
The British monarchy was eventually restored in 1660 after Cromwell's death, and in preparation for the coronation of King Charles II, who had been living in exile in France, new jewels were made based on records and memory of the lost items.[43] The new regalia were supplied by the banker and Royal Goldsmith, Sir Robert Vyner at a cost of £12,184[44][lower-alpha 5] – as much as three new warships.[46] The king appointed as Court Jeweller the gem merchant Sir John Chardin who owned a large quantity of precious stones accumulated on his travels in Asia.[47] The Coronation Chair had been retained and used for Cromwell's installation as Lord Protector at Westminster Hall. A medieval anointing spoon and three swords had survived and were returned to the Crown.[43] Between 1660 and 1663, at the additional cost of some £18,000, almost two tons (4,400 lb) of altar and banqueting plate were made for the king.[48]

In 1669, the Jewels went on public display in the Jewel House at the Tower of London. The Deputy Keeper of the Jewel House, Talbot Edwards took the regalia out of a cupboard and showed it to visitors for a small fee.[49] This informal arrangement was ended two years later when Colonel Thomas Blood, an Irish-born army officer loyal to Parliament, attacked the 77-year-old and, with the help of three accomplices, made off with a crown, a sceptre and the Sovereign's Orb. They were apprehended at the perimeter, and all the items were recovered, though some had been damaged: the crown was flattened with a mallet in an attempt to conceal it, and there was a dent in the orb.[50] Ever since, the Crown Jewels have been protected by armed guards.[49]
Since the Restoration, there have been many additions and alterations to the regalia.[lower-alpha 6] A new set of regalia was commissioned in 1685 for Mary of Modena, the first queen consort to be crowned since the Restoration, Charles II having been unmarried when he took the throne.[52] Another, more elaborate set had to be made four years later when Mary II was crowned as joint sovereign with her husband William III. Starting with their successor, Queen Anne, gemstones would be hired for coronations and replaced with paste or crystal for display in the Jewel House, a practice which continued until the early 20th century.[43]
During World War II,[53] the Crown Jewels were stored in the basement of Windsor Castle.[54][lower-alpha 7] The most valuable gems were removed from their settings and sealed in a pot which could be taken elsewhere if there was an emergency.[55] After the war, 34 boxes containing the Crown Jewels were kept in a vault at the Bank of England while the Jewel House was repaired; it had been struck by a bomb.[56] In 1947, the Jewels went back on display at the Tower of London.[57] In 1953, 910 years after the coronation of its namesake, St Edward's Crown was placed on the head of Queen Elizabeth II in what is now the only ceremony of its kind in Europe.[43] Today, the Crown Jewels are permanently set with 23,578 diamonds, rubies, emeralds and sapphires,[58] and they are seen in the Jewel House by around 2.5 million visitors from across the world every year.[59]
Crowns
While some of the crowns are used by every monarch, others have been made specially for monarchs and queens consort.
St Edward's Crown

The centrepiece of the coronation regalia is named after Edward the Confessor, and is placed on the monarch's head at the actual moment of crowning by the Archbishop of Canterbury.[60] Made of gold in 1661, St Edward's Crown has four fleurs-de-lis and four crosses pattée with two depressed arches on top. Surmounting the arches is a jewelled monde and cross pattée. Its frame is embellished with 444 precious and semi-precious stones, including amethysts, garnets, peridots, rubies, sapphires, topazes, tourmalines and zircons. The crown is 30 cm (12 in) tall, and at a weight of 2.23 kg (5 lb) it has been noted to be extremely heavy.[61] After 1689, monarchs chose to be crowned with a lighter, bespoke coronation crown or their state crown. The tradition of using St Edward's Crown was revived in 1911 for the coronation of George V.[60] In 1953, Queen Elizabeth II opted to use a stylised image of this crown in coats of arms, badges, logos and various other insignia throughout the Commonwealth realms to symbolise her royal authority.[62]
Imperial State Crown
A much lighter crown is worn by the newly crowned monarch when he or she leaves Westminster Abbey, and at the annual State Opening of Parliament.[63] The current Imperial State Crown was made in 1937 for George VI and is a virtual copy of the one made in 1838 for Queen Victoria which had fallen into a poor state of repair;[64] its empty gold frame can be seen at the Tower of London.[1] The crown was altered in 1953 when it was resized to fit Queen Elizabeth II and the arches were lowered by 2.5 cm (1 in) to give it a more feminine appearance.[65] It is made of gold, silver and platinum, and has four crosses pattée and fleurs-de-lis, with two arches surmounted by a monde and cross pattée. The crown is decorated with 2,868 diamonds, 273 pearls, 17 sapphires, 11 emeralds and 5 rubies.[66] Among the largest stones are the Black Prince's Ruby (a spinel) set in the front cross, beneath which is the 317-carat (63 g) Cullinan II diamond, also known as the Second Star of Africa. At the back of the crown is set the 104-carat (21 g) Stuart Sapphire, and in the top cross is St Edward's Sapphire, reputedly taken from the ring of Edward the Confessor when his body was reinterred at Westminster Abbey in 1163. Three of the pearls hanging below the monde are said to have been owned by Queen Elizabeth I.[67]
Consort crowns

The wives of kings – queens consort – traditionally wore the Crown of Mary of Modena, wife of James II, who first wore it at their coronation in 1685. Originally set with 561 hired diamonds and 129 pearls, it is now set with crystals and cultured pearls for display in the Jewel House along with a matching diadem that consorts wore in procession to the abbey.[68] By the 19th century, the crown was judged to be too theatrical and in a poor state of repair, so a new crown was made for Queen Adelaide, wife of William IV, to wear in 1831 using gemstones from her own collection of jewellery.[69] Its empty frame is on display in the Martin Tower at the Tower of London.[70]
