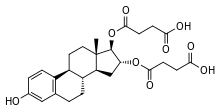
Estriol succinate
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | 514-68-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 10577 |
| ChemSpider | 10133 |
| UNII | AS13K2DY03 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H32O9 |
| Molar mass | 488.53 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Estriol succinate (INN) (brand names Sinapause, Styptanon, Synapasa, Synapausa, Synapause, Hemostyptanon, Orgastyptin, Ovestin, Evalon), or oestriol succinate (BAN), also known as estriol disuccinate or estriol hemisuccinate, as well as estriol 16α,17β-di(hydrogen succinate), is a semisynthetic, steroidal estrogen that is marketed in Europe, Hong Kong, and Mexico and was introduced in 1966.[1][2][3] It is an estrogen ester, specifically, an ester of estriol.[1] The drug is described as a weak estrogen (relative to estradiol valerate, which is described as a strong estrogen).[4] It was introduced in 1966 and is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms.[5] The drug is also available in sodium salt form as oestriol sodium succinate (BAN) (brand names Pausan, Styptanon).[1][2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. p. 899. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- 1 2 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 407–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ↑ I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 114–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ↑ Winnifred Berg Cutler; Celso-Ramón García (1984). The medical management of menopause and premenopause: their endocrinologic basis. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-397-50631-6.
- ↑ William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1481–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.