Solar eclipse of August 11, 1999
| Solar eclipse of August 11, 1999 | |
|---|---|
|
Totality from France | |
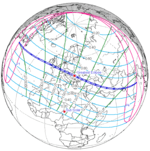 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.5062 |
| Magnitude | 1.0286 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 143 sec (2 m 23 s) |
| Coordinates | 45°06′N 24°18′E / 45.1°N 24.3°E |
| Max. width of band | 112 km (70 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 11:04:09 |
| References | |
| Saros | 145 (21 of 77) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9506 |
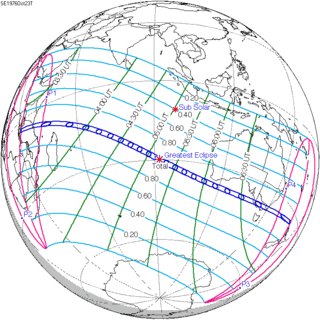
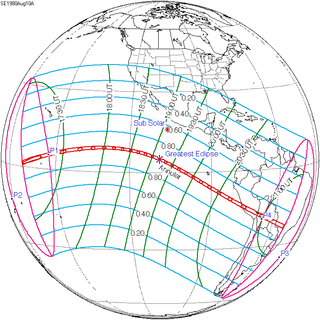
A total solar eclipse occurred on 11 August 1999 with an eclipse magnitude of 1.029. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The path of the Moon's shadow began in the Atlantic Ocean and, before noon, was traversing the southern United Kingdom, northern France, Belgium, Luxembourg, southern Germany, Austria, Slovenia, Croatia, Hungary, and northern FR Yugoslavia (Vojvodina). Its maximum was at 11:03 UTC at 45°06′N 24°18′E / 45.1°N 24.3°E in Romania (next to a town called Ocnele Mari near Râmnicu Vâlcea); and it continued across Bulgaria, the Black Sea, Turkey, Iran, southern Pakistan and Srikakulam in India and ended in the Bay of Bengal.
It was the first total eclipse visible from Europe since 22 July 1990, and the first visible in the United Kingdom since 29 June 1927.
Observations
Because of the high population densities in areas of the path, this was one of the most-viewed total solar eclipses in human history;[1] although some areas in the path of totality (mainly in Western Europe) offered impaired visibility due to adverse weather conditions.
Some of the organized eclipse-watching parties along the path of totality set up video projectors on which people could watch the shadow as it raced towards them.[2] There was substantial coverage on International TV stations of the progress of the eclipse shadow. The Moon's shadow was also observed from the Russian Mir space station; during the eclipse, video from Mir was broadcast live on television.
- The BBC concentrated its coverage efforts on the first landfall of the shadow across the western end of Cornwall (from St Ives to Lizard), which was packed with an extraordinary number of visitors, although Cornwall did not have nearly as many as expected leading to many specially organised events to be left with very small attendance. The veteran eclipse-watcher Patrick Moore was brought in to head a live programme, but the eclipse was clouded out. BBC One also produced a special version of their Balloon Idents for the event. Unfortunately, the BBC did not have a presence at Goonhilly on the Lizard Peninsula, one of the few places in Cornwall where the clouds parted just in time for the total eclipse to be visible.
- Some of the best viewing conditions were to be had mid-Channel, where ferries were halted in calm conditions to obtain an excellent view. Hundreds of people who gathered on the island of Alderney also experienced the event.
- A gathering of several thousand people at the airport in Soissons, France, which was on the path of totality, were denied all but a few fleeting glimpses of the eclipse through the overcast sky. Frustratingly, the clouds cleared completely just a few minutes after the eclipse.
- In contrast, the overcast sky in Amiens, France, where thousands had gathered, cleared only minutes before the eclipse began.
- Further inland, viewing conditions were also perfect at Vouziers, a French country town gridlocked by Belgian cars from day-visitors. The patchy cloud covering cleared a short time before the shadow arrived. Some photos from Vouziers were used on the subsequent BBC Sky at Night programme.
- The San Francisco Exploratorium featured a live webcast from a crowded town square in Amasya, Turkey.
- Doordarshan, the national TV channel in India broadcast a live coverage from Srikakulam, hosted by the renowned TV personality, Mona Bhattacharya.
- A Bulgarian Air Force MiG-21 two-seater was used by the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences to study the solar corona. The MiG-21, flying at 1600–1700 km/h (M=1,4-1,5) at an altitude of 13,000m, was able to stay in the moon's umbra for 6min. The photographer, an air force pilot, used two film cameras, both fitted with 200mm lenses and infrared filters, and one Digital8 video camera. The flight was sponsored by Mobiltel.
- Hungary's most popular tourist destination, Lake Balaton and its surrounding area fell into the path of the eclipse entirely, which made the area even more popular for that day. The motorway leading there was crowded, many people had to watch the eclipse while caught in a traffic jam.
