East Flanders
| East Flanders Dutch: Oost-Vlaanderen | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Province of Belgium | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Coordinates: 51°00′N 03°45′E / 51.000°N 3.750°ECoordinates: 51°00′N 03°45′E / 51.000°N 3.750°E | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Region |
| ||
| Capital | Ghent | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Jan Briers | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 2,991 km2 (1,155 sq mi) | ||
| Population (1 January 2016)[1] | |||
| • Total | 1,486,722 | ||
| • Density | 500/km2 (1,300/sq mi) | ||
| Website |
www | ||
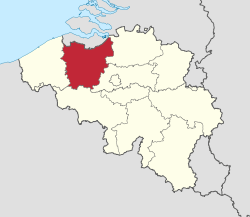
East Flanders (Dutch: Oost-Vlaanderen [ˌoːst ˈflaːndərə(n)],[2] French: (Province de) Flandre-Orientale, German: Ostflandern) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders (clockwise from the North) on Zeelandic Flanders (the Netherlands) and (in Belgium) on the provinces of Antwerp, Flemish Brabant (both in Flanders), of Hainaut (Wallonia) and of West Flanders (Flanders). It has an area of 2,991 km² which is divided into six administrative districts (arrondissementen in Dutch) containing 65 municipalities. The provincial population is 1,408,484 and the capital is Ghent.
History
During the short-lived Napoleonic Empire, most of the area of the modern province was part of the Department of Escaut, named after the River Scheldt. Following the defeat of Napoleon, the entity was renamed after its geographical location in the eastern part of historic Flanders; although the province is actually situated in the western portion of Flanders, in the contemporary sense of the word.
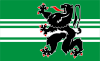
The provincial flag has a black lion with red tongue and claws, on a background of horizontal white and green stripes. This is a recent adaptation; formerly, East Flanders used the Flemish flag, a black lion on a yellow background, as in the current coat of arms. The old flag is still publicly used, e.g. for road signs.
Geography
The province has several geographic and/or tourist regions:
Important rivers are the Scheldt and the Leie which merge in Ghent. The Dender merges into the Scheldt in the city of Dendermonde.
Subdivisions
East Flanders is divided into 6 administrative arrondissements (districts), subdivided into a total of 65 municipalities. In addition, there are 3 judicial and 3 electoral arrondissements.
| District | Ghent District: | Oudenaarde District: | Eeklo District: | Aalst District: | Dendermonde District: | Sint-Niklaas District: |
| Location | 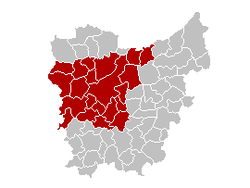 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
BE.OV.GT
|
BE.OV.OD
|
BE.OV.EK
|
BE.OV.AL
|
BE.OV.DM
|
BE.OV.SN
| |
| Municipalities |
Demographics
The province had a population of 1,445,831 as of 1 January 2011. It had 734,000 inhabitants in 1380 and about a million in 1900.
The capital and biggest city is Ghent, also the second largest city in the Flemish Region. Other smaller cities are Aalst, Sint-Niklaas and Dendermonde in the east of the province.
Government
The provincial council (provincieraad) consists of 72 members which were last elected in the 2012 elections. Previously it consisted of 84 members. The council currently consists of the following political parties:
- N-VA (Flemish nationalists): 21 members
- CD&V (Christian democrats): 15 members
- Open VLD (liberals): 15 members
- sp.a (social democrats): 9 members
- Vlaams Belang (far-right nationalists): 6 members
- Groen (greens): 6 members
Six people chosen by and from the council form the daily government, called the deputation (deputatie). The deputation of East Flanders is a coalition of the political parties CD&V, Open Vld and sp.a. The biggest party in the council, N-VA, is not included.
The daily government is led by the governor, who is appointed by the Flemish Government. André Denys (VLD) has been the governor of East Flanders from 26 November 2004 until 21 January 2013.[3] Jan Briers, who is not member of a political party but was nominated by N-VA, succeeded him on 1 February 2013.
The province has a yearly budget of approximately 300 million euro.
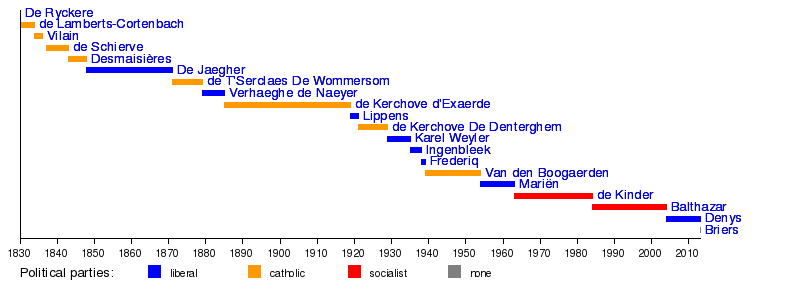
Governors
- 1830: Pierre De Ryckere
- 1830–1834: Werner de Lamberts-Cortenbach
- 1834–1836: Charles Vilain XIIII
- 1837–1843: Louis de Schiervel
- 1843–1848: Leander Desmaisières
- 1848–1871: Edouard De Jaegher (lib.)
- 1871–1879: Emile de T'Serclaes De Wommersom
- 1879–1885: Léon Verhaeghe de Naeyer (lib.)
- 1885–1919: Raymond de Kerchove d'Exaerde
- 1919–1921: Maurice Lippens (lib.)
- 1921–1929: André de Kerchove de Denterghem (lib.)
- 1929–1935: Karel Weyler (lib.)
- 1935–1938: Jules Ingenbleek (lib.)
- 1938–1939: Louis Frederiq (lib)
- 1939–1954: Maurice Van den Boogaerde
- 1954–1963: Albert Mariën (lib.)
- 1963–1984: Roger de Kinder (BSP)
- 1984–2004: Herman Balthazar (SP.A)
- 2004-2013: André Denys (VLD)
- 2013-present: Jan Briers (none; nominated by N-VA)
Timeline:
References
- ↑ Population per municipality as of 1 January 2016 (XLS; 397 KB)
- ↑ In isolation, Vlaanderen is pronounced [ˈvlaːndərə(n)].
- ↑ "The governor, province East Flanders". Retrieved 2006-03-14.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to East Flanders. |
- (Dutch) Official Website
 |
Zeeland (NL) |  | ||
| West Flanders | |
Antwerp Flemish Brabant | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Hainaut |