Economy of Virginia
 Seal of Virginia | |
| Statistics | |
|---|---|
| GDP | $423,860,000,000 [1] |
GDP per capita | $44,762[2] |
Population below poverty line | 10.2%[3] |
| 0.456 [4] | |
Labor force | 4,259,500[5] |
| Unemployment | 6.1%[6] |
| Public finances | |
| Revenues | $16,411,055,000[7] |
| Expenses | $40,024,000,000 [8] |
The Economy of Virginia is well balanced with diverse sources of income. From the Hampton Roads area to Richmond and down to Lee County in the southwest includes military installations, cattle, tobacco and peanut farming in Southside Virginia. Tomatoes recently surpassed soy as the most profitable crop in Virginia. Tobacco, peanuts and hay are also important agricultural products from the commonwealth.[9] Wineries and vineyards in the Northern Neck and along the Blue Ridge Mountains also have become increasingly popular. Northern Virginia (once considered the state's dairy capital) hosts software, communications, consulting, defense contracting, diplomats, and considerable components of the professional government sector. As of the 2000 census, Virginia had the highest number of counties and independent cities (15) in the top 100 wealthiest jurisdictions in the United States based upon median income, in addition, Virginia tied with Colorado as having the most counties (10) in the top 100 based on per capita income. Loudoun and Fairfax counties in Northern Virginia have the highest and second highest median household income, respectively, of all counties in the United States as of 2006.
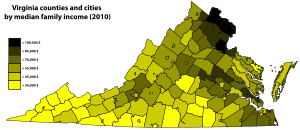
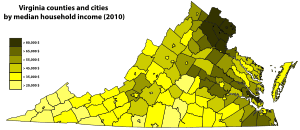

Background

The state GDP of Virginia was $383 billion in 2007, higher than the larger state of Michigan[10] and comparable to Saudi Arabia.[11] The per capita personal income was $35,477 in 2004. As of 2000, Virginia had the highest number of counties and independent cities, fifteen, in the top one-hundred wealthiest jurisdictions in the United States based upon median income. In addition, Virginia tied with Colorado as having the most counties, ten, in the top one-hundred based on per capita income.[12]
In 2006 and 2007, Forbes magazine voted Virginia as having the best climate for business in the United States citing economic growth, business costs/incentives and quality of life.[13] CNBC ranked Virginia as the top state for business in 2007 as well.[14]
Richmond is one of 12 cities in the country having a Federal Reserve bank. It, along with the New York and San Francisco Federal Reserve banks are the only ones that cover a non-state (Washington, D.C.).
There are seven Fortune 500 companies headquartered in Northern Virginia, and nine in the Richmond area (most of which are within the city itself.) Only five metro areas in the country have more Fortune 500 companies than the Richmond area. Virginia has seventeen total Fortune 500 companies, ranking the state tenth nationwide. Additionally, ten Fortune 1000 companies are in Northern Virginia, with a total of twenty-nine in the state.[15] With only 1% of the Hispanic American population, the state claims 3.6% of Hispanic 500 companies.[16]
Virginia, arguably the wealthiest southern state before the Civil War, recovered from the Civil War and the Great Depression much faster than the rest of the South. Today, Virginia is still one of the wealthiest states in the South. Virginia is also one of twenty-two right-to-work states.[17]

Virginia is also comparable to Alaska and ahead of North Dakota and New Mexico in per capita defense spending.[18]
|
Federal Agencies in Arlington | |
|---|---|
| Agency | Location |
| Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) | Ballston |
| Army National Guard Readiness Center | George Mason Drive |
| Bureau of Diplomatic Security | Rosslyn |
| Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) | Virginia Square |
| Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) | Columbia Pike |
| Department of Defense (DOD) | Pentagon |
| Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation | Virginia Square |
| Immigration & Naturalization Service (INS) | Ballston |
| Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) | Rosslyn |
| National Foreign Affairs Training Center | Route 50 |
| National Guard Bureau | Pentagon |
| National Science Foundation (NSF) | Ballston |
| Nuclear Waste Technical Review Board | Courthouse |
| Office of the Inspector General | Rosslyn |
| Office of Naval Research (ONR) | Ballston |
| Transportation Security Administration (TSA) | Pentagon City |
| US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) | Pentagon City |
| U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service | Ballston |
| US Marshals Service | Crystal City |
| US Trade & Development Agency | Rosslyn |
|
Federal Agencies outside of Arlington | |
|---|---|
| Agency | Location |
| Central Intelligence Agency | McLean |
| Defense Contract Audit Agency | Fort Belvoir |
| Defense Logistics Agency | Fort Belvoir |
| Defense Technical Information Center | Fort Belvoir |
| Mount Weather Emergency Operations Center | near Bluemont |
| National Reconnaissance Office | Chantilly |
| United States Geological Survey (USGS) | Reston |
| United States Patent and Trademark Office (PTO) | Alexandria |
Technology