Thus began a tradition of each queen consort having a crown made specially for her. In 1902, a European-style crown, flatter and with more arches than traditional British crowns, was made for Queen Alexandra, wife of Edward VII, to wear at their coronation. Set with over 3,000 diamonds, it was the first crown to include the 105-carat (21 g) Koh-i-Noor diamond which had been presented to Queen Victoria following the British conquest of the Punjab.[71] The second was Queen Mary's Crown; also unusual for a British crown in having eight half-arches instead of the traditional four, the crown was made in 1911 for the coronation of Queen Mary and George V. It contains 2,200 diamonds and has contained Cullinans III and IV. In 1914, both Cullinan stones and the Koh-i-Noor were replaced with crystal replicas and, at the same time, the arches were made detachable so it could be worn as a circlet or open crown.[72] Mary paid for the Art Deco-inspired crown out of her own pocket, and the queen had originally hoped that it would be used by future queens consort.[73]
The Queen Mother's Crown is a platinum crown made for Queen Elizabeth, the wife of George VI, to wear at their coronation in 1937. It is the only crown for a British king or queen to be made entirely of platinum,[72] and was modelled on Queen Mary's Crown, but has four half-arches instead of eight.[74] Its arches are detachable at the crosses pattée, allowing it to be worn as a circlet. The crown is decorated with about 2,800 diamonds, most notably the Koh-i-Noor in the middle of the front cross. It also contains a replica of the 22.5-carat (5 g) Lahore Diamond given to Queen Victoria by the East India Company in 1851,[75] and a 17.3-carat (3 g) diamond given to her by Abdülmecid I, Sultan of the Ottoman Empire, in 1856.[76] The crown was laid on top of Elizabeth's coffin during her lying in state and at her funeral in 2002.[77]
Prince of Wales coronets

The relatively modest Coronet of Frederick was made in 1728 for Frederick, Prince of Wales, the eldest son of George II. It takes the form laid down in a royal warrant issued by Charles II which states that the heir apparent of the Crown shall use and bear a coronet of crosses and fleurs-de-lis with one arch surmounted by a ball and cross.[78] The single arch denotes that the Prince of Wales is inferior to the monarch but outranks the other royal children, whose coronets have no arches.[79] Frederick never wore his gold coronet; instead, it was placed on a cushion in front of him when he took his seat in the House of Lords. It was used by his son, George III, then his son, George IV, and last used by Edward VII when he was Prince of Wales.[80] Due to its age, a new silver-gilt coronet was made for his son, the future George V, to wear at his coronation in 1902. In contrast to the earlier coronet, which has a depressed arch, the arch on this one is raised. At George's own coronation in 1911, the coronet was worn by his son, Edward, the next Prince of Wales.[81] After he became king in 1936, Edward VIII abdicated later the same year and, as the Duke of Windsor, went into exile in France, taking the 1902 coronet with him; it remained abroad until his death in 1972. In its absence, another coronet had to be made for the investiture of Prince Charles in 1969.[82] Unlike the defunct coronets,[1] this one is not a part of the Crown Jewels but the Honours of the Principality of Wales.[83]
Non-coronation crowns
In the Jewel House there are two crowns that were not intended to be used at a coronation. Queen Victoria's Small Diamond Crown is just 10 cm (4 in) tall, and was made in 1870 using diamonds taken from a large necklace belonging to the queen, who wore the crown on top of her widow's cap following the death of her husband, Prince Albert. Towards the end of her reign, she often wore it at State Openings of Parliament in place of the much heavier Imperial State Crown.[84] After the queen's death in 1901, her daughter-in-law Queen Alexandra wore the crown, and it was also worn by Queen Mary.[85] The Imperial Crown of India was created in 1911 when George V visited the Delhi Durbar with Queen Mary to be proclaimed (but not crowned) as Emperor of India before the princes and rulers of the country.[86] Since the British constitution prohibits the removal of Crown Jewels from the United Kingdom, a new crown had to be made specially for the event, with emeralds, rubies, sapphires and 6,100 diamonds. The silver-gilt crown is the only crown of a British sovereign to have eight half-arches. It has not been used since George V returned from India and is now a part of the Crown Jewels.[87]
Processional objects
A coronation begins with the procession into Westminster Abbey.
Swords

Three swords are carried into the abbey by high-ranking peers of the realm: the blunt Sword of Mercy (also known as Curtana), the Sword of Spiritual Justice and the Sword of Temporal Justice.[88] All three are believed to have been supplied at the time of James VI & I between 1610 and 1620, probably by Robert South, a member of the Worshipful Company of Cutlers,[89] using blades that were created in the 1580s by Italian bladesmiths Giandonato and Andrea Ferrara. Before the 17th century it was usual practice for new swords to be made for each coronation.[33] During the civil war they were sold for £5 to Roger Humphreys who returned them to the Crown at the Restoration.[89] Their first recorded use was at the coronation of James II in 1685.[90]
Two other swords are used. The two-handed Sword of State,[lower-alpha 8] made in 1678, symbolises the monarch's royal authority.[92] It is also carried before the monarch at State Openings of Parliament.[93] Its wooden sheath is bound in crimson velvet decorated with silver-gilt emblems of England, Scotland and Ireland, fleurs-de-lis and portcullises. In the centre is the royal badge of joint-sovereigns William III and Mary II, for whose coronation the sheath was made in 1689.[94] The lion of England and unicorn of Scotland form the cross-piece to the sword's handle. At coronations, a peer gives the Sword of State to the Lord Great Chamberlain who places it on a table in St Edward's Chapel.[95]
The jewelled Sword of Offering, made in 1820, has a gilded leather sheath, a blade of Damascus steel, and is encrusted with 3,476 precious stones.[96] George IV paid £5,988 for the sword out of his own pocket.[97] It remained in the private ownership of the Royal Family until 1903 when it was deposited with the Crown Jewels by Edward VII.[98] The monarch is girded with the sword and offers it at the altar in Westminster Abbey as a promise to "stop the growth of iniquity, protect the Holy Church of God, help and defend widows and orphans, restore the things that are gone to decay, maintain the things that are restored, punish and reform what is amiss, and confirm what is in good order" throughout his or her reign.[99] Afterwards, it is returned to the Keeper of the Jewel House by the abbey in exchange for a token sum of £5,[46] and the sword is borne unsheathed for the rest of the ceremony.[100]
