Sombor
| Sombor Сомбор | ||
|---|---|---|
| City | ||
|
Sombor Town Hall | ||
| ||
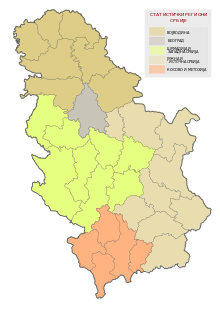
 Location of the municipality of Sombor within Serbia | ||
| Coordinates: 45°47′N 19°07′E / 45.783°N 19.117°ECoordinates: 45°47′N 19°07′E / 45.783°N 19.117°E | ||
| Country |
| |
| Province |
| |
| District | West Bačka | |
| City status | 17 February 1749 | |
| Settlements | 16 | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Saša Todorović | |
| Area[1] | ||
| • Municipality | 1,178 km2 (455 sq mi) | |
| Population (2011 census)[2] | ||
| • Town | 48,000 | |
| • Municipality | 85,903 | |
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | |
| Postal code | 25000 | |
| Area code | +381 25 | |
| Car plates | SO | |
| Website |
www | |
Sombor (Serbian: Сомбор / Sombor pronounced [sɔ̂mbɔr], Hungarian: Zombor, Rusyn: Zombor (Зомбор)) is a city located in the province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The city has a total population of 47,623 (as of 2011), while its administrative area (including neighboring villages) has 85,903 inhabitants. It is the administrative center of the West Bačka District.
Name and etymology
In Serbian, the city is known as Sombor (Сомбор), in Hungarian and German as Zombor, in Croatian and Bunjevac as Sombor, in Rusyn as Zombor (Зомбор), and in Turkish as Sonbor.
The older Hungarian name for the city was Czoborszentmihály. The name originates from the Czobor family, who were the owners of this area in the 14th century (The family name came from the Slavic name Cibor). The Serbian name for the city (Sombor) also came from the family name Czobor, and was first recorded in 1543, although the city was mentioned in historical documents under several more names, such as Samobor, Sambor, Sambir, Sonbor, Sanbur, Zibor, and Zombar.
An unofficial Serbian name used for the city is Ravangrad (Раванград), which means "flat town" in English.
History

_-_main_street.jpg)
The first historical record about the city is from 1340. The city was administered by the Kingdom of Hungary until the 16th century, when it became part of the Ottoman Empire. During the establishment of Ottoman authority, local Hungarian population left from this region. During the Ottoman administration, the city was populated mostly by ethnic Serbs.[3] It was called "Sonbor" during Ottoman administration and was a kaza centre in Sanjak of Segedin at first in Budin Province till 1596, and then in Eğri Province between 1596 and 1687.
In 1665, a well-known traveller, Evlia Celebi, visited Sombor and wrote: "All the folk (in the city) are not Hungarian, but Wallachian-Christian (Serb[3]). These places are something special; they do not belong to Hungary, but are a part of Bačka and Wallachia. Most of the inhabitants are traders, and all of them wear frontiersmen clothes; they are very polite and brave people." According to Celebi, the city had 200 shops, 14 mosques and about 2,000 houses.
Since 12 September 1687, the city was under Habsburg administration, and was included into the Habsburg Military Frontier. Ottomans attempted to recapture it during Battle of Zenta in 11 September 1697. However their attack was repulsed. In 1717, the first Orthodox elementary school was opened. Five years later a Roman Catholic elementary school was opened as well. In 1745 Sombor was excluded from the Military Frontier and was included into Bacsensis County. In 1749 Sombor gained royal free city status. In 1786, the city became the seat of Bacsensis-Bodrogiensis County. According to 1786 data, the population of the city numbered 11,420 people, mostly Serbs.
According to the 1843 data, Sombor had 21,086 inhabitants, of whom 11,897 were Orthodox Christians, 9,082 Roman Catholics, 56 Jewish, and 51 Protestants. The main language spoken in the city at this time was Serbian, and the second largest language was German. In 1848/1849, Sombor was part of the Serbian Vojvodina, a Serb autonomous region within Austrian Empire, while between 1849 and 1860, it was part of the Voivodeship of Serbia and Temes Banat, a separate Austrian crown land. Sombor was a seat of the district within voivodship. After the abolishment of this crown land, Sombor again became the seat of the Bacsensis-Bodrogiensis (Bács-Bodrog, Bačka-Bodrog) County.

