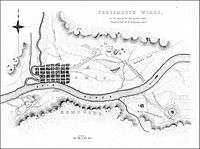
Portsmouth Earthworks
| Location |
Portsmouth, Ohio, Southern Ohio and Northeastern Kentucky, |
|---|---|
| Region | Southern Ohio and Northeastern Kentucky |
| History | |
| Founded | 100 BCE |
| Abandoned | 500 CE |
| Cultures | Adena culture, Hopewell culture |
| Architecture | |
| Architectural styles | earthworks |
| Architectural details |
Number of monuments: |
|
Horseshoe Mound | |
  | |
| Location | Scioto County, Ohio |
| Nearest city | Portsmouth, Ohio |
| Coordinates | 38°44′35.70″N 82°58′38.39″W / 38.7432500°N 82.9773306°W |
| Built | 499-0 BCE, 499-0 CE, 1000-500 CE |
| NRHP Reference # | 74001621 |
| Added to NRHP | 1974[1] |
|
Portsmouth Earthworks, Group A | |
  | |
| Location | Greenup County, Kentucky |
|---|---|
| Nearest city | South Portsmouth |
| Coordinates | 38°43′17.76″N 83°1′22.98″W / 38.7216000°N 83.0230500°WCoordinates: 38°43′17.76″N 83°1′22.98″W / 38.7216000°N 83.0230500°W |
| Built | 499-0 BCE, 499-0 CE, 1000-500 CE, 1499-1000 CE, 1749-1500 CE, 1750-1799 CE |
| NRHP Reference # | 80001534[1] |
| Added to NRHP | December 4, 1980 |
The Portsmouth Earthworks are a large prehistoric mound complex constructed by the Ohio Hopewell culture mound builder indigenous peoples of eastern North America (100 BCE to 500 CE).[2] The site was one of the largest earthwork ceremonial centers constructed by the Hopewell and is located at the confluence of the Scioto and Ohio Rivers, in present-day Ohio.
The majority of the mound complex site is now covered by the city of Portsmouth in Scioto County, Ohio.[2] Several individual sections of the complex have been included on the National Register of Historic Places.
Description
Originally, the Portsmouth Earthworks consisted of three sections extending over twenty miles of the Ohio River valley, crossing from Ohio to Kentucky in several places. It was surveyed and mapped by E. G. Squier in 1847 for inclusion in the seminal archaeological and anthrolopological work Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley.[3]
Portsmouth Earthworks, Group B

The northern most section was made up of a number of circular enclosures, two large horseshoe-shaped enclosures, and three sets of parallel-walled roads leading away in different directions. One set of walled roads extends across the Ohio River into South Portsmouth, Kentucky to the southwest to Portsmouth Earthworks, Group A. Another set of walled roads lead to the southeast where it also crossed the Ohio River and lead to Portsmouth Earthworks, Group C.[3] The third set of walled roads lead to the northwest for an undetermined distance, and may point to Tremper Mound and Works, some 5 miles away. The City of Portsmouth maintains a public park which includes one of the remaining horseshoe-shaped enclosures, known as Mound Park, it is the only publicly accessible part of the complex.[2] Under the name Horseshoe Mound it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.[2]
Portsmouth Earthworks, Group A

Also known as the Old Fort Earthworks (15Gp1) it is a series of rectangular enclosures near South Portsmouth in Greenup County, Kentucky. Group A is a large square enclosure with two series of parallel walls extending from the northeast and southwest corners. The Old Fort Earthworks consist of several sites, including the Old Fort Earthworks (15Gp1), Mays Mound (15Gp16), Hicks Mound (15Gp265), Stephenson Mound (15Lw139), and several other unnamed mounds and enclosures. It is also the location of Lower Shawneetown, a protohistoric/historic Fort Ancient and Shawnee settlement and colonial trading post which are all part of the Lower Shawneetown Archeological District,[4] along with the Thompson and Hansen Sites
Portsmouth Earthworks, Group C
Also known as the Biggs Site (15Gp8), Group C was a large series of concentric circles surrounding a central cone mound, believed to have been built by the Adena culture. This section of the earthworks is located in Greenup County, Kentucky several miles to the east of South Shore, but connected to Group B by a causeway.
Gallery of Squier and Davis maps
See also
References
- 1 2 "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. 2009-03-13.
- 1 2 3 4 "Portsmouth Earthworks-Ohio History Central". Retrieved 2009-06-06.
- 1 2 Ephraim George Squier; Edwin Hamilton Davis (1848). Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley. Smithsonian Institution. pp. 179–187.
- ↑ Applegate, Darlene (2008), "Chapter 5:Woodland period", in Pollack, David, The Archaeology of Kentucky:an update (PDF), 1, Kentucky Heritage Council, pp. 524–525, ISBN 978-1-934492-28-4
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Portsmouth Earthworks. |