According to the American Electronics Association, Virginia has the highest concentration of technology workers of any state.[19] Computer chips became the state's highest-grossing export in 2006, surpassing its traditional top exports of coal and tobacco, combined. The Dulles Technology Corridor centered on the border of Fairfax County and Loudoun County near Dulles International Airport has a high concentration of Internet, communication technology and software engineering firms.
The state's biotechnology industry is not centralized, but growing, highlighted by the building of the Virginia BioTechnology Research Park biotech incubator in Richmond and the opening of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Janelia Farm in Northern Virginia.
Virginia's nanotechnology industry, centered in Hampton Roads and Northern Virginia, accounted for $1 billion in manufactured goods in 2006. Researchers in Hampton Roads, many of whom hold patents in the field, believe the region has an advantage in the commercialization of nanotechnology due to the amount of research, much of it spearheaded by NASA's Langley Research Center.[20]
Taxation
Virginia collects personal income tax in five income brackets, ranging from 3.0% to 5.75%. The sales and use tax rate is 4%. The tax rate on food is 1.5%. There is an additional 1% local tax, for a total of a 5% combined sales tax on most Virginia purchases and a combined tax rate of 2.5% on food.[21] Virginia's property tax is set and collected at the local government level and varies throughout the commonwealth. Real estate is taxed at the local level based on 100% of fair market value. Effective true tax rates on real estate vary and are set by locality. Tangible personal property also is taxed at the local level and is based on a percentage or percentages of original cost. Tangible personal property includes, but is not limited to, machinery and equipment, furniture, fixtures, and trucks and automobiles. The Virginia General Assembly exempted intangible personal property from taxation in 1984 by making the tax rate zero. Virginia does not collect inheritance taxes; however, its estate tax is decoupled from the federal estate tax laws, and therefore the Commonwealth imposes its own estate tax.
See also
References
- ↑ "Graph: Total Gross Domestic Product by State for Virginia (VANGSP) - FRED - St. Louis Fed". Research.stlouisfed.org. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ "Graph: Per Capita Personal Income in Virginia (VAPCPI) - FRED - St. Louis Fed". Research.stlouisfed.org. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ "State Rankings-Statistical Abstract of the United States-Persons Below Poverty Level". Census.gov. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ "American FactFinder". Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ "Graph: Civilian Labor Force in Virginia (VALFN) - FRED - St. Louis Fed". Research.stlouisfed.org. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ "Unemployment Rate in Virginia (VAUR) - FRED - St. Louis Fed". Research.stlouisfed.org. 2012-01-24. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ "State Government Tax Collections Viewable Data". Census.gov. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ Fiscal Year 2009 State Expenditure Report, National Association of State Budget Officers, 2010, archived from the original (PDF) on 30 March 2011
- ↑ "2006 Report on Agricultural Production". The Virginian Pilot. Retrieved 2007-10-18.
- ↑ "BEA statistics for 1997-2007 GSP's". Bea.gov. 2010-12-23. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ "International Monetary Fund, World Economic Outlook Database, April 2008: Nominal GDP list of countries. Data for the year 2007". Imf.org. 2006-09-14. Retrieved 2012-03-09.
- ↑ "Per capita personal income". Regional Economic Information System. Bureau of Economic Analysis. April 2007. Retrieved 2007-11-24.
- ↑ Badenhausen, Kurt (2006-08-16). "Virginia: The Best State For Business". Forbes. Archived from the original on 2008-02-24. Retrieved 2007-10-07.
- ↑ Cohn, Scott (2007-07-13). "America's Top States For Business -- On The Road In Virginia". CNBC. Retrieved 2007-10-07.
- ↑ "Fortune 500 2007: States: Virginia". Money. April 30, 2007. Retrieved 2008-01-03.
- ↑ "Hispanic Business 500 - 2008 Directory". HispanTelligence. 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ↑ Right to Work States: Virginia (Va. Code Ann. §§ 40.1-58 through 40.1-69)
- ↑ "Federal Domestic Spending Up 9 Percent in 2001, Census Bureau". United States Census Bureau. 2002. Archived from the original on 2007-08-10. Retrieved 2007-10-07.
- ↑ Kazmierczak, Matthew (2007-04-24). "D.C. Capital Region Is A Growing High-Tech Hub". American Electronics Association. Retrieved 2007-10-07.
- ↑ http://content.hamptonroads.com/story.cfm?story=119982&ran=129934
- ↑ "State Sales Tax Rates". Federation of Tax Administrators. Retrieved 2007-09-24.