Solar eclipse of July 11, 2010
| Solar eclipse of July 11, 2010 | |
|---|---|
|
Totality from Hao, French Polynesia | |
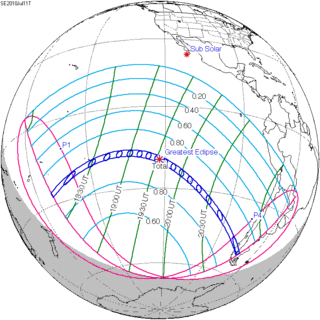 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | -0.6788 |
| Magnitude | 1.058 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 320 sec (5 m 20 s) |
| Coordinates | 19°42′S 121°54′W / 19.7°S 121.9°W |
| Max. width of band | 259 km (161 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 17:09:41 |
| (U1) Total begin | 18:15:15 |
| Greatest eclipse | 19:34:38 |
| (U4) Total end | 20:51:42 |
| (P4) Partial end | 21:57:16 |
| References | |
| Saros | 146 (27 of 76) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9530 |
The total solar eclipse of July 11, 2010, occurred over the southern Pacific Ocean.[1] A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Visibility
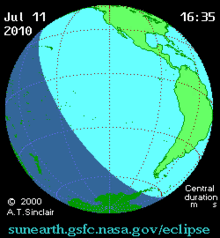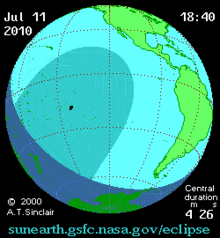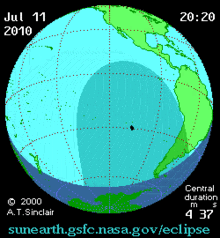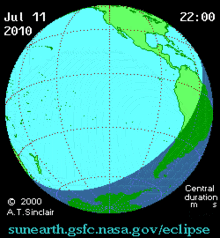
The eclipse on this day was one of the most remote in recorded history. It was visible over much of the southern Pacific Ocean, touching several atolls in French Polynesia, the Cook Islands, Easter Island, and Argentina's Patagonian plains.[2]
Fred Espenak, a NASA astrophysicist, said:
"One of the most unique things about this particular eclipse is that it crosses a unique and interesting archaeological site: Easter Island. On Easter Island there are these great statues... There's a lot of mystery about these statues, but in any case, this is the first total eclipse to hit the island in about 1,400 years."[3]
The best one occurred in French Polynesia, where it was seen in 98 percent, At the spectacular eclipse, The diamond ring effect and the Baily's beads happened.
It ended at sunset over the southern tips of Argentina and Chile in South America, including the town of El Calafate. The Sun's altitude was only 1° during the 2 minute 47 second total phase, but Argentino Lake offered an adequate line-of-sight to the eclipse hanging just above the rugged Andes skyline.[1]
A 58% partiality occurred at sunset in Santiago, Chile, but it was not visible due to adverse weather conditions. In other cities such as Valparaíso and Coquimbo, clearer skies permitted the event to be witnessed in continental Chile.
Observations


Total eclipse began 700 kilometers (430 mi) southeast of Tonga at approximately 18:15 UTC and reached Easter Island by 20:11 UTC.[4] The global sky photography project The World At Night stationed photographers throughout the eclipse's visibility track. Eclipse chasers photographed the event on board a chartered airplane, cruise ships, numerous Pacific islands, and in Argentina's Patagonia region. Totality was observed for four minutes and 41 seconds (4:41) on Easter Island,[2] where it was observed for the first time in 1,400 years.[5] Approximately 4,000 observers visited Easter Island for this eclipse, including tourists, scientists, photographers, filmmakers and journalists,[6] prompting an increase in security at its important moai archeological sites. The eclipse occurred at the same time that the final game of the 2010 FIFA World Cup was being played in South Africa, and many soccer fans in Tahiti watched the match instead of observing the partial eclipse with a high percentage of obscuring the sun by about 98 percent.[4][7] The path of totality of this eclipse barely missed some significant inhabited islands, including passing just about 20 km north of the northern end of Tahiti.
This eclipse was the first one to happen over French Polynesia in 350 years. An estimated 5,000 tourists visited various islands in the archipelago to observe the event. Nearly 120,000 pairs of special glasses were distributed for observers.[8] Eclipse chasers were also able to observe the eclipse at El Calafate, near the southern tip of Argentina, before the sun set just two minutes later.[2]
Several hours after the eclipse was observed in continental Chile, a magnitude 6.2 earthquake struck in the Antofagasta Region. There were no major injuries or damage in the nearby cities of Calama, Chile and San Pedro de Atacama.[9]
Related eclipses
- It was preceded two weeks earlier by the partial lunar eclipse on June 26, 2010.