- one French and two British Concordes briefly followed the eclipse with tourists on board[3]
Gallery

 From Lake Balaton, Hungary
From Lake Balaton, Hungary
Notable times and coordinates
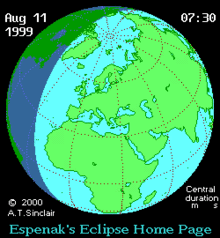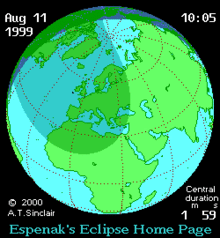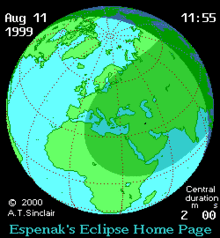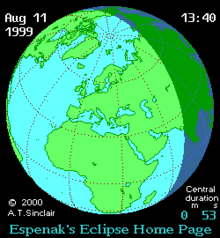
| Event | Time (UTC) | Coordinates[4] |
|---|---|---|
| 1st penumbral contact with earth surface (P1) | 08:26:17 | |
| 1st external umbral contact (U1) | 09:29:55 | 41°2.0′N 65°5.4′W / 41.0333°N 65.0900°W |
| 2nd internal umbral contact (U2) | 09:30:53 | 43°0.1′N 57°55.8′W / 43.0017°N 57.9300°W |
| Greatest eclipse | 11:03:07 | 45°4.8′N 24°17.3′E / 45.0800°N 24.2883°E[5] |
| 3rd internal umbral contact (U3) | 12:35:33 | 19°39.7′N 80°20.4′E / 19.6617°N 80.3400°E |
| 4th external umbral contact (U4) | 12:36:26 | 17°33.5′N 87°17.1′E / 17.5583°N 87.2850°E |
| 4th penumbral contact with earth surface (P4) | 13:40:08 |
Type of the eclipse
| Nature of the eclipse | Total |
| Gamma | 0.5063 |
| Magnitude | 1.0286 |
| Duration at greatest eclipse point | 143 s (2 min 23 s) at 11:03:07 UTC, in Romania: 45°04′48″N 24°17′18″E / 45.08000°N 24.28833°E |
| Maximum pathwidth | 112.3 km |
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1997–2000
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1997 to 2000 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |||
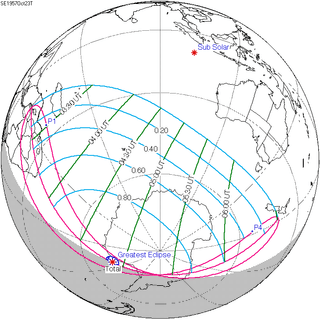
120 Chita, Russia | March 9, 1997 Total |
125 | September 2, 1997 Partial | |||
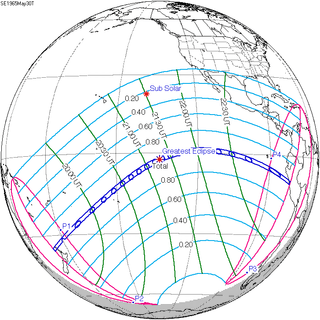
| 130 | February 26, 1998 Total |
135 | August 22, 1998 Annular | |||
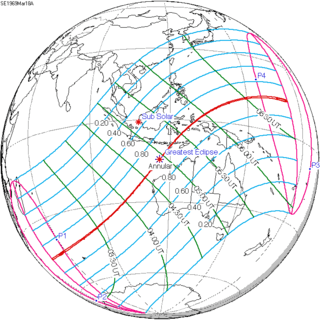
| 140 | February 16, 1999 Annular |
145 Totality from France | August 11, 1999 Total | |||
| 150 | February 5, 2000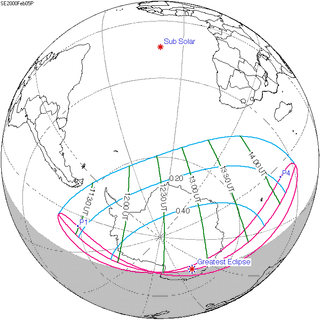 Partial |
155 | July 31, 2000 Partial | |||
| Partial solar eclipses on July 1, 2000 and December 25, 2000 occur in the next lunar year eclipse set. | ||||||
Saros 145
This solar eclipse is a part of Saros cycle 145, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 77 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on January 4, 1639, and reached a first annular eclipse on June 6, 1891. It was a hybrid event on June 17, 1909, and total eclipses from June 29, 1927 through September 9, 2648. The series ends at member 77 as a partial eclipse on April 17, 3009. The longest eclipse will occur on June 25, 2522, with a maximum duration of totality of 7 minutes, 12 seconds. [6]
| Series members 16–26 occur between 1901 and 2100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 16 | 17 | 18 |
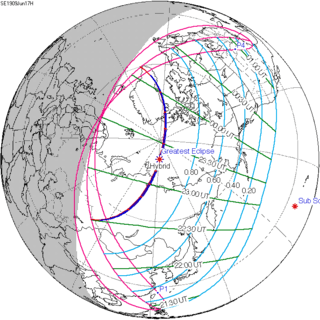 June 17, 1909 |
 June 29, 1927 |
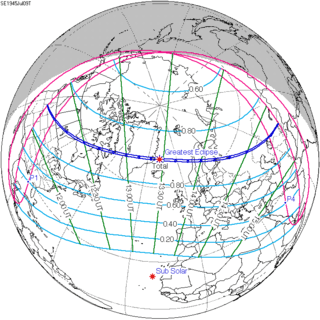 July 9, 1945 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 |
 July 20, 1963 |
 July 31, 1981 |
 August 11, 1999 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 |
 August 21, 2017 |
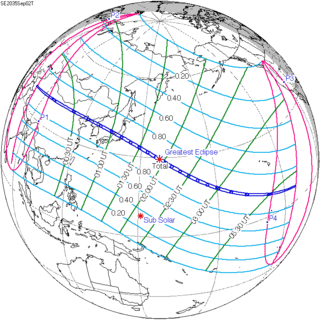 September 2, 2035 |
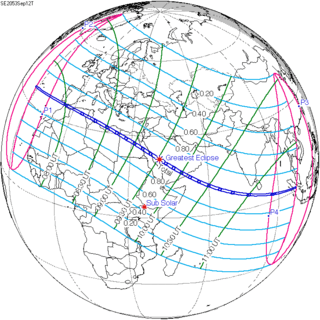 September 12, 2053 |
| 25 | 26 | |