According to the 1910 census, the population of Sombor was 30,593 people, of whom 11,881 spoke the Serbian language, 10,078 spoke the Hungarian language, 6,289 spoke the Bunjevac language, 2,181 spoke the German language.
In 1918, Sombor became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (later known as the Kingdom of Yugoslavia). Between 1918 and 1922 it was part of Bačka County, between 1922 and 1929 part of Bačka Oblast, and between 1929 and 1941 part of Danube Banovina.
In 1941, city was occupied by the Axis powers and annexed by Hungary. Many prominent citizen from Serbian community were interned and later executed. In 1944, Yugoslav partisans and Soviet Red Army expelled Axis forces from the city. Since 1944, Sombor was part of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina of the new Socialist Yugoslavia and (since 1945) socialist Serbia. Today, Sombor is the seat of the West Bačka District.
Geography
Climate
Climate in this area has mild differences between highs and lows, and there is adequate rainfall year-round. The Köppen Climate Classification subtype for this climate is "Cfb" (Marine West Coast Climate/Oceanic climate).[4]
| Climate data for Sombor (1981–2010, extremes 1961–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 19.3 (66.7) |
21.3 (70.3) |
27.6 (81.7) |
29.5 (85.1) |
35.1 (95.2) |
37.1 (98.8) |
40.3 (104.5) |
39.5 (103.1) |
35.7 (96.3) |
29.4 (84.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
20.7 (69.3) |
40.3 (104.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 3.6 (38.5) |
6.3 (43.3) |
12.0 (53.6) |
17.8 (64) |
23.3 (73.9) |
26.1 (79) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.5 (83.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
18.1 (64.6) |
10.2 (50.4) |
4.5 (40.1) |
16.9 (62.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −0.1 (31.8) |
1.4 (34.5) |
6.2 (43.2) |
11.6 (52.9) |
17.1 (62.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
16.5 (61.7) |
11.3 (52.3) |
5.4 (41.7) |
1.1 (34) |
11.2 (52.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −3.4 (25.9) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
1.2 (34.2) |
5.8 (42.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
13.8 (56.8) |
15.2 (59.4) |
14.7 (58.5) |
10.7 (51.3) |
6.2 (43.2) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −27.2 (−17) |
−26.3 (−15.3) |
−20.3 (−4.5) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
2.0 (35.6) |
7.3 (45.1) |
4.6 (40.3) |
−2.2 (28) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
−23.7 (−10.7) |
−27.2 (−17) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 37.3 (1.469) |
29.9 (1.177) |
36.4 (1.433) |
45.2 (1.78) |
60.0 (2.362) |
81.5 (3.209) |
66.2 (2.606) |
53.1 (2.091) |
54.4 (2.142) |
47.3 (1.862) |
53.7 (2.114) |
47.4 (1.866) |
612.4 (24.11) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 11 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 128 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 84 | 78 | 70 | 66 | 64 | 65 | 64 | 66 | 71 | 75 | 82 | 86 | 72 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 62.2 | 97.5 | 147.6 | 191.8 | 244.1 | 259.5 | 290.3 | 274.3 | 197.1 | 152.5 | 80.4 | 53.0 | 2,050.4 |
| Source: Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia[5] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Ethnic groups in the Sombor administrative area
The population of the Sombor administrative area (as of 2011) is composed of:[6]
- Serbs = 54,370 (63.29%)
- Hungarians = 9,874 (11.49%)
- Croats = 7,070 (8.23%)
- Bunjevci = 2,058 (2.4%)
- Roma = 1,015 (1,18%)
- Yugoslavs = 852 (0.99%)
- Others and undeclared = 10,664 (12.41%)
The population of the Sombor town itself is composed of (2011 census):[6]
- Serbs = 32,180 (67.57%)
- Croats = 2,863 (6.01%)
- Hungarians = 2,851 (5.99%)
- Bunjevci = 1,629 (3.42%)
- Yugoslavs = 594 (1.25%)
- Montenegrins = 475 (1.00%)
- Others and undeclared = 7,031 (14.77%)
Settlements with Serb ethnic majority (in 2002) are: Sombor, Aleksa Šantić, Gakovo, Kljajićevo, Kolut, Rastina, Riđica, Stanišić, Stapar, and Čonoplja. Settlements with Croat/Šokac ethnic majority (in 2002) are: Bački Breg and Bački Monoštor. Settlements with Hungarian ethnic majority (in 2002) are: Bezdan, Doroslovo, and Telečka. Ethnically mixed settlement with relative Hungarian majority is Svetozar Miletić.
