Goalpara district
| Goalpara district | |
|---|---|
| District | |
|
Tea plantation in Goalpara district | |
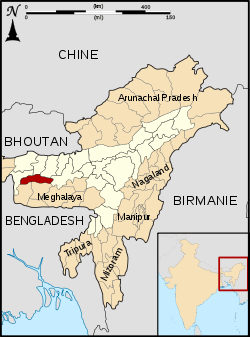 Goalpara district's location in Assam | |
| Country | India |
| State | Assam |
| Headquarters | Goalpara |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,824 km2 (704 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 1,008,959 |
| • Density | 550/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+05:30) |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-AS, IN-AS-GP |
| Website | http://goalpara.gov.in/ |
Goalpara district (Pron:ˌgəʊɑ:lˈpɑ:rə) (Assamese: গোৱালপাৰা জিলা) is an administrative district in the state of
History
It was a princely state ruled by the Rajbongsi Kings and the then ruler of the undivided kingdom. Presently the erstwhile Goalpara district is divided into Kokrajhar, Bongaigaon, Dhubri, and Goalpara district.
The name of the district Goalpara is widely said to have originally derived from `Gwaltippika` meaning `Guwali village` or the village of the milk men.[1] The history of Goalpara goes back to several centuries. Based on the Chinese traveler `Hiuentsang` report, Sir Edward Gait had concluded that the erstwhile capital of the state of Kumar Bhaskar Varman was either in Goalpara district or in Cooch Behar. The district came under British rule in 1765. Before this, the area was under the control of the Koch dynasty. It was also part of greater British Bengal. In 1826 the British accessed Assam and Goalpara was annexed to Assam in 1874, along with the creation of district headquarters at Dhubri.
On 1 July 1983 two districts were split from Goalpara: Dhubri and Kokrajhar.[2] On 29 September 1989 Bongaigaon district was created from parts of Goalpara and Kokrajhar.[2]
Geography
The district headquarters are located at Goalpara. Goalpara district occupies an area of 1,824 square kilometres (704 sq mi),[3] comparatively equivalent to South Korea's Jeju-do.[4] nbkjnkdasjnfjkd iojd jjl opiopqwe weopemeopm;ldkasdopkopqkm pek [--0o42=- r3-0i30- 0- er90 rkhdsmd=-32 3=-01 mdfg0- =-0 3-9=0-4 mi43o0= 32t
Economy
In 2006 the Indian government named Goalpara one of the country's 250 most backward districts (out of a total of 640).[5] It is one of the eleven districts in Assam currently receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF).[5]
Political Divisions
There are four Assam Legislative Assembly constituencies in this district: Dudhnoi, Goalpara East, Goalpara West, and Jaleswar.[6] Dudhnoi is designated for scheduled tribes.[6] Dudhnoi is in the Gauhati Lok Sabha constituency, whilst the other three are in the Dhubri Lok Sabha constituency.[7]
Demographics
According to the 2011 census Goalpara district has a population of 1,008,959,[8] roughly equal to the nation of Cyprus[9] or the US state of Montana.[10] This gives it a ranking of 444th in India (out of a total of 640).[8] The district has a population density of 553 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,430/sq mi) .[8] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 22.74%.[8] Goalpara has a sex ratio of 962 females for every 1000 males,[8] and a literacy rate of 68.67%.[8]
Muslims 441,516 (53.71%), Hindus 314,157, and Christians 64,662.
Toursist Attractions
The Goalpara district is endowed with natural beauty and archaeological treasures. The important tourist spots of the district include:
- Sri Surya Pahar, a very significant but relatively unknown archaeological site in Assam, a hill which showcases the remains of cultural heritage of three important religions of India, Buddhism, Jainism and Hinduism.
- Dadan Hill has a Shiva Temple on its top. The temple was established by a general of the army of King Bana of Sonitpur named Dadan. The mystical hill is surrounded by mythological stories related to the bygone era.
- Pir Majhar is situated at the heart of the Goalpara town, a tomb of a saint named Hazarat Sayed Abul Kasem Kharasani. He is a saint who was respected by Hindus and Muslims alike.
- Hulukanda hill is located at the heart of Goalpara.
- Sri Tukreswari hill
- Paglartek Baba at Barbhita
- Urpod beel of Agia
- Dhamar Risen beel of Lakhipur are some other attractions of the district.
References
- ↑ A brief history of Goalpara District
- 1 2 Law, Gwillim (2011-09-25). "Districts of India". Statoids. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
- ↑ Srivastava, Dayawanti et al. (ed.) (2010). "States and Union Territories: Assam: Government". India 2010: A Reference Annual (54th ed.). New Delhi, India: Additional Director General, Publications Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India), Government of India. p. 1116. ISBN 978-81-230-1617-7.
- ↑ "Island Directory Tables: Islands by Land Area". United Nations Environment Program. 1998-02-18. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
Jeju-do 1,825km2
- 1 2 Ministry of Panchayati Raj (September 8, 2009). "A Note on the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme" (PDF). National Institute of Rural Development. Retrieved September 27, 2011.
- 1 2 "List of Assembly Constituencies showing their Revenue & Election District wise break - up" (PDF). Chief Electoral Officer, Assam website. Retrieved 26 September 2011.
- ↑ "List of Assembly Constituencies showing their Parliamentary Constituencies wise break - up" (PDF). Chief Electoral Officer, Assam website. Retrieved 26 September 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ↑ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". Retrieved 2011-10-01.
Cyprus 1,120,489 July 2011 est.
- ↑ "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
Montana 989,415
External links
 |
Bongaigaon district | Barpeta district |  | |
| Dhubri district | |
Kamrup district | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| West Garo Hills, Meghalaya | East Garo Hills, Meghalaya |
Coordinates: 26°26′N 90°22′E / 26.433°N 90.367°E
