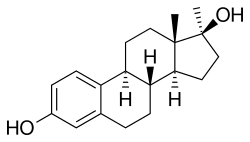
Methylestradiol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, Renodiol |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | 17α-Methylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol; NSC-52245 |
| CAS Number | 302-76-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 66413 |
| ChemSpider | 59787 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 286.40854 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Methylestradiol, or 17α-methylestradiol (17α-ME), is a semisynthetic, steroidal estrogen that has been sold in combination with normethandrone (methylestrenolone), an anabolic-androgenic steroid and progestin and , under brand names including Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, Renodiol for the treatment of menopausal symptoms in Brazil, Venezuela, and Indonesia.[1][2][3] Due to the presence of the 17α-methyl group, methylestradiol cannot be deactivated by oxidation of the 17β-hydroxy group, resulting in improved metabolic stability and potency relative to estradiol analogously to ethinyl estradiol (17α-ethinylestradiol).[4] In addition to its clinical use, methylestradiol has been studied as a radiopharmaceutical.[5]
Methylestradiol is an active metabolite of the anabolic-androgenic steroids methyltestosterone (17α-methyltestosterone) and metandienone (17α-methyl-δ1-testosterone) and is responsible for their estrogenic side effects such as gynecomastia (breast development) and fluid retention.[4][6][6]
See also
References
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 898–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ Drugs.com. "Methylestradiol". Retrieved 2 January 2016.
- ↑ IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer (2007). Combined Estrogen-progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-progestogen Menopausal Therapy. World Health Organization. pp. 389–. ISBN 978-92-832-1291-1.
- 1 2 Detlef Thieme; Peter Hemmersbach (18 December 2009). Doping in Sports. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 470–. ISBN 978-3-540-79088-4.
- ↑ Feenstra A, Vaalburg W, Nolten GM, Reiffers S, Talma AG, Wiegman T, van der Molen HD, Woldring MG (1983). "Estrogen receptor binding radiopharmaceuticals: II. Tissue distribution of 17 alpha-methylestradiol in normal and tumor-bearing rats". J. Nucl. Med. 24 (6): 522–8. PMID 6406650.
- 1 2 William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 533–. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.