Śāradā script
| Śāradā | |
|---|---|
 Kashmiri Shaivaite manuscript (17th or 18th century) | |
| Type | |
| Languages | Sanskrit, Kashmiri |
Time period | c. 800 CE–present (almost extinct) |
Parent systems | |
Child systems |
Gurmukhī Takri Landa |
Sister systems |
Nāgarī Siddhaṃ |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| ISO 15924 |
Shrd, 319 |
Unicode alias | Sharada |
| U+11180–U+111DF | |
|
[a] The Semitic origin of the Brahmic scripts is not universally agreed upon. | |
| Brahmic scripts |
|---|
| The Brahmic script and its descendants |
|
Northern Brahmic
|
The Śāradā or Sarada or Sharada script is an abugida writing system of the Brahmic family of scripts, developed around the 8th century. It was used for writing Sanskrit and Kashmiri. The Gurmukhī script was developed from Śāradā. Originally more widespread, its use became later restricted to Kashmir, and it is now rarely used except by the Kashmiri Pandit community for ceremonial purposes.
This is a native script of Kashmir and named after the deity, Goddess Sharda.[1] Śāradā is another name for Saraswati, the goddess of learning.
Letters
Independent vowel signs

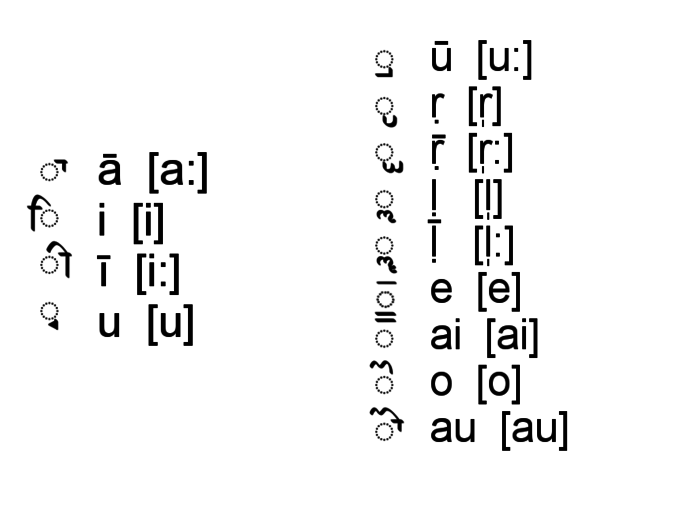
Dependent vowel signs
Consonants

Numerals

Sharada script uses its own signs for the positional decimal numeral system.
Image gallery
 Sharada vowels
Sharada vowels Sharada consonant signs
Sharada consonant signs Sanskrit (above; devanagari script) and Kashmiri language (below; sharada script)
Sanskrit (above; devanagari script) and Kashmiri language (below; sharada script)
Unicode
Śāradā script was added to the Unicode Standard in January, 2012 with the release of version 6.1.
The Unicode block for Śāradā script, called Sharada, is U+11180–U+111DF:
| Sharada[1][2] Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+1118x | 𑆀 | 𑆁 | 𑆂 | 𑆃 | 𑆄 | 𑆅 | 𑆆 | 𑆇 | 𑆈 | 𑆉 | 𑆊 | 𑆋 | 𑆌 | 𑆍 | 𑆎 | 𑆏 |
| U+1119x | 𑆐 | 𑆑 | 𑆒 | 𑆓 | 𑆔 | 𑆕 | 𑆖 | 𑆗 | 𑆘 | 𑆙 | 𑆚 | 𑆛 | 𑆜 | 𑆝 | 𑆞 | 𑆟 |
| U+111Ax | 𑆠 | 𑆡 | 𑆢 | 𑆣 | 𑆤 | 𑆥 | 𑆦 | 𑆧 | 𑆨 | 𑆩 | 𑆪 | 𑆫 | 𑆬 | 𑆭 | 𑆮 | 𑆯 |
| U+111Bx | 𑆰 | 𑆱 | 𑆲 | 𑆳 | 𑆴 | 𑆵 | 𑆶 | 𑆷 | 𑆸 | 𑆹 | 𑆺 | 𑆻 | 𑆼 | 𑆽 | 𑆾 | 𑆿 |
| U+111Cx | 𑇀 | 𑇁 | 𑇂 | 𑇃 | 𑇄 | 𑇅 | 𑇆 | 𑇇 | 𑇈 | 𑇉 | 𑇊 | 𑇋 | 𑇌 | 𑇍 | ||
| U+111Dx | 𑇐 | 𑇑 | 𑇒 | 𑇓 | 𑇔 | 𑇕 | 𑇖 | 𑇗 | 𑇘 | 𑇙 | 𑇚 | 𑇛 | 𑇜 | 𑇝 | 𑇞 | 𑇟 |
| Notes | ||||||||||||||||
See also
- Lipi – writing scripts in Buddhist, Hindu and Jaina texts
- Sharada Peeth in Kashmir
References
- ↑ "Pandits to visit Sharda temple". The Hindu. 17 May 2006. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
External links
- ancientscripts.com
- Prevalence of the Śāradā Script in Afghanistan
- Akṣara List of the Manuscript of Abhidharmadīpa , ca. the 11th Century, Collection of Sanskrit Mss. Formerly Preserved in the China Ethnic Library
- Modern Kashmiri Dictionary: Android based electronic Kashmiri Dictionary