Alpha-adrenergic agonist
| Alpha Adrenergic agonist | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
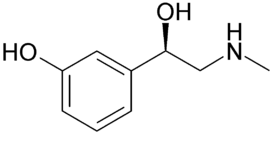 Skeletal structor formula of phenylephrine, a common nasal decongestant | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Use | Decongestant, Hypotension, Bradycardia, Hypothermia etc. |
| ATC code | N07 |
| Biological target | Alpha adrenergic receptors of the α subtype |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D000316 |
An adrenergic alpha-agonist (or alpha-adrenergic agonists) are a class sympathomimetic agents that selectively stimulates alpha adrenergic receptors. The alpha-adrenergic receptor has two subclasses α1 and α2. Alpha 2 receptors are associated with sympatholytic properties. α Adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of alpha blockers. Alpha adrenoreceptor ligands mimic the action of epinephrine and norepinephrine signaling in the heart, smooth muscle and central nervous system, with norepinephrine being the highest affinity. The activation of α1 stimulates the membrane bound enzyme phospholipase C, and α2 inhibits the enzyme Adenylate cyclase. Inactivation of adenylate cyclase in turn leads to the inactivation of the secondary messenger Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and induces smooth muscle and blood vessel constriction.
Classes
Although complete selectivity between receptor agonism is rarely achieved, some agents have partial selectivity.
α1 agonist
α1 agonist: stimulates phospholipase C activity. (vasoconstriction and mydriasis; used as vasopressors, nasal decongestants and eye exams). Selected examples are:
α2 agonist
α2 agonist: inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity, reduces brainstem vasomotor center-mediated CNS activation; used as antihypertensive, sedative & treatment of opiate dependence and alcohol withdrawal symptoms). Selected examples are:
- Clonidine (mixed alpha2-adrenergic and imidazoline-I1 receptor agonist)
- Guanfacine,[2] (preference for alpha2A-subtype of adrenoceptor)
- Guanabenz (most selective agonist for alpha2-adrenergic as opposed to imidazoline-I1)
- Guanoxabenz (metabolite of guanabenz)
- Guanethidine (peripheral alpha2-receptor agonist)
- Xylazine,[3]
- Tizanidine
- Medetomidine
- Methyldopa
- Methylnorepinephrine
- Fadolmidine
- Dexmedetomidine
Undetermined/unsorted
The following agents are also listed as agonists by MeSH.[4]
- amidephrine
- amitraz
- anisodamine
- apraclonidine
- brimonidine
- cirazoline
- detomidine
- dexmedetomidine
- epinephrine
- ergotamine
- etilefrine
- indanidine
- lofexidine
- medetomidine
- mephentermine
- metaraminol
- methoxamine
- mivazerol
- naphazoline
- norepinephrine
- norfenefrine
- octopamine
- oxymetazoline
- phenylpropanolamine
- rilmenidine
- romifidine
- synephrine
- talipexole
Clinical significance
Alpha-adrenergic agonists, more specifically the auto receptors of alpha 2 neurons, are used in the treatment of glaucoma by decreasing the production of aqueous fluid by the ciliary bodies of the eye and also by increasing uveoscleral outflow. Medications such as clonidine target pre-synaptic auto receptors, therefore leading to an overall of decrease in norepinephrine.
See also
References
- ↑ Declerck I, Himpens B, Droogmans G, Casteels R (September 1990). "The alpha 1-agonist phenylephrine inhibits voltage-gated Ca2(+)-channels in vascular smooth muscle cells of rabbit ear artery". Pflugers Arch. 417 (1): 117–9. doi:10.1007/BF00370780. PMID 1963492.
- ↑ Sagvolden T (2006). "The alpha-2A adrenoceptor agonist guanfacine improves sustained attention and reduces overactivity and impulsiveness in an animal model of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)". Behav Brain Funct. 2: 41. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-2-41. PMC 1764416
 . PMID 17173664.
. PMID 17173664. - ↑ Atalik KE, Sahin AS, Doğan N (April 2000). "Interactions between phenylephrine, clonidine and xylazine in rat and rabbit aortas". Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 22 (3): 145–7. PMID 10893695.
- ↑ MeSH list of agents 82000316
External links
- Adrenergic alpha-Agonists at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)