The defunct Irish Sword of State, made in 1681, also resides at the Tower of London, and was held by the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland prior to Ireland gaining independence from the United Kingdom in 1922.[101] At 1.27 m (4 ft) long, it is the largest sword in the collection.[1]
St Edward's Staff
St Edward's Staff is a 1.4-metre (5 ft) long gold walking stick made for Charles II in 1661. It has a plain monde and cross at the top and a steel pike at the bottom.[102] This object is almost certainly a copy of the "long rod of silver gilt" mentioned in the list of royal plate and jewels destroyed in 1649.[103] The staff's intended role in the coronation has been forgotten since medieval times, and so it is carried into the abbey by a peer as a holy relic and laid on the altar, where it remains throughout the ceremony.[104]
Trumpets

The Crown Jewels include 16 silver trumpets dating from between 1780 and 1848.[1] In the Tower of London, nine of these are draped with red silk damask banners embroidered with coats of arms in gold, originally made for the coronation of Queen Victoria in 1838.[105] They have not been used since the Corps of State Trumpeters was disbanded by the Duke of Wellington as a cost-cutting measure in the 19th century.[106] The trumpeters' main job was to sound a fanfare at key points in the coronation where they occupied a gallery above the choir screen.[107] Today, the bands of the Household Cavalry and Royal Air Force play their own trumpets at state occasions.[108][109]
Maces
Beginning life as weapons carried by the king's sergeants-at-arms, or bodyguards, maces evolved into ceremonial objects carried by the king's officers.[110] Today, they are used to represent the monarch's authority. The House of Commons can only operate when the royal mace – dating from the reign of Charles II – is present at the table. Two other maces are used by the House of Lords; one is placed on the Woolsack before the house meets and is absent from the chamber when the monarch is there in person.[111] Originally, there were 16 silver-gilt maces, but only 13 survive, 10 of which are on display at the Tower of London. Two of these are carried in the royal procession at State Openings of Parliament and coronations. Each mace is about 1.5 m (5 ft) long and weighs an average of 10 kg (22 lb).[112]
Anointing objects
When a monarch is anointed, the Dean of Westminster pours holy anointing oil from the Ampulla into the Coronation Spoon.[113]
The ampulla, 20 cm (8 in) tall and weighing 660 g (23 oz), is a hollow gold vessel made in 1661 and shaped like an eagle with outspread wings. Its head unscrews, enabling the vessel to be filled, and the oil exits via a hole in the beak.[114] Fourteenth-century legend has it that the Virgin Mary appeared in front of St Thomas Becket, Archbishop of Canterbury from 1162 until his murder in 1170, and presented to him a gold eagle and some oil for anointing future kings of England.[115]
The 27-centimetre (11 in) long spoon, which dates from the late 12th century, is silver-gilt and set with four pearls. A ridge divides the bowl in half, creating grooves into which the Archbishop of Canterbury dips two fingers and anoints the monarch on the hands, chest, and forehead, confirming him or her as head of the Church of England.[116] It is the oldest surviving piece of regalia, first recorded in the Royal Collection in 1349, and was probably made for Henry II or Richard I.[117] In 1649, Oliver Cromwell sold the spoon to Clement Kynnersley, Yeoman of the Removing Wardrobe, who returned it to Charles II upon the restoration of the monarchy.[118]

Robes and ornaments
The anointing is followed by the investment with the coronation robes and ornaments.
Robes

Robes include the Supertunica, a dalmatic made for George V in 1911; and the Imperial Mantle, a pallium made for George IV in 1821. Both robes are of gold thread and together weigh 10 kg (22 lb). A new girdle and stole were made in 1953 for Queen Elizabeth II by the Worshipful Company of Girdlers. The stole is embroidered with the floral emblems of Australia, Canada, England, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Scotland, Sri Lanka and Wales. The leek of Wales was used instead of the yellow daffodil as it would not have contrasted well against the gold thread.[119] All the robes have priestly connotations and their form has changed little since medieval times.[120]
Spurs
Spurs remade for Charles II are taken from the altar and presented to the monarch. They are made of solid gold, richly embossed with floral patterns and scrolls, and have straps of crimson velvet embroidered in gold. Known originally as St George's Spurs, they are one of the emblems of knighthood and chivalry, and with the swords they denote the sovereign's role as head of the Armed Forces. Gold spurs were introduced into the coronation ceremony in 1189 at the coronation of Richard I. Historically, the spurs were fastened to the monarch's feet but since the Restoration they are simply brushed against the heels of kings or shown to queens and placed on the altar.[121]
Armills
The Armills are gold bracelets of sincerity and wisdom.[122] Like the spurs, they were first used at English coronations in the 12th century.[123] For Queen Elizabeth II's coronation in 1953, a new set of plain 22-carat gold armills lined with crimson velvet was made and presented on behalf of various Commonwealth governments. Each bracelet is fitted with an invisible hinge and a clasp in the form of a Tudor rose. The hallmark includes a tiny portrait of the Queen.[124] They are on display at the Tower of London along with an older pair made for Charles II.[96] The 17th century bracelets, 4 cm (2 in) wide and 7 cm (3 in) in diameter, are champlevé enamelled on the surface with roses, thistles and harps – the national symbols of England, Scotland and Ireland – as well as fleurs-de-lis.[125] The Queen continued to wear the armills on leaving the abbey and could be seen wearing them later, with the Imperial State Crown and Sovereign's Ring, during her appearance on the balcony of Buckingham Palace.[126]
Orbs

The Sovereign's Orb, a type of globus cruciger, is a hollow gold sphere about 16.5 cm (6 in) in diameter and weighing 1.2 kg (3 lb) that was made for Charles II in 1661.[127] A band of gems and pearls runs along the equator and there is a half-band on the top hemisphere. Atop the orb is an amethyst surmounted by a jewelled cross symbolising the Christian world.[128] Altogether, the orb is decorated with 375 pearls, 365 diamonds, 18 rubies, 9 emeralds, 9 sapphires, 1 amethyst and 1 piece of glass.[129] It is handed to the sovereign during the investiture rite of the coronation and is borne later in the left hand when leaving Westminster Abbey.[130] Queen Mary II's Orb is a smaller version made in 1689 for Mary II to hold at her joint coronation with William III; it was never used again, and is set with imitation gems and cultured pearls.[131] However, both orbs, the sovereign's sceptres and the Imperial State Crown were laid on top of Queen Victoria's coffin for its journey from Osborne House to London and her state funeral in 1901.[132][lower-alpha 9] No official reason was given for using Mary II's orb, though it may have been intended to reflect Victoria's dual position as Queen of the United Kingdom and Empress of India.[114]
