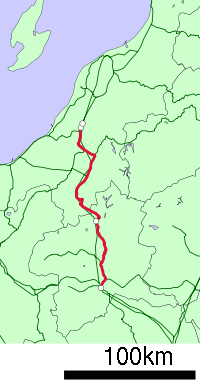
Jōetsu Line
| Joetsu Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
An E129 series EMU at Echigo-Nakazato Station in April 2016 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | 上越線 | ||
| Type | Heavy rail | ||
| Locale | Gunma, Niigata prefectures | ||
| Termini |
Takasaki Miyauchi | ||
| Stations | 34 | ||
| Operation | |||
| Opened | 1920 | ||
| Operator(s) |
| ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 162.6 km (101.03 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) | ||
| Electrification | 1,500 V DC overhead catenary | ||
| |||
The Joetsu Line (上越線 Jōetsu-sen) is a major railway line in Japan, owned by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). It connects Takasaki Station in Gunma Prefecture with Miyauchi Station in Niigata Prefecture, linking the northwestern Kanto region and the Sea of Japan coast of the Chūbu region. The name refers to the old provinces of Kōzuke (上野) and Echigo (越後), which the line connects.
Services
Before the opening of the Joetsu Shinkansen in 1982, the Joetsu Line had frequent service by express trains connecting Tokyo and Niigata. With the opening of the Jōetsu Shinkansen, however, the line became dominated by local and freight trains.
The branch of the Joetsu Shinkansen between Echigo-Yuzawa Station and Gala-Yuzawa Station (the Gala-Yuzawa Line) technically belongs to the Joetsu Line.
Stations
| Station | Japanese | Distance (km) | Transfers | Location | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between Stations |
Total | |||||
| Takasaki | 高崎 | - | 0.0 | Takasaki | Gunma | |
| Takasakitonyamachi | 高崎問屋町 | 2.8 | 2.8 | |||
| Ino | 井野 | 1.2 | 4.0 | |||
| Shin-Maebashi | 新前橋 | 3.3 | 7.3 | ■Ryōmō Line | Maebashi | |
| Gumma-Sōja | 群馬総社 | 4.8 | 12.1 | |||
| Yagihara | 八木原 | 5.6 | 17.7 | Shibukawa | ||
| Shibukawa | 渋川 | 3.4 | 21.1 | ■Agatsuma Line | ||
| Shikishima | 敷島 | 6.4 | 27.5 | |||
| Tsukuda | 津久田 | 3.0 | 30.5 | |||
| Iwamoto | 岩本 | 5.8 | 36.3 | Numata | ||
| Numata | 沼田 | 5.0 | 41.3 | |||
| Gokan | 後閑 | 5.2 | 46.5 | Minakami, Tone District | ||
| Kamimoku | 上牧 | 7.1 | 53.6 | |||
| Minakami | 水上 | 5.4 | 59.0 | |||
| Yubiso | 湯檜曽 | 3.7 | 62.7 | |||
| Doai | 土合 | 6.6 | 69.3 | |||
| Tsuchitaru | 土樽 | 10.8 | 80.1 | Yuzawa, Minamiuonuma District | Niigata | |
| Echigo-Nakazato | 越後中里 | 7.3 | 87.4 | |||
| Iwappara-Ski-jō-mae | 岩原スキー場前 | 3.7 | 91.1 | |||
| Echigo-Yuzawa | 越後湯沢 | 3.1 | 94.2 |
| ||
| Ishiuchi | 石打 | 6.4 | 100.6 | Minamiuonuma | ||
| Ōsawa | 大沢 | 4.0 | 104.6 | |||
| Jōetsu International Skiing Ground | 上越国際スキー場前 | 1.0 | 105.6 | |||
| Shiozawa | 塩沢 | 2.3 | 107.9 | |||
| Muikamachi | 六日町 | 3.9 | 111.8 | ■Hokuetsu Express Hokuhoku Line | ||
| Itsukamachi | 五日町◇ | 6.6 | 118.4 | |||
| Urasa | 浦佐 | 5.5 | 123.9 | |||
| Yairo | 八色 | 3.1 | 127.0 | |||
| Koide | 小出 | 5.2 | 132.2 | ■Tadami Line | Uonuma | |
| Echigo-Horinouchi | 越後堀之内 | 2.5 | 134.7 | |||
| Kita-Horinouchi | 北堀之内 | 3.4 | 138.1 | |||
| Echigo-Kawaguchi | 越後川口 | 4.7 | 142.8 | ■Iiyama Line | Nagaoka | |
| Ojiya | 小千谷 | 6.6 | 149.4 | Ojiya | ||
