Shibata, Niigata
| Shibata 新発田市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
|
Ruins of Shibata Castle | |||
| |||
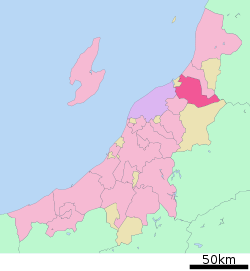 Location of Shibata in Niigata Prefecture | |||
 Shibata
| |||
| Coordinates: 37°57′3.1″N 139°19′40.3″E / 37.950861°N 139.327861°ECoordinates: 37°57′3.1″N 139°19′40.3″E / 37.950861°N 139.327861°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Chūbu (Kōshin'etsu) (Hokuriku) | ||
| Prefecture | NIigata | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 533.10 km2 (205.83 sq mi) | ||
| Population (June 2016) | |||
| • Total | 98,025 | ||
| • Density | 184/km2 (480/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| Symbols | |||
| • Tree | Sakura | ||
| • Flower | Iris | ||
| Phone number | 0254-22-3101 | ||
| Address | 4-10-4 Chūōchō, Shibata-shi, Niigata-ken 957-8686 | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Shibata (新発田市 Shibata-shi) is a city located in northern Niigata Prefecture, in the Hokuriku region of Japan. As of 1 June 2016, the city had an estimated population of 98,025 and a population density of 184 persons per km². Its total area was 533.10 square kilometres (205.83 sq mi).
Geography
Shibata is located in a mostly inland region of north-central Niigata Prefecture, with a small shoreline of the Sea of Japan. The area is noted for extremely heavy snowfall in winter.
Surrounding municipalities
History
The area of present-day Shibata was part of ancient Echigo Province. The area developed as a castle town for Shibata Domain under the Tokugawa shogunate during the Edo period. The modern town of Shibata was established on April 1, 1889 with the creation of the municipalities system. It was elevated to city status on January 1, 1947. On July 7, 2003 the town of Toyoura (from Kitakanbara District) was merged into Shibata. Likewise, on May 1, 2005 the town of Shiunji, and the village of Kajikawa (both from Kitakanbara District) were merged into Shibata.
Economy
The economy of Shibata is dominated by the agricultural sector, with rice as the primary crop.
Education
Shibata has 22 public elementary schools and 10 public middle schools. There are seven public high school, and also one special education school. Keiwa College is also located in Shibata.
Transportation
Railway
- JR East
- Uetsu Main Line: (Kamiyama) - Tsukioka - Nakaura - Shibata - Kaji - Kanazuka - (Nakajō)
- Hakushin Line: (Kuroyama) - Sasaki - Nishi-Shibata - Shibata
Highway
- Nihonkai-Tōhoku Expressway
- Japan National Route 7
- Japan National Route 113
- Japan National Route 290
- Japan National Route 460
Sister city relations
.svg.png) - Uijeongbu, Gyeonggi Province, South Korea[1] (friendship city)
- Uijeongbu, Gyeonggi Province, South Korea[1] (friendship city) - St. James, Missouri, US[1]
- St. James, Missouri, US[1] - Orange City, Iowa, US[1]
- Orange City, Iowa, US[1]
Local attractions
The ruins of Shibata Castle (新発田城 Shibata-jō) are the main visitor attraction and provide the backdrop to the spring cherry blossom viewing parties. Also of note is the Shimizuen (清水園) garden and Ijimino park (五十公野公園 Ijimino kōen).
Tsukioka Onsen (月岡温泉) is one of the most famous hot springs in Niigata Prefecture.
 Shimizuen garden
Shimizuen garden Tsukioka Onsen
Tsukioka Onsen
References
- 1 2 3 Prefecture "International Exchange" Check
|url=value (help). List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Retrieved 1 July 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shibata, Niigata. |
 Shibata travel guide from Wikivoyage
Shibata travel guide from Wikivoyage- Shibata City official website (Japanese)
- Niigata Prefecture Official Travel Guide (multilingual)