Rings
The Sovereign's Ring dates from 1831. Before then, each monarch received a new ring to symbolise his or her "marriage" to the nation, but the current ring has been used by all monarchs from William IV to Queen Elizabeth II, with the exception of Queen Victoria, whose fingers were too small to retain it.[52] In the centre of the gold ring is an octagonal sapphire, 1.5 cm (1 in) in diameter, overlaid with a square ruby and four long, narrow rubies to form a cross. Around the sapphire is a circle of 14 brilliant diamonds.[133] The general design is intended to represent the red Cross of St George on the blue background of St Andrew's Cross.[124]
A small copy of the ring was made for Victoria, who wrote in a letter, "The Archbishop had (most awkwardly) put the ring on the wrong finger, and the consequence was that I had the greatest difficulty to take it off again, which I at last did with great pain".[134] In fact, the ring had been sized to fit the queen's little finger instead of her ring finger due to a misunderstanding by the jewellers.[135] It was left to the Crown upon her death in 1901 and is on display at the Tower of London.[136]
The Queen Consort's Ring, set with diamonds and rubies, has been worn at coronations by all wives of kings from Queen Adelaide onwards.[137]
Sceptres
The sceptre, a symbolic ornamental rod held by the monarch at a coronation, is most likely derived from the shepherd's staff, via the crozier of a bishop; it may, however, be a remnant of the ceremonial spear that was presented to kings and queens at coronations in different parts of the world in early history.[138]

Two gold sceptres made in 1661 are part of the coronation regalia.[129] The Sovereign's Sceptre with Cross is a token of his or her temporal power as head of state. The whole object is 92 cm (3 ft) long, weighs around 1.17 kg (3 lb), and is decorated with 333 diamonds, 31 rubies, 15 emeralds, 7 sapphires, 6 spinels and 1 composite amethyst.[139] In 1910, it was redesigned to incorporate Cullinan I, also known as the Great Star of Africa, which, at over 530 carats (106 g), is still the largest clear cut diamond in the world. It was part of a rough diamond weighing 3,025 carats (605 g) found in South Africa in 1905 and was named after the chairman of the mining company, Thomas Cullinan.[140] The gold clasps holding it can be opened and the stone removed to be worn as a pendant hanging from Cullinan II, which is set in the Imperial State Crown, to form a brooch – Queen Mary, wife of George V, often wore it like this.[67] Above the pear-shaped diamond is the amethyst surmounted by a cross pattée encrusted with an emerald and small diamonds. During the coronation, the monarch bears the Sceptre with Cross in the right hand.[141]

The less ornate Sovereign's Sceptre with Dove, also called the Rod of Equity and Mercy, is emblematic of his or her spiritual role as head of the Church of England.[142] It is a bit longer at 1.1 m (4 ft) but weighs about the same as the Sceptre with Cross. The sceptre is decorated with 94 diamonds, 53 rubies, 10 emeralds, 4 sapphires and 3 spinels.[139] At the top is a gold monde, on which sits a white enamelled dove with its wings outspread; the eyes, beak and feet are gold leaf. The dove has been used to represent the Holy Ghost, who guides the sovereign's actions, for many centuries. In France, it was the custom to release white doves inside Notre-Dame de Reims after the coronation of monarchs. Circling the rod are bands of diamonds, rubies, emeralds and sapphires. The Sceptre with Dove is borne in the left hand, and as the sovereign holds both sceptres, he or she is crowned with St Edward's Crown.[143]
The Crown Jewels include two sceptres originally made for Mary of Modena, the wife of James II, in 1685: a gold sceptre with a cross known as the Queen Consort's Sceptre with Cross and another topped by a dove known as the Queen Consort's Ivory Rod with Dove, which, as the name suggests, is made of ivory. Unlike the sovereign's dove, this one has folded wings and is relatively small.[144] It was last used by Queen Elizabeth, later known as the Queen Mother, at the coronation of her husband George VI in 1937. For the coronation of Mary II, the wife and joint sovereign of William III, a more elaborate gold sceptre with dove was commissioned in 1689. It has not been used since, and went missing for several decades, only to be found in 1814 at the back of a cupboard in the Tower of London.[129]
Altar plate

In the Jewel House there is a collection of chalices, patens and dishes – all silver-gilt except five gold communion vessels – that are displayed on the high altar or in front of the royal box at Westminster Abbey during a coronation, and used at various other times.[146]
One of the most striking pieces is a large dish weighing 13 kg (29 lb), in the centre of which is a relief depiction of the Last Supper. Around the edge at the top, bottom and sides are four engravings of biblical scenes: the Washing of the Feet, the Walk to Emmaus, the Coming of the Holy Ghost, and Christ's Commission to the Apostles, divided by scrolls of foliage. Made by London goldsmith Henry Greenway in 1664 for the Duke of York and later acquired by Charles II, it stands on the high altar during the coronation ceremony.[147]
Other pieces include the altar dish and flagon made in 1691 by Francis Garthorne and St John Hoyte respectively for the royal chapel at the Tower of London. The dish measures 70 cm (2 ft) across; it also has a depiction of the Last Supper, below which is the coat of arms of William and Mary.[148] Its rim is engraved with cherubs, scrollwork and fruit. The flagon is 42.5 cm (1 ft) tall and has similar decoration.[149] Both pieces are still used in the chapel three times a year on Easter, Whitsun and Christmas, and they have been displayed in Westminster Abbey at coronations since 1821.[150]
The Maundy Dish is one of six used by the Queen at Royal Maundy for handing out alms to elderly people in recognition of their service to the church and local community. The ceremony, which takes place in a different cathedral every year, entirely replaced the ancient custom of washing the feet of the poor in 1730, and the dish, though it bears the cypher of William and Mary, dates from the reign of Charles II. Two purses containing specially minted coins are taken from the dish and presented to each recipient.[151]