| Echigo-Takiya | 越後滝谷 | 7.2 | 156.6 | Nagaoka | ||
| Miyauchi | 宮内 | 6.0 | 162.6 | ■Shinetsu Main Line (for Naoetsu) | ||
| Through to Nagaoka on the Shinetsu Main Line | ||||||
| Nagaoka | 長岡 | 1.6 | 165.6 |
|
Nagaoka | Niigata |
Rolling stock
Takasaki—Minakami
- 115 series 4-car EMUs
- 211 series 4-car EMUs (since August 2016)
Four-car 211 series EMUs entered service on the section between Takasaki and Minakami from 23 August 2016.[1]
 A 115 series EMU at Takasaki Station on a Joetsu Line service in December 2015
A 115 series EMU at Takasaki Station on a Joetsu Line service in December 2015- A 211-3000 series EMU
Minakami—Nagaoka
Present
- E129 series 2/4-car EMUs (Since November 2015)
Former
- 115 series 2/3/4-car EMUs (until March 2016)
 A 115 series EMU at Echigo-Yuzawa Station
A 115 series EMU at Echigo-Yuzawa Station
History
The Nippon Railway opened the Takasaki to Maebashi (now Shinmaebashi) section in 1884. The company was nationalised in 1906.
The first railway between Niigata and the east coast of Honshu was the Ban'etsu West Line, completed in 1914. In 1920, it was decided to build the Jōetsu Line as a more direct route between Tokyo and Niigata. The Miyauchi to Echigo-Yuzawa section opened in stages between 1920 and 1925, and the Shinmaebashi to Minakami section of the line opened in stages between 1921 and 1928.
In 1931, with the completion of the 9,702 m Shimizu tunnel, the Echigo-Yuzawa - Minakami section of the line opened, including electrification at 1,500 V DC between Echigo-Yuzawa and Ishiuchi. When completed, the line shortened the Ueno to Niigata route by 98 km, and included two spiral sections in the tunnels.
In 1947, the Takasaki to Minakami and Ishiuchi to Miyauchi sections were electrified, making this one of the first non-urban JNR lines to be completely electrified.
The Takasaki to Shinmaebashi section was double-tracked in 1957, and the rest of the line was double-tracked between 1961 and 1967, the final section involving the construction of the 13,500 m Arashimizu tunnel. Passengers catching Miyauchi-bound trains at Yubiso and Doai stations do so from platforms situated within the Arashimizu tunnel.
Service disruptions
The 2004 Chūetsu earthquake seriously damaged the Jōetsu Line, closing the Minakami to Miyauchi section for about two months. Single-line operation at speeds limited to 30-45 km/h then resumed, being raised to 45-65 km/h four months after the earthquake, and the second track reopened, also with speed restrictions, 5 months after the quake. Full service was restored 9 months after the line had first closed.
In late July 2011, torrential rainfall damage resulted in the closure of the Echigo-Yuzawa - Muikamachi section for two weeks.
References
This article incorporates material from the corresponding article in the Japanese Wikipedia.
- ↑ 上越線・吾妻線で211系の営業運転開始 [211 series enter service on Joetsu Line and Agatsuma Line]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 24 August 2016. Retrieved 27 August 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Jōetsu Line. |
- Stations of the Jōetsu Line (JR East) (Japanese)

.svg.png)