- In Saros cycle 146, this eclipse repeats every 18 years 11 days, previously on total solar eclipse of June 30, 1992 and next on total solar eclipse of July 22, 2028.
- In a tritos cycle, it repeats every 10 years 11 months, previous as the total solar eclipse of August 11, 1999 and followed by the annular solar eclipse of June 10, 2021.
- The next total solar eclipse will occur on November 13, 2012. The path of totality ends about 500 km west of Chile but the eclipse will be partial on sundown from the coast, and 2000 km east of New Zealand.
Solar eclipses 2008–2011
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2008–2011 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |
121 Partial from Christchurch |
2008 February 7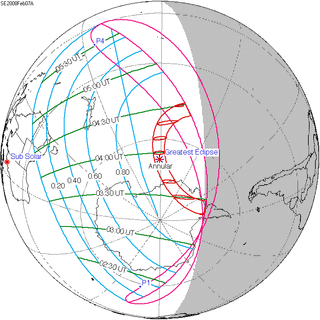 Annular |
126 Novosibirsk, Russia |
2008 August 1 Total | |
131 Bandar Lampung, Indonesia |
2009 January 26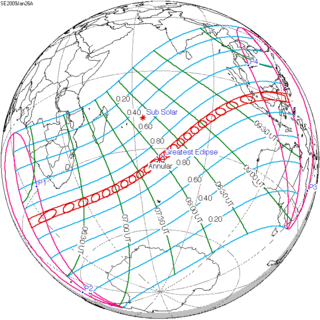 Annular |
136 Kurigram, Bangladesh |
2009 July 22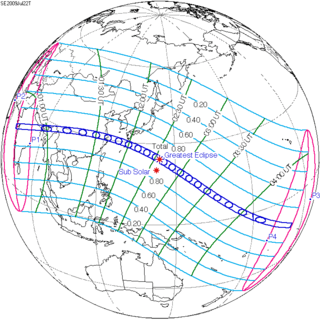 Total | |
| 141 Bangui, Central African Republic |
2010 January 15 Annular |
146 Hao, French Polynesia |
2010 July 11 Total | |
151 Partial from Vienna, Austria |
2011 January 4 Partial (north) |
156 | 2011 July 1 Partial (south) | |
| Partial solar eclipses on June 1, 2011, and November 25, 2011, occur on the next lunar year eclipse set. | ||||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from north to south between July 11, 1953 and July 11, 2029 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 10-11 | April 29-30 | February 15-16 | December 4 | September 21-23 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 11, 1953 |
 April 30, 1957 |
 February 15, 1961 |
 December 4, 1964 |
 September 22, 1968 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
 July 10, 1972 |
 April 29, 1976 |
 February 16, 1980 |
 December 4, 1983 |
 September 23, 1987 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 April 29, 1995 |
 February 16, 1999 |
 December 4, 2002 |
 September 22, 2006 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 11, 2010 |
 April 29, 2014 |
 February 15, 2018 |
 December 4, 2021 |
 September 21, 2025 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 11, 2029 | ||||
Notes
- 1 2 "Total Solar Eclipse of 2010 July 11". NASA. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- 1 2 3 Malik, Tariq (July 12, 2010). "Total solar eclipse blots out sun, amazes skywatchers". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ "Solar Eclipse to Darken Easter Island Sunday". National Geographic Society. July 8, 2010. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- 1 2 "Total solar eclipse crosses South Pacific". BBC News. July 11, 2010. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ Yang, Yi (July 9, 2010). "Solar Eclipse: First to Hit Easter Island in 1400 Years". The Epoch Times. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ Eclipse chasing: four minutes of bliss, Australian Geographic, July 16, 2010
- ↑ Tee, Gillian (July 10, 2010). "Solar eclipse predicted at same time as World Cup final". CNN. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ "French Polynesia awaits first solar eclipse in 350 years". Australia Network. July 10, 2010. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
- ↑ "6.2 Magnitude Earthquake Strikes Chile Hours After Solar Eclipse". All Headline News. July 12, 2010. Retrieved July 12, 2010.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2010 July 11. |
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- NASA pdf map
- Eclipser: 2010 July 11 Total Solar Eclipse
- Eclipse.org.uk: Total Eclipse of the Sun: 2010 July 11
- www.spaceweather.com
- Easter Island Eclipse, APOD 7/14/2010
- Andes Sunset Eclipse, APOD 7/15/2010, totality from 400 meters above Argentino Lake
- The Crown of the Sun, APOD 7/21/2010, totality from Easter Island
- Diamond Ring and Shadow Bands, APOD 7/24/2010, totality from Hao, French Polynesia
- Eclipse on the Beach, APOD 7/30/2010, totality from Anakena Beach, Easter Island
- Eclipse Shadow Cone Over Patagonia, APOD 8/4/2010, totality from Patagonia, Argentina