A pair of 96-centimetre (3 ft) tall candlesticks made in the 17th century stand on either side of the high altar. These are engraved all over with scrolls, leaves and flowers, and were also used at the lying in state of Edward VII at Buckingham Palace in 1910.[152]
Banqueting plate

Until the 19th century, the coronation was followed by a banquet at Westminster Hall; the last banquet was held in 1821 for George IV.[153]
Silverware used at the banquets include the Plymouth Fountain, a wine fountain made by the German goldsmith Peter Oehr and presented to Charles II by the city of Plymouth upon the restoration of the monarchy. Gilded for the coronation of George II in 1726, it is 77.5 cm (3 ft) tall, weighs 14.1 kg (31 lb), and is decorated with flowers, fruit, dolphins, mermaids and sea monsters.[154] In theory, a barrel of wine would be placed high up in the rafters of the banqueting hall; from this a pipe ran to a hole at the base of the fountain, and the wine rose to the top, cascading into a large repoussé bowl. The fountain was highly impractical due to the inability to control the rate of flow, and no record exists of it being used in this way at any banquet, though it may have served as a fruit bowl.[150]
The nautical theme is continued in the silver-gilt Wine Cistern, also known as the Grand Punch Bowl; it weighs 257 kg (40 st), is 0.76 m (2 ft) tall, 1.38 m (5 ft) long and 1.01 m (3 ft) wide, and can hold 144 bottles of wine on ice.[155] It was designed by the painter and illustrator Thomas Stothard and made by Rundell & Bridge in 1829 for George IV.[156] The bowl is cast as a giant oyster shell with a scene of Bacchanalian figures harvesting grapes along the rim. On the underside of the shell – supported by a base of crashing waves – hang limpets and stalactites to represent a sea cave.[157] Weighing almost a quarter of a ton, it is the heaviest surviving piece of English banqueting plate.[156] In 1841, the cistern was re-purposed as a punch bowl by Queen Victoria, with the addition of a ladle created by Barnard & Sons. The ivory-stemmed ladle is 1.05 m (3 ft) long and has a silver-gilt bowl in the form of a nautilus shell.[158]
The Exeter Salt, a 45 cm (1 ft) tall salt cellar in the form of a castle, was presented to Charles II by the city of Exeter. It was made in 1630 and is set with around 70 gemstones. Each of its four main compartments held about 29 g (1 oz) of salt, and smaller compartments held pepper and spices.[159] The salt is the only surviving work of the German goldsmith Johann Hass.[160] Eleven smaller salts named after St George were originally made for a St George's Day banquet of the Knights of the Garter and Charles II in the 17th century. The Queen Elizabeth Salt was made by London goldsmith Affabel Partridge in 1572 during the reign of Elizabeth I for a member of the aristocracy; it was acquired by the Crown at the time of Charles II. Complementing the salts are twelve salt spoons made for the coronation of George IV.[161]
Christening fonts
.jpg)
Charles II, unmarried when he took the throne, persuaded his Treasury to pay for a christening font and basin. His marriage to Catherine of Braganza produced no heir, but the font may have been used to baptise some of his 13 illegitimate children. It was last used in 1796, while the basin found a new role as an altar dish in the 19th century and is on display with the altar plate at the Tower of London.[162]
A christening ewer and basin made by the Garrard & Co. founder George Wickes in 1735 were used at the christening of the future George III in 1738. His father, Frederick, Prince of Wales, had been banished from the royal court by George II and was forbidden to use the Charles II Font.[162] An inscription at the front of the ewer records its use at the christening of George III's son, Prince Alfred, in 1780. The handle of the ewer is topped by a figure of Hercules slaying the Hydra, symbolising the triumph of virtue over vice.[163]
The silver-gilt Lily Font was made in 1840 by E.E.J. & W. Barnard for the christening of Victoria, Princess Royal, the first child of Queen Victoria, who declined to use the Charles II Font because of its unseemly history. The font weighs 9.94 kg (22 lb) and is decorated with water lilies symbolising purity and new life.[164] It was used at the christening of Princess Charlotte of Cambridge in 2015.[163]
Ownership and value
The Crown Jewels, part of the Royal Collection,[165] do not belong to the state,[166] but are owned by Queen Elizabeth II in right of the Crown.[167] Their ownership is regarded as inalienable and passes from one monarch to the next.[168] However, a 17th-century ruling by Sir Edward Coke, which states "the ancient jewels of the Crown are heirlooms and shall descend to the next successor and are not divisible by testament", contains an exception allowing the monarch to dispose of objects via letters patent under the Privy Seal.[169] In practice it is unlikely the Crown Jewels will ever be sold,[168] nor are they insured against loss,[170] and are officially priceless.[171]
Crown Jeweller
Appointed by the monarch, the Crown Jeweller is responsible for the maintenance and, when they leave the Tower of London, security, of the regalia, plate, and fonts. Except for the monarch, only the Crown Jeweller is authorised to handle the Crown Jewels; others may do so with his or her permission.[172] The office holder is on call day and night, all year round to attend to the Jewels.[173] William Summers, the fifth incumbent (1962–91), said of his job: "Where the Crown goes, there go I".[172]
The post was created in 1843 by Queen Victoria, who issued a royal warrant to Garrard & Co., and the title of Crown Jeweller was vested in an employee of the company.[174] Until then, Rundell & Bridge had been charged with preparing the objects for use at state occasions and their maintenance in general.[175] To celebrate Garrard & Co.'s 150th anniversary as the warrant holder, a banquet attended by the Princess Royal was held at Goldsmiths' Hall, London, in 1993.[172]
In 2007, Buckingham Palace announced that Garrard & Co.'s services were no longer required, the reason cited being that it was time for a change.[176] The company had been acquired by a private equity firm in 2006.[177] Family business G. Collins & Sons were appointed as the new Crown Jewellers.[178] In 2012, Martin Swift of Mappin & Webb became the eighth Crown Jeweller after Harry Collins gave up the role.[179]
See also
Notes
- ↑ This figure counts the candlesticks as two objects.