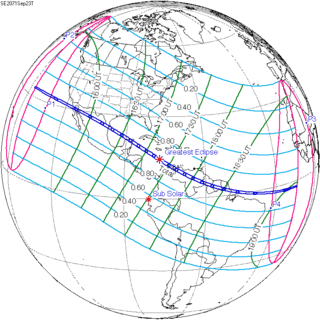 September 23, 2071 |
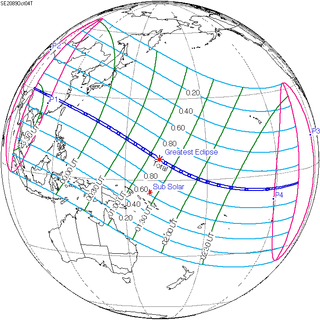 October 4, 2089 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 21 eclipse events between August 12, 1942 and August 11, 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| August 10-12 | May 30 | March 18 | January 4-5 | October 23-24 |
| 115 | 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 |
 August 12, 1942 |
 May 30, 1946 |
 March 18, 1950 |
 January 5, 1954 |
 October 23, 1957 |
| 125 | 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 |
 August 11, 1961 |
 May 30, 1965 |
 March 18, 1969 |
 January 4, 1973 |
 October 23, 1976 |
| 135 | 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 |
 August 10, 1980 |
 May 30, 1984 |
 March 18, 1988 |
 January 4, 1992 |
 October 24, 1995 |
| 145 | 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 |
 August 11, 1999 |
 May 31, 2003 |
 March 19, 2007 |
 January 4, 2011 |
 October 23, 2014 |
| 155 | ||||
 August 11, 2018 | ||||
See also
Notes
- ↑ Solar show in sky or on the Internet - Baltimore Sun
- ↑ "ISMB 99". Bioinf.mpi-sb.mpg.de. Retrieved 2013-10-01.
- ↑ Hatherill, Chris (9 March 2016). "When Astronomers Chased a Total Eclipse in a Concorde". Vice (magazine). Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ↑ Path of the Total Solar Eclipse of 1999 Aug 11, eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov
- ↑ Total Solar Eclipse of 1999 Aug 11 (GIF image), eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov
- ↑ Espenak, Fred (Project & Website Manager), Statistics for Solar Eclipses of Saros 145, NASA, updated 2009 September 26.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1999 August 11. |
- Eclipse at hermit.org
- "Club Krile Magazine", Vol. 11, 1999, "Air Group 2000" Publishing, Sofia, Bulgaria
- The Total Solar Eclipse of 1999 August 11
- Russia expedition
- Photos
- Turkey. Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site
- Hungary. Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site
- France. Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site
- Bulgaria
- Bulgaria
- Solar Corona Shape
- Exploratorium Webcast: Solar Eclipse August 11, 1999
- KryssTal - Eclipse in Cornwall (UK)—totality not seen but scene photographed
- Solar eclipse of August 11, 1999 Romania, shown in Romanian Maximum Card
- Solar eclipse of August 11, 1999 Romania, shown in Romanian Maximum Card
- Images from Turkey by Crayford Manor House Astronomical Society
- A Crescent Sunrise, APOD 8/17/1999, partial eclipse from Quebec, Canada
- Sun Block, APOD 8/18/1999, totality from Hungary
- Light From The Dark Sun, APOD 8/19/1999, totality from Siofok, Hungary
- At The Sun's Edge, APOD 8/20/1999, totality near Bagdere, Turkey
- The Big Corona, APOD 4/8/2001, totality by Fred Espenak
- Total Eclipse of the Active Sun, APOD 6/20/2001, from Kecel, Hungary
- Diamond Ring in the Sun, APOD 6/21/2001, totality from eastern Turkey
- Looking Back at an Eclipsed Earth, APOD 9/26/2004, total eclipse shadow seen from Mir spacestation, chosen as APOD again on 6/10/2007
- Russian scientist observed eclipse
- The 1999 Eclipse in England

