Korku language
| Korku | |
|---|---|
| Region | Central India (Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra) |
Native speakers | 570,000 (2001 census)[1] |
| Balbodh style of the Devanagari script[2] | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
kfq |
| Glottolog |
kork1243[3] |
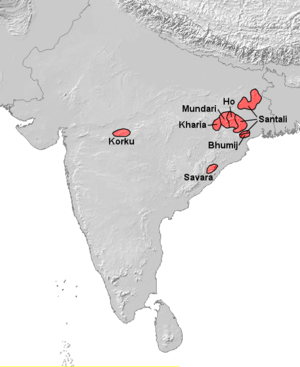
The Korku language is the language of the Korku tribe of central India. It belongs to the Kolarian or Munda family, isolated in the midst of a Dravidian (Gondi) population.
Korkus are also closely associated with the Nihali people, many of whom have traditionally lived in special quarters of Korku villages.[4] Korku is spoken by half a million people, mainly in four districts of southern Madhya Pradesh (Khandwa, Harda, Betul, Hoshangabad) and three districts of northern Maharashtra (Rajura and Korpana tahsils of Chandrapur district, Manikgarh pahad area near Gadchandur in Chandrapur district) (Amravati, Buldana, Akola). Korku is spoken in a declining number of villages and is gradually being replaced by Hindi.
Etymology
The name Korku comes from Koro-ku (-ku is the animate plural), Koro 'person, member of the Korku community' (Zide 2008).[5]
Varieties
Zide (2008:256) lists the following dialects.
- Kurku proper is spoken in the west. Most available data is from the Melghat subdialect. Other subdialects include Betul-Hoshangabad. The Lahi variety of Hoshangabad is notable for its loss of the dual.
- Muwasi (Mowasi, Mawasi) is spoken in the east, in areas such as Chhindwara district of northeastern Maharashtra.
Distribution
Korku is spoken in the following regions (Zide 2008:256):
- South-central Madhya Pradesh
- East Nimar district (Khandwa district)
- Betul district
- Hoshangabad district
- Northeastern Maharashtra
- Amravati district (majority of speakers in Maharashtra)
- Buldana district
- Akola district
- Chhindwara district (Mawasi speakers)
Grammar
Nouns may have either one of the three genders: masculine, feminine, or neuter. Adjectives are placed before the nouns they qualify.
Writing system
The Korku language uses the Balbodh style of the Devanagari script, which is also used to write the Marathi language.[2]
Endangerment
The use of the Korku language has been heavily influenced by larger hegemonic languages, especially Hindi. That influence affects not just language but also the customs and culture of traditional Korku people. A few groups have been more successful in preserving their language, specifically the Potharia Korku (from the Vindhya Mountains).[6]
The national census of 2001 reported 574,481 people claiming to speak Korku, an un-scheduled language.[7]
References
- ↑ Korku at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- 1 2 Sebeok, Thomas Albert (ed.). Current Trends in Linguistics. Walter de Gruyter. p. 425. Archived from the original on 7 December 2014.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Korku". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Nihali
- ↑ Cust, R. N. "Grammatical Note and Vocabulary of the Language of the Kor-ku, a Kolarian Tribe in Central India." The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. no. 2 (1884): 164 - 179. JSTOR 25196986
- ↑ Fuchs, Stephen. "Thirty Korku Dancing Songs." Asian Folklore Studies. no. 1 (2000): 109-140. JSTOR 1179030
- ↑ Sengupta, Papia. "Endangered Languages: Some Concerns." Economic And Political Weekly. no. 32 (2009): 17-19. JSTOR 25663414
- Zide, Norman. 2008. "Korku". In Anderson, Gregory D.S (ed). The Munda languages, 256-298. Routledge Language Family Series 3.New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-32890-X.
Further reading
- Nagaraja, K. S. (1999). Korku language: grammar, texts, and vocabulary. Tokyo: Institute for the Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies.
- Zide, N. H. (1963). Korku noun morphology. [Chicago: South Asian Languages Program, University of Chicago.
- Zide, N. H. (1960). Korku verb morphology. [S.l: s.n.
External links
- Ae... kalaavati... a korku song at YouTube.com