- ↑ Technically, the Crown Jewels are the regalia and vestments used or worn by monarchs and queens consort at a coronation. However, the term is commonly used to refer to the contents of the Jewel House.[2] The inventory in Keay (2011) extends to items displayed in the Martin Tower and the Palace of Westminster.
- ↑ Until then, kings had been portrayed on coinage wearing helmets and circlets.[13]
- ↑ Thomas Frederick Tout gives an illuminating second-hand account of one such theft in A Mediæval Burglary (1916).
- ↑ Vyner outsourced work to fellow members of the Goldsmiths' Company.[45]
- ↑ A comprehensive list of additions and alterations up to the coronation of Queen Victoria can be found in Jones, pp. 63–72. It should be noted that plans to remove the fleurs-de-lis from the State Crown of George I and replace them with motifs of roses, thistles and shamrocks for the coronation of George IV were abandoned.[51]
- ↑ A persistent rumour that the Crown Jewels were illegally shipped out of the United Kingdom during WWII and stored at the Sun Life Building in Montreal, Canada was deliberately spread in Montreal to account for increased activity at the building, which secretly housed a large amount of gold from Europe.[55]
- ↑ Any sword carried before the monarch is a sword of state but only this one is named the Sword of State.[91]
- ↑ Queen Victoria's Small Diamond Crown replaced the Imperial State Crown for the queen's lying in state at Osborne House.[84]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Keay, pp. 189–195.
- ↑ "Crown Jewels". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). 267. United Kingdom: House of Commons. 27 November 1995. col. 447W.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 5.
- ↑ Keay, dust jacket.
- ↑ Keay, p. 9.
- ↑ Keith Parfitt (1995). Iron Age Burials from Mill Hill, Deal. British Museum Press. ISBN 978-0-7141-2304-2.
- ↑ Twining, p. 102.
- ↑ Keay, p. 12.
- ↑ Sam Newton (2004). The Origins of Beowulf and the Pre-Viking Kingdom of East Anglia. DS Brewer. p. 44. ISBN 978-0-85991-472-7.
- ↑ "Helmet from the ship-burial at Sutton Hoo". British Museum. Archived from the original on 22 February 2015.
- ↑ The Sutton Hoo Ship-burial: Arms and Armour and Regalia. 2. British Museum. 1978. ISBN 978-0-7141-1331-9.
- ↑ Keay, p. 17.
- ↑ Steane, p. 31.
- ↑ Keay, pp. 13–18.
- 1 2 3 Keay, pp. 18–20.
- ↑ David M Nicholas (2014). The Evolution of the Medieval World: Society, Government & Thought in Europe 312–1500. Routledge. p. 220. ISBN 978-1-317-89543-5.
- ↑ Coronation Exhibition. British Museum. 1902. p. 14.
- 1 2 Ronald Lightbown, "The English Coronation Regalia before the Commonwealth" in Blair, vol. 1. pp. 257–353.
- ↑ Rose, p. 14.
- ↑ Keay, p. 22.
- ↑ Patricia Williams, ed. (2012). Historical Texts from Medieval Wales. Modern Humanities Research Association. p. xxxii. ISBN 978-1-907322-60-0.
- ↑ David John Breeze; Thomas Owen Clancy; Richard Welander (2003). The Stone of Destiny: Artefact and Icon. Society of Antiquaries of Scotland. p. 201. ISBN 978-0-903903-22-6.
- ↑ "The Coronation Chair". Westminster Abbey. Retrieved 17 July 2016.
- ↑ Michael Prestwich (1988). Edward I. University of California Press. p. 474. ISBN 978-0-520-06266-5.
- ↑ "The Wars of Independence". Scotland's History. BBC Scotland. Retrieved 26 July 2016.
- ↑ Sir Francis Palgrave, ed. (1836). "Edward II". The Antient Kalendars and Inventories of the Treasury of His Majesty's Exchequer. 3. G. Eyre and A. Spottiswoode. pp. 138–140.
- ↑ Keay, pp. 33–34.
- ↑ Steane, p. 35.
- ↑ Dale Hoak, "The iconography of the crown imperial", in Hoak, pp. 55, 63.
- ↑ Martin Biddle (1986). "Seasonal Festivals and Residence". In R. Allen Brown. Anglo-Norman Studies VIII: Proceedings of the Battle Conference, 1985. Boydell & Brewer. pp. 51–72. ISBN 978-0-85115-444-2.
- ↑ Fiona Louise Kisby (1996). The Early-Tudor Royal Household Chapel, 1485–1547. 1. University of London. p. 146.
- ↑ David Dean, "Image and ritual in the Tudor parliaments" in Hoak, p. 243.
- 1 2 Keay, p. 30.
- 1 2 Keay, p. 32.
- ↑ Rose, pp. 44–45.
- ↑ Jennifer Loach; G. W. Bernard; Penry Williams (1999). Edward VI. Yale University Press. p. 36. ISBN 978-0-300-07992-0.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 15.
- ↑ John Nichols, ed. (1828). The Progresses, Processions, and Magnificent Festivities of James I, His Royal Consort, Family and Court. 2. J.B. Nichols. p. 45.
- ↑ Brian Barker (1976). When the Queen was Crowned. Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd. p. 80. ISBN 978-0-7100-8397-5.
- ↑ Keay, p. 40.
- ↑ Arthur Jefferies Collins (1955). Jewels and Plate of Queen Elizabeth I: The Inventory of 1574. Trustees of the British Museum. p. 266.