Historical population of the town has been as follows:
- 1961: 37,760
- 1971: 44,100
- 1981: 48,454
- 1991: 48,993
- 2002: 51,471
- 2011: 47,623
Inhabited settlements in the municipality
of Sombor
●

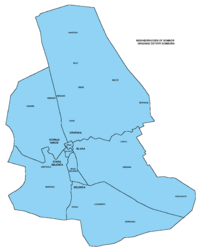
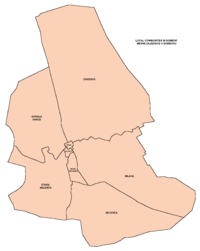
Sombor municipality includes the city of Sombor and the following villages:
- Aleksa Šantić
- Bački Breg
- Bački Monoštor
- Bezdan
- Gakovo
- Doroslovo
- Kljajićevo
- Kolut
- Rastina
- Riđica
- Svetozar Miletić
- Stanišić
- Stapar
- Telečka
- Čonoplja
Smaller and suburban settlements include
Culture


Sombor is famous for its greenery, cultural life and beautiful 18th and 19th century center. The most important cultural institutions are the National Theater, the Regional Museum, the Modern Art Gallery, the Milan Konjović Art Gallery, the Teacher's College, the Serbian Reading House, and the Grammar School. Teacher's College, founded in 1778, is the oldest college in Serbia and the region.
Sombor's rich history includes the oldest institution for higher education in the Serbian language. The town is also home of numerous minority organisations, including the Hungarian Pocket Theater Berta Ferenc, the Croatian Society Vladimir Nazor, the Jewish Municipality and several other smaller organisations including German and Romani clubs.
There are two monasteries in this city:
- Sombor Orthodox Monastery, founded in 1928–1933
- Carmelite Catholic monastery, founded in 1904
Buildings and architecture
 Županija building housing city and municipality administration
Županija building housing city and municipality administration The old town hall of Sombor and the Holy Trinity Square
The old town hall of Sombor and the Holy Trinity Square Sombor theater building
Sombor theater building Sombor main street with the water fountain
Sombor main street with the water fountain Catholic church viewed from the park
Catholic church viewed from the park Catholic church in Sombor
Catholic church in Sombor
Sports
Radnički Sombor is the main football club from the city.
ŽRK Ravangrad Sombor is the main handball club from city.
Local media
Newspapers
- Somborske novine[7]
TV stations
Radio stations
- Radio Marija (95,7)
- Radio Sombor (97.5)[10]
- Radio Fortuna (106.6)
Internet media
- SOinfo.org[11]
Twin cities
Twin cities:
Regional cooperation:
Transportation
Buses
Buses offer direct connections to major Serbian cities including Belgrade, Novi Sad and Subotica, as well as many regional towns. Among the companies operating in the area is Severtrans.
Rail
The is linked by direct rail links to Novi Sad and Subotica, among others.
Air
The municipality houses Sombor Airport.
See also
References
- ↑ "Municipalities of Serbia, 2006". Statistical Office of Serbia. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
- ↑ "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia: Comparative Overview of the Number of Population in 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991, 2002 and 2011, Data by settlements" (PDF). Statistical Office of Republic Of Serbia, Belgrade. 2014. ISBN 978-86-6161-109-4. Retrieved 2014-06-27.
- 1 2 http://www.sombor.rs/istorija
- ↑ Climate Summary for Sombor
- ↑ "Monthly and annual means, maximum and minimum values of meteorological elements for the period 1981–2010" (in Serbian). Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia. Retrieved April 9, 2015.
- 1 2 "Population by ethnicity – Sombor". Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia (SORS). Retrieved 4 March 2013.
- ↑ http://www.somborskenovine.co.rs/
- ↑ http://www.rtvspektar.co.rs/
- ↑ http://rtvsrece.com/
- ↑ http://www.radiosombor.co.rs/
- ↑ http://www.soinfo.org/
- Slobodan Ćurčić, Broj stanovnika Vojvodine, Novi Sad, 1996.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sombor. |