- ↑ Keay, p. 43.
- 1 2 3 4 Royal Household. "Symbols of the Monarchy: The Crown Jewels". British Monarchy website. Archived from the original on 9 March 2015.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 6.
- ↑ Helen Jacobsen (2012). Luxury and Power: The Material World of the Stuart Diplomat, 1660–1714. Oxford University Press. p. 16. ISBN 978-0-19-969375-7.
- 1 2 "Crown Jewels factsheet 2" (PDF). Historic Royal Palaces. Retrieved 29 January 2016.
- ↑ Twining, p. 158.
- ↑ Shirley Bury, "The Coronation from the Restoration of the Monarchy to 1953" in Blair, vol. 1. p. 368.
- 1 2 Mears; Thurley; Murphy, pp. 46–47.
- ↑ Peter Hammond (1981). The Tower of London: Young Visitor's Guide. HM Stationery Office. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-11-671054-3.
- ↑ The Diamond Diadem at the Royal Collection.
- 1 2 Lawrence E. Tanner (6 June 1953). "The Queen's coronation: The story of the regalia". Country Life. pp. 52–61. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ↑ "Take Crown Jewels to Bank of England". Toronto Daily Star. Canadian Press. 1 June 1945. p. 4.
- ↑ Theo Aronson (1997). Princess Margaret: A Biography. M. O'Mara Books. p. 81. ISBN 978-1-85479-248-8.
- 1 2 Alfred Draper (1979). Operation Fish: The Race to Save Europe's Wealth, 1939–1945. Cassell. pp. 255–257. ISBN 978-0-304-30068-6.
- ↑ Elizabeth Hennessy (1992). A Domestic History of the Bank of England, 1930–1960. Cambridge University Press. p. 237. ISBN 978-0-521-39140-5.
- ↑ Martin Rivington Holmes; Hervey Degge Wilmot Sitwell (1972). The English Regalia: Their History, Custody & Display. HM Stationery Office. p. 76.
- ↑ See the new revamped Crown Jewels exhibit at the Tower of London (YouTube video). Daily Mirror. 29 March 2012. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- ↑ Maev Kennedy; Katy Roberts (28 March 2012). "Crown Jewels go on show for major new exhibition". The Guardian. Retrieved 26 July 2016.
- 1 2 Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 23.
- ↑ St Edward's Crown at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ "Victorian Coat of Arms". Victoria State Government. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 29.
- ↑ Keay, pp. 174–175.
- ↑ Keay, p. 183.
- ↑ The Imperial State Crown at the Royal Collection.
- 1 2 Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 30.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 25.
- ↑ Keay, p. 137.
- ↑ Stephen Goodwin (17 December 1996). "Crowning glory at Tower exhibition". Independent. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- ↑ Keay, pp. 164–166.
- 1 2 Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 27.
- ↑ Keay, p. 175.
- ↑ Keay, p. 178.
- ↑ Ronald Allison; Sarah Riddell (1991). The Royal Encyclopedia. Macmillan Press. p. 134. ISBN 978-0-333-53810-4.
- ↑ Leslie Field (1997). The Queen's Jewels. Harry N. Abrams. ISBN 978-0-8109-8172-0.
- ↑ "Priceless gem in Queen Mother's crown". BBC News. 4 April 2002. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ↑ Sir Bernard Burke (2009). The General Armory of England, Scotland, Ireland, and Wales. Heritage Books. p. 59. ISBN 978-0-7884-3719-9.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 24.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 31.
- ↑ The Prince of Wales's Coronet (1902) at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Doug Lennox (2009). Now You Know: Royalty. Dundurn. p. 85. ISBN 978-1-77070-406-0.
- ↑ "Prince of Wales' regalia 'should be displayed in Wales'". BBC News. 28 May 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- 1 2 Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 32.
- ↑ Queen Victoria's Small Diamond Crown at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ The Imperial Crown of India at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 33.
- ↑ Christopher Harper-Bill; Ruth Harvey (1990). The Ideals and Practice of Medieval Knighthood III: Papers from the Fourth Strawberry Hill Conference, 1988. Boydell & Brewer Ltd. p. 134. ISBN 978-0-85115-265-3.
- 1 2 Strong, p. 268.
- ↑ Leopold George Wickham Legg (1901). English Coronation Records. A. Constable & Co. p. 25.
- ↑ Rose, p. 49.
- ↑ Keay, pp. 96–97.
- ↑ "Queen's Speech: The traditions of State Opening of Parliament". The Telegraph. 18 November 2009. Retrieved 27 February 2016.
- ↑ Twining, p. 172.
- ↑ Brian Hoey (1992). All the Queen's Men: Inside the Royal Household. HarperCollins. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-246-13851-4.
- 1 2 Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 16.
- ↑ The Jewelled Sword of Offering at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Keay, p. 127.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 77.
- ↑ Rose, p. 50.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 9.
- ↑ St Edward's Staff at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Twining, p. 143.
- ↑ Keay, p. 63.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 10.
- ↑ Arthur Grimwade, "The State Trumpets" in Blair, vol. 2. pp. 491–496.
- ↑ Jones, p. 54.
- ↑ "The Band of the Household Cavalry". British Army. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- ↑ "The Central Band of the RAF". Royal Air Force. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 50.
- ↑ "Mace (The)". Parliament.uk. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 8.
- ↑ King George's Jubilee Trust, p. 25.
- 1 2 Twining, p. 173.
- ↑ The Ampulla at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ The Coronation Spoon at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Strong, pp. 78–79.
- ↑ Strong, p. 271.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 14.
- ↑ The Supertunica at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 39.
- ↑ Michele Brown (1983). Ritual of Royalty: The Ceremony and Pageantry of Britain's Monarchy. Prentice Hall. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-13-781047-5.
- ↑ Rose, p. 52.
- 1 2 Twining, p. 171.
- ↑ The Armills at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 17.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 19.
- ↑ The Sovereign's Orb at the Royal Collection.
- 1 2 3 Rose, p. 42.
- ↑ King George's Jubilee Trust, pp. 26, 31.
- ↑ Rose, p. 46.
- ↑ The Sketch: A Journal of Art and Actuality. 33. Ingram Brothers. 1901. p. 86.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 18.
- ↑ Arthur Christopher Benson, ed. (1907). The Letters of Queen Victoria. 1. John Murray. p. 123.
- ↑ Rose, p. 107.
- ↑ Rose, p. 54.
- ↑ The Queen Consort's Ring at the Royal Collection.
- ↑
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a work in the public domain: Younghusband; Davenport, p. 2.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a work in the public domain: Younghusband; Davenport, p. 2.
- 1 2 Rose, p. 41.
- ↑ The Sovereign's Sceptre with Cross at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 27.
- ↑ Adolphe Napoléon Didron (1851). Christian Iconography. 1. Henry G. Bohn. pp. 449–450.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 28.
- ↑ Younghusband; Davenport, p. 29.
- ↑ Coronation Record Number. The Illustrated London News. 1937. p. 33.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 34.
- ↑ Altar Dish (1664) at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Altar Dish (1691) at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Flagon (1691) at the Royal Collection.
- 1 2 Younghusband; Davenport, p. 44.
- ↑ Office for the Royal Maundy (2011). The Maundy Service (PDF). Westminster Abbey.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, pp. 35–36.
- ↑ "Coronation banquets". Parliament.uk. Retrieved 14 February 2016.
- ↑ The Plymouth Fountain at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, pp. 42–43.
- 1 2 Keay, p. 150.
- ↑ Mears, p. 54.
- ↑ Ladle at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Keay, p. 70.
- ↑ The Exeter Salt at the Royal Collection.
- ↑ Mears; Thurley; Murphy, pp. 39–40.
- 1 2 Mears; Thurley; Murphy, p. 44.
- 1 2 "Queen Victoria's font to be used for Princess Charlotte's baptism". The Yorkshire Post. 5 July 2015. Retrieved 10 December 2015.
- ↑ Jonathan Marsden (2010). Victoria & Albert: Art & Love. Royal Collection Trust. p. 268. ISBN 978-1-9056-8621-6.
- ↑ "Visiting the Crown Jewels". Historic Royal Palaces. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- ↑ "Royal Collection". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). 211. United Kingdom: House of Commons. 13 July 1992. col. 801–2.
- ↑ "Crown Jewels". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). 211. United Kingdom: House of Commons. 16 July 1992. col. 944W.
- 1 2 Vernon Bogdanor (1997). The Monarchy and the Constitution. Oxford University Press. p. 190. ISBN 978-0-19-829334-7.
- ↑ Arthur MacGregor, ed. (1989). The Late King's Goods: Collections, Possessions and Patronage of Charles I in the Light of the Commonwealth Sale Inventories. Alistair McAlpine. p. 259. ISBN 978-0-19-920171-6.
- ↑ "Royal Residences". Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). 407. United Kingdom: House of Commons. 19 June 2003. col. 353W.
- ↑ "Crown Jewels factsheet" (PDF). Historic Royal Palaces. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- 1 2 3 Diana Scarisbrick (1993). "Diana Scarisbrick on Garrard's 150 years". Country Life. Vol. 187 (48–51 ed.). p. 53.
- ↑ Christopher Middleton (2 June 2012). "How the Queen's man about crowns brought sparkle to her celebrations". The Telegraph. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
- ↑ Vivienne Becker (28 March 2012). "Jewellery duty". How To Spend It. Financial Times. Retrieved 15 May 2016.
- ↑ Gordon Campbell (2006). The Grove Encyclopedia of Decorative Arts. Oxford University Press. p. 409. ISBN 978-0-19-518948-3.
- ↑ James David Draper (2008). Cameo Appearances. New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art. p. 55. ISBN 978-1-58839-282-4.
- ↑ "Garrard to lose Royal Jeweller role". Evening Standard. 10 February 2007. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ↑ Julia Robinson (18 July 2007). "Family firm fit for the Queen". The Telegraph. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ↑ Richard Eden (15 July 2012). "The Queen appoints new Crown Jeweller". The Telegraph. Retrieved 8 December 2015.
Bibliography
- Blair, Claude, ed. (1998). The Crown Jewels: The History of the Coronation Regalia …. The Stationery Office. ISBN 978-0-11-701359-9.
- Hoak, Dale, ed. (2002). Tudor Political Culture. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-52014-0.
- Jones, Edward Alfred (1908). The Old Royal Plate in the Tower of London. Fox, Jones & Co. ASIN B004BWZDGY.
- Keay, Anna (2011). The Crown Jewels: The Official Illustrated History. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-51575-4.
- King George's Jubilee Trust (1937). The Coronation of … King George VI and Queen Elizabeth. Odhams Press. ASIN B000NNCSEK.
- Mears, Kenneth J. (1988). The Tower of London: 900 Years of English History. Phaidon. ISBN 978-0-7148-2527-4.
- Mears, Kenneth J.; Thurley, Simon; Murphy, Claire (1994). The Crown Jewels. Historic Royal Palaces. ASIN B000HHY1ZQ.
- Rose, Tessa (1992). The Coronation Ceremony and the Crown Jewels. HM Stationery Office. ISBN 978-0-117-01361-2.
- Steane, John (2003). The Archaeology of the Medieval English Monarchy. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-64159-8.
- Strong, Roy (2006). Coronation: From the 8th to the 21st Century. Harper Perennial. ISBN 978-0-00-716055-6.
- Twining, Edward Francis (1960). A History of the Crown Jewels of Europe. B. T. Batsford. ASIN B00283LZA6.
- Younghusband, Sir George; Davenport, Cyril (1919). The Crown Jewels of England. Cassell & Co. ASIN B00086FM86.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom. |
- The Royal Collection Trust
- The Crown Jewels at the Tower of London website
- The Crown Jewels at the Royal Family website
- The Crown Jewels (1967) by British Pathé
- The Crown Jewels (1937) by